Abstract
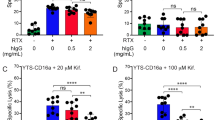
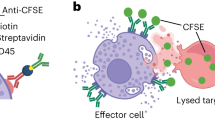
Natural killer (NK) activity is mediated by a small population of peripheral blood cells that exhibit the homogeneous morphology of large granular lymphocytes (LGL)1–4. In recent studies, human NK cell clones5,6 have been shown to contain a 200,000-Mr (relative molecular mass) protease-resistant chondroitin sulphate A proteo-glycan, which has been localized to the secretory granule by X-ray dispersive analysis and by its resistance to cleavage by extracellular addition of chondroitinase AC or ABC (ref. 7). In the present study, we have used six different human NK cell clones to demonstrate that release of 35S-proteoglycan correlates closely with cytolytic activity against various NK cell targets. When NK activity is blocked by monoclonal antibodies at either the effector cell level (LFA-1)8 or at the target cell level (TNKTAR)9, there is a concomitant decrease in exocytosis of proteoglycan. Monoclonal antibodies directed against recognition structures, for example anti-NKTa and anti-T3 (ref. 10), function as soluble stimuli, capable of initiating the release of 35S-proteoglycan. Taken together, these results provide strong evidence for the stimulus-specific release of chondroitin sulphate A proteoglycans from NK cells when the cytolytic process is activated.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herberman, R.B. & Ortaldo, J.R. Science 214, 24–30 (1981).
Trinchieri, G. & Perussia, B. Lab. Invest. 50, 489–513 (1984).
Ortaldo, J.R., Sharrow, S.H., Timonen, T. & Herberman, R.B. J. Immun. 127, 2401–2409 (1981).
Zarling, J.M., Clouse, K.A., Biddison, W.E. & Kung, P.C. J. Immun. 127, 2575–2580 (1981).
Hercend, T., Reinherz, E.L., Meuer, S., Schlossman, S.F. & Ritz, J Nature 301, 158–159 (1983).
Schmidt, R.E., Bartley, G., Levine, H., Schlossman, S.F. & Ritz, J.K. J.Immun. 135, 672–678 (1985).
MacDermott, R.P. et al. J. exp. Med. (in the press).
Schmidt, R.E. et al. J. Immun. 135, 1020–1025 (1985).
Hercend, T. et al. Eur. J. Immun. 14, 844–852 (1984).
Hercend, T. et al. J. exp. Med. 158, 1547–1560 (1983).
Hercend, T., Meuer, S.C, Reinherz, E, Schlossman, S.F. & Ritz, J. J.Immun. 129, 1299–1305 (1982).
Hercend, T. et al. J. Clin. Invest. 75, 932–943 (1985).
Haynes, B.F. et al. J. Immun. 126, 1409–1414 (1981).
Moingeon, P. et al. J. Immun. 134, 2930–2934 (1985).
Hildreth, J.E.K., Gotch, F.M., Hildreth, P.D.K. & McMichael, A.J. Eur. J. Immun. 13, 202–208 (1983).
Springer, T.A. et al. Immun. Rev. 68, 171–192 (1982).
Ritz, J. et al. Science 228, 1540–1543 (1985).
Henkart, P.A., Millard, P.J., Reynolds, C.W. & Henkart, M.P. J. exp. Med. 160, 75–93 (1984).
Pasternak, M.S. & Eisen, H.N. Nature 314, 743–745 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, R., MacDermott, R., Bartley, G. et al. Specific release of proteoglycans from human natural killer cells during target lysis. Nature 318, 289–291 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1038/318289a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/318289a0
This article is cited by
-
Investigation of serum endocan and serglycin levels in obstructive sleep apnea
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -) (2023)
-
Prof. Dr. med. Reinhold Ernst Schmidt (17.12.1951–23.01.2022)
Zeitschrift für Rheumatologie (2022)
-
The TLR-2/TLR-6 agonist macrophage-activating lipopeptide-2 augments human NK cell cytotoxicity when PGE2 production by monocytes is inhibited by a COX-2 blocker
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2015)
-
Role of gamma-secretase in human umbilical-cord derived mesenchymal stem cell mediated suppression of NK cell cytotoxicity
Cell Communication and Signaling (2014)
-
Granzymes, cytotoxic granules and cell death: the early work of Dr. Jurg Tschopp
Cell Death & Differentiation (2012)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.