Abstract
Background/Objectives:
Although adipokines and insulin resistance are known to be correlated with body fatness, it is unclear whether they are independently related to weight gain experience. We examined the associations of serum adipokines and marker of insulin resistance with past weight gain during adulthood by taking the degree of attained body mass index (BMI) level into consideration.
Subjects/Methods:
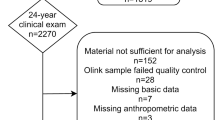
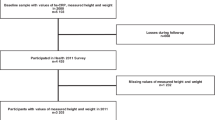
Subjects were 399 Japanese municipal employees, aged ⩾30 years, who participated in a health survey. Serum adipokines were measured using a Luminex suspension bead-based multiplexed array. Weight change during adulthood was calculated as the difference between measured current weight and recalled weight at the age of 20 years. Multiple regression was performed to calculate mean adipokine levels and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) according to weight gain (<5 kg, 5–9.9 kg, or ⩾10 kg) with adjustment for current BMI.
Results:
Weight gain from the age of 20 years was significantly and positively associated with leptin levels even after adjustment for current BMI (P for trend <0.001), whereas it was significantly and inversely associated with adiponectin levels in a BMI-adjusted model among subjects aged ⩾40 years (P for trend=0.03). Weight gain was associated with HOMA-IR in a BMI-unadjusted model (P for trend <0.001), but this association was largely attenuated after adjustment for BMI. Resistin, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and visfatin were not associated with past weight gain.
Conclusions:
Results suggest that a large weight gain during adulthood is associated with higher leptin and lower adiponectin levels independently of the degree of attained BMI level.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mokdad AH, Ford ES, Bowman BA, Dietz WH, Vinicor F, Bales VS et al. Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. JAMA 2003; 289: 76–79.
Haslam DW, James WP . Obesity. Lancet 2005; 366: 1197–1209.
McLellan F . Obesity rising to alarming levels around the world. Lancet 2002; 359: 1412.
Yoon KH, Lee JH, Kim JW, Cho JH, Choi YH, Ko SH et al. Epidemic obesity and type 2 diabetes in Asia. Lancet 2006; 368: 1681–1688.
Hu FB . Obesity Epidemiology. Oxford University Press: New York, 2008.
Hu FB, Willett WC, Li T, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Manson JE . Adiposity as compared with physical activity in predicting mortality among women. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 2694–2703.
Nanri A, Mizoue T, Takahashi Y, Noda M, Inoue M, Tsugane S . Weight change and all-cause, cancer and cardiovascular disease mortality in Japanese men and women: the Japan Public Health Center-Based Prospective Study. Int J Obes (Lond) 2010; 34: 348–356.
Hosono S, Matsuo K, Hirose K, Ito H, Suzuki T, Kawase T et al. Weight gain during adulthood and body weight at age 20 are associated with the risk of endometrial cancer in Japanese women. J Epidemiol 2011; 21: 466–473.
Suzuki R, Iwasaki M, Inoue M, Sasazuki S, Sawada N, Yamaji T et al. Body weight at age 20 years, subsequent weight change and breast cancer risk defined by estrogen and progesterone receptor status—the Japan public health center-based prospective study. Int J Cancer 2011; 129: 1214–1224.
Li TY, Rana JS, Manson JE, Willett WC, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA et al. Obesity as compared with physical activity in predicting risk of coronary heart disease in women. Circulation 2006; 113: 499–506.
Schienkiewitz A, Schulze MB, Hoffmann K, Kroke A, Boeing H . Body mass index history and risk of type 2 diabetes: results from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC)-Potsdam Study. Am J Clin Nutr 2006; 84: 427–433.
Nanri A, Mizoue T, Takahashi Y, Matsushita Y, Noda M, Inoue M et al. Association of weight change in different periods of adulthood with risk of type 2 diabetes in Japanese men and women: the Japan Public Health Center-Based Prospective Study. J Epidemiol Community Health 2011; 65: 1104–1110.
Alley DE, Chang VW . Metabolic syndrome and weight gain in adulthood. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2010; 65: 111–117.
Janssen I, Katzmarzyk PT, Ross R . Duration of overweight and metabolic health risk in American men and women. Ann Epidemiol 2004; 14: 585–591.
Hajer GR, van Haeften TW, Visseren FL . Adipose tissue dysfunction in obesity, diabetes, and vascular diseases. Eur Heart J 2008; 29: 2959–2971.
Coelho M, Oliveira T, Fernandes R . Biochemistry of adipose tissue: an endocrine organ. Arch Med Sci 2013; 9: 191–200.
Rasouli N, Kern PA . Adipocytokines and the metabolic complications of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008; 93: S64–S73.
Wannamethee SG, Lowe GD, Rumley A, Cherry L, Whincup PH, Sattar N . Adipokines and risk of type 2 diabetes in older men. Diabetes Care 2007; 30: 1200–1205.
Chen CY, Asakura M, Asanuma H, Hasegawa T, Tanaka J, Toh N et al. Plasma adiponectin levels predict cardiovascular events in the observational Arita Cohort Study in Japan: the importance of the plasma adiponectin levels. Hypertens Res 2012; 35: 843–848.
Aleksandrova K, Boeing H, Jenab M, Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, Jansen E, van Duijnhoven FJ et al. Total and high-molecular weight adiponectin and risk of colorectal cancer: the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition Study. Carcinogenesis 2012; 33: 1211–1218.
Polyzos SA, Toulis KA, Goulis DG, Zavos C, Kountouras J . Serum total adiponectin in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Metabolism 2011; 60: 313–326.
Zimmet P, Hodge A, Nicolson M, Staten M, de Courten M, Moore J et al. Serum leptin concentration, obesity, and insulin resistance in Western Samoans: cross sectional study. BMJ 1996; 313: 965–969.
Hu FB, Chen C, Wang B, Stampfer MJ, Xu X . Leptin concentrations in relation to overall adiposity, fat distribution, and blood pressure in a rural Chinese population. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2001; 25: 121–125.
Isoppo de Souza C, Rosa DD, Ettrich B, Cibeira GH, Giacomazzi J, Tusset P et al. Association of adipokines and adhesion molecules with indicators of obesity in women undergoing mammography screening. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2012; 9: 97.
Sandeep S, Velmurugan K, Deepa R, Mohan V . Serum visfatin in relation to visceral fat, obesity, and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Asian Indians. Metabolism 2007; 56: 565–570.
Azuma K, Katsukawa F, Oguchi S, Murata M, Yamazaki H, Shimada A et al. Correlation between serum resistin level and adiposity in obese individuals. Obes Res 2003; 11: 997–1001.
Cnop M, Havel PJ, Utzschneider KM, Carr DB, Sinha MK, Boyko EJ et al. Relationship of adiponectin to body fat distribution, insulin sensitivity and plasma lipoproteins: evidence for independent roles of age and sex. Diabetologia 2003; 46: 459–469.
Stefanska A, Sypniewska G, Blaszkiewicz B, Ponikowska I, Szternel L, Chojnowski J . Long-term weight gain and metabolic syndrome, adiponectin and C-reactive protein in women aged 50–60 years. Adv Med Sci 2010; 55: 186–190.
Pham NM, Akter S, Kurotani K, Nanri A, Sato M, Hayabuchi H et al. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and markers of insulin resistance in a Japanese working population. Eur J Clin Nutr 2012; 66: 1323–1328.
Wu H, Yu Z, Qi Q, Li H, Sun Q, Lin X . Joint analysis of multiple biomarkers for identifying type 2 diabetes in middle-aged and older Chinese: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2011; 1: e000191.
Wallace TM, Levy JC, Matthews DR . Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care 2004; 27: 1487–1495.
Ainsworth BE, Haskell WL, Whitt MC, Irwin ML, Swartz AM, Strath SJ et al. Compendium of physical activities: an update of activity codes and MET intensities. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2000; 32: S498–S504.
Peng XD, Xie H, Zhao Q, Wu XP, Sun ZQ, Liao EY . Relationships between serum adiponectin, leptin, resistin, visfatin levels and bone mineral density, and bone biochemical markers in Chinese men. Clin Chim Acta 2008; 387: 31–35.
Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, Kriauciunas A, Stephens TW, Nyce MR et al. Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N Engl J Med 1996; 334: 292–295.
Kern PA, Di Gregorio GB, Lu T, Rassouli N, Ranganathan G . Adiponectin expression from human adipose tissue: relation to obesity, insulin resistance, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression. Diabetes 2003; 52: 1779–1785.
Kyle UG, Genton L, Slosman DO, Pichard C . Fat-free and fat mass percentiles in 5225 healthy subjects aged 15 to 98 years. Nutrition 2001; 17: 534–541.
Park KG, Park KS, Kim MJ, Kim HS, Suh YS, Ahn JD et al. Relationship between serum adiponectin and leptin concentrations and body fat distribution. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2004; 63: 135–142.
Matsushita Y, Nakagawa T, Yamamoto S, Takahashi Y, Yokoyama T, Mizoue T et al. Visceral fat area cutoff for the detection of multiple risk factors of metabolic syndrome in Japanese: the Hitachi Health Study. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2012; 20: 1744–1749.
Lim U, Turner SD, Franke AA, Cooney RV, Wilkens LR, Ernst T et al. Predicting total, abdominal, visceral and hepatic adiposity with circulating biomarkers in Caucasian and Japanese American women. PLoS One 2012; 7: e43502.
Degawa-Yamauchi M, Bovenkerk JE, Juliar BE, Watson W, Kerr K, Jones R et al. Serum resistin (FIZZ3) protein is increased in obese humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 5452–5455.
Furuhashi M, Ura N, Higashiura K, Murakami H, Shimamoto K . Circulating resistin levels in essential hypertension. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2003; 59: 507–510.
Tamakoshi K, Yatsuya H, Kondo T, Hirano T, Hori Y, Yoshida T et al. The accuracy of long-term recall of past body weight in Japanese adult men. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2003; 27: 247–252.
Lee SA, Kallianpur A, Xiang YB, Wen W, Cai Q, Liu D et al. Intra-individual variation of plasma adipokine levels and utility of single measurement of these biomarkers in population-based studies. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2007; 16: 2464–2470.
Lissner L, Odell PM, D'Agostino RB, Stokes J 3rd, Kreger BE, Belanger AJ et al. Variability of body weight and health outcomes in the Framingham population. N Engl J Med 1991; 324: 1839–1844.
Luo J, Margolis KL, Adami HO, Lopez AM, Lessin L, Ye W . Body size, weight cycling, and risk of renal cell carcinoma among postmenopausal women: the Women's Health Initiative (United States). Am J Epidemiol 2007; 166: 752–759.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the study participants for their cooperation and participation. We also thank Seiko Miyazaki and Yasutaka Horiuchi (Kyushu University); Emi Tanaka, Youko Tsuruda, Misaki Hirose, Meishu Sai, Miho Isayama, Midori Sasaki, Mie Shimomura and Azumi Uehara (Fukuoka Women’s University); Yaeko Nagano (retired nurse); and Akiko Hayashi, Yu Teruyama, Kae Saito, Kayoko Washizuka and Yuho Mizoue (National Center for Global Health and Medicine) for their help in data collection. We extend our thanks to Kazuko Nagase and Dai Suzuki (National Center for Global Health and Medicine) for their contributions to measurements of serum adipokines. This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) (21390213) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (To Dr Mizoue), a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B) (21790598) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology and a Grant of National Center for Global Health and Medicine (To Dr Nanri), a grant from National Center for Global Health and Medicine and a grant from National Institute of Biomedical Innovation (To Dr Yasuda).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kimura, Y., Pham, N., Yasuda, K. et al. Association of adulthood weight gain with circulating adipokine and insulin resistance in the Japanese population. Eur J Clin Nutr 69, 462–466 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2014.257
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2014.257
This article is cited by
-
Circulating leptin levels are associated with adiposity in survivors of childhood brain tumors
Scientific Reports (2020)