Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access pH effects on the electrochemical reduction of CO(2) towards C2 products on stepped copper
pH effects on the electrochemical reduction of CO(2) towards C2 products on stepped copper
CO2 conversion to reduced products provides a use for greenhouse gases, but reaction complexity stymies mechanistic studies. Here, authors present a microkinetic model for CO2 and CO reduction on copper, based on ab initio simulations, to elucidate pH’s impact on competitive reaction pathways.
- Xinyan Liu
- , Philomena Schlexer
- & Karen Chan
-
Article
| Open Access Minimizing the electrosorption of water from humid ionic liquids on electrodes
Minimizing the electrosorption of water from humid ionic liquids on electrodes
Ionic liquid electrolytes can impart increased operational voltage and energy density in supercapacitors, but water may diminish performance. Here the authors show that the hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity of ionic liquids can influence electrosorption of water and ultimately the supercapacitor performance.
- Sheng Bi
- , Runxi Wang
- & Guang Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Differentiation between enamines and tautomerizable imines in the oxidation reaction with TEMPO
Differentiation between enamines and tautomerizable imines in the oxidation reaction with TEMPO
Tautomerization of imines into enamines is the basis of their similar reactivity; however, minor structural changes may lead to different outcomes. Here, the authors show that the reaction of cyclohexanone and amines in presence of TEMPO affords either α-amino-enones or arylamines depending on the intermediate imine structure.
- Xiaoming Jie
- , Yaping Shang
- & Weiping Su
-
Article
| Open Access Double dative bond between divalent carbon(0) and uranium
Double dative bond between divalent carbon(0) and uranium
While chemical bonding between carbon and the d- and p-block elements is relatively well-studied, that between carbon and the f-block elements remains comparatively poorly understood. Here, the authors synthesize a series of uranium−carbone complexes in which carbon forms an unprecedented double dative bond to uranium.
- Wei Su
- , Sudip Pan
- & Congqing Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of copper-free Sonogashira reaction operates through palladium-palladium transmetallation
Mechanism of copper-free Sonogashira reaction operates through palladium-palladium transmetallation
Although the Sonogashira coupling of acetylenes and vinyl/aryl halides has been applied for decades, many mechanistic questions have remained unanswered. Here, the authors provide experimental and theoretical support for two interlinked palladium cycles operating in the debated Sonogashira coupling mechanism.
- Martin Gazvoda
- , Miha Virant
- & Janez Košmrlj
-
Correspondence
| Open Access The diamine cation is not a chemical example where density functional theory fails
The diamine cation is not a chemical example where density functional theory fails
- Zulfikhar A. Ali
- , Fredy W. Aquino
- & Bryan M. Wong
-
Article
| Open Access Thermal transport crossover from crystalline to partial-crystalline partial-liquid state
Thermal transport crossover from crystalline to partial-crystalline partial-liquid state
Phase-change materials are applied as thermoelectric converters and battery electrodes, but underlying mechanisms are not fully understood. Here, the authors comprehensively describe thermal transport mechanisms of lithium sulfide based on molecular dynamics and first-principles simulations.
- Yanguang Zhou
- , Shiyun Xiong
- & Ming Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Manipulating azobenzene photoisomerization through strong light–molecule coupling
Manipulating azobenzene photoisomerization through strong light–molecule coupling
Manipulation of the photochemistry of molecules is traditionally achieved through synthetic chemical modifications. Here the authors use computational photochemistry to show how to control azobenzene photoisomerization through hybrid light–molecule states (polaritons).
- J. Fregoni
- , G. Granucci
- & S. Corni
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical shifts in molecular solids by machine learning
Chemical shifts in molecular solids by machine learning
Solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance combined with quantum chemical shift predictions is limited by high computational cost. Here, the authors use machine learning based on local atomic environments to predict experimental chemical shifts in molecular solids with accuracy similar to density functional theory.
- Federico M. Paruzzo
- , Albert Hofstetter
- & Lyndon Emsley
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast carbon monoxide photolysis and heme spin-crossover in myoglobin via nonadiabatic quantum dynamics
Ultrafast carbon monoxide photolysis and heme spin-crossover in myoglobin via nonadiabatic quantum dynamics
Myoglobin bound to carbon monoxide undergoes an ultrafast light-induced reaction, which ends up in a photolyzed carbon monoxide and a spin transition of the iron center. Here, the authors employ quantum wavepacket dynamics to show that photolysis precedes the spin transition, a mechanism dominated by strong electron-nuclear couplings.
- Konstantin Falahati
- , Hiroyuki Tamura
- & Miquel Huix-Rotllant
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum machine learning for electronic structure calculations
Quantum machine learning for electronic structure calculations
With the rapid development of quantum computers, quantum machine learning approaches are emerging as powerful tools to perform electronic structure calculations. Here, the authors develop a quantum machine learning algorithm, which demonstrates significant improvements in solving quantum many-body problems.
- Rongxin Xia
- & Sabre Kais
-
Article
| Open Access Two-site H2O2 photo-oxidation on haematite photoanodes
Two-site H2O2 photo-oxidation on haematite photoanodes
Understanding fundamental processes that occur using solar-to-fuel conversion materials is crucial for constructing effective renewable energy collection. Here, authors find the hydrogen peroxide light-driven hole-scavenging mechanism over haematite to proceed with two active sites rather than one
- Yotam Y. Avital
- , Hen Dotan
- & Arik Yochelis
-
Article
| Open Access Vibrational control of selective bond cleavage in dissociative chemisorption of methanol on Cu(111)
Vibrational control of selective bond cleavage in dissociative chemisorption of methanol on Cu(111)
Dissociative chemisorption of methanol on metal surfaces is a key step for hydrogen production. Here the authors use quasi-quantized molecular dynamics simulations to alter the branching ratios for methanol dissociative chemisorption on Cu(111) via selectively exciting specific vibrational modes.
- Jialu Chen
- , Xueyao Zhou
- & Bin Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Towards exact molecular dynamics simulations with machine-learned force fields
Towards exact molecular dynamics simulations with machine-learned force fields
Simultaneous accurate and efficient prediction of molecular properties relies on combined quantum mechanics and machine learning approaches. Here the authors develop a flexible machine-learning force-field with high-level accuracy for molecular dynamics simulations.
- Stefan Chmiela
- , Huziel E. Sauceda
- & Alexandre Tkatchenko
-
Article
| Open Access Deep neural networks for accurate predictions of crystal stability
Deep neural networks for accurate predictions of crystal stability
Crystal stability prediction is of paramount importance for novel material discovery, with theoretical approaches alternative to expensive standard schemes highly desired. Here the authors develop a deep learning approach which, just using two descriptors, provides crystalline formation energies with very high accuracy.
- Weike Ye
- , Chi Chen
- & Shyue Ping Ong
-
Article
| Open Access Nanomaterials design for super-degenerate electronic state beyond the limit of geometrical symmetry
Nanomaterials design for super-degenerate electronic state beyond the limit of geometrical symmetry
No substances with greater degrees of degeneracy than spherical atoms are known, due to geometrical limitations. In this work the authors combine density functional theory and tight-binding models to predict metal clusters with higher-fold degeneracies than spherical atoms, which are ascribed to dynamical symmetry.
- Naoki Haruta
- , Takamasa Tsukamoto
- & Kimihisa Yamamoto
-
Article
| Open Access Role of hydrogen bonding in hysteresis observed in sorption-induced swelling of soft nanoporous polymers
Role of hydrogen bonding in hysteresis observed in sorption-induced swelling of soft nanoporous polymers
Water uptake of natural polymers is accompanied by swelling and changes in the internal structure of the polymeric system but the exact mechanism of water-uptake and swelling remained unknown. Here the authors use atom-scale simulations to identify a molecular mechanism which is responsible for hysteresis in sorption-induced swelling in natural polymers.
- Mingyang Chen
- , Benoit Coasne
- & Jan Carmeliet
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic engineering of high-density isolated Co atoms on graphene with proximal-atom controlled reaction selectivity
Atomic engineering of high-density isolated Co atoms on graphene with proximal-atom controlled reaction selectivity
Controllable synthesis of single atom catalysts with sufficiently high metal loading remains challenging due to the tendency of agglomeration. Here the authors synthesize a series of stable atomically dispersed cobalt atoms on graphene with high Co loadings via the regeneration of active sites by atomic layer deposition.
- Huan Yan
- , Xiaoxu Zhao
- & Jiong Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Interfacing with silica boosts the catalysis of copper
Interfacing with silica boosts the catalysis of copper
Metal-support interaction plays an important role in heterogeneous catalysis, but silica has been rarely reported as an effective support to create active metal-support interfaces for promoting catalytic reactions. Here, the authors discover that Cu/SiO2 interface creates an exceptional effect to promote catalytic hydrogenation of esters.
- Chaofa Xu
- , Guangxu Chen
- & Nanfeng Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding the apparent fractional charge of protons in the aqueous electrochemical double layer
Understanding the apparent fractional charge of protons in the aqueous electrochemical double layer
A detailed atomic-scale description of the electrochemical interface is essential to the understanding of electrochemical energy transformations. Here, the authors investigate the solvated proton at the electrochemical interface and show that it unexpectedly carries a fractional charge.
- Leanne D. Chen
- , Michal Bajdich
- & Jens K. Nørskov
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembly directed one-step synthesis of [4]radialene on Cu(100) surfaces
Self-assembly directed one-step synthesis of [4]radialene on Cu(100) surfaces
Radialenes have distinct structural, electronic and chemical properties from other hydrocarbons, but their synthesis remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a copper catalyzed one-step synthetic protocol of [4]radialene via the cyclotetramerization of phenylacetylene molecules upon thermal activation.
- Qing Li
- , Jianzhi Gao
- & Minghu Pan
-
Article
| Open Access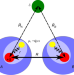 Tailoring van der Waals dispersion interactions with external electric charges
Tailoring van der Waals dispersion interactions with external electric charges
The description of van der Waals interactions should often account for coupling with pervasive electric fields, but this effect has been omitted in atomistic simulations. Here, the authors develop a model to study the effects of external charge on long-range van der Waals interactions.
- Andrii Kleshchonok
- & Alexandre Tkatchenko
-
Article
| Open Access High-throughput discovery of organic cages and catenanes using computational screening fused with robotic synthesis
High-throughput discovery of organic cages and catenanes using computational screening fused with robotic synthesis
Supramolecular assemblies remain of great importance to a variety of fields, yet their targeted design and synthesis remains highly challenging. Here, Cooper and colleagues combine computational screening with high-throughput robotic synthesis and discover 33 new organic cage molecules that form cleanly in one-pot syntheses.
- R. L. Greenaway
- , V. Santolini
- & A. I. Cooper
-
Article
| Open Access Influence of atomic site-specific strain on catalytic activity of supported nanoparticles
Influence of atomic site-specific strain on catalytic activity of supported nanoparticles
Detailed knowledge of how strain influences catalytic reactions remains elusive. Here, the authors experimentally measure the strain in supported Pt nanoparticles on alumina and ceria with atomic resolution and computationally explore how the strain affects the CO oxidation reaction.
- Torben Nilsson Pingel
- , Mikkel Jørgensen
- & Eva Olsson
-
Article
| Open Access Selective ensembles in supported palladium sulfide nanoparticles for alkyne semi-hydrogenation
Selective ensembles in supported palladium sulfide nanoparticles for alkyne semi-hydrogenation
Developing robust catalysts for alkyne semi-hydrogenation remains a challenge. Here, the authors introduce a scalable protocol to prepare crystal phase and orientation controlled Pd3S nanoparticles supported on carbon nitride, exhibiting unparalleled semi-hydrogenation performance due to a high density of active and selective ensembles.
- Davide Albani
- , Masoud Shahrokhi
- & Javier Pérez-Ramírez
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding crystallization pathways leading to manganese oxide polymorph formation
Understanding crystallization pathways leading to manganese oxide polymorph formation
Minor variations in synthesis conditions can redirect crystallization pathways through different nonequilibrium intermediates. Here, the authors present a theoretical framework to predict which polymorphs appear during MnO2 precipitation, which is validated by in situ X-ray scattering of reaction progression.
- Bor-Rong Chen
- , Wenhao Sun
- & Laura T. Schelhas
-
Article
| Open Access Accelerating the discovery of insensitive high-energy-density materials by a materials genome approach
Accelerating the discovery of insensitive high-energy-density materials by a materials genome approach
The synthesis of explosive materials that are stable, highly dense, and have low sensitivity to external stimuli is a challenge. Here, the authors use a genomic approach to accelerate the discovery of insensitive high explosive molecules with good detonation and low sensitivity properties.
- Yi Wang
- , Yuji Liu
- & Yong Tian
-
Article
| Open Access Assigning the absolute configuration of single aliphatic molecules by visual inspection
Assigning the absolute configuration of single aliphatic molecules by visual inspection
Deciphering absolute configuration of individual molecules directly by visual inspection remains a highly attractive goal. Here, the authors determine the absolute configuration and orientation of a single [123]tetramantane molecule adsorbed on Cu(111) using low temperature atomic force microscopy with a CO-functionalized tip.
- Daniel Ebeling
- , Marina Šekutor
- & Peter R. Schreiner
-
Article
| Open Access Computational design of high-performance ligand for enantioselective Markovnikov hydroboration of aliphatic terminal alkenes
Computational design of high-performance ligand for enantioselective Markovnikov hydroboration of aliphatic terminal alkenes
Trial-and-error methods to identify suitable ligands for transition metal catalysis are time-consuming and costly. Here, the authors developed a combined experimental and computational approach to design chiral ligands for the enantioselective Markovnikov hydroboration of aliphatic terminal alkenes.
- Hiroaki Iwamoto
- , Tsuneo Imamoto
- & Hajime Ito
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum Monte Carlo simulations of a giant {Ni21Gd20} cage with a S = 91 spin ground state
Quantum Monte Carlo simulations of a giant {Ni21Gd20} cage with a S = 91 spin ground state
Paramagnetic metal clusters with large ground spin states often possess attractive magnetic behaviors for information storage or solid-state cooling applications. Here, the authors design a giant {Ni21Gd20} cage, which using quantum monte carlo simulations they predict to possess a spin ground state approaching S = 91.
- Wei-Peng Chen
- , Jared Singleton
- & Yan-Zhen Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access On-surface synthesis of a nitrogen-embedded buckybowl with inverse Stone–Thrower–Wales topology
On-surface synthesis of a nitrogen-embedded buckybowl with inverse Stone–Thrower–Wales topology
Heteroatom doping of buckybowls is a viable route to tune their intrinsic physico-chemical properties, but their synthesis remains challenging. Here, the authors report on a combined in-solution and on-surface synthetic strategy towards the fabrication of a buckybowl containing two fused nitrogen-doped pentagonal rings.
- Shantanu Mishra
- , Maciej Krzeszewski
- & Daniel T. Gryko
-
Article
| Open Access Heterogeneous Fe3 single-cluster catalyst for ammonia synthesis via an associative mechanism
Heterogeneous Fe3 single-cluster catalyst for ammonia synthesis via an associative mechanism
The current industrial ammonia synthesis relies on the Haber-Bosch process that is limited by the Brønsted–Evans–Polanyi relation. Here, the authors propose a new strategy that an anchored Fe3 on θ-Al2O3(010) surface serves as a heterogeneous single cluster catalyst for ammonia synthesis from first-principles calculations and microkinetic analysis.
- Jin-Cheng Liu
- , Xue-Lu Ma
- & Jun Li
-
Article
| Open Access Simultaneous complementary photoswitching of hemithioindigo tweezers for dynamic guest relocalization
Simultaneous complementary photoswitching of hemithioindigo tweezers for dynamic guest relocalization
Controlling complex photoresponsive systems while minimizing light input is highly challenging. Here, the authors report two photoswitchable molecular tweezers responding to the same light signals with opposite changes in their binding affinities towards a guest molecule allowing for its “light-economic” relocation.
- Sandra Wiedbrauk
- , Thomas Bartelmann
- & Henry Dube
-
Article
| Open Access Calculating curly arrows from ab initio wavefunctions
Calculating curly arrows from ab initio wavefunctions
Despite being essential to organic chemistry, the curly arrow notation of reaction mechanisms has been treated with suspicion due to its unclear connection with quantum mechanics. Here, the authors show that analysis of wavefunction 'tiles' along a reaction coordinate reveals the electron motion depicted by curly arrows.
- Yu Liu
- , Philip Kilby
- & Timothy W. Schmidt
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding the adsorption process in ZIF-8 using high pressure crystallography and computational modelling
Understanding the adsorption process in ZIF-8 using high pressure crystallography and computational modelling
Understanding host–guest interactions and structural changes within porous materials is crucial for enhancing gas storage properties. Here, the authors combine cryogenic loading of gases with high pressure crystallography and computational techniques to obtain atomistic detail of adsorption-induced structural and energetic changes in ZIF-8.
- Claire L. Hobday
- , Christopher H. Woodall
- & Stephen A. Moggach
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental determination of the energy difference between competing isomers of deposited, size-selected gold nanoclusters
Experimental determination of the energy difference between competing isomers of deposited, size-selected gold nanoclusters
The equilibrium structures and dynamics of a nanoscale system are regulated by a complex potential energy surface (PES), a key target of theoretical calculations but experimentally elusive. Here, the authors report the measurement of a key PES parameter for size-selected Au nanoclusters soft-landed on amorphous silicon nitride supports.
- D. M. Foster
- , R. Ferrando
- & R. E. Palmer
-
Article
| Open Access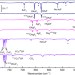 Oxygen radical character in group 11 oxygen fluorides
Oxygen radical character in group 11 oxygen fluorides
While transition metal complexes bearing terminal oxido ligands are common, those of group 11 elements have yet to be experimentally observed. Here, Riedel and colleagues synthesise molecular oxygen fluorides of copper, silver and gold, and show that the oxo ligands possess radical character.
- Lin Li
- , Tony Stüker
- & Sebastian Riedel
-
Article
| Open Access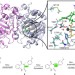 Catalytic mechanism and molecular engineering of quinolone biosynthesis in dioxygenase AsqJ
Catalytic mechanism and molecular engineering of quinolone biosynthesis in dioxygenase AsqJ
The catalytic activity of dioxygenase AsqJ is strictly relying on the methylation of quinolone substrates. Here, the authors apply molecular simulations, X-ray crystallography and in vitro biochemical studies to the engineering of dioxygenase AsqJ with improved catalytic activity for modified non-methylated surrogates.
- Sophie L. Mader
- , Alois Bräuer
- & Ville R. I. Kaila
-
Article
| Open Access Reactivity of He with ionic compounds under high pressure
Reactivity of He with ionic compounds under high pressure
Helium was long thought to be unable to form stable solid compounds, until a recent discovery that helium reacts with sodium at high pressure. Here, the authors demonstrate the driving force for helium reactivity, showing that it can form new compounds under pressure without forming any local chemical bonds.
- Zhen Liu
- , Jorge Botana
- & Mao-sheng Miao
-
Article
| Open Access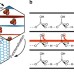 Effect of friction on oxidative graphite intercalation and high-quality graphene formation
Effect of friction on oxidative graphite intercalation and high-quality graphene formation
Scalable graphene production from graphite via an intercalation-oxidation-reduction process is still hampered by low reproducibility and many lattice defects. Here, the authors show that reducing molecular friction by using highly crystalline graphite and mild oxidizing conditions is the key to high quality graphene.
- Steffen Seiler
- , Christian E. Halbig
- & Siegfried Eigler
-
Article
| Open Access Directed gas phase formation of silicon dioxide and implications for the formation of interstellar silicates
Directed gas phase formation of silicon dioxide and implications for the formation of interstellar silicates
Interstellar silicates play a key role in star formation, however their synthetic routes are not fully understood. Here, the authors provide evidence for the formation of SiO2 along with SiO via low-temperature gas phase chemistry.
- Tao Yang
- , Aaron M. Thomas
- & Tom J. Millar
-
Article
| Open Access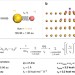 Insight into induced charges at metal surfaces and biointerfaces using a polarizable Lennard–Jones potential
Insight into induced charges at metal surfaces and biointerfaces using a polarizable Lennard–Jones potential
Molecular dynamics models for predicting the behavior of metallic nanostructures typically do not take into account polarization effects in metals. Here, the authors introduce a polarizable Lennard–Jones potential that provides quantitative insight into the role of induced charges at metal surfaces and related complex material interfaces.
- Isidro Lorenzo Geada
- , Hadi Ramezani-Dakhel
- & Hendrik Heinz
-
Article
| Open Access Protactinium and the intersection of actinide and transition metal chemistry
Protactinium and the intersection of actinide and transition metal chemistry
The role of the 5f and 6d orbitals in the chemical bonding of the actinide elements remains debated. Here, the authors synthesize and study a tetranuclear protactinium peroxo cluster and demonstrate that protactinium represents an intersection of actinide (5f) and transition metal (6d) chemistries.
- Richard E. Wilson
- , Stephanie De Sio
- & Valérie Vallet
-
Article
| Open Access Microkinetics of alcohol reforming for H2 production from a FAIR density functional theory database
Microkinetics of alcohol reforming for H2 production from a FAIR density functional theory database
The production of hydrogen from biomass is of fundamental importance for a sustainable future. Here, the authors present a multiscale method that allows the formulation of scaling relationships and microkinetics of C1-C2 alcohol decomposition based on a density functional theory open database.
- Qiang Li
- , Rodrigo García-Muelas
- & Núria López
-
Article
| Open Access Elucidation of the origin of chiral amplification in discrete molecular polyhedra
Elucidation of the origin of chiral amplification in discrete molecular polyhedra
The sergeants-and-soldiers effect, in which a few chiral units induce chirality in a large number of achiral molecules, is difficult to quantify at the molecular level. Here, the authors devise an elegant strategy—combining theory and a system of pure organic polyhedra with chiral and achiral vertices—to understand the mechanism of chiral amplification in discrete molecular assemblies.
- Yu Wang
- , Hongxun Fang
- & Xiaoyu Cao
-
Article
| Open Access Orientation of non-spherical protonated water clusters revealed by infrared absorption dichroism
Orientation of non-spherical protonated water clusters revealed by infrared absorption dichroism
Protein-bound water clusters play a key role for proton transport and storage in molecular biology. Here, the authors show by simulations and experiments that the orientation of non-spherical protonated water clusters in bacteriorhodopsin is unveiled by polarization-resolved infrared spectroscopy.
- Jan O. Daldrop
- , Mattia Saita
- & Roland R. Netz
-
Article
| Open Access The Chemical Fluctuation Theorem governing gene expression
The Chemical Fluctuation Theorem governing gene expression
A unified framework to understand gene expression noise is still lacking. Here the authors derive a universal theorem relating the biological noise with dynamics of birth and death processes and present a model of transcription dynamics, allowing analytical prediction of the dependence of mRNA noise on mRNA lifetime variability.
- Seong Jun Park
- , Sanggeun Song
- & Jaeyoung Sung
-
Article
| Open Access Electron affinity of liquid water
Electron affinity of liquid water
The electron affinity of liquid water is a fundamental property which has not yet been accurately measured. Here, the authors predict this property by coupling path-integral molecular dynamics with ab initio potentials and electronic structure calculations, revisiting several estimates used in the literature.
- Alex P. Gaiduk
- , Tuan Anh Pham
- & Giulia Galli
-
Article
| Open Access VAMPnets for deep learning of molecular kinetics
VAMPnets for deep learning of molecular kinetics
Extracting kinetic models from high-throughput molecular dynamics (MD) simulations is laborious and prone to human error. Here the authors introduce a deep learning framework that automates construction of Markov state models from MD simulation data.
- Andreas Mardt
- , Luca Pasquali
- & Frank Noé

 Halogen-bonded cocrystallization with phosphorus, arsenic and antimony acceptors
Halogen-bonded cocrystallization with phosphorus, arsenic and antimony acceptors