Featured
-
-
Article |
 Quasi-experimental evaluation of a nationwide diabetes prevention programme
Quasi-experimental evaluation of a nationwide diabetes prevention programme
Analysis of the largest behaviour change programme for prediabetes globally provides causal evidence that lifestyle advice and counselling implemented at scale can improve key cardiovascular risk factors.
- Julia M. Lemp
- , Christian Bommer
- & Pascal Geldsetzer
-
Article |
 A hormone complex of FABP4 and nucleoside kinases regulates islet function
A hormone complex of FABP4 and nucleoside kinases regulates islet function
Hormonal FABP4 is discovered to be a pivotal regulator of an adipose–beta-cell endocrine axis that coordinates energy status and metabolic organ function, and targeting this axis improved metabolic outcomes.
- Kacey J. Prentice
- , Jani Saksi
- & Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
-
Article |
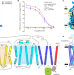 Structural basis of inhibition of the human SGLT2–MAP17 glucose transporter
Structural basis of inhibition of the human SGLT2–MAP17 glucose transporter
Using cryogenic electron microscopy, the structure of the human SGLT2–MAP17 complex captured in the empagliflozin-bound state reveals the inhibitory mechanism of these anti-diabetic drugs.
- Yange Niu
- , Rui Liu
- & Lei Chen
-
Article |
 REV-ERB in GABAergic neurons controls diurnal hepatic insulin sensitivity
REV-ERB in GABAergic neurons controls diurnal hepatic insulin sensitivity
REV-ERB in GABAergic neurons orchestrates the rhythmic sensitivity of hepatic glucose production to insulin-mediated suppression that peaks at wakening, with implications in the extended dawn phenomenon.
- Guolian Ding
- , Xin Li
- & Zheng Sun
-
Article |
 Identification of type 2 diabetes loci in 433,540 East Asian individuals
Identification of type 2 diabetes loci in 433,540 East Asian individuals
A meta-analysis of genome-wide association study data from 77,418 individuals of East Asian ancestry with type 2 diabetes identifies novel variants associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Cassandra N. Spracklen
- , Momoko Horikoshi
- & Xueling Sim
-
Article |
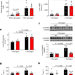 Glucagon stimulates gluconeogenesis by INSP3R1-mediated hepatic lipolysis
Glucagon stimulates gluconeogenesis by INSP3R1-mediated hepatic lipolysis
A role and mechanism of action are identified for INSP3R1 in the stimulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis and mitochondrial oxidation by glucagon, suggesting that INSP3R1 may be a target for ameliorating dysregulation of hepatic glucose metabolism.
- Rachel J. Perry
- , Dongyan Zhang
- & Gerald I. Shulman
-
Review Article |
 The integrative biology of type 2 diabetes
The integrative biology of type 2 diabetes
A Review of studies into insulin resistance and hepatic gluconeogenesis associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes.
- Michael Roden
- & Gerald I. Shulman
-
Perspective
| Open Access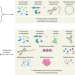 The Integrative Human Microbiome Project
The Integrative Human Microbiome Project
Over ten years, the Human Microbiome Project has provided resources for studying the microbiome and its relationship to disease; this Perspective summarizes the key achievements and findings of the project and its relationship to the broader field.
- Lita M. Proctor
- , Heather H. Creasy
- & Curtis Huttenhower
-
Letter |
 FOXK1 and FOXK2 regulate aerobic glycolysis
FOXK1 and FOXK2 regulate aerobic glycolysis
The Forkhead transcription factors FOXK1 and FOXK2, which are induced by starvation, reprogram cellular metabolism to induce aerobic glycolysis.
- Valentina Sukonina
- , Haixia Ma
- & Sven Enerbäck
-
Article |
 Cryo-EM structure of the activated GLP-1 receptor in complex with a G protein
Cryo-EM structure of the activated GLP-1 receptor in complex with a G protein
The structure of the GLP-1 receptor complexed with its ligand offers insight into the mechanism of class B G-protein-coupled receptor activation.
- Yan Zhang
- , Bingfa Sun
- & Georgios Skiniotis
-
Letter |
 Fatty acid synthesis configures the plasma membrane for inflammation in diabetes
Fatty acid synthesis configures the plasma membrane for inflammation in diabetes
Mice with macrophages deficient in fatty acid synthase exhibit lower levels of diabetes-related insulin resistance and inflammation, qualities that are restored on addition of exogenous cholesterol.
- Xiaochao Wei
- , Haowei Song
- & Clay F. Semenkovich
-
Letter |
 Depletion of fat-resident Treg cells prevents age-associated insulin resistance
Depletion of fat-resident Treg cells prevents age-associated insulin resistance
Fat-resident regulatory T cells (fTreg cells) accumulate in adipose tissue of mice as a function of age, but not obesity; mice without fTreg cells are protected against age-associated insulin resistance, but remain susceptible to obesity-associated insulin resistance and metabolic disease, indicating different aetiologies of age-associated versus obesity-associated insulin resistance.
- Sagar P. Bapat
- , Jae Myoung Suh
- & Ye Zheng
-
Article |
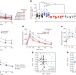 Artificial sweeteners induce glucose intolerance by altering the gut microbiota
Artificial sweeteners induce glucose intolerance by altering the gut microbiota
Non-caloric artificial sweeteners (NAS), widely used food additives considered to be safe and beneficial alternatives to sugars, are shown here to lead to the development of glucose intolerance through compositional and functional changes in the gut microbiota of mice, and the deleterious metabolic effects are transferred to germ-free mice by faecal transplant; NAS-induced dysbiosis and glucose intolerance are also demonstrated in healthy human subjects.
- Jotham Suez
- , Tal Korem
- & Eran Elinav
-
Letter |
 High-resolution structure of the human GPR40 receptor bound to allosteric agonist TAK-875
High-resolution structure of the human GPR40 receptor bound to allosteric agonist TAK-875
The X-ray crystal structure of human GPR40 receptor in the presence of TAK-875, an orally available, potent and selective human GPR40 agonist.
- Ankita Srivastava
- , Jason Yano
- & Kengo Okada
-
Letter |
 Endocrinization of FGF1 produces a neomorphic and potent insulin sensitizer
Endocrinization of FGF1 produces a neomorphic and potent insulin sensitizer
Pharmacological fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF1) normalizes blood glucose in diabetic mice by means of an FGF receptor signalling pathway that is independent of its mitogenic activity.
- Jae Myoung Suh
- , Johan W. Jonker
- & Ronald M. Evans
-
Letter |
 A common Greenlandic TBC1D4 variant confers muscle insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes
A common Greenlandic TBC1D4 variant confers muscle insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes
An association mapping study of type-2-diabetes-related quantitative traits in the Greenlandic population identified a common variant in TBC1D4 that increases plasma glucose levels and serum insulin levels after an oral glucose load and type 2 diabetes risk, with effect sizes several times larger than any previous findings of large-scale genome-wide association studies for these traits.
- Ida Moltke
- , Niels Grarup
- & Torben Hansen
-
Article |
 Structure of the human glucagon class B G-protein-coupled receptor
Structure of the human glucagon class B G-protein-coupled receptor
The X-ray crystal structure of the human glucagon receptor, a potential drug target for type 2 diabetes, offers a structural basis for molecular recognition by class B G-protein-coupled receptors.
- Fai Yiu Siu
- , Min He
- & Raymond C. Stevens
-
Letter |
 Biguanides suppress hepatic glucagon signalling by decreasing production of cyclic AMP
Biguanides suppress hepatic glucagon signalling by decreasing production of cyclic AMP
Biguanides such as metformin, which is the most widely prescribed drug for type-2 diabetes, are shown to antagonize the actions of glucagon by decreasing the levels of cyclic AMP.
- Russell A. Miller
- , Qingwei Chu
- & Morris J. Birnbaum
-
News & Views |
 Resident risks
Resident risks
An innovative method for probing the genomes of the vast community of microorganisms that inhabit the human gut provides an alternative approach to identifying risk factors for type 2 diabetes. See Letter p.55
- Julia Oh
- & Julia A. Segre
-
Research Highlights |
 Cells turn back clock in diabetes
Cells turn back clock in diabetes
-
Article |
 A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes
A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes
The authors have developed a new method, metagenome-wide association study (MGWAS), to compare the combined genetic content of the faecal microbiota of healthy people versus patients with type 2 diabetes; they identify multiple microbial species and metabolic pathways that are associated with either cohort and show that some of these may be used as biomarkers.
- Junjie Qin
- , Yingrui Li
- & Jun Wang
-
Letter |
 Targeting VEGF-B as a novel treatment for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes
Targeting VEGF-B as a novel treatment for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes
Inhibition of VEGF-B signalling is shown to limit ectopic fatty-acid accumulation, restore peripheral insulin sensitivity and muscle glucose uptake, and preserve pancreatic islet functionality.
- Carolina E. Hagberg
- , Annika Mehlem
- & Ulf Eriksson
-
Outlook |
 Pathology: Cause and effect
Pathology: Cause and effect
Decades of study into the causes of diabetes have produced no definitive answers.
- Erika Jonietz
-
Outlook |
 Prevention: Nipped in the bud
Prevention: Nipped in the bud
While type 1 diabetes might be promising ground for a vaccine, the most effective way to avoid type 2 remains good old-fashioned diet and exercise.
- Scott P. Edwards
-
Article |
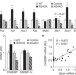 A novel ChREBP isoform in adipose tissue regulates systemic glucose metabolism
A novel ChREBP isoform in adipose tissue regulates systemic glucose metabolism
Downregulation of the glucose transporter GLUT4 in adipose tissue occurs early in the development of type 2 diabetes; here GLUT4-mediated glucose uptake is shown to induce a novel form of the transcription factor ChREBP, which regulates de novo lipogenesis and systemic glucose metabolism.
- Mark A. Herman
- , Odile D. Peroni
- & Barbara B. Kahn
-
News |
 The rise of the 'narciss-ome'
The rise of the 'narciss-ome'
Profiles of a researcher's genes, proteins and more show personalized genomic medicine in action.
- Carina Dennis
-
Letter |
 MicroRNAs 103 and 107 regulate insulin sensitivity
MicroRNAs 103 and 107 regulate insulin sensitivity
- Mirko Trajkovski
- , Jean Hausser
- & Markus Stoffel
-
Letter |
 9p21 DNA variants associated with coronary artery disease impair interferon-γ signalling response
9p21 DNA variants associated with coronary artery disease impair interferon-γ signalling response
A non-coding region on chromosome 9p21 was previously shown to associate with coronary artery disease and type 2 diabetes, and the region has been implicated in regulating neighbouring genes. Here, 33 distinct enhancers within this region are identified, showing that SNPs in one of the enhancers affect STAT1 binding. Furthermore, it is shown that in human vascular endothelial cells the enhancer interval physically interacts with a number of specific loci and that IFN-γ activation strongly affects the chromatin structure and transcriptional regulation of the 9p21 locus, including STAT1 binding, long-range enhancer interactions and expression of neighbouring genes.
- Olivier Harismendy
- , Dimple Notani
- & Kelly A. Frazer
-
News & Views |
 Diabetes in India
Diabetes in India
With the spread of fast-food outlets and more sedentary lifestyles, the prevalence of diabetes in India is rising alarmingly. But the subpopulations at risk and the symptoms of the disease differ from those in the West.
- Jared Diamond
-
Letter |
 Chronic high-fat diet in fathers programs β-cell dysfunction in female rat offspring
Chronic high-fat diet in fathers programs β-cell dysfunction in female rat offspring
Here it is shown that the consumption of a high-fat diet by male rats has an intergenerational effect: it leads to the dysfunction of pancreatic β-cells in female offspring. Relative to controls, these offspring showed an early onset of impaired insulin secretion and glucose tolerance, which worsened with time. The results add to our understanding of the complex genetic and environmental factors that are leading to the global epidemic of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
- Sheau-Fang Ng
- , Ruby C. Y. Lin
- & Margaret J. Morris
-
News |
 Evidence mounts against diabetes drug
Evidence mounts against diabetes drug
Studies continue to find heart-attack risk.
- Heidi Ledford

 Genetic risk converges on regulatory networks mediating early type 2 diabetes
Genetic risk converges on regulatory networks mediating early type 2 diabetes