Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Far-travelled 3700 km lateral magma propagation just below the surface of Venus
Far-travelled 3700 km lateral magma propagation just below the surface of Venus
In this study, the authors trace lateral magma movement in a ~ 3700 km long fracture on Venus. This Great Dyke of Atla Regio is the longest so-far traced on Venus (and in the solar system) and belongs to a giant radiating dyke swarm of the Ozza Mons volcano of the Atla Regio plume.
- H. El Bilali
- & R. E. Ernst
-
Article
| Open Access Oxide nanolitisation-induced melt iron extraction causes viscosity jumps and enhanced explosivity in silicic magma
Oxide nanolitisation-induced melt iron extraction causes viscosity jumps and enhanced explosivity in silicic magma
Oxide nanolites crystallisation in natural magma increases melt, and hence bulk magma viscosity mainly due to iron extraction. This increase can be sufficient to drive magma fragmentation depending on magma degassing and ascent dynamics.
- Francisco Cáceres
- , Kai-Uwe Hess
- & Donald B. Dingwell
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale silicate melt textures determine volcanic ash surface chemistry
Nanoscale silicate melt textures determine volcanic ash surface chemistry
Nanotexture-sensitive fracture focusing during magma fragmentation determines the surface chemistry of volcanic ash particles, thereby modifying the reactive interface and subsequent environmental impacts
- Adrian J. Hornby
- , Paul M. Ayris
- & Donald B. Dingwell
-
Article
| Open Access Volcaniclastic density currents explain widespread and diverse seafloor impacts of the 2022 Hunga Volcano eruption
Volcaniclastic density currents explain widespread and diverse seafloor impacts of the 2022 Hunga Volcano eruption
During the 2022 Hunga Volcano eruption, 10 km3 of seafloor material was removed, fueling long-run out seafloor density currents. These powerful currents damaged seafloor cables over a length of >100 km, reshaped the seafloor, and caused mass-mortality of seafloor life.
- Sarah Seabrook
- , Kevin Mackay
- & Michael J. M. Williams
-
Article
| Open Access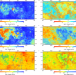 Comprehensive mapping of lunar surface chemistry by adding Chang'e-5 samples with deep learning
Comprehensive mapping of lunar surface chemistry by adding Chang'e-5 samples with deep learning
In this study, the authors map the lunar surface chemistry. They achieve this through a combination of deep learning and actual samples from the Chinese Chang’e-5 mission.
- Chen Yang
- , Xinmei Zhang
- & Ziyuan Ouyang
-
Article
| Open Access Near-surface magma flow instability drives cyclic lava fountaining at Fagradalsfjall, Iceland
Near-surface magma flow instability drives cyclic lava fountaining at Fagradalsfjall, Iceland
This study of volcanic gas chemistry during pulsatory lava fountaining at Fagradalsfjall volcano in Iceland reveals that the intermittency stems from pressure cycles and gas-melt separation within a shallow magma-filled cavity.
- Samuel Scott
- , Melissa Pfeffer
- & Andri Stefánsson
-
Article
| Open Access Magmatic connectivity among six Galápagos volcanoes revealed by satellite geodesy
Magmatic connectivity among six Galápagos volcanoes revealed by satellite geodesy
Reddin et al. use satellite radar to measure deformation at six Galápagos volcanoes. They observe correlated deformation signals between multiple volcanoes and attribute them to temporally varying plume supply into interconnected magmatic systems.
- Eoin Reddin
- , Susanna K. Ebmeier
- & Santiago Aguaiza
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Reported ultra-low lava viscosities from the 2021 La Palma eruption are potentially biased
Reported ultra-low lava viscosities from the 2021 La Palma eruption are potentially biased
- Guillem Gisbert
- , Valentin R. Troll
- & Juan Carlos Carracedo
-
Article
| Open Access Volcanic evolution of an ultraslow-spreading ridge
Volcanic evolution of an ultraslow-spreading ridge
A new age map of the rift valley at an ultraslow-spreading ridge reveals that 50% of the lava flows are <25,000 years old. The study documents a continuous volcanic surface renewal with eruptions occurring throughout the width of the rift valley.
- H. H. Stubseid
- , A. Bjerga
- & R. B. Pedersen
-
Article
| Open Access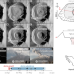 Lava dome cycles reveal rise and fall of magma column at Popocatépetl volcano
Lava dome cycles reveal rise and fall of magma column at Popocatépetl volcano
Satellite imagery enhanced with deep learning sheds light on the mechanisms driving lava dome construction-destruction cycles. Results suggest that gas retention and escape from the magma system control the dome and crater morphological evolution.
- Sébastien Valade
- , Diego Coppola
- & Servando De la Cruz-Reyna
-
Article
| Open Access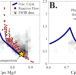 Porosity evolution of mafic crystal mush during reactive flow
Porosity evolution of mafic crystal mush during reactive flow
In this study, the authors use a thermodynamically constrained model of melt-mush reaction to simulate the chemical, mineralogical, and physical consequences of reactive flow in a multi-component mush system.
- Matthew L. M. Gleeson
- , C. Johan Lissenberg
- & Paula M. Antoshechkina
-
Article
| Open Access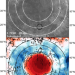 Evidence for structural control of mare volcanism in lunar compressional tectonic settings
Evidence for structural control of mare volcanism in lunar compressional tectonic settings
On the Moon, evidence has been found for the preexisting fault reactivation origin (tectonic inversion) of contractional wrinkle ridges in mare basins and the consequent structural control of volcanic eruptions in compressional tectonic settings.
- Feng Zhang
- , Alberto Pizzi
- & Yongliao Zou
-
Article
| Open Access Revised Minoan eruption volume as benchmark for large volcanic eruptions
Revised Minoan eruption volume as benchmark for large volcanic eruptions
The authors use seismic and sedimentology data to estimate the volume of the Minoan eruption. The results show that the Plinian phase contributed most to the distal tephra fall, and that the pyroclastic flow volume is significantly smaller than previously assumed.
- Jens Karstens
- , Jonas Preine
- & Christian Berndt
-
Article
| Open Access The fragmentation-induced fluidisation of pyroclastic density currents
The fragmentation-induced fluidisation of pyroclastic density currents
Fragmentation-induced fluidization occurs in concentrated pyroclastic density currents where rapid particle breakage causes flow compaction and subsequent high pore fluid pressure, reducing friction and explaining their long runout.
- Eric C. P. Breard
- , Josef Dufek
- & Braden Walsh
-
Article
| Open Access Genesis of Hawaiian lavas by crystallization of picritic magma in the deep mantle
Genesis of Hawaiian lavas by crystallization of picritic magma in the deep mantle
Here the authors demonstrate that Hawaiian lavas are formed by partial melting of mantle peridotite with subsequent fractionation of clinopyroxene and garnet in the deep magma chamber (90 km) and reequilibration with harzburgite at a shallower depth (<60 km).
- Junlong Yang
- , Chao Wang
- & Zhenmin Jin
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Silica is unlikely to be soluble in upper crustal carbonatite melts
Silica is unlikely to be soluble in upper crustal carbonatite melts
- Michael Anenburg
- & Tibor Guzmics
-
Article
| Open Access Subduction initiation triggered the Caribbean large igneous province
Subduction initiation triggered the Caribbean large igneous province
Using a large-scale 3D geodynamic model, the authors show how the transfer of subduction zone from the Pacific to the Atlantic triggered the formation of a mantle plume at the origin of the Cretaceous Caribbean Large Igneous province.
- Nicolas Riel
- , João C. Duarte
- & Anton Popov
-
Article
| Open Access Magmatic plumbing and dynamic evolution of the 2021 La Palma eruption
Magmatic plumbing and dynamic evolution of the 2021 La Palma eruption
In a new study, the authors use seismological methods to understand the eruption of La Palma 2021. Results suggest a preparatory phase of de-stabilisation of a mushy reservoir, and a co-eruptive phase with seismicity controlled by the drainage and interplay of two reservoirs.
- Carmen del Fresno
- , Simone Cesca
- & Carmen López
-
Article
| Open Access Velocity-dependent heat transfer controls temperature in fracture networks
Velocity-dependent heat transfer controls temperature in fracture networks
Heat transfer in a fracture network is heterogeneous as it depends pre-dominantly on flow velocity and fracture aperture. This finding has direct implications for the heat distribution and exploitation in geothermal and associated natural systems.
- Thomas Heinze
- & Nicola Pastore
-
Article
| Open Access Magma recharge and mush rejuvenation drive paroxysmal activity at Stromboli volcano
Magma recharge and mush rejuvenation drive paroxysmal activity at Stromboli volcano
Petrological studies along with volcano monitoring data relate the unusual 2019 explosive activity at Stromboli volcano (Italy) to deep magma recharges up to a few days prior the eruption and a direct link between deep and shallow magma reservoirs.
- Chiara Maria Petrone
- , Silvio Mollo
- & Mark Reagan
-
Comment
| Open AccessThe harmful legacy of colonialism in natural hazard risk
The colonial practices of geoscience have created long term vulnerabilities to natural hazards. In this comment the ongoing consequence are explored of colonialism as well as the actions that are needed to be taken to reduce natural hazard risk.
- Jazmin P. Scarlett
-
Article
| Open Access Volcanically hosted venting with indications of ultramafic influence at Aurora hydrothermal field on Gakkel Ridge
Volcanically hosted venting with indications of ultramafic influence at Aurora hydrothermal field on Gakkel Ridge
The Aurora hydrothermal field (Arctic Ocean) is hosted in volcanic rocks but also shows evidence of mantle rock influence in the shallow sub-surface. Our discovery is pertinent to disciplines from marine mining to the search for life beyond Earth.
- Christopher R. German
- , Eoghan P. Reeves
- & Antje Boetius
-
Article
| Open Access Hidden pressurized fluids prior to the 2014 phreatic eruption at Mt Ontake
Hidden pressurized fluids prior to the 2014 phreatic eruption at Mt Ontake
Phreatic volcanic eruptions can be unexpected and devastating. Here the authors, using seismic-based methodologies, find that pressurized fluids accumulated 5 months before the deadly phreatic eruption at Mt Ontake; a period previously considered as completely quiescent.
- Corentin Caudron
- , Yosuke Aoki
- & Toshiko Terakawa
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic model of the El Laco magnetite-apatite deposits by extrusion of iron-rich melt
Genetic model of the El Laco magnetite-apatite deposits by extrusion of iron-rich melt
Can volcanoes erupt ore deposits? This study combines observations, experiments, and simulations to show that iron ore deposits on El Laco volcano formed by eruption of melt sourced from separation of Fe-rich melt from a silicate magma body beneath.
- Tobias Keller
- , Fernando Tornos
- & Jenny Suckale
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-depleted hydrogen isotopes in hydrated glass record Late Cretaceous glaciation in Antarctica
Ultra-depleted hydrogen isotopes in hydrated glass record Late Cretaceous glaciation in Antarctica
Analysis of volcanic glass from the Transantarctic Mountains suggests that 90 Million years ago glaciation was widespread in Antarctica, a period in Earth’s history when the continent was considered to be ice-free and part of a global greenhouse.
- Demian A. Nelson
- , John M. Cottle
- & Alfredo Camacho
-
Article
| Open Access In-conduit capture of sub-micron volcanic ash particles via turbophoresis and sintering
In-conduit capture of sub-micron volcanic ash particles via turbophoresis and sintering
Here the authors document evidence of ultrafine ash captured within ash-venting nozzles at Cordón Caulle volcano (Chile). This decouples eruptive processes from the emitted products, as explained by a new model of in-vent ash migration and sticking.
- Jamie I. Farquharson
- , Hugh Tuffen
- & C. Ian Schipper
-
Article
| Open Access Endogenically sourced volatiles on Charon and other Kuiper belt objects
Endogenically sourced volatiles on Charon and other Kuiper belt objects
We show cryovolcanic eruptions released sufficient methane to source volatile products on Charon. Irradiated methane products are found on other Kuiper belt objects, so endogenically sourced volatiles could be important across the Kuiper belt.
- Stephanie M. Menten
- , Michael M. Sori
- & Ali M. Bramson
-
Article
| Open Access Sulfur and chlorine budgets control the ore fertility of arc magmas
Sulfur and chlorine budgets control the ore fertility of arc magmas
Earth’s largest copper deposits form in continental arcs, yet it is not well understood what determines whether a magmatic system generates economic mineralization or not. Here the authors show that the abundance of chlorine and sulfur, rather than the abundance of ore metals controls magmatic ore fertility.
- Carter Grondahl
- & Zoltán Zajacz
-
Article
| Open Access Responding to eruptive transitions during the 2020–2021 eruption of La Soufrière volcano, St. Vincent
Responding to eruptive transitions during the 2020–2021 eruption of La Soufrière volcano, St. Vincent
The 2020 – 2021 eruption of La Soufrière volcano transitioned from an effusive to explosive eruption style. Here the authors show that input from multiple monitoring datasets and an evolving conceptual model were key to anticipating and responding to the eruptive transition at the La Soufrière volcano, St. Vincent, in a resource-constrained setting.
- E. P. Joseph
- , M. Camejo-Harry
- & R. S. J. Sparks
-
Article
| Open Access Primitive noble gases sampled from ocean island basalts cannot be from the Earth’s core
Primitive noble gases sampled from ocean island basalts cannot be from the Earth’s core
Li et al. established a liquid-liquid partition model based on ab initio calculations to reveal that He and Ne strongly fractionate during core-mantle separation, which concludes the primitive volatiles seen in hotspots cannot be from the core.
- Yunguo Li
- , Lidunka Vočadlo
- & John P. Brodholt
-
Article
| Open Access Diverse mantle components with invariant oxygen isotopes in the 2021 Fagradalsfjall eruption, Iceland
Diverse mantle components with invariant oxygen isotopes in the 2021 Fagradalsfjall eruption, Iceland
The 2021 eruption in the Reykjanes Peninsula of Iceland was the first in 800 years and was supplied by melts from diverse mantle source domains with near-identical oxygen isotope ratios, providing a unique insight into the Icelandic mantle plume.
- I. N. Bindeman
- , F. M. Deegan
- & T. R. Walter
-
Article
| Open Access Modest volcanic SO2 emissions from the Indonesian archipelago
Modest volcanic SO2 emissions from the Indonesian archipelago
Indonesia is the country with the most active volcanoes, several of which are renowned for climate-changing eruptions. Here the authors show a rather moderate sulfur emissions budget and reinforce the idea that sulfur-rich eruptions reflect long-term accumulation of volatiles in the reservoirs.
- Philipson Bani
- , Clive Oppenheimer
- & Mita Marlia
-
Article
| Open Access Dendritic crystallization in hydrous basaltic magmas controls magma mobility within the Earth’s crust
Dendritic crystallization in hydrous basaltic magmas controls magma mobility within the Earth’s crust
In situ 4D experiments at high temperature and moderate pressure reveal that rapid dendritic crystallization in hydrous basaltic magmas promotes a rheological transition within minutes, controlling magma mobility within the Earth’s crust.
- Fabio Arzilli
- , Margherita Polacci
- & Mike R. Burton
-
Article
| Open Access Eruption of ultralow-viscosity basanite magma at Cumbre Vieja, La Palma, Canary Islands
Eruption of ultralow-viscosity basanite magma at Cumbre Vieja, La Palma, Canary Islands
The rheological properties of the 2021 Cumbre Vieja magma on La Palma, Canary Islands is investigated. The study indicates that this eruption was fueled by magma having among the lowest viscosities observed for mafic systems, and consequently produced lavas that were flowing in the supercritical and possibly turbulent regime.
- Jonathan M. Castro
- & Yves Feisel
-
Article
| Open Access Low-degree mantle melting controls the deep seismicity and explosive volcanism of the Gakkel Ridge
Low-degree mantle melting controls the deep seismicity and explosive volcanism of the Gakkel Ridge
Joint implementation of seismic tomography and numerical thermo-mechanical modeling sheds light to the causes of explosive submarine volcanic eruptions on the Gakkel Ridge and deeply penetrating seismicity down to 25 km depth.
- Ivan Koulakov
- , Vera Schlindwein
- & Aleksey Ivanov
-
Article
| Open Access Trans-crustal structural control of CO2-rich extensional magmatic systems revealed at Mount Erebus Antarctica
Trans-crustal structural control of CO2-rich extensional magmatic systems revealed at Mount Erebus Antarctica
Episodic magma eruption and CO2 release to the atmosphere are controlled where two structural trends meet to cause dilatancy.
- G. J. Hill
- , P. E. Wannamaker
- & P. Kyle
-
Article
| Open Access Inflated pyroclasts in proximal fallout deposits reveal abrupt transitions in eruption behaviour
Inflated pyroclasts in proximal fallout deposits reveal abrupt transitions in eruption behaviour
Jones et al. identify a new type of volcanic deposit, inflated pyroclasts, that form by continued gas expansion post-deposition. They show how these deposits can be indicative of abrupt transitions in eruptive behaviour at mafic volcanoes.
- Thomas J. Jones
- , Yannick Le Moigne
- & Donald B. Dingwell
-
Article
| Open Access 22 years of satellite imagery reveal a major destabilization structure at Piton de la Fournaise
22 years of satellite imagery reveal a major destabilization structure at Piton de la Fournaise
At Piton de la Fournaise volcano, satellite deformation allows to constrain the geometry of 57 magmatic intrusions. Versatile modeling reveals that a major spoon-shaped destabilization structure accommodates intrusions and seaward flank displacement.
- Quentin Dumont
- , Valérie Cayol
- & Aline Peltier
-
Article
| Open Access Seismic precursors to the Whakaari 2019 phreatic eruption are transferable to other eruptions and volcanoes
Seismic precursors to the Whakaari 2019 phreatic eruption are transferable to other eruptions and volcanoes
Volcanic eruptions that occur without warning can be deadly in touristic and populated areas. Using a machine learning approach, the authors here discover distinctive patterns hidden in the seismic signals of a number of New Zealand and Alaskan volcanoes, that occur before most of the eruptions studied.
- Alberto Ardid
- , David Dempsey
- & Shane Cronin
-
Article
| Open Access Fibre optic distributed acoustic sensing of volcanic events
Fibre optic distributed acoustic sensing of volcanic events
Fibre Optic Distributed Acoustic Sensing on Mount Etna provides new opportunities for monitoring volcanic processes and demonstrates nonlinear interaction of infrasound wave with scoria layer, mapping its thickness and illuminating hidden structures.
- Philippe Jousset
- , Gilda Currenti
- & Charlotte M. Krawczyk
-
Article
| Open Access Large-scale cryovolcanic resurfacing on Pluto
Large-scale cryovolcanic resurfacing on Pluto
Giant icy volcanos (cryovolcanos) on Pluto are unique in the imaged solar system and provide evidence for unexpected, active geology late in Pluto’s history.
- Kelsi N. Singer
- , Oliver L. White
- & Kimberly Ennico-Smith
-
Article
| Open Access Melt stripping and agglutination of pyroclasts during the explosive eruption of low viscosity magmas
Melt stripping and agglutination of pyroclasts during the explosive eruption of low viscosity magmas
The pyroclast properties and features can provide insights into the dynamics of explosive eruptions of low viscosity magma. Here, the authors show how lava droplets, or pyroclasts are subject to melt removal and melt addition during transport in a gas jet and present a method to reconstruct eruption conditions from the pyroclast textures.
- Thomas J. Jones
- , James K. Russell
- & Lea Hollendonner
-
Article
| Open Access Destructiveness of pyroclastic surges controlled by turbulent fluctuations
Destructiveness of pyroclastic surges controlled by turbulent fluctuations
The hazards of pyroclastic surges remain poorly mitigated globally. Here, the authors show that their destructiveness is amplified by turbulent excursions of dynamic pressure energy that focusses inside the largest eddies and internal gravity waves.
- Ermanno Brosch
- , Gert Lube
- & Luke Fullard
-
Article
| Open Access Thermochemical anomalies in the upper mantle control Gakkel Ridge accretion
Thermochemical anomalies in the upper mantle control Gakkel Ridge accretion
The ultimate driver of ultraslow spreading ridges is unknown. Here the authors use spreading rates derived directly from isotopic ages of seafloor samples to link magmatic and amagmatic segments with thermochemical variations in the upper mantle.
- John M. O’Connor
- , Wilfried Jokat
- & Anthony A. P. Koppers
-
Review Article
| Open Access Volcanic activity and hazard in the East African Rift Zone
Volcanic activity and hazard in the East African Rift Zone
New observations of volcanic and magmatic activity in Africa are changing our views of continental rifting and raising awareness of the associated hazards. However, despite a shift from crisis response to reducing disaster risks, limited capacity means mitigating geohazards remains challenging.
- Juliet Biggs
- , Atalay Ayele
- & Tim J. Wright
-
Article
| Open Access Fluid migrations and volcanic earthquakes from depolarized ambient noise
Fluid migrations and volcanic earthquakes from depolarized ambient noise
Deep fluids inside volcanoes disrupt the oscillations of signals produced by wind and sea. Imaging this disruption through space and time allows tracking hazardous fluid migrations leading to earthquakes before they reach the surface.
- S. Petrosino
- & L. De Siena
-
Article
| Open Access The Tharsis mantle source of depleted shergottites revealed by 90 million impact craters
The Tharsis mantle source of depleted shergottites revealed by 90 million impact craters
The ejection sites of the martian meteorites are still unknown. Here, the authors build a database of 90 million craters and show that Tharsis region is the most likely source of depleted shergottites ejected 1.1 Ma ago, thus confirming that some portions of the mantle were recently anomalously hot.
- A. Lagain
- , G. K. Benedix
- & K. Miljković
-
Article
| Open Access Volumetric extrusive rates of silicic supereruptions from the Afro-Arabian large igneous province
Volumetric extrusive rates of silicic supereruptions from the Afro-Arabian large igneous province
Quantifying the tempo of large-volume silicic magma generation and eruption is a long-standing but elusive task. Here we show that the three largest sequentially dated eruptions, totaling >4,300 km3, occurred within 48 ± 34 kyr and yield the highest known long term volumetric extrusive rate of silicic volcanism on Earth.
- Jennifer E. Thines
- , Ingrid A. Ukstins
- & Mark Schmitz
-
Article
| Open Access Episodic transport of discrete magma batches beneath Aso volcano
Episodic transport of discrete magma batches beneath Aso volcano
Repetitive shallow resonances provide a pathway to unravelling episodic magma transport deep in the magma plumbing system. Episodic deformation of ~1 nanoradian over ~100 s beneath Aso volcano potentially provides a link between long-term volcanic output and short-term eruption dynamics.
- Jieming Niu
- & Teh-Ru Alex Song

 Levitation and dynamics of bodies in supersaturated fluids
Levitation and dynamics of bodies in supersaturated fluids