Abstract
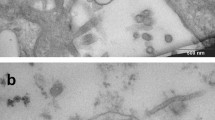
CLARKE1 showed that a strain of tick-borne encephalitis virus, ‘A52’, isolated in Finland2, is antigenically identical with the Central European tick-borne encephalitis viruses. Sokol et al.3 reported that the particles of the ‘Hypr’ strain of Central European tick-borne encephalitis virus purified from mouse brain suspension were predominantly spherical, and about 30 mµ in size. The same strain in HeLa cells has been demonstrated to be round-shaped with a dense inner body and a transparent outer zone surrounded by a surface membrane4. In the present work the negative staining technique5 was used to determine the size and shape of particles of the strain ‘A52’, grown in tissue culture.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clarke, D. H., Symp. Czech. Acad. Sci., 3, 67 (1962).
Oker-Blom, N., Kääriäinen, L., Brummer-Korvenkontio, M., and Weckström, P., Symp. Czech. Acad. Sci., 3, 423 (1962).
Sokol, F., Zelma, J., Libikova, H., and Rosenberg, M., Symp. Czech. Acad. Sci., 3, 113 (1962).
Kovac, W., Kunz, Ch., and Stockinger, L., Arch. Ges. Virusforsch., 11, 544 (1962).
Brenner, S., and Horne, R. W., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 34, 103 (1959).
Salminen, A., Ann. Med. Exp. Fenn., 40, 174 (1962).
Smith, C. E. G., and Holt, D., Symp. Czech. Acad. Sci., 3, 98 (1962).
Sharp, D. G., Taylor, A. R., Beard, D., and Beard, J. W., Arch. Path., 36, 167 (1943).
Dalton, A. J., Haguenau, Fr., and Moloney, J. B., J. Nat. Cancer Inst., 29, 1177 (1962).
Zeigel, R. F., and Rauscher, F. J., J. Nat. Cancer Inst., 30, 207 (1963).
Sharp, D. G., and Bracke, E. C., Virology, 10, 419 (1960).
Elford, W. J., Chu, C. M., Dawson, J. M., Dudgeon, J. A., Fulton, F., and Smiles, J., Brit. J. Exp. Path., 29, 590 (1948).
Bonar, R. A., Heine, U., Beard, D., and Beard, J. W., J. Nat. Cancer Inst., 30, 949 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
WECKSTRÖM, P., NYHOLM, M. Electron Microscopy of a Tick-borne Encephalitis Virus. Nature 205, 211–212 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1038/205211a0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/205211a0
This article is cited by
-
Comparative study of infectious and formaldehyde-inactivated tick-borne encephalitis virus particles
Archives of Virology (1984)
-
Zur Gr��enbestimmung des Virus der Fr�hsommer-Meningo-Encephalitis
Archiv f�r die gesamte Virusforschung (1965)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.