Featured
-
-
Letter |
 Synthetic chiral light for efficient control of chiral light–matter interaction
Synthetic chiral light for efficient control of chiral light–matter interaction
Freely propagating, locally and globally chiral electric fields are introduced, enabling full control over intensity, polarization and propagation direction of the nonlinear enantio-sensitive optical response of randomly oriented chiral molecules.
- David Ayuso
- , Ofer Neufeld
- & Olga Smirnova
-
Letter |
 Resonant excitation and all-optical switching of femtosecond soliton molecules
Resonant excitation and all-optical switching of femtosecond soliton molecules
By driving ultrafast soliton molecules with an all-optical external perturbation and monitoring their response in real time, a form of spectroscopy of soliton molecules akin to optical spectroscopy of chemical bonds is introduced.
- F. Kurtz
- , C. Ropers
- & G. Herink
-
Letter |
 Topological strong-field physics on sub-laser-cycle timescale
Topological strong-field physics on sub-laser-cycle timescale
Responses to high-intensity mid-infrared laser light are theoretically investigated in the Haldane system. It is found that the primary electronic response, optical tunnelling and high-harmonic emission are sensitive to the topological phase of matter.
- R. E. F. Silva
- , Á. Jiménez-Galán
- & M. Ivanov
-
Review Article |
 Front-induced transitions
Front-induced transitions
Front-induced transitions have been used in dispersion-engineered waveguides for frequency conversion, optical delays, and bandwidth and pulse duration manipulation. This Review provides a theoretical description of the subject and highlights the potential for light manipulation in guided optics.
- Mahmoud A. Gaafar
- , Toshihiko Baba
- & Alexander Yu. Petrov
-
Article |
 Lightwave-driven gapless superconductivity and forbidden quantum beats by terahertz symmetry breaking
Lightwave-driven gapless superconductivity and forbidden quantum beats by terahertz symmetry breaking
The terahertz field-induced changes in the superconducting properties of a Nb3Sn film are investigated by time- and frequency-resolved terahertz spectroscopy. A gapless superconducting state and symmetry-forbidden odd-order coherent modes are observed.
- X. Yang
- , C. Vaswani
- & J. Wang
-
Article |
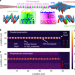 Self-organized nonlinear gratings for ultrafast nanophotonics
Self-organized nonlinear gratings for ultrafast nanophotonics
Femtosecond laser pulses can generate self-organized nonlinear gratings in nanophotonic waveguides, providing both quasi-phase-matching and group-velocity matching for second-harmonic generation, and enabling simultaneous χ2 and χ3 nonlinear processes for laser-frequency-comb stabilization.
- Daniel D. Hickstein
- , David R. Carlson
- & Scott B. Papp
-
-
Article |
 Computational time-of-flight diffuse optical tomography
Computational time-of-flight diffuse optical tomography
By combining a single-photon time-of-flight camera with computational processing of the spatial and full temporal photon distribution data, an object embedded inside a strongly diffusive medium can be imaged over more than 80 transport mean free paths in a contactless manner on the timescale of the order of 1 s.
- Ashley Lyons
- , Francesco Tonolini
- & Daniele Faccio
-
Article |
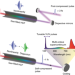 High-energy pulse self-compression and ultraviolet generation through soliton dynamics in hollow capillary fibres
High-energy pulse self-compression and ultraviolet generation through soliton dynamics in hollow capillary fibres
Optical soliton dynamics in large-core hollow capillary fibres is demonstrated. The findings enable the scaling of soliton effects by several orders of magnitude to the multi-millijoule energy and terawatt peak power levels, and open up opportunities for new-generation table-top light sources for ultrafast strong-field physics and advanced spectroscopy.
- John C. Travers
- , Teodora F. Grigorova
- & Federico Belli
-
Article |
 Computed stereo lensless X-ray imaging
Computed stereo lensless X-ray imaging
Stereo images of gold nanoparticles in a pyramid shape are reconstructed from X-ray coherent diffraction patterns. Depth information is retrieved by computing disparity maps without a priori knowledge of the sample shape.
- J. Duarte
- , R. Cassin
- & H. Merdji
-
Letter |
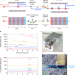 Generation of narrow-band X-ray free-electron laser via reflection self-seeding
Generation of narrow-band X-ray free-electron laser via reflection self-seeding
A nearly Fourier-limited X-ray free-electron laser beam is generated by a self-seeding scheme. The beam in the first half of the undulators is monochromatized via Bragg reflection, and is subsequently amplified in the remaining undulators.
- Ichiro Inoue
- , Taito Osaka
- & Makina Yabashi
-
Article |
 Dual-energy electron beams from a compact laser-driven accelerator
Dual-energy electron beams from a compact laser-driven accelerator
A laser-based scheme for the simultaneous generation of two temporally synchronized electron beams with individually adjustable energies offers new opportunities for ultrafast pump–probe experiments.
- J. Wenz
- , A. Döpp
- & S. Karsch
-
Letter |
 Double-blind holography of attosecond pulses
Double-blind holography of attosecond pulses
Double-blind holography allows reconstruction of the missing spectral phases and characterization of the unknown signals in both isolated-pulse and double-pulse scenarios, facilitating the study of complex electron dynamics via a single-shot and linear measurement.
- O. Pedatzur
- , A. Trabattoni
- & N. Dudovich
-
Letter |
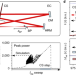 Temporal solitons in free-space femtosecond enhancement cavities
Temporal solitons in free-space femtosecond enhancement cavities
Temporal dissipative soliton formation in a free-space femtosecond enhancement cavity with a thin Kerr medium is reported. Locking a 350-fs, 1,035-nm pulse train with a repetition rate of 100 MHz to this cavity-soliton state generates a 37-fs sech2-shaped pulse with a peak-power enhancement of 3,200.
- N. Lilienfein
- , C. Hofer
- & I. Pupeza
-
Article |
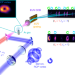 Controlling the polarization and vortex charge of attosecond high-harmonic beams via simultaneous spin–orbit momentum conservation
Controlling the polarization and vortex charge of attosecond high-harmonic beams via simultaneous spin–orbit momentum conservation
Simultaneous spin and orbital angular momentum conservation enables control over the divergence and polarization of EUV vortex beams, paving the way to ultrafast studies of chiral systems using high-harmonic beams with designer spin and orbital angular momentum.
- Kevin M. Dorney
- , Laura Rego
- & Carlos Hernández-García
-
-
Article |
 Coherent extreme-ultraviolet emission generated through frustrated tunnelling ionization
Coherent extreme-ultraviolet emission generated through frustrated tunnelling ionization
Coherent extreme-ultraviolet emission through frustrated tunnelling ionization is observed from He atoms excited by intense few-cycle infrared laser pulses. Its intensity depends on the ellipticity and the carrier-envelope phase of the infrared laser.
- Hyeok Yun
- , Je Hoi Mun
- & Kyung Taec Kim
-
News & Views |
 Folding photography in the time domain
Folding photography in the time domain
Exploiting an optical cavity that folds space in time in a conventional lens design provides a novel route for time-resolved imaging and depth sensing.
- Sylvain Gigan
-
Article |
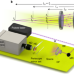 Photography optics in the time dimension
Photography optics in the time dimension
By folding large spaces in time using an off-resonant Fabry–Pérot cavity in camera sensors, new capabilities such as ultrafast multi-zoom imaging and ultrafast multispectral imaging, of use for time-resolved imaging and depth-sensing optics, are found.
- Barmak Heshmat
- , Matthew Tancik
- & Ramesh Raskar
-
News & Views |
 The heat is on
The heat is on
The generation of hot electrons in plasmonic nanostructures is of scientific and technological interest, putting the community under pressure to better understand the hot-electron mechanisms and to increase the light conversion efficiency of plasmonic nanosystems for chemical reactions and photodetection.
- Rachel Won
-
-
Letter |
 Phase-matched extreme-ultraviolet frequency-comb generation
Phase-matched extreme-ultraviolet frequency-comb generation
Using high-temperature gas mixtures as the generation medium to increase the translational velocity of Xe atoms through the focus of a femtosecond enhancement cavity, phase-matched extreme-ultraviolet emission at a repetition rate of 77 MHz and with an average power of ~ 2 mW in a single harmonic order is achieved.
- Gil Porat
- , Christoph M. Heyl
- & Jun Ye
-
News & Views |
 Locking the waveform with a quartz crystal
Locking the waveform with a quartz crystal
High-order harmonics in the extreme-ultraviolet regime can be produced and a stable waveform-locked attosecond pulse can be formed when quartz is excited by a strong short-pulsed laser, providing a robust path towards attosecond photonics.
- Shambhu Ghimire
-
News & Views |
 Complete polarization control
Complete polarization control
The polarization state of isolated attosecond pulses generated by high-order harmonic generation can now be manipulated at will. The development opens the door for a multitude of ultrafast experiments to investigate chiral media.
- Emma R. Simpson
- & Johan Mauritsson
-
Article |
 Segmented terahertz electron accelerator and manipulator (STEAM)
Segmented terahertz electron accelerator and manipulator (STEAM)
By sending few-microjoule single-cycle terahertz pulses to a segmented terahertz electron accelerator and manipulator, 70 MV m–1 peak acceleration fields, 2 kT m–1 focusing gradients, 140 µrad fs–1 streaking gradient and bunch compression to 100 fs are achieved.
- Dongfang Zhang
- , Arya Fallahi
- & Franz X. Kärtner
-
-
Letter |
 High-harmonic spectroscopy of ultrafast many-body dynamics in strongly correlated systems
High-harmonic spectroscopy of ultrafast many-body dynamics in strongly correlated systems
A highly nonlinear optical response can be used to time-resolve light-induced phase transitions with few-femtosecond to sub-femtosecond accuracy, paving the way for time-resolving highly correlated many-body dynamics in strongly correlated systems with few-femtosecond accuracy.
- R. E. F. Silva
- , Igor V. Blinov
- & M. Ivanov
-
Article |
 Ultimate waveform reproducibility of extreme-ultraviolet pulses by high-harmonic generation in quartz
Ultimate waveform reproducibility of extreme-ultraviolet pulses by high-harmonic generation in quartz
High-harmonic generation in quartz offers immunity to the extreme-ultraviolet waveform against the intensity and phase noise of the driving laser pulse, extending precision waveform synthesis to the extreme ultraviolet.
- M. Garg
- , H. Y. Kim
- & E. Goulielmakis
-
Article |
 Single-shot measurement of phase and amplitude by using a heterodyne time-lens system and ultrafast digital time-holography
Single-shot measurement of phase and amplitude by using a heterodyne time-lens system and ultrafast digital time-holography
The use of a phase-sensitive time-lens system allows single-shot recording of both the amplitude and phase of random and complex signals with a high temporal resolution of ~80 fs over a long time window of ~40 ps.
- Alexey Tikan
- , Serge Bielawski
- & Pierre Suret
-
Letter |
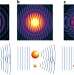 Femtosecond X-ray Fourier holography imaging of free-flying nanoparticles
Femtosecond X-ray Fourier holography imaging of free-flying nanoparticles
Femtosecond X-ray Fourier holography imaging with record-high lateral resolution below 20 nm is demonstrated. Phase information is encoded into the interference of the diffraction patterns of a reference particle with a measurement sample.
- Tais Gorkhover
- , Anatoli Ulmer
- & Christoph Bostedt
-
-
News & Views |
 Highly efficient nanoscale X-ray sources
Highly efficient nanoscale X-ray sources
Irradiating arrays of metal nanowires with intense femtosecond laser pulses produces high-brightness picosecond X-ray pulses. By specifically tailoring the plasma properties, up to 20% conversion efficiency of optical light into X-rays can be achieved.
- Daniel Rolles
-
Article |
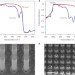 Active tuning of surface phonon polariton resonances via carrier photoinjection
Active tuning of surface phonon polariton resonances via carrier photoinjection
Infrared surface phonon polariton tuning is achieved by photoinjecting free carriers into resonators.
- Adam D. Dunkelberger
- , Chase T. Ellis
- & Joshua D. Caldwell
-
News & Views |
 Circular-polarization modulator
Circular-polarization modulator
Switching the handedness of circularly polarized light requires separately controlling the phases of orthogonal components while maintaining their magnitudes, ideally with gigahertz operation rates. Ultrafast switching has now been realized via all-optical control of birefringent metamaterials.
- Qiushi Liu
- & Ming Liu
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Imaging ultrafast electron dynamics
Imaging ultrafast electron dynamics
A feasible route towards electron microscopy at the attosecond timescale is now possible thanks to the implementation of an optical gating approach.
- Alberto Simoncig
-
-
News & Views |
 Optical waveform reconstruction
Optical waveform reconstruction
The direct measurement of few-cycle optical waveforms with arbitrary polarization and weak intensity is now made possible thanks to extreme ultraviolet interferometry with isolated attosecond pulses.
- Pascal Salières
-
News & Views |
 Femtosecond polarization switching
Femtosecond polarization switching
High-speed control of polarization may lead to ultrafast modulators and help explore polarization-dependent ultrafast dynamics in matter. Now, femtosecond polarization switching is realized through intraband optical excitation in an ultrathin semiconductor layer.
- Dongfang Li
-
Review Article |
 Time stretch and its applications
Time stretch and its applications
Photonic time-stretch techniques and their applications are reviewed. The approach enables the observation of signals that are otherwise too short or rapid for conventional measurement.
- Ata Mahjoubfar
- , Dmitry V. Churkin
- & Bahram Jalali
-
Article |
 Vectorial optical field reconstruction by attosecond spatial interferometry
Vectorial optical field reconstruction by attosecond spatial interferometry
An optical method for the temporal and spatial reconstruction of the electric field of few-cycle pulses is developed. The method is based on two attosecond technologies: extreme-ultraviolet interferometry and a directional electric field detector.
- P. Carpeggiani
- , M. Reduzzi
- & G. Sansone
-
Article |
 High-temporal-resolution electron microscopy for imaging ultrafast electron dynamics
High-temporal-resolution electron microscopy for imaging ultrafast electron dynamics
Ultrafast electron microscopy with an order-of-magnitude enhancement in the typical temporal resolution is demonstrated, permitting the imaging of ultrafast electron dynamics that last a few tens of femtoseconds.
- M. Th. Hassan
- , J. S. Baskin
- & A. H. Zewail
-
Article |
 Femtosecond optical polarization switching using a cadmium oxide-based perfect absorber
Femtosecond optical polarization switching using a cadmium oxide-based perfect absorber
Indium-doped cadmium oxide performs polarization switching on a subpicosecond timescale.
- Yuanmu Yang
- , Kyle Kelley
- & Igal Brener
-
Letter |
 Relativistic electron beams driven by kHz single-cycle light pulses
Relativistic electron beams driven by kHz single-cycle light pulses
A laser–plasma accelerator delivering 5-MeV electrons at kHz repetition rate is demonstrated. It is achieved in the laser-wakefield-acceleration regime by using a multi-mJ laser system delivering near-single-cycle laser pulses of 3.4-fs duration.
- D. Guénot
- , D. Gustas
- & J. Faure
-
-
News & Views |
 Attosecond nanophotonics
Attosecond nanophotonics
Combining attosecond science and nanophotonics potentially offers a route to enhance control over light–matter interactions at the nanoscale and provide a promising platform for information processing.
- Giulio Vampa
- , Hanieh Fattahi
- & Ferenc Krausz
-
News & Views |
 Tailoring extreme-ultraviolet light
Tailoring extreme-ultraviolet light
The emission direction and timing of extreme-ultraviolet light can now be manipulated through an opto-optical approach that uses an infrared pulse to control the spatial and spectral phase of free induction decay resulting from atoms excited by attosecond light.
- Taro Sekikawa
- & Kenichi L. Ishikawa
-
Article |
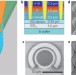 Photon-trapping microstructures enable high-speed high-efficiency silicon photodiodes
Photon-trapping microstructures enable high-speed high-efficiency silicon photodiodes
Light-trapping nanoscale holes are exploited to improve the speed and efficiency of silicon photodiodes with intrinsic layers less than 2 μm thick.
- Yang Gao
- , Hilal Cansizoglu
- & M. Saif Islam

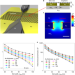 Ultrafast and energy-efficient all-optical switching with graphene-loaded deep-subwavelength plasmonic waveguides
Ultrafast and energy-efficient all-optical switching with graphene-loaded deep-subwavelength plasmonic waveguides Supercrystal creation
Supercrystal creation Phase in focus
Phase in focus Mapping cell dynamics at visible wavelengths
Mapping cell dynamics at visible wavelengths