Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Review Article
| Open Access Application of combinatorial optimization strategies in synthetic biology
Application of combinatorial optimization strategies in synthetic biology
Our efforts to build complex synthetic biology circuits are impeded by limited knowledge of optimal combinations. In this review, the authors consider current combinatorial methods and look to emerging technologies.
- Gita Naseri
- & Mattheos A. G. Koffas
-
Article
| Open Access A redox-based electrogenetic CRISPR system to connect with and control biological information networks
A redox-based electrogenetic CRISPR system to connect with and control biological information networks
Redox-responsive transcriptional regulators can enable user-specified electronic control over biological functions. Here the authors demonstrate electronic control of CRISPRa and CRISPRi using redox signalling.
- Narendranath Bhokisham
- , Eric VanArsdale
- & William E. Bentley
-
Article
| Open Access Investigating the dynamics of microbial consortia in spatially structured environments
Investigating the dynamics of microbial consortia in spatially structured environments
The spatial organisation of microbial communities is caused by the interplay of biotic and abiotic factors. Here the authors design a microfluidic platform to quantify the spatiotemporal parameters influencing diffusion-mediated interactions, and use this device to investigate information transmission and metabolic cross-feeding in synthetic microbial consortia.
- Sonali Gupta
- , Tyler D. Ross
- & Ophelia S. Venturelli
-
Article
| Open Access Model-driven generation of artificial yeast promoters
Model-driven generation of artificial yeast promoters
A small set of promoters is used for most genetic construct design in S. cerevisiae. Here, the authors develop a predictive model of promoter activity trained on a data set of over one million sequences and use it to design large sets of high-activity promoters.
- Benjamin J. Kotopka
- & Christina D. Smolke
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic hybrids of six yeast species
Synthetic hybrids of six yeast species
Many industrial organisms are the result of recent or ancient allopolypoidy events. Here the authors iteratively combine the genomes of six yeast species to generate a viable hybrid.
- David Peris
- , William G. Alexander
- & Chris Todd Hittinger
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable genetic devices through simultaneous control of transcription and translation
Tunable genetic devices through simultaneous control of transcription and translation
Synthetic genetic circuits are sensitive to their environment and host cell, requiring many rounds of physical reassembly to achieve a desired function. Here the authors use a multi-level regulatory motif to dynamically tune the function of genetic parts as a step towards robust adaptive circuits.
- Vittorio Bartoli
- , Grace A. Meaker
- & Thomas E. Gorochowski
-
Article
| Open Access Improved GPCR ligands from nanobody tethering
Improved GPCR ligands from nanobody tethering
Antibodies conjugated to bioactive compounds can allow targeted delivery of therapeutics. Here the authors present a strategy for fusing nanobodies to suboptimal GPCR peptide ligands to potently and selectively activate receptors.
- Ross W. Cheloha
- , Fabian A. Fischer
- & Hidde L. Ploegh
-
Article
| Open Access Multiplex secretome engineering enhances recombinant protein production and purity
Multiplex secretome engineering enhances recombinant protein production and purity
Host cell proteins can contaminate biotherapeutics and compromise and degrade their quality. Here the authors use modelling and CRISPR to delete secreted host proteins in CHO cells, leading to improved monoclonal antibody production and purity.
- Stefan Kol
- , Daniel Ley
- & Nathan E. Lewis
-
Article
| Open Access Large scale active-learning-guided exploration for in vitro protein production optimization
Large scale active-learning-guided exploration for in vitro protein production optimization
Cell-free lysates are a major platform for in vitro protein production but batch-to-batch variation makes production difficult to predict. Here the authors develop an active learning approach to optimising buffer conditions to bring homemade lysates up to commercial production potential.
- Olivier Borkowski
- , Mathilde Koch
- & Jean-Loup Faulon
-
Article
| Open Access A fully orthogonal system for protein synthesis in bacterial cells
A fully orthogonal system for protein synthesis in bacterial cells
Ribosome engineering is an emerging powerful approach for synthetic protein synthesis. Here the authors invert the Ribo-T system, using the engineered ribosome to translate the proteome while the native ribosome translates specific mRNA.
- Nikolay A. Aleksashin
- , Teresa Szal
- & Alexander S. Mankin
-
Article
| Open Access Perturbing proteomes at single residue resolution using base editing
Perturbing proteomes at single residue resolution using base editing
Base editors allow for the precise modification of genes. Here the authors use Target-AID to systematically test 17,000 sites across the yeast genome.
- Philippe C. Després
- , Alexandre K. Dubé
- & Christian R. Landry
-
Perspective
| Open Access Developing a new class of engineered live bacterial therapeutics to treat human diseases
Developing a new class of engineered live bacterial therapeutics to treat human diseases
The role microbes play in human health and the ability of synthetic biology to engineer microbial properties opens up new ways of treating disease. In this perspective, the authors describe the design and development of these living therapeutics.
- Mark R. Charbonneau
- , Vincent M. Isabella
- & Caroline B. Kurtz
-
Article
| Open Access DNA punch cards for storing data on native DNA sequences via enzymatic nicking
DNA punch cards for storing data on native DNA sequences via enzymatic nicking
Current synthetic DNA-based data storage systems have high recording costs, read-write latency and error-rates that make them uncompetitive compared to traditional digital storage. The authors use nicks in native DNA to encode data in parallel and create access sites for in-memory computations.
- S. Kasra Tabatabaei
- , Boya Wang
- & Olgica Milenkovic
-
Article
| Open Access Effective CRISPRa-mediated control of gene expression in bacteria must overcome strict target site requirements
Effective CRISPRa-mediated control of gene expression in bacteria must overcome strict target site requirements
The use of CRISPRa in bacteria lacks predictive rules for identifying effective gRNA target sites. Here the authors define features of bacterial promoters that impose stringent requirements on effective sites.
- Jason Fontana
- , Chen Dong
- & Jesse G. Zalatan
-
Article
| Open Access Polychromatic solar energy conversion in pigment-protein chimeras that unite the two kingdoms of (bacterio)chlorophyll-based photosynthesis
Polychromatic solar energy conversion in pigment-protein chimeras that unite the two kingdoms of (bacterio)chlorophyll-based photosynthesis
The spectra of light used by photosynthetic organisms are determined by their pigmentation colour palettes. Here Liu et al. show that a genetically-encoded chimera of light-harvesting proteins from plants and reaction centres from purple bacteria allows for polychromatic solar energy harvesting.
- Juntai Liu
- , Vincent M. Friebe
- & Michael R. Jones
-
Article
| Open Access An expanded library of orthogonal split inteins enables modular multi-peptide assemblies
An expanded library of orthogonal split inteins enables modular multi-peptide assemblies
Inteins allow the joining of protein segments through scarless ligation. Here the authors assess 34 inteins to establish a library of 15 mutually orthogonal split inteins for in vivo applications, 10 of which are also active in vitro.
- Filipe Pinto
- , Ella Lucille Thornton
- & Baojun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Lipid analogs reveal features critical for hemolysis and diminish granadaene mediated Group B Streptococcus infection
Lipid analogs reveal features critical for hemolysis and diminish granadaene mediated Group B Streptococcus infection
Granadaene, produced by Group B Streptococcus (GBS), is a long polyene lipid involved in cellular toxicity and hemolytic activity. Here, the authors synthesize and characterize granadaene-like compounds and show that a non-toxic analog diminishes GBS infection in mice when incorporated into a vaccine formulation.
- Blair Armistead
- , Pilar Herrero-Foncubierta
- & Lakshmi Rajagopal
-
Article
| Open Access Abundance of conserved CRISPR-Cas9 target sites within the highly polymorphic genomes of Anopheles and Aedes mosquitoes
Abundance of conserved CRISPR-Cas9 target sites within the highly polymorphic genomes of Anopheles and Aedes mosquitoes
Genetic variation in natural populations could represent gene drive resistant alleles, preventing successful application for population management. Here the authors survey 1280 genomes from three mosquito species and concludes natural variation will not be detrimental to deploying gene drive technology.
- Hanno Schmidt
- , Travis C. Collier
- & Gregory C. Lanzaro
-
Article
| Open Access Cell-in-the-loop pattern formation with optogenetically emulated cell-to-cell signaling
Cell-in-the-loop pattern formation with optogenetically emulated cell-to-cell signaling
Synthetic biological pattern formation is challenging to engineer due to theoretical complexity and practical limitations. Here, the authors introduce a cell-in-the-loop approach in which cells interact through in silico signaling.
- Melinda Liu Perkins
- , Dirk Benzinger
- & Mustafa Khammash
-
Article
| Open Access Decorating bacteria with self-assembled synthetic receptors
Decorating bacteria with self-assembled synthetic receptors
Cell surface proteins mediate the interactions between cells and their extracellular environment. Here the authors design synthetic biomemetic receptor-like sensors that facilitate programmable interactions between bacteria and their target.
- Naama Lahav-Mankovski
- , Pragati Kishore Prasad
- & David Margulies
-
Article
| Open Access Caliciviral protein-based artificial translational activator for mammalian gene circuits with RNA-only delivery
Caliciviral protein-based artificial translational activator for mammalian gene circuits with RNA-only delivery
Synthetic RNA-based circuits allow for gene regulation without the risk of mutagenesis. Here the authors demonstrate a Caliciviral VPg-based Translational activator which allows translational activation of synthetic mRNAs.
- Hideyuki Nakanishi
- & Hirohide Saito
-
Review Article
| Open Access Multiplexed CRISPR technologies for gene editing and transcriptional regulation
Multiplexed CRISPR technologies for gene editing and transcriptional regulation
Multiplexed CRISPR technologies have recently emerged as powerful approaches for genetic editing and transcriptional regulation. Here the authors review this emerging technology and discuss challenges and considerations for future studies.
- Nicholas S. McCarty
- , Alicia E. Graham
- & Rodrigo Ledesma-Amaro
-
Article
| Open Access A progesterone biosensor derived from microbial screening
A progesterone biosensor derived from microbial screening
Bacteria represent an unexploited reservoir of biosensing proteins. Here the authors use genomic screens and functional assays to isolate a progesterone sensing allosteric transcription factor and use a FRET-based method to develop an optical progesterone sensor.
- Chloé Grazon
- , R C. Baer
- & James E. Galagan
-
Article
| Open Access A genome-wide approach for identification and characterisation of metabolite-inducible systems
A genome-wide approach for identification and characterisation of metabolite-inducible systems
Inducible gene expression tools have important applications as genetically encoded biosensors. Here the authors conduct a genome-wide approach to identify and utilise functional sensors.
- Erik K. R. Hanko
- , Ana C. Paiva
- & Naglis Malys
-
Article
| Open Access Inducible cell-to-cell signaling for tunable dynamics in microbial communities
Inducible cell-to-cell signaling for tunable dynamics in microbial communities
Biotechnology innovations require the precise control over microbial dynamics. Here the authors engineer an inducible quorum sensing system to fine tune population and community level behaviour.
- Arianna Miano
- , Michael J. Liao
- & Jeff Hasty
-
Article
| Open Access In vitro ribosome synthesis and evolution through ribosome display
In vitro ribosome synthesis and evolution through ribosome display
Directed evolution of the ribosome is challenging because the requirement of cell viability limits the mutations that can be made. Here the authors develop a platform for in vitro ribosome synthesis and evolution (RISE) to overcome these constraints.
- Michael J. Hammerling
- , Brian R. Fritz
- & Michael C. Jewett
-
Article
| Open Access Optogenetic engineering to probe the molecular choreography of STIM1-mediated cell signaling
Optogenetic engineering to probe the molecular choreography of STIM1-mediated cell signaling
Optogenetic tools have been used to control cellular behaviours but their use to probe structure-function relations of signalling proteins are underexplored. Here the authors engineer optogenetic modules into STIM1 to dissect molecular details of STIM1-mediated signalling and control various cellular events.
- Guolin Ma
- , Lian He
- & Yubin Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access DNA-based artificial molecular signaling system that mimics basic elements of reception and response
DNA-based artificial molecular signaling system that mimics basic elements of reception and response
Cells communicate with the outside world to maintain homeostasis. Here the authors design a synthetic biology DNA-based signalling system AMSsys that responds to the presence of ATP.
- Ruizi Peng
- , Liujun Xu
- & Weihong Tan
-
Article
| Open Access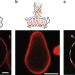 Controlled division of cell-sized vesicles by low densities of membrane-bound proteins
Controlled division of cell-sized vesicles by low densities of membrane-bound proteins
Membrane fission of a cell into two daughters is a core ability of cell-based life. Here the authors show that in artificial cells division can be controlled by regulating membrane curvature using low protein density.
- Jan Steinkühler
- , Roland L. Knorr
- & Reinhard Lipowsky
-
Article
| Open Access In vitro self-replication and multicistronic expression of large synthetic genomes
In vitro self-replication and multicistronic expression of large synthetic genomes
A main objective of synthetic biology is the creation of chemical systems capable of replication and evolution. Here, the authors demonstrate combined self-replication and expression of multipartite genomes in vitro.
- K. Libicher
- , R. Hornberger
- & H. Mutschler
-
Article
| Open Access Improved betulinic acid biosynthesis using synthetic yeast chromosome recombination and semi-automated rapid LC-MS screening
Improved betulinic acid biosynthesis using synthetic yeast chromosome recombination and semi-automated rapid LC-MS screening
SCRaMbLE can lead to great genetic diversity for product biosynthesis but is limited by screening methods. Here the authors develop a rapid workflow using automation, ultra-fast LC/MS and barcoded nanopore sequencing to identify best performing strains.
- G.-O. F. Gowers
- , S. M. Chee
- & T. Ellis
-
Article
| Open Access Designing minimal genomes using whole-cell models
Designing minimal genomes using whole-cell models
Genome engineering will one day benefit from computational tools that can design genomes with desired functions. Here the authors develop computational design-simulate-test algorithms to design minimal genomes based on the whole-cell model of Mycoplasma genitalium.
- Joshua Rees-Garbutt
- , Oliver Chalkley
- & Claire Grierson
-
Article
| Open Access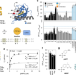 Minimally disruptive optical control of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B
Minimally disruptive optical control of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B
Protein tyrosine phosphatases regulate many cellular processes but are difficult to study in their native context. Here the authors develop an approach for using light to control the activity of a disease-relevant phosphatase without interfering with its native cellular organization.
- Akarawin Hongdusit
- , Peter H. Zwart
- & Jerome M. Fox
-
Article
| Open Access The COMET toolkit for composing customizable genetic programs in mammalian cells
The COMET toolkit for composing customizable genetic programs in mammalian cells
Engineering mammalian cellular functions requires a toolkit of orthogonal and well-characterized genetic components. Here the authors develop COMET: an ensemble of transcription factors, promoters, and accompanying models for the design and construction of genetic programs.
- Patrick S. Donahue
- , Joseph W. Draut
- & Joshua N. Leonard
-
Article
| Open Access High-throughput identification of synthetic riboswitches by barcode-free amplicon-sequencing in human cells
High-throughput identification of synthetic riboswitches by barcode-free amplicon-sequencing in human cells
Riboswitches can mediate ligand-dependent RNA cleavage and splicing to control gene expression. Here the authors present a method to functionally screen large libraries and identify functional variants.
- Benjamin Strobel
- , Maike Spöring
- & Sebastian Kreuz
-
Perspective
| Open Access Organizing genome engineering for the gigabase scale
Organizing genome engineering for the gigabase scale
Genome-scale engineering requires the integration of a wide range of in silico and in vivo technologies, as well data management procedures and legal infrastructure. Here the authors provide a list of recommendations to address these challenges.
- Bryan A. Bartley
- , Jacob Beal
- & Elizabeth A. Strychalski
-
Article
| Open Access Compartmentalized microbes and co-cultures in hydrogels for on-demand bioproduction and preservation
Compartmentalized microbes and co-cultures in hydrogels for on-demand bioproduction and preservation
Large scale suspension fermentation technology is not easily portable or reusable. Here the authors describe a hydrogel system suitable for long-term and reusable production with both single and multi-organism consortia.
- Trevor G. Johnston
- , Shuo-Fu Yuan
- & Hal S. Alper
-
Article
| Open Access Rewiring of endogenous signaling pathways to genomic targets for therapeutic cell reprogramming
Rewiring of endogenous signaling pathways to genomic targets for therapeutic cell reprogramming
Current cellular rewiring designs are typically tailored to detect single inputs. Here the authors present GEARs that function independently of engineered receptor/reporter systems and directly reroute endogenous signaling pathways to alternative genomic loci using dCas9-directed gene expression.
- Krzysztof Krawczyk
- , Leo Scheller
- & Martin Fussenegger
-
Article
| Open Access Optogenetic regulation of endogenous proteins
Optogenetic regulation of endogenous proteins
Optogenetic approaches to control protein-protein interactions usually require overexpression of the target proteins. Here the authors integrate intrabodies into near-infrared- and blue-light activatable optogenetic tools to control endogenous proteins in mammalian cells.
- Taras A. Redchuk
- , Maksim M. Karasev
- & Vladislav V. Verkhusha
-
Article
| Open Access Interaction variability shapes succession of synthetic microbial ecosystems
Interaction variability shapes succession of synthetic microbial ecosystems
Cellular interactions are a major driver of microbial communities and shown highly variable in strength. Here the authors construct synthetic consortia and mathematical models to elucidate the role of interaction variability in driving ecosystem succession.
- Feng Liu
- , Junwen Mao
- & Ting Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Programmed magnetic manipulation of vesicles into spatially coded prototissue architectures arrays
Programmed magnetic manipulation of vesicles into spatially coded prototissue architectures arrays
To execute higher-order functions, cells self-assemble into spatially coded tissue configurations. Here the authors magnetically assembly giant unilamellar vesicles into three dimensional tissue-mimic structures with collective osmotic stability.
- Qingchuan Li
- , Shubin Li
- & Xiaojun Han
-
Article
| Open Access Implementing digital computing with DNA-based switching circuits
Implementing digital computing with DNA-based switching circuits
DNA strand displacement reactions can be difficult to scale up for computational tasks. Here the authors develop DNA switching circuits that achieve high-speed computing with fewer molecules.
- Fei Wang
- , Hui Lv
- & Chunhai Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-functional genome-wide CRISPR system for high throughput genotype–phenotype mapping
Multi-functional genome-wide CRISPR system for high throughput genotype–phenotype mapping
Genome-scale engineering is generally limited to single methods of alteration such as overexpression, repression or deletion. Here the authors present a tri-functional CRISPR system that can engineer complex synergistic interactions in a genome-wide manner.
- Jiazhang Lian
- , Carl Schultz
- & Huimin Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access In vitro implementation of robust gene regulation in a synthetic biomolecular integral controller
In vitro implementation of robust gene regulation in a synthetic biomolecular integral controller
Feedback mechanisms for synthetic gene circuits are necessary to provide robustness to external perturbations. Here the authors validate a biomolecular controller based on a sigma and anti-sigma factor to achieve stable gene expression in the face of external disturbances in an in vitro synthetic gene circuit.
- Deepak K. Agrawal
- , Ryan Marshall
- & Eduardo D Sontag
-
Article
| Open Access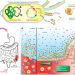 Engineered E. coli Nissle 1917 for the delivery of matrix-tethered therapeutic domains to the gut
Engineered E. coli Nissle 1917 for the delivery of matrix-tethered therapeutic domains to the gut
Anti-inflammatory treatments for gastrointestinal diseases can often have detrimental side effects. Here the authors engineer E. coli Nissle 1917 to create a fibrous matrix that has a protective effect in DSS-induced colitis mice.
- Pichet Praveschotinunt
- , Anna M. Duraj-Thatte
- & Neel S. Joshi
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic and tunable metabolite control for robust minimal-equipment assessment of serum zinc
Dynamic and tunable metabolite control for robust minimal-equipment assessment of serum zinc
Tightly controlling cell output is challenging, which has limited development and applications of bacterial sensors. Here the authors develop tunable, fast-responding sensors to control production of metabolic pigments and use them to assess zinc deficiency in a low-cost, minimal equipment fashion.
- Monica P. McNerney
- , Cirstyn L. Michel
- & Mark P. Styczynski
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic chimeric nucleases function for efficient genome editing
Synthetic chimeric nucleases function for efficient genome editing
CRISPR-Cas systems have well characterized, modular structures. Here the authors use that architecture to design a Cas12a library of 560 synthetic chimeras, with altered PAM preferences and specificities.
- R. M. Liu
- , L. L. Liang
- & R. T. Gill
-
Article
| Open Access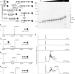 Cytoplasmic glycoengineering enables biosynthesis of nanoscale glycoprotein assemblies
Cytoplasmic glycoengineering enables biosynthesis of nanoscale glycoprotein assemblies
Established bacterial glycoengineering platforms limit access to protein and glycan substrates. Here the authors design a cytoplasmic protein glycosylation system, Glycoli, to generate a variety of multivalent glycostructures.
- Hanne L. P. Tytgat
- , Chia-wei Lin
- & Timothy G. Keys
-
Article
| Open Access A cell-free biosynthesis platform for modular construction of protein glycosylation pathways
A cell-free biosynthesis platform for modular construction of protein glycosylation pathways
Constructing biosynthetic pathways to study and engineer glycoprotein structures is difficult. Here, the authors use GlycoPRIME, a cell-free workflow for mixing-and-matching glycosylation enzymes, to evaluate 37 putative glycosylation pathways and discover routes to 18 new glycoprotein structures
- Weston Kightlinger
- , Katherine E. Duncker
- & Michael C. Jewett

 A Cas9 with PAM recognition for adenine dinucleotides
A Cas9 with PAM recognition for adenine dinucleotides