Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into an atypical secretory pathway kinase crucial for Toxoplasma gondii invasion
Structural insights into an atypical secretory pathway kinase crucial for Toxoplasma gondii invasion
Host cell invasion by Toxoplasma gondii depends on the heavily phosphorylated RON complex, but the relevance and regulation of these modifications are not understood. Here, the authors identify the kinase RON13 as a key virulence factor, determine its structure and show that it phosphorylates the RON complex.
- Gaëlle Lentini
- , Rouaa Ben Chaabene
- & Dominique Soldati-Favre
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for CSPG4 as a receptor for TcdB and a therapeutic target in Clostridioides difficile infection
Structural basis for CSPG4 as a receptor for TcdB and a therapeutic target in Clostridioides difficile infection
Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 (CSPG4) is a potential receptor for C. difficile toxin B (TcdB) during C. difficile infections (CDIs). Here, the cryo-EM structure of a TcdB–CSPG4 complex and CDI mouse models offer insights into CSPG4 role in CDIs and suggest a therapeutic strategy targeting TcdB.
- Peng Chen
- , Ji Zeng
- & Rongsheng Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for the ARF GAP activity and specificity of the C9orf72 complex
Structural basis for the ARF GAP activity and specificity of the C9orf72 complex
C9orf72:SMCR8:WDR41 complex has been reported to have GAP activity for both ARF family proteins and the RAB proteins RAB8A and RAB11A. Here the authors provide structural and biochemical evidence for a specific function of the C9orf72 complex as an ARF GAP, and a structural framework for the GAP activity of the longin-containing GAP family.
- Ming-Yuan Su
- , Simon A. Fromm
- & James H. Hurley
-
Article
| Open Access Designed and biologically active protein lattices
Designed and biologically active protein lattices
Organising proteins in 2D and 3D is needed to develop complex bimolecular materials for a range of applications. Here, the authors report the encapsulation of ferritin and apoferritin in DNA-based voxels with programmed assembly to generate both 2D and 3D protein lattices and demonstrate the retention of protein function.
- Shih-Ting Wang
- , Brian Minevich
- & Oleg Gang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for late maturation steps of the human mitoribosomal large subunit
Structural basis for late maturation steps of the human mitoribosomal large subunit
Mitochondrial ribosomes (mitoribosomes) are characterized by a distinct architecture and thus biogenesis pathway. Here, cryo-EM structures of mitoribosome large subunit assembly intermediates elucidate final steps of 16 S rRNA folding, methylation and peptidyl transferase centre (PTC) completion, as well as functions of several mitoribosome assembly factors.
- Miriam Cipullo
- , Genís Valentín Gesé
- & Joanna Rorbach
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast coherent motion and helix rearrangement of homodimeric hemoglobin visualized with femtosecond X-ray solution scattering
Ultrafast coherent motion and helix rearrangement of homodimeric hemoglobin visualized with femtosecond X-ray solution scattering
Femtosecond time-resolved X-ray solution scattering (fs-TRXSS) measurements provide information on the structural dynamics of proteins in solution. Here, the authors present a structure refinement method for the analysis of fs-TRXSS data and use it to characterise the ultrafast structural changes of homodimeric haemoglobin.
- Yunbeom Lee
- , Jong Goo Kim
- & Hyotcherl Ihee
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of GTPase-mediated mitochondrial ribosome biogenesis and recycling
Structural basis of GTPase-mediated mitochondrial ribosome biogenesis and recycling
Maturation of the ribosomal peptidyl transferase center (PTC) is mediated by universally conserved GTPases. Here, cryo-EM structures of mitochondrial ribosomal large subunit assembly intermediates and of mature ribosomes offer insight into the roles of several assembly factors, including GTPBP6’s role in both ribosome biogenesis and recycling.
- Hauke S. Hillen
- , Elena Lavdovskaia
- & Ricarda Richter-Dennerlein
-
Article
| Open Access Multivalency transforms SARS-CoV-2 antibodies into ultrapotent neutralizers
Multivalency transforms SARS-CoV-2 antibodies into ultrapotent neutralizers
Here, the authors combine three different antibody specificities and an Fc domain on a single multivalent molecule, resulting in high neutralization activity despite viral sequence variability.
- Edurne Rujas
- , Iga Kucharska
- & Jean-Philippe Julien
-
Article
| Open Access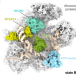 Stepwise maturation of the peptidyl transferase region of human mitoribosomes
Stepwise maturation of the peptidyl transferase region of human mitoribosomes
Mammalian mitoribosomes feature dramatically reduced ribosomal RNAs and follow mitochondria specific assembly pathways. Here the authors describe the process of human mitochondrial ribosome maturation that results in the formation of the ribosomal active site region, including the peptidyl transferase loop and the two tRNA-binding loops.
- Tea Lenarčič
- , Mateusz Jaskolowski
- & Nenad Ban
-
Article
| Open Access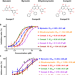 Identification of pyrogallol as a warhead in design of covalent inhibitors for the SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease
Identification of pyrogallol as a warhead in design of covalent inhibitors for the SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease
SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease (3CLpro) is essential for coronavirus replication and of great interest as an antiviral drug target. Here, the authors show that the naturally occurring flavonoid myricetin is a non-peptidomimetic and covalent inhibitor of 3CLpro, and they solve crystal structures of 3CLpro with myricetin and derivatives, which reveal that the pyrogallol group covalently modifies the catalytic cysteine.
- Haixia Su
- , Sheng Yao
- & Yechun Xu
-
Article
| Open Access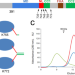 Structural basis of mechano-chemical coupling by the mitotic kinesin KIF14
Structural basis of mechano-chemical coupling by the mitotic kinesin KIF14
KIF14 is a mitotic kinesin whose malfunction is associated with cerebral and renal developmental defects and several cancers. Here the authors use cryoEM to determine 20 structures of KIF14 constructs bound to microtubules in the presence of different nucleotide analogues and provide the structural basis for a coordinated chemo-mechanical kinesin translocation model.
- Matthieu P.M.H. Benoit
- , Ana B. Asenjo
- & Hernando Sosa
-
Article
| Open Access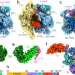 Distinct mechanisms of the human mitoribosome recycling and antibiotic resistance
Distinct mechanisms of the human mitoribosome recycling and antibiotic resistance
High-resolution cryo-EM structures and biochemical analyses of the human mitoribosome, in complex with mitochondria-specific factors mediating mitoribosome recycling, RRFmt and EF-G2mt, offer insight into mechanisms of mitoribosome recycling and resistance to antibiotic fusidic acid.
- Ravi Kiran Koripella
- , Ayush Deep
- & Rajendra K. Agrawal
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering the protein dynamics of an ancestral luciferase
Engineering the protein dynamics of an ancestral luciferase
Directed evolution commonly relies on point mutations but InDels frequently occur in evolution. Here the authors report a protein-engineering framework based on InDel mutagenesis and fragment transplantation resulting in greater catalysis and longer glow-type bioluminescence of the ancestral luciferase.
- Andrea Schenkmayerova
- , Gaspar P. Pinto
- & Jiri Damborsky
-
Article
| Open Access Reliable identification of protein-protein interactions by crosslinking mass spectrometry
Reliable identification of protein-protein interactions by crosslinking mass spectrometry
Cross-linking mass spectrometry (MS) can identify protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks but assessing the reliability of these data remains challenging. To address this issue, the authors develop and validate a method to determine the false-discovery rate of PPIs identified by cross-linking MS.
- Swantje Lenz
- , Ludwig R. Sinn
- & Juri Rappsilber
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of ABCF-mediated resistance to pleuromutilin, lincosamide, and streptogramin A antibiotics in Gram-positive pathogens
Structural basis of ABCF-mediated resistance to pleuromutilin, lincosamide, and streptogramin A antibiotics in Gram-positive pathogens
Mitochondrial ribosomes (mitoribosomes) are characterized by a distinct architecture and thus biogenesis pathway. Here, cryo-EM structures of mitoribosome large subunit assembly intermediates elucidate final steps of 16 S rRNA folding, methylation and peptidyl transferase centre (PTC) completion, as well as functions of several mitoribosome assembly factors.
- Caillan Crowe-McAuliffe
- , Victoriia Murina
- & Daniel N. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access Large Stokes shift fluorescence activation in an RNA aptamer by intermolecular proton transfer to guanine
Large Stokes shift fluorescence activation in an RNA aptamer by intermolecular proton transfer to guanine
Fluorogenic RNA aptamers such as Chili display strong fluorescence enhancement upon aptamer–ligand complex formation. Here, the authors provide insights into the mechanism of fluorescence activation of Chili by solving the crystal structures of Chili with its bound positively charged ligands DMHBO+ and DMHBI+, and they reveal that Chili uses an excited state proton transfer mechanism based on time-resolved optical spectroscopy measurements.
- Mateusz Mieczkowski
- , Christian Steinmetzger
- & Claudia Höbartner
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanistic insights into the R-loop formation and cleavage in CRISPR-Cas12i1
Mechanistic insights into the R-loop formation and cleavage in CRISPR-Cas12i1
Here, structures of the Cas12i1 R-loop complexes before and after target DNA cleavage and biochemical assays offer detailed insights into the mechanisms of target DNA duplex unwinding, R-loop formation and DNA cleavage, and suggest that Cas12i1 forms a 19-bp long DNA-RNA heteroduplex with the crRNA guide region.
- Bo Zhang
- , Diyin Luo
- & Songying Ouyang
-
Article
| Open Access Activation of PARP2/ARTD2 by DNA damage induces conformational changes relieving enzyme autoinhibition
Activation of PARP2/ARTD2 by DNA damage induces conformational changes relieving enzyme autoinhibition
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 2 (PARP2) is activated by 5′-phosphorylated DNA breaks but the molecular mechanism is not fully understood. Here, the authors report a crystal structure of PARP2 bound to an activating DNA fragment, providing insights into the structural changes that lead to PARP2 activation.
- Ezeogo Obaji
- , Mirko M. Maksimainen
- & Lari Lehtiö
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insight on assembly-line catalysis in terpene biosynthesis
Structural insight on assembly-line catalysis in terpene biosynthesis
Substrate channeling can improve biosynthetic efficiency and has been implicated in the reactions of fusicoccadiene synthase. Here, the authors analyze this bifunctional enzyme complex by cryoEM, cross-linking MS and integrative modeling, providing structural insights into how substrate channeling is achieved.
- Jacque L. Faylo
- , Trevor van Eeuwen
- & David W. Christianson
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for inhibition of the AAA-ATPase Drg1 by diazaborine
Structural basis for inhibition of the AAA-ATPase Drg1 by diazaborine
The AAA-ATPase Drg1 is a key factor in eukaryotic ribosome biogenesis that initiates cytoplasmic maturation of the large subunit. Here the authors report the structure of Drg1 in complex with its specific inhibitor diazaborine and provide insight into the mechanism of inhibition and specificity of this class of inhibitors.
- Michael Prattes
- , Irina Grishkovskaya
- & Helmut Bergler
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and mechanism of the human NHE1-CHP1 complex
Structure and mechanism of the human NHE1-CHP1 complex
Sodium/proton exchanger 1 (NHE1) and its obligate binding partner Calcineurin B-homologous protein 1 (CHP1) regulate intracellular pH and volume homeostasis. Structures of the human NHE1-CHP1 complex offer insight into the regulation of NHE1 pH-sensitivity by CHP1 and into the interactions with NHE1 inhibitors.
- Yanli Dong
- , Yiwei Gao
- & Yan Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access R2DT is a framework for predicting and visualising RNA secondary structure using templates
R2DT is a framework for predicting and visualising RNA secondary structure using templates
Non-coding RNA function is poorly understood, partly due to the challenge of determining RNA secondary (2D) structure. Here, the authors present a framework for the reproducible prediction and visualization of the 2D structure of a wide array of RNAs, which enables linking RNA sequence to function.
- Blake A. Sweeney
- , David Hoksza
- & Anton I. Petrov
-
Article
| Open Access Sugar phosphate activation of the stress sensor eIF2B
Sugar phosphate activation of the stress sensor eIF2B
The activity of translation initiation factor eIF2B is known to be modulated through stress-responsive phosphorylation of its substrate eIF2. Here, the authors uncover the regulation of eIF2B by the binding of sugar phosphates, suggesting a link between nutrient status and the rate of protein synthesis.
- Qi Hao
- , Jin-Mi Heo
- & Carmela Sidrauski
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein recognition of human cell junction protein PALS1
Structural basis for SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein recognition of human cell junction protein PALS1
SARS-CoV-2 viruses are known to hijack human proteins in order to facilitate their own virulence and replication. In this study, Liu and colleagues present structural analysis of how this phenomenon occurs between SARS-CoV-2 viral envelope protein and human PALS1. The findings provide insights in to viral-host recognition.
- Jin Chai
- , Yuanheng Cai
- & Qun Liu
-
Article
| Open Access The zinc-finger protein Red1 orchestrates MTREC submodules and binds the Mtl1 helicase arch domain
The zinc-finger protein Red1 orchestrates MTREC submodules and binds the Mtl1 helicase arch domain
The human PAXT complex and the MTREC complex in fission yeast are important exosome cofactors, serving in the degradation of specific noncoding RNAs. Here, the authors combine structural, biochemical and in vivo methods to show how Red1 recruits the Mtl1 helicase by an interface not seen before in helicase-adaptor complexes.
- Nikolay Dobrev
- , Yasar Luqman Ahmed
- & Irmgard Sinning
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale architecture of a VAP-A-OSBP tethering complex at membrane contact sites
Nanoscale architecture of a VAP-A-OSBP tethering complex at membrane contact sites
Membrane contact sites (MCS) are subcellular regions where two organelles appose their membranes to exchange small molecules, including lipids. Here authors designed an in vitro MCS suitable for cryotomography and sub-tomogram analysis which sheds light on the recruitment of proteins of different sizes within MCS of adjustable thickness.
- Eugenio de la Mora
- , Manuela Dezi
- & Daniel Lévy
-
Article
| Open Access Clostridioides difficile specific DNA adenine methyltransferase CamA squeezes and flips adenine out of DNA helix
Clostridioides difficile specific DNA adenine methyltransferase CamA squeezes and flips adenine out of DNA helix
Clostridioides difficile adenine methyltransferase A (CamA) is required for the sporulation and colonization of the pathogen that causes gastrointestinal infections. Here, the authors characterise CamA kinetically and present its crystal structure bound to the DNA recognition sequence, which reveals DNA distortions including bending and the flipping of the target adenine out of the DNA helix, as well as protein conformational changes upon cofactor binding.
- Jujun Zhou
- , John R. Horton
- & Xiaodong Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Bladder cancer therapy using a conformationally fluid tumoricidal peptide complex
Bladder cancer therapy using a conformationally fluid tumoricidal peptide complex
Partially unfolded alpha-lactalbumin forms an oleic acid complex with antitumorigenic properties. Here, the authors define a structurally flexible, peptide-based oleate complex and report a phase I/II clinical trial where this complex is used to treat patients with bladder cancer.
- Antonín Brisuda
- , James C. S. Ho
- & Catharina Svanborg
-
Article
| Open Access Assessment of protein–protein interfaces in cryo-EM derived assemblies
Assessment of protein–protein interfaces in cryo-EM derived assemblies
Here, the authors present Protein Interface-score (PI-score), a machine learning-based metric that has been trained on protein–protein interfaces’ features from high-resolution crystal structures. They use the PI-score to evaluate the protein–protein interfaces in more than 1000 PDB-deposited cryo-EM structures and show that it can be used as a complementary assessment tool for cryo-EM model validation.
- Sony Malhotra
- , Agnel Praveen Joseph
- & Maya Topf
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of TFIIH/Rad4–Rad23–Rad33 in damaged DNA opening in nucleotide excision repair
Cryo-EM structure of TFIIH/Rad4–Rad23–Rad33 in damaged DNA opening in nucleotide excision repair
The conserved eukaryotic nucleotide excision repair (NER) pathway protects the genome from a wide variety of environmentally induced DNA lesions. Here, the authors provide insights into how NER is initiated on lesions by determining the cryo-EM structure of the yeast TFIIH/Rad4–Rad23-Rad33 complex bound to a DNA containing a single carcinogen-DNA adduct.
- Trevor van Eeuwen
- , Yoonjung Shim
- & Kenji Murakami
-
Article
| Open Access Proline/arginine dipeptide repeat polymers derail protein folding in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Proline/arginine dipeptide repeat polymers derail protein folding in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
The most frequent cause of familial Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) and Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD) are hexanucleotide repeat expansions in the non-coding region of the C9ORF72 gene that are translated into five dipeptide repeat (DPR) proteins. Here, the authors show that proline/arginine (PR) DPRs inhibit the prolyl isomerase PPIA and reveal the molecular mechanism of the impaired protein folding activity of PPIA by performing NMR measurements and determining a PR DPR bound PPIA crystal structure.
- Maria Babu
- , Filippo Favretto
- & Markus Zweckstetter
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-target mode of action of silver against Staphylococcus aureus endows it with capability to combat antibiotic resistance
Multi-target mode of action of silver against Staphylococcus aureus endows it with capability to combat antibiotic resistance
Silver (Ag) has been used as an antimicrobial agent since a long time, but its molecular mechanism of action was not elucidated due to technical challenges. Here, the authors develop a mass spectrometric approach to identify the Ag-proteome in Staphylococcus aureus, and capture a molecular snapshot of the dynamic bactericidal mode of action of Ag through targeting multiple biological pathways.
- Haibo Wang
- , Minji Wang
- & Hongzhe Sun
-
Article
| Open Access A histone H3K4me1-specific binding protein is required for siRNA accumulation and DNA methylation at a subset of loci targeted by RNA-directed DNA methylation
A histone H3K4me1-specific binding protein is required for siRNA accumulation and DNA methylation at a subset of loci targeted by RNA-directed DNA methylation
In plants, RNA-directed DNA methylation (RdDM) is a de novo DNA methylation pathway that is responsible for transcriptional silencing of repetitive elements. Here, the authors characterized a new RdDM factor, RDM15, and show that it is required for RdDM-dependent DNA methylation and siRNA accumulation at a subset of RdDM target loci.
- Qingfeng Niu
- , Zhe Song
- & Zhaobo Lang
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structure of dopamine D1 receptor in complex with G protein and a non-catechol agonist
Crystal structure of dopamine D1 receptor in complex with G protein and a non-catechol agonist
Recently, a class of non-catechol Dopamine D1 receptor (D1R) selective agonists with novel scaffold and improved pharmacological properties were reported. Here, authors report the crystal structure of D1R in complex with stimulatory G protein (Gs) and a non-catechol agonist Compound 1 which explains the selectivity of this scaffold for D1R over other aminergic receptors and the mechanism of activating D1R.
- Bingfa Sun
- , Dan Feng
- & Brian K. Kobilka
-
Article
| Open Access A metal ion orients SARS-CoV-2 mRNA to ensure accurate 2′-O methylation of its first nucleotide
A metal ion orients SARS-CoV-2 mRNA to ensure accurate 2′-O methylation of its first nucleotide
The SARS-CoV-2 nsp16/nsp10 enzyme complex methylates the 2′-OH of the first nucleotide of the viral mRNA, converting the Cap-0 to Cap-1, which helps the virus to evade immune surveillance in the host cell. Here, the authors present the crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 nsp16/nsp10 with the bound Cap-1 RNA nucleotide product and a post-release SAH containing structure.
- Thiruselvam Viswanathan
- , Anurag Misra
- & Yogesh K. Gupta
-
Article
| Open Access A unified route for flavivirus structures uncovers essential pocket factors conserved across pathogenic viruses
A unified route for flavivirus structures uncovers essential pocket factors conserved across pathogenic viruses
Understanding virus assembly could identify potential drug targets. Here the authors use a safe and efficient method to solve pathogenic flavivirus structures, revealing two lipid-like ligands within highly conserved pockets of the stem region of envelope protein that are important for virus maturation.
- Joshua M. Hardy
- , Natalee D. Newton
- & Daniel Watterson
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of the human LONP1 protease reveal regulatory steps involved in protease activation
Structures of the human LONP1 protease reveal regulatory steps involved in protease activation
The human mitochondrial protease LONP1 is an AAA+ ATP-dependent quality control protease. Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structures of human LONP1 in three distinct states and provide insights into the mechanism and regulation of this important protease.
- Mia Shin
- , Edmond R. Watson
- & Gabriel C. Lander
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the mature Rous sarcoma virus lattice reveals a role for IP6 in the formation of the capsid hexamer
Structure of the mature Rous sarcoma virus lattice reveals a role for IP6 in the formation of the capsid hexamer
Inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) is a known assembly cofactor for HIV-1. Here, the authors show the role of IP6 in the assembly of the Rous sarcoma virus (RSV). Reported cryo-ET structures of mature capsid-like particles (CLPs) suggest that IP6 modulates the formation of capsid polyhedrons of variable shape.
- Martin Obr
- , Clifton L. Ricana
- & Robert A. Dick
-
Article
| Open Access Architecture of the Sema3A/PlexinA4/Neuropilin tripartite complex
Architecture of the Sema3A/PlexinA4/Neuropilin tripartite complex
Secreted class 3 semaphorins (Sema3s) form tripartite complexes with a plexin receptor and neuropilin co-receptor to transduce signals for neuronal axon guidance and other processes. Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structure of the extracellular Sema3A/PlexinA4/Neuropilin1 complex that provides further insights into the interactions among semaphorin, plexin and neuropilin and reveals long flexible linkers in semaphorin and neuropilin that are important for complex formation.
- Defen Lu
- , Guijun Shang
- & Xuewu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access The SUN1-SPDYA interaction plays an essential role in meiosis prophase I
The SUN1-SPDYA interaction plays an essential role in meiosis prophase I
Telomeres attach to the nuclear envelope to facilitate homolog pairing during meiosis prophase I. Here, the authors show that SUN1 and SPDYA interact, and demonstrate that this interaction is important for telomere structure and function, and essential to mice gametogenesis.
- Yanyan Chen
- , Yan Wang
- & Ming Lei
-
Article
| Open Access TAPBPR promotes antigen loading on MHC-I molecules using a peptide trap
TAPBPR promotes antigen loading on MHC-I molecules using a peptide trap
The molecular chaperones tapasin and TAPBPR play important roles in defining the repertoire of peptides displayed by MHC class I. Here, the authors combine NMR, ITC, fluorescence polarization measurements and deep mutational scanning analyses to reveal a peptide editing mechanism, where the G24-R36 loop in TAPBPR acts as a molecular trap to promote the selection of high-affinity peptide cargo.
- Andrew C. McShan
- , Christine A. Devlin
- & Nikolaos G. Sgourakis
-
Article
| Open Access Distinct EH domains of the endocytic TPLATE complex confer lipid and protein binding
Distinct EH domains of the endocytic TPLATE complex confer lipid and protein binding
AtEH/Pan1 proteins contain two N-terminal Eps15 homology (EH) domains and are subunits of the endocytic TPLATE complex present in plants. Here, the authors combine X-ray crystallography, NMR and MD simulations with biochemical and in planta analysis to characterize the two AtEH1/Pan1 EH domains and reveal their structural differences and complementary functional roles.
- Klaas Yperman
- , Anna C. Papageorgiou
- & Daniel Van Damme
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of the mature and infective Mayaro virus at 4.4 Å resolution reveals features of arthritogenic alphaviruses
Cryo-EM structure of the mature and infective Mayaro virus at 4.4 Å resolution reveals features of arthritogenic alphaviruses
Mayaro virus (MAYV) is an emerging arbovirus in Central and South America that is transmitted by mosquitoes and causes arthritogenic disease. Here, the authors present the 4.4 Å resolution cryo-EM structure of MAYV and describe specific features of the virus, which could be exploited for the design of MAYV-specific diagnostics and therapeutics.
- Helder V. Ribeiro-Filho
- , Lais D. Coimbra
- & Rafael Elias Marques
-
Article
| Open Access Structural understanding of non-nucleoside inhibition in an elongating herpesvirus polymerase
Structural understanding of non-nucleoside inhibition in an elongating herpesvirus polymerase
Various herpesvirus therapeutics target the viral DNA polymerase. Here, the authors present the crystal structure of herpesvirus polymerase in the elongating state with bound primer-template DNA and the broad-spectrum non-nucleoside inhibitor PNU-183792, which is of interest for further drug design.
- Robert P. Hayes
- , Mee Ra Heo
- & Daniel Klein
-
Article
| Open Access Inhibition mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 main protease by ebselen and its derivatives
Inhibition mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 main protease by ebselen and its derivatives
Ebselen is an organoselenium drug that inhibits the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro). Here, the authors co-crystallised Mpro with ebselen and an ebselen derivative and observed an enzyme bound organoselenium covalent adduct in the crystal structures, which was also confirmed by mass spectrometry analysis.
- Kangsa Amporndanai
- , Xiaoli Meng
- & S. Samar Hasnain
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of cortical microtubules from human parasite Toxoplasma gondii identifies their microtubule inner proteins
Cryo-EM structure of cortical microtubules from human parasite Toxoplasma gondii identifies their microtubule inner proteins
Cortical microtubules (MTs) in Apicomplexa are specialized MTs involved in maintaining the parasite’s shape and are, as such, unusually stable. Here, cryo-EM analysis of cortical MTs from Toxoplasma gondii offers insight into the mechanism of their stabilization by three bona fide microtubule inner proteins.
- Xiangli Wang
- , Yong Fu
- & Rui Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of substrate recognition and thermal protection by a small heat shock protein
Structural basis of substrate recognition and thermal protection by a small heat shock protein
Structural insights into the small heat shock proteins (sHsps) complexes with their substrates are sparse. Here, cryo-EM structure of a plastid sHsp, Hsp21, in complex with a bona fide substrate 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase (DXPS), suggests the anti-aggregation mechanism employed by sHsps.
- Chuanyang Yu
- , Stephen King Pong Leung
- & Wilson Chun Yu Lau
-
Article
| Open Access Self-association of MreC as a regulatory signal in bacterial cell wall elongation
Self-association of MreC as a regulatory signal in bacterial cell wall elongation
MreC is a membrane-associated protein that modulates the activity of the elongasome, a protein complex that controls cell wall formation in rod-shaped bacteria. Here, the authors use electron cryo-microscopy and X-ray crystallography to determine the structure of a self-associated form of MreC in atomic detail.
- Alexandre Martins
- , Carlos Contreras-Martel
- & Andréa Dessen
-
Article
| Open Access Allostery through DNA drives phenotype switching
Allostery through DNA drives phenotype switching
Most insights on DNA-mediated allostery upon transcription factor (TF) binding were either based on artificial promoters or found to be short-ranged. Here authors use single-molecule FRET and cryo-EM to show that Bacillus subtilis bacteria utilize long-range allostery in a stochastic and reversible phenotype switch.
- Gabriel Rosenblum
- , Nadav Elad
- & Hagen Hofmann

 Engineering an anti-HER2 biparatopic antibody with a multimodal mechanism of action
Engineering an anti-HER2 biparatopic antibody with a multimodal mechanism of action