Abstract
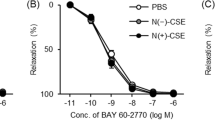
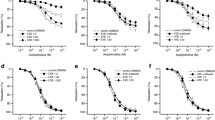
The first goal of this study was to examine the effect of secondhand smoking on neurogenic, endothelium- and cGMP-dependent relaxant responses of rabbit corpus cavernosum smooth muscle. Our second goal was to determine whether such an effect can be prevented by oral administration of L-arginine. Male New Zealand rabbits were divided into control, chronic passive cigarette smoking and L-arginine treatment groups. Relaxant or contractile responses in isolated corpus cavernosum smooth muscle strips were determined by using in vitro muscle technique. There was no significant difference in the relaxant response of the strips to papaverine, sodium nitroprusside and contractile response to KCl among the groups. Relaxant responses to acetylcholine and electrical field stimulation and contractile response to phenylephrine were significantly decreased in the strips of the smoking group than that of the control group. The impaired relaxations of strips were markedly improved by treatment of L-arginine, but the contractile responses to phenylephrine were not affected. These data indicate that secondhand smoking may impair both neurogenic and endothelium-dependent relaxation of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle, and may contribute to the etiology of impotence. Chronic dietary supplementation with L-arginine offsets the impairment of neurogenic and endothelial relaxation. Therefore, we suggest that secondhand smoking exposure to cigarette produces selective impairment of neurogenic and endothelium-dependent relaxation of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle via a mechanism related to the decreased production and/or availability of nitric oxide.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burnett AL . Nitric oxide in the penis: physiology and pathology. J Urol 1997; 157: 320–324.
Andersson K . Pharmacology of penile erection. Pharmacol Rev 2001; 53: 417–450.
Rajfer J et al. Nitric oxide as a mediator of relaxation of the corpus cavernosum response to nonadrenergic noncholinergic neurotransmission. N Engl J Med 1992; 326: 90–94.
Azadzoi KM et al. Modulation of penile corpus cavernosum smooth muscle tone by the endothelium-derived nitric oxide and cyclooxygenase products. J Urol 1992; 147: 220–225.
Ignarro LJ et al. Nitric oxide and cyclic GMP formation upon electrical field stimulation cause relaxation of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1990; 170: 830–843.
Shabsigh R, Fishman IJ, Schum C, Dunn JK . Cigarette smoking and other vascular risk factors in vasculogenic impotence. Urology 1991; 38: 227–231.
Ledda A . Cigarette smoking, hypertension and erectile dysfunction. Curr Med Res Opin 2000; 16: S13.
Miller TA . Diagnostic evaluation of erectile dysfunction. Am Fam Phys 2000; 61: 95–104.
Török J et al. Passive smoking impairs endothelium-dependent relaxation of isolated rabbit arteries. Physiol Res 2000; 49: 135–141.
Freichlag JA et al. Cigarette smoke impairs endothelium-dependent relaxation in rabbit superficial femoral veins. J Surg Res 1999; 81: 77–80.
Celermajer DS et al. Passive smoking and impaired endothelium-dependent arterial dilatation in healthy young adults. N Engl J Med 1996; 334: 150–155.
Hutchison SJ et al. Secondhand tobacco smoke impairs rabbit pulmonary artery endothelium-dependent relaxation. Chest 2001; 120: 2004–2012.
Hutcison SJ et al. Chronic dietary L-arginine prevents endothelial dysfunction secondary to environmental tobacco smoke in normocholesterolemic rabbits. Hypertension 1997; 29: 1186–1191.
Hutchison SJ et al. Effects of L-arginine on atherogenesis and endothelial dysfunction due to secondhand smoke. Hypertension 1999; 34: 44–50.
Azadzoi KM, Saenz de Tejada I . Diabetes mellitus impairs neurogenic and endothelium-dependent relaxation of rabbit corpus cavernosum smooth muscle. J Urol 1992; 148: 1587–1591.
Azadzoi KM, Saenz de Tejada I . Hypercholesterolemia impairs endothelium-dependent relaxation of rabbit corpus cavernosum smooth muscle. J Urol 1991; 146: 238–240.
Özdemirci S et al. Impaired neurogenic and endothelium-dependent relaxant responses of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle from hyperthyroid rabbits. Eur J Pharmacol 2001; 428: 105–111.
Utkan T et al. Aging impairs nitric-oxide-mediated relaxant responses of rabbit corporal smooth muscle of rabbit corporal smooth muscle. Nitric-oxide Biol Chem 2002; 6: 342–346.
Roy AC, Ton SM, Kottegada SR, Ratnam SS . Ability of human corpora cavernosa muscle to generate prostaglandins and thromboxanes in vitro. IRCS Med Sci 1984; 12: 608–609.
Jeremy JY, Morgan RJ, Mikhailidis DP, Dandana P . Prostacycline synthesis by the corpora cavernosa of the human penis: evidence for muscarinic control and pathological implicants. Prostagland Leukotr Med 1986; 23: 211–216.
Reinders JH, Brinkman HJ, vanMourik JA, de Groot PG . Cigarette smoke impairs endothelial cell prostacyclin production. Arteriosclerosis 1986; 6: 15–23.
Moncada S, Palmer RMJ, Higgs EA . Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology and o-pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev 1991; 43: 109–142.
Xie Y et al. Effect of long-term passive smoking on erectile function and penile nitric oxide synthase in the rat. J Urol 1997; 157: 1121–1126.
Carrier S et al. Age decreases nitric oxide synthase containing nerve fibers in the rat penis. J Urol 1997; 157: 1088–1092.
Saenz de Tejada I et al. Impaired neurogenic and endothelium-mediated relaxation of penile smooth muscle from diabetic men with impotence. N Engl J Med 1989; 320: 1025–1030.
Jidan DB et al. Age-related increase in an advanced glycosylation endproduct in penile tissue. World J Urol 1995; 13: 369–379.
Bucalo R, Tracey KJ, Cerani A . Advanced glycosylation products quench nitric oxide and mediate defective endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in experimental diabetes. J Clin Invest 1991; 87: 432–434.
Nicholl ID, Bucala R . Advanced glycation endproducts and cigarette smoking. Cell Mol Biol 1998; 44: 1025–1033.
Braunlee M, Cerani A, Vlassora H . Advanced glycosylation end products in tissue and biochemical basis of diabetic complications. N Engl J Med 1988; 318: 1315–1316.
Seffel AD et al. Advanced glycation end products in human penis: elevation in diabetic tissue, site of deposition and possible effect through iNOS or eNOS. Urology 1997; 50: 1016–1026.
Cerami C et al. Tobacco smoke is a source of toxic reactive glycation products. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 13915–13920.
Park EM, Park YM, Gwak YS . Oxidative damage in tissues of rats exposed to cigarette smoke. Free Radic Biol Med 1998; 25: 79–86.
Ota Y et al. Impairment of endothelium-dependent relaxation of rabbit aortas by cigarette smoke extract role of free radicals and attenuation by captopril. Atherosclerosis 1997; 131: 195–202.
Mays BW et al. Ascorbic acid prevents cigarette smoke injury to endothelium-dependent arterial relaxation. J Surg Res 1999; 84: 35–39.
Klotz T et al. Effectiveness of oral L-arginine in first-line treatment of erectile dysfunction in a controlled crossover study. Urol Int 1999; 63: 220–223.
Chen J et al. Effect of oral administration of high-dose nitric oxide donor L-arginine in men with organic erectile dysfunction: results of a double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled study. BJU Int 1999; 83: 269–273.
Yildirim S et al. The effects of long-term oral administration of L-arginine on the erectile response of rabbits with alloxan-induced diabetes. BJU Int 1999; 83: 679–685.
Kanno K et al. L-arginine infusion induces hypotension and diuresis/natriuresis with concomitant increased urinary excretion of nitirite/nitrate and cGMP in humans. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 1992; 19: 619.
Kharitonov SA, Lubec B, Hjlm M, Barnes PJ . L-arginine increases exhaled nitric oxide in normal human subjects. Clin Sci 1995; 88: 135.
Moody JA et al. Effects of long-term oral administration of L-arginine on the rat erectile response. J Urol 1997; 158: 942–947.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Research Foundation (200250) by the Kocaeli University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Göçmez, S., Utkan, T., Duman, C. et al. Secondhand tobacco smoke impairs neurogenic and endothelium-dependent relaxation of rabbit corpus cavernosum smooth muscle: improvement with chronic oral administration of L-arginine. Int J Impot Res 17, 437–444 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901341
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901341
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Improvement of penile neurogenic and endothelial relaxant responses by chronic administration of resveratrol in rabbits exposed to unpredictable chronic mild stress
International Journal of Impotence Research (2018)
-
Restorative effect of resveratrol on expression of endothelial and neuronal nitric oxide synthase in cavernous tissues of chronic unpredictable mild stress-exposed rats: an impact of inflammation
International Journal of Impotence Research (2018)
-
Testosterone deficiency causes penile fibrosis and organic erectile dysfunction in aging men. Evaluating association among Age, TDS and ED
BMC Surgery (2012)
-
Effects of chronic low- and high-dose ethanol intake on the nitrergic relaxations of corpus cavernosum and penile nitric oxide synthase in the rabbit
International Journal of Impotence Research (2012)