Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access DeepRank: a deep learning framework for data mining 3D protein-protein interfaces
DeepRank: a deep learning framework for data mining 3D protein-protein interfaces
The authors present DeepRank, a deep learning framework for the data mining of large sets of 3D protein-protein interfaces (PPI). They use DeepRank to address two challenges in structural biology: distinguishing biological versus crystallographic PPIs in crystal structures, and secondly the ranking of docking models.
- Nicolas Renaud
- , Cunliang Geng
- & Li C. Xue
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of phosphate sensing and signaling revealed by rice SPX1-PHR2 complex structure
Mechanism of phosphate sensing and signaling revealed by rice SPX1-PHR2 complex structure
SPX proteins sense phosphate levels in plant cells by binding to inositol polyphosphates (InsP) and suppressing the activity of PHR transcription factors. Here the authors show that when bound to InsP6, the rice SPX1 protein inhibits the activity of PHR2 by attenuating both its dimerization and DNA binding activity.
- Jia Zhou
- , Qinli Hu
- & Weiman Xing
-
Article
| Open Access Regulation of the EphA2 receptor intracellular region by phosphomimetic negative charges in the kinase-SAM linker
Regulation of the EphA2 receptor intracellular region by phosphomimetic negative charges in the kinase-SAM linker
Eph receptor tyrosine kinases and their ephrin ligands mediate cell-cell communication. Here, the authors assess the structure and dynamics of the EphA2 intracellular region and uncover complex effects of phosphorylation within the linker region between EphA2 kinase and SAM domains.
- Bernhard C. Lechtenberg
- , Marina P. Gehring
- & Elena B. Pasquale
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of an exosite on the SOCS2-SH2 domain that enhances SH2 binding to phosphorylated ligands
Discovery of an exosite on the SOCS2-SH2 domain that enhances SH2 binding to phosphorylated ligands
SOCS2 is a key regulator of growth hormone and cytokine signaling, which recognizes phosphotyrosine (pTyr)-modified targets via a central SH2 domain. Here, the authors discover and characterize an exosite on this SH2 domain that can bind a non-phosphorylated peptide to enhance SOCS2:pTyr affinity.
- Edmond M. Linossi
- , Kunlun Li
- & Sandra E. Nicholson
-
Article
| Open Access Catalytic flexibility of rice glycosyltransferase OsUGT91C1 for the production of palatable steviol glycosides
Catalytic flexibility of rice glycosyltransferase OsUGT91C1 for the production of palatable steviol glycosides
Steviol glycosides from the plant Stevia rebaudiana are already used as lowcalorie sweeteners, but the most abundant naturally occurring compounds have a bitter aftertaste. Here, the authors characterize and engineer rice glycosyltransferase OsUGT91C1 to facilitate the large-scale production of naturally rare but palatable glycosides Reb D and Reb M
- Jinzhu Zhang
- , Minghai Tang
- & Wei Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Conformational changes in Lassa virus L protein associated with promoter binding and RNA synthesis activity
Conformational changes in Lassa virus L protein associated with promoter binding and RNA synthesis activity
The L protein of segmented, negative strand RNA viruses contains the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase essential for virus amplification. Here, the authors report cryoEM structures of the Lassa virus L protein in active, RNA-bound states, and provide mechanistic insights.
- Tomas Kouba
- , Dominik Vogel
- & Stephen Cusack
-
Article
| Open Access Kinetic and structural mechanism for DNA unwinding by a non-hexameric helicase
Kinetic and structural mechanism for DNA unwinding by a non-hexameric helicase
UvrD is a model helicase from the non-hexameric Superfamily 1. Here, the authors use optical tweezers to measure directly the stepwise translocation of UvrD along a DNA hairpin, and propose a mechanism in which UvrD moves one base pair at a time, but sequesters the nascent single strands, releasing them after a variable number of ATP hydrolysis cycles.
- Sean P. Carney
- , Wen Ma
- & Yann R. Chemla
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of Rad26-assisted rescue of stalled RNA polymerase II in transcription-coupled repair
Mechanism of Rad26-assisted rescue of stalled RNA polymerase II in transcription-coupled repair
Here the authors provide models of RNA polymerase II bound to the yeast CSB ortholog Rad26 in different nucleotide states; explain how Rad26 domain motions help the polymerase progress past DNA lesions; and interpret the effects of CSB-associated disease mutations.
- Chunli Yan
- , Thomas Dodd
- & Ivaylo Ivanov
-
Article
| Open Access Mounting, structure and autocleavage of a type VI secretion-associated Rhs polymorphic toxin
Mounting, structure and autocleavage of a type VI secretion-associated Rhs polymorphic toxin
Rearrangement hot spots (Rhs) proteins are bacterial polymorphic toxin systems. Here, the authors show that Rhs1 forms a complex with the Type VI secretion system (T6SS) spike protein VgrG and the EagR chaperone. They also present the cryo-EM structure of the Rhs1-EagR complex and propose a model for Rhs loading and delivery by the T6SS.
- Dukas Jurėnas
- , Leonardo Talachia Rosa
- & Eric Cascales
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for the E3 ligase activity enhancement of yeast Nse2 by SUMO-interacting motifs
Structural basis for the E3 ligase activity enhancement of yeast Nse2 by SUMO-interacting motifs
Nse2 is a SUMO E3 ligase component of the Smc5/6 multisubunit complex involved in the DNA repair and chromosome integrity. Here, the structure of the Nse2 in complex with an E2-SUMO thioester mimetic reveals the combined action of two SIM motifs during the E3- dependent conjugation reaction.
- Nathalia Varejão
- , Jara Lascorz
- & David Reverter
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structures of phosphatidyl serine synthase PSS reveal the catalytic mechanism of CDP-DAG alcohol O-phosphatidyl transferases
Crystal structures of phosphatidyl serine synthase PSS reveal the catalytic mechanism of CDP-DAG alcohol O-phosphatidyl transferases
CDP-diacylglycerol (CDP-DAG) alcohol O-phosphatidyl transferases (CDP-APs) are conserved in archaea, bacteria, and eukaryotes and catalyze the de novo synthesis of phospho-lipids from the precursor CDP-DAG and an alcohol. Here, the authors present the crystal structures of the Methanocaldococcus jannaschii phosphatidyl serine synthase (MjPSS) in four different states and suggest a model for its catalytic mechanism.
- Martin Centola
- , Katharina van Pee
- & Özkan Yildiz
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of Ty3 retrotransposon integration at RNA Polymerase III-transcribed genes
Structural basis of Ty3 retrotransposon integration at RNA Polymerase III-transcribed genes
Ty3 retrotransposon integrates with an exquisite specificity upstream of RNA Polymerase III-transcribed genes, such as transfer RNAs. Here the authors resolve a cryo-EM structure of an active Ty3 intasome in complex with a TFIIIB-bound tRNA promoter, shedding light into the molecular determinants of harmless retrotransposition.
- Guillermo Abascal-Palacios
- , Laura Jochem
- & Alessandro Vannini
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular architecture of black widow spider neurotoxins
Molecular architecture of black widow spider neurotoxins
The venom of Latrodectus spiders contains seven Latrotoxins (LaTXs), among them α-latrocrustatoxin (LCT) and δ- latroinsectotoxins δ-LIT. LaTXs bind to specific receptors on the surface of neuronal cells and target the molecular exocytosis machinery. Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structure of the α-LCT monomer and the δ-LIT dimer, which reveal that LaTXs are organized in four domains and they discuss the potential oligomerisation mechanism that takes place before LaTXs membrane insertion. Both recombinant α-LCT and δ-LIT form channels in artificial membrane bilayers, that are stabilized by Ca2+ ions.
- Minghao Chen
- , Daniel Blum
- & Christos Gatsogiannis
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into proteolytic activation of the human Dispatched1 transporter for Hedgehog morphogen release
Structural insights into proteolytic activation of the human Dispatched1 transporter for Hedgehog morphogen release
Dispatched (Disp) RND transporter, activated by Furin-mediated proteolytic cleavage, mediates the release of the lipid-modified Hedgehog (Hh) ligands. Here, the authors report structures of human Disp1 (hDisp1) before and after cleavage, and in complex with lipid-modified Sonic hedgehog (Shh), with insights into the mechanisms of hDisp1 activation and function.
- Wanqiu Li
- , Linlin Wang
- & Xin Gong
-
Article
| Open Access Structural evolution of a DNA repair self-resistance mechanism targeting genotoxic secondary metabolites
Structural evolution of a DNA repair self-resistance mechanism targeting genotoxic secondary metabolites
Microbial DNA glycosylases associated with the biosynthesis of DNA-damaging antibiotics have evolved self-resistance for their cognate natural products. Here, the authors provide evidence that cellular self-resistance is enabled by reduced affinity of the glycosylases for the excision products of the corresponding DNA lesions.
- Elwood A. Mullins
- , Jonathan Dorival
- & Brandt F. Eichman
-
Article
| Open Access Helicobacter pylori FabX contains a [4Fe-4S] cluster essential for unsaturated fatty acid synthesis
Helicobacter pylori FabX contains a [4Fe-4S] cluster essential for unsaturated fatty acid synthesis
Helicobacter pylori FabX, a dehydrogenase/isomerase flavoprotein, is required for unsaturated fatty acid synthesis. Here, the authors characterize FabX substrate recognition and catalytic mechanism, and reveal that it contains an atypical [4Fe-4S] cluster, which is essential and participates in the catalytic cycle.
- Jiashen Zhou
- , Lin Zhang
- & Liang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM snapshots of a native lysate provide structural insights into a metabolon-embedded transacetylase reaction
Cryo-EM snapshots of a native lysate provide structural insights into a metabolon-embedded transacetylase reaction
How is acetyl-CoA produced in the context of the endogenous, eukaryotic pyruvate dehydrogenase complex metabolon? Here the authors dissect the embedded transacetylase reaction through biochemical, cryo-EM, HADDOCKing and molecular dynamics methods.
- Christian Tüting
- , Fotis L. Kyrilis
- & Panagiotis L. Kastritis
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of tweety homolog proteins TTYH2 and TTYH3 reveal a Ca2+-dependent switch from intra- to intermembrane dimerization
Structures of tweety homolog proteins TTYH2 and TTYH3 reveal a Ca2+-dependent switch from intra- to intermembrane dimerization
Tweety Homologs (TTYHs) are highly conserved membrane proteins, whose functions remain poorly understood. Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structures of murine TTYH2 and TTYH3 that form cis-dimers in the presence of Ca2+, whereas in the absence of Ca2+ TTYH2 adopts monomeric and trans-dimeric structures. The presented structures lack ion conducting pathways, which is consistent with results from electrophysiology measurements.
- Baobin Li
- , Christopher M. Hoel
- & Stephen G. Brohawn
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of HIV-1 Vpr in complex with the human nucleotide excision repair protein hHR23A
Structure of HIV-1 Vpr in complex with the human nucleotide excision repair protein hHR23A
Vpr is a HIV-1 accessory virulence factor that also interacts with the human DNA repair protein hHR23A. Here, the authors present the structure of Vpr in complex with the C-terminal half of hHR23A comprising the XPC-binding and ubiquitin-associated domains, which reveals that hHR23A interacts with the DCAF1-binding and not the substrate-binding Vpr surface and further illustrates how Vpr acts as a versatile structural adapter that targets diverse DNA repair pathways.
- In-Ja L. Byeon
- , Guillermo Calero
- & Angela M. Gronenborn
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and functional analysis of the promiscuous AcrB and AdeB efflux pumps suggests different drug binding mechanisms
Structural and functional analysis of the promiscuous AcrB and AdeB efflux pumps suggests different drug binding mechanisms
Resistance-nodulation-cell division (RND)-type tripartite efflux pumps confer multidrug resistance to Gram-negative bacteria. Here, structural and functional analyses of AdeB from Acinetobacter baumannii and AcrB from Escherichia coli provide insight into their different drug-binding and conformational drug transport states.
- Alina Ornik-Cha
- , Julia Wilhelm
- & Klaas M. Pos
-
Article
| Open Access A structured RNA motif locks Argonaute2:miR-122 onto the 5’ end of the HCV genome
A structured RNA motif locks Argonaute2:miR-122 onto the 5’ end of the HCV genome
The RNA genome of the Hepatitis C Virus binds to the liver-specific miR122. Here the authors report the crystal structure of the Ago2:miR122:HCV complex showing that the viral RNA’s structural element traps the Ago2:miR-122 complex on the 5’ end of the viral genome to protect it from degradation.
- Luca F. R. Gebert
- , Mansun Law
- & Ian J. MacRae
-
Article
| Open Access Development of a BCL-xL and BCL-2 dual degrader with improved anti-leukemic activity,
Development of a BCL-xL and BCL-2 dual degrader with improved anti-leukemic activity,
Simultaneous targeting of BCL-xL and BCL-2 is an attractive approach for cancer treatment. Based on information gained by computational structure modelling, the authors develop a PROTAC that induces degradation of both BCL-xL and BCL-2 and effectively targets BCL-xL/2-dependent leukaemia cells.
- Dongwen Lv
- , Pratik Pal
- & Daohong Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access The structural basis for the phospholipid remodeling by lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3
The structural basis for the phospholipid remodeling by lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3
During phosphatidylcholine (PC) remodeling re-acylation is catalyzed by lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferases (LPCAT). Here, the authors present crystal and cryo-EM structures of chicken LPCAT3 in the apo-, acyl donor-bound and acyl receptor-bound states, and based on the structures and further functional analysis they discuss the mechanism of the enzyme.
- Qing Zhang
- , Deqiang Yao
- & Yu Cao
-
Article
| Open Access Architecture of the outer-membrane core complex from a conjugative type IV secretion system
Architecture of the outer-membrane core complex from a conjugative type IV secretion system
DNA transfer between two bacterial cells is mediated by the conjugative type 4 secretion systems (T4SSs). Here, the authors report the structure of a complete T4SS outer-membrane core complex (OMCC), revealing distinct C17 and C13 symmetries of its central inner and peripheral outer ring regions, respectively.
- Himani Amin
- , Aravindan Ilangovan
- & Tiago R. D. Costa
-
Article
| Open Access N-terminal tyrosine of ISCU2 triggers [2Fe-2S] cluster synthesis by ISCU2 dimerization
N-terminal tyrosine of ISCU2 triggers [2Fe-2S] cluster synthesis by ISCU2 dimerization
[2Fe-2S] protein cofactors are essential for life and are synthesized on ISCU2 scaffolds. Here, the authors show that hydrophobic interaction of two conserved N-terminal tyrosines induces ISCU2 dimerization and concomitant [2Fe-2S] cluster synthesis.
- Sven-A. Freibert
- , Michal T. Boniecki
- & Roland Lill
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structures of intermediates suggest an alternative catalytic reaction cycle for cytochrome c oxidase
Cryo-EM structures of intermediates suggest an alternative catalytic reaction cycle for cytochrome c oxidase
Cytochrome c oxidase is a fundamental enzyme of life and its mechanism is not fully understood yet. Here, the authors present four cryo-EM structures of different intermediate states, which suggest an alternative cytochrome c oxidase reaction cycle.
- F. Kolbe
- , S. Safarian
- & H. Michel
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the class C orphan GPCR GPR158 in complex with RGS7-Gβ5
Structure of the class C orphan GPCR GPR158 in complex with RGS7-Gβ5
The orphan GPR158 receptor belongs to the class C GPCR family and interacts with the regulator of G protein signaling 7 (RGS7)-Gβ5 complex. Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structure of human GPR158, which reveals that the extracellular domain contains a PAS domain, and they also determine the structures of GPR158 in complex with either one or two RGS7-Gβ5 heterodimers and discuss implications for the signaling mechanism.
- Eunyoung Jeong
- , Yoojoong Kim
- & Yunje Cho
-
Article
| Open Access Human RIPK3 maintains MLKL in an inactive conformation prior to cell death by necroptosis
Human RIPK3 maintains MLKL in an inactive conformation prior to cell death by necroptosis
The pseudokinase MLKL is activated by the upstream kinase RIPK3 in the necroptotic pathway but the structural basis of MLKL activation is not well understood yet. Here, the authors present the crystal structures of the human RIPK3:MLKL complex and human RIPK3 kinase alone, which reveal structural differences between human and murine RIPK3 and they discuss mechanistic implications.
- Yanxiang Meng
- , Katherine A. Davies
- & James M. Murphy
-
Article
| Open Access Phosphorylation activates the yeast small heat shock protein Hsp26 by weakening domain contacts in the oligomer ensemble
Phosphorylation activates the yeast small heat shock protein Hsp26 by weakening domain contacts in the oligomer ensemble
Small heat shock proteins (sHsps) form large spherical assemblies and their regulation is not well understood. Here, the authors provide insights into the mechanism of Hsp26 activation by characterising phospho-mimetic mutants of yeast Hsp26. They present cryo-EM structures of the wild-type Hsp26 40mer and its phospho-mimetic mutants that reveal the location of the thermosensor in the oligomer, and the authors also show that the thermosensor domain is targeted by phosphorylation, which relieves the intrinsic inhibition of chaperone activity.
- Moritz Mühlhofer
- , Carsten Peters
- & Johannes Buchner
-
Article
| Open Access HPF1 dynamically controls the PARP1/2 balance between initiating and elongating ADP-ribose modifications
HPF1 dynamically controls the PARP1/2 balance between initiating and elongating ADP-ribose modifications
HPF1 controls the ADP-ribosylation activity of PARP1/2 in response to DNA breaks. Here, the authors show that HPF1 regulates the balance between ADP-ribose initiation and elongation through a dynamic interaction that accelerates the initiation rate on serine residues.
- Marie-France Langelier
- , Ramya Billur
- & John M. Pascal
-
Article
| Open Access MDA5 disease variant M854K prevents ATP-dependent structural discrimination of viral and cellular RNA
MDA5 disease variant M854K prevents ATP-dependent structural discrimination of viral and cellular RNA
MDA5 is the primary immune sensor for SARS-CoV-2 and many other viruses. Mutations in MDA5 can cause disease. Here the authors employ CryoEM and biochemical methods to show how steric constraints cause MDA5 to misrecognize endogenous RNA as viral RNA.
- Qin Yu
- , Alba Herrero del Valle
- & Yorgo Modis
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structures of the elusive Rhizobium etli l-asparaginase reveal a peculiar active site
Crystal structures of the elusive Rhizobium etli l-asparaginase reveal a peculiar active site
L-asparaginases catalyse the hydrolysis of L-asparagine to L-aspartic acid and ammonia. Here, the authors present high resolution crystal structures of Rhizobium etli L-asparaginase that contains a Zn2+ binding site without a catalytic role and discuss the catalytic mechanism of the enzyme.
- Joanna I. Loch
- , Barbara Imiolczyk
- & Mariusz Jaskolski
-
Article
| Open Access Distinct conformations of the HIV-1 V3 loop crown are targetable for broad neutralization
Distinct conformations of the HIV-1 V3 loop crown are targetable for broad neutralization
The V3-crown of the HIV-1 envelope protein largely elicits non-neutralizing antibodies. Here, the authors show that the V3-crown can be targeted by broadly neutralizing designed ankyrin repeat proteins recognizing two conformations one of which resembles CCR5- bound V3.
- Nikolas Friedrich
- , Emanuel Stiegeler
- & Alexandra Trkola
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of prokaryotic ubiquitin-like protein Pup in complex with depupylase Dop reveal the mechanism of catalytic phosphate formation
Structures of prokaryotic ubiquitin-like protein Pup in complex with depupylase Dop reveal the mechanism of catalytic phosphate formation
Pupylation is a bacterial post-translational protein modification, where the small ubiquitin-like protein Pup is covalently attached to lysine side chains of target proteins, which is a reversible process and depupylation is catalysed by the depupylase enzyme, Dop. Here, the authors present crystal structures of Dop in different functional states, which together with biochemical experiments provide insights into the catalytic mechanism of this enzyme.
- Hengjun Cui
- , Andreas U. Müller
- & Eilika Weber-Ban
-
Article
| Open Access Abemaciclib is a potent inhibitor of DYRK1A and HIP kinases involved in transcriptional regulation
Abemaciclib is a potent inhibitor of DYRK1A and HIP kinases involved in transcriptional regulation
Abemaciclib is a third generation CDK-directed drug used in the treatment of HR + /HER2 negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer. Here the authors demonstrate that members of the Homeodomain-interacting protein kinases (HIPKs) HIPK3 and DYRK1A are also targeted by Abemaciclib.
- Ines H. Kaltheuner
- , Kanchan Anand
- & Matthias Geyer
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of actin-dependent activation of nucleotidyl cyclase toxins from bacterial human pathogens
Mechanism of actin-dependent activation of nucleotidyl cyclase toxins from bacterial human pathogens
The nucleotidyl cyclase toxin exoenzyme Y (ExoY), which is secreted by the human pathogens Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Vibrio vulnificus is activated by actin. Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structures of PaExoY bound to F-actin and VvExoY in complex with G-actin-profilin. These structures together with molecular dynamics simulations and enzymatic assays provide insights into the activation mechanism for both bacterial cyclase toxin families that interact with either F- or G-actin.
- Alexander Belyy
- , Felipe Merino
- & Stefan Raunser
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of the regulation of the normal and oncogenic methylation of nucleosomal histone H3 Lys36 by NSD2
Structural basis of the regulation of the normal and oncogenic methylation of nucleosomal histone H3 Lys36 by NSD2
An upregulation of NSD2, a histone H3 lysine 36 (H3K36) methyltransferase is linked to multiple myeloma and other types of cancer. Here, the authors provide insights into the regulatory mechanism of NSD2 by determining the 2.8 Å cryo-EM structure of the NSD2 bound nucleosome complex, and based on MD simulations they discuss how two oncogenic mutations enhance NSD2 activity.
- Ko Sato
- , Amarjeet Kumar
- & Toru Sengoku
-
Article
| Open Access Structural dynamics in the water and proton channels of photosystem II during the S2 to S3 transition
Structural dynamics in the water and proton channels of photosystem II during the S2 to S3 transition
The oxygen-evolving complex in Photosystem II (PSII) catalyzes the light-driven oxidation of water to oxygen and it is still under debate how the water reaches the active site. Here, the authors analyse time-resolved XFEL-based crystal structures of PSII that were determined at room temperature and report the structures of the waters in the putative channels surrounding the active site at various time-points during the reaction cycle and conclude that the O1 channel is the likely water intake pathway and the Cl1 channel the likely proton release pathway.
- Rana Hussein
- , Mohamed Ibrahim
- & Junko Yano
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of Escherichia coli cytochrome bd-II type oxidase with bound aurachin D
Structure of Escherichia coli cytochrome bd-II type oxidase with bound aurachin D
Terminal bd oxidases endow bacterial pathogens with resistance to cellular stressors. The authors report the structure of E. coli bd-II type oxidase with the bound inhibitor aurachin D, providing a structural basis for the design of specifically binding antibiotics.
- Antonia Grauel
- , Jan Kägi
- & Thorsten Friedrich
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure provides insights into the dimer arrangement of the O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine transferase OGT
Cryo-EM structure provides insights into the dimer arrangement of the O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine transferase OGT
The modification of proteins with O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine (OGlcNAc) plays roles in regulation of numerous cellular functions while incorrect O-GlcNAcylation patterns are linked to disease. Here, the authors report a cryo-EM structure of full-length O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT), the only enzyme responsible for O-GlcNAcylation.
- Richard W. Meek
- , James N. Blaza
- & Gideon J. Davies
-
Article
| Open Access 2-Oxoglutarate derivatives can selectively enhance or inhibit the activity of human oxygenases
2-Oxoglutarate derivatives can selectively enhance or inhibit the activity of human oxygenases
The human 2-oxoglutarate (2OG) oxygenases FIH and AspH are relevant drug targets. Here, the authors show that synthetic and naturally occurring 2OG derivatives can selectively modulate FIH and AspH activities, suggesting that these compounds may serve as a basis to develop 2OG oxygenase-targeting probes and drugs.
- Yu Nakashima
- , Lennart Brewitz
- & Christopher J. Schofield
-
Article
| Open Access Extended antibody-framework-to-antigen distance observed exclusively with broad HIV-1-neutralizing antibodies recognizing glycan-dense surfaces
Extended antibody-framework-to-antigen distance observed exclusively with broad HIV-1-neutralizing antibodies recognizing glycan-dense surfaces
Here, the authors analyse the distance between the body of an antibody and a protein antigen denoted as the Antibody-Framework-to-Antigen Distance (AFAD) for about 2000 non-redundant antibody-protein antigen complexes in the Protein Data Bank. They observe that antibodies with exceptionally long AFADs were all broad HIV-1-neutralizing antibodies that targeted densely glycosylated regions on the HIV-1-envelope trimer. The connection between long AFAD and dense glycan was further validated by the cryo-EM structure of antibody 2909 recognizing a glycan hole and by glycan shielding analyses based on molecular dynamics simulations.
- Myungjin Lee
- , Anita Changela
- & Peter D. Kwong
-
Article
| Open Access A site of vulnerability at V3 crown defined by HIV-1 bNAb M4008_N1
A site of vulnerability at V3 crown defined by HIV-1 bNAb M4008_N1
Mapping of the HIV Env surface epitopes targeted by broadly neutralizing antibodies (bNAbs) is of great interest for HIV-1 vaccine design. Here, the authors present the 3.2 Å cryo-EM structure of the bNAb M4008_N1 in complex with BG505 DS-SOSIP, an engineered native-like Env trimer and observe that the bNAb epitope is centered at the V3 crown and that M4008_N1 uses its CDR H3 to form an extended β-sheet with the β-hairpin of the V3 crown in a conformation stabilized in the prefusion trimer.
- Kun-Wei Chan
- , Christina C. Luo
- & Xiang-Peng Kong
-
Article
| Open Access Nascent chains can form co-translational folding intermediates that promote post-translational folding outcomes in a disease-causing protein
Nascent chains can form co-translational folding intermediates that promote post-translational folding outcomes in a disease-causing protein
Alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT) deficiency results from misfolding-prone AAT variants. Here the authors show that AAT forms co-translational folding intermediates on the ribosome that persist upon release and determine its folding fate. They show too that the ribosome can also modulate misfolding-prone AAT intermediates during their synthesis.
- Elena Plessa
- , Lien P. Chu
- & Lisa D. Cabrita
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of the interaction between SETD2 methyltransferase and hnRNP L paralogs for governing co-transcriptional splicing
Structural basis of the interaction between SETD2 methyltransferase and hnRNP L paralogs for governing co-transcriptional splicing
Interaction between SETD2 and hnRNP L has previously been shown to be implicated in coupling gene transcription and mRNA processing. Here the authors elucidate the molecular basis of this functional interaction, showing that the RRM domain of hnRNP L possesses non-overlapping binding interfaces for engaging RNA and SETD2.
- Saikat Bhattacharya
- , Suman Wang
- & Fudong Li
-
Article
| Open Access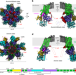 Structure and activation mechanism of the hexameric plasma membrane H+-ATPase
Structure and activation mechanism of the hexameric plasma membrane H+-ATPase
The plasma membrane H+ -ATPase is responsible for maintenance of the plasma membrane potential, which provides energy for the transport of nutrients, and the plasma membrane H+ -ATPase in S. cerevisiae (Pma1) is a P3A-type ATPase that assembles and functions as a hexamer. Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structures of autoinhibited and activated native Pma1 hexamers purified with endogenous lipids and they propose a mechanism for proton pumping across the membrane by this family of H+ -ATPases.
- Peng Zhao
- , Chaoran Zhao
- & Lin Bai
-
Article
| Open Access Role of mutations and post-translational modifications in systemic AL amyloidosis studied by cryo-EM
Role of mutations and post-translational modifications in systemic AL amyloidosis studied by cryo-EM
Systemic AL amyloidosis is caused by misfolding of immunoglobulin light chains (LCs) but how post-translational modifications (PTMs) of LCs influence amyloid formation is not well understood. Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structure of an AL amyloid fibril derived from the heart tissue of a patient that is partially pyroglutamylated, N-glycosylated and contains an intramolecular disulfide bond. Based on their structure and biochemical experiments the authors conclude that the mutational changes, disulfide bond and glycosylation determine the fibril protein fold and that glycosylation protects the fibril core from proteolytic degradation.
- Lynn Radamaker
- , Sara Karimi-Farsijani
- & Marcus Fändrich
-
Article
| Open Access Pseudoknot length modulates the folding, conformational dynamics, and robustness of Xrn1 resistance of flaviviral xrRNAs
Pseudoknot length modulates the folding, conformational dynamics, and robustness of Xrn1 resistance of flaviviral xrRNAs
Exoribonuclease-resistant RNAs (xrRNAs) are RNA elements that block the exoribonucleolytic degradation of RNA. Here the authors show how a long-range pseudoknot length modulates the Mg2+-dependence of flaviviral xrRNA’s folding, conformational dynamics and Xrn1 resistance.
- Xiaolin Niu
- , Ruirui Sun
- & Xianyang Fang
-
Article
| Open Access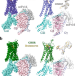 Structural basis of human ghrelin receptor signaling by ghrelin and the synthetic agonist ibutamoren
Structural basis of human ghrelin receptor signaling by ghrelin and the synthetic agonist ibutamoren
Ghrelin is a central orexigenic peptide hormone in human energy homeostasis that is also known as ‘hunger hormone’ and signals through its GPCR, GHSR. Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structures of the human GHSR-Gi signaling complex with bound ghrelin and the synthetic non-peptide agonist ibutamoren that are of interest for drug design.
- Heng Liu
- , Dapeng Sun
- & Cheng Zhang

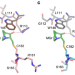 Structural basis of reactivation of oncogenic p53 mutants by a small molecule: methylene quinuclidinone (MQ)
Structural basis of reactivation of oncogenic p53 mutants by a small molecule: methylene quinuclidinone (MQ)