Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access The YΦ motif defines the structure-activity relationships of human 20S proteasome activators
The YΦ motif defines the structure-activity relationships of human 20S proteasome activators
The proteasome complexes, composed of 20S core particles and one or two regulatory particles (proteasome activators), degrade most eukaryotic proteins. Here, the authors identify a sequence motif and resolve its interactions mediating the activation of the human 20S proteasome.
- Kwadwo A. Opoku-Nsiah
- , Andres H. de la Pena
- & Jason E. Gestwicki
-
Article
| Open Access Structural snapshots of V/A-ATPase reveal the rotary catalytic mechanism of rotary ATPases
Structural snapshots of V/A-ATPase reveal the rotary catalytic mechanism of rotary ATPases
The rotary ATPases use a rotary catalytic mechanism to drive transmembrane proton movement powered by ATP hydrolysis. Here, the authors report a collection of V/A-ATPase V1 domain structures, providing insights into rotary mechanism of the enzyme and potentially other rotary motor proteins driven by ATP hydrolysis.
- J. Kishikawa
- , A. Nakanishi
- & K. Yokoyama
-
Article
| Open Access Differential recognition of canonical NF-κB dimers by Importin α3
Differential recognition of canonical NF-κB dimers by Importin α3
Nuclear translocation of the p50/p65 heterodimer is essential for NF-κB signaling. Here, the authors identify a bipartite Nuclear Localization Signal in the NF-κB p50/p65 heterodimer that is recognized with high affinity by importin α3.
- Tyler J. Florio
- , Ravi K. Lokareddy
- & Gino Cingolani
-
Article
| Open Access Evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in the human host
Evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in the human host
The SARS-CoV-2 spike has been evolving in the human population. The variants of concern alpha and beta evolved to optimise spike openness and so ability to bind its receptor ACE2, the affinity towards the receptor, and stability upon receptor binding.
- Antoni G. Wrobel
- , Donald J. Benton
- & Steven J. Gamblin
-
Article
| Open Access The molecular basis of FimT-mediated DNA uptake during bacterial natural transformation
The molecular basis of FimT-mediated DNA uptake during bacterial natural transformation
Many bacteria can take up exogenous DNA, in a process that often requires surface appendages composed of thousands of protein subunits called pilins. Here, Braus et al. show that a minor pilin binds directly to DNA and is important for DNA uptake in the pathogen Legionella pneumophila.
- Sebastian A. G. Braus
- , Francesca L. Short
- & Manuela K. Hospenthal
-
Article
| Open Access Ubiquitin and a charged loop regulate the ubiquitin E3 ligase activity of Ark2C
Ubiquitin and a charged loop regulate the ubiquitin E3 ligase activity of Ark2C
Attachment of ubiquitin to proteins is tightly regulated and controls many signalling pathways. Here, the authors show that addition of ubiquitin by the RING E3 ligases Arkadia and Ark2C is enhanced by ubiquitin and a charged loop that precedes the RING domain.
- Andrej Paluda
- , Adam J. Middleton
- & Catherine L. Day
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of a SARS-CoV-2 omicron spike protein ectodomain
Cryo-EM structure of a SARS-CoV-2 omicron spike protein ectodomain
This study determined the structure of the spike protein of the SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant, revealing a predominantly open conformation of the molecule that may help omicron infect cells more efficiently than do previous variants.
- Gang Ye
- , Bin Liu
- & Fang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of leukotriene B4 receptor 1 activation
Structural basis of leukotriene B4 receptor 1 activation
In the paper, Dr. Wang et al reported a cryo-EM structure of the human leukotriene B4 receptor 1 (BLT1) in complex with its native ligand leukotriene B4 (LTB4) in an active conformation complexed with Gi protein. The structure reveals the molecule determinant of LTB4 binding and the mechanism of receptor activation. These structural information will boost the understanding of LTB4-BLT1 signaling and provide a rational basis for designing novel anti-leukotriene drugs.
- Na Wang
- , Xinheng He
- & Yuanzheng He
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of cooperative N-glycan processing by the multi-modular endoglycosidase EndoE
Mechanism of cooperative N-glycan processing by the multi-modular endoglycosidase EndoE
EndoE is a multi-domain glycoside hydrolase of the human pathogen Enterococcus faecalis. Here, the authors present crystal structures of EndoE and provide biochemical insights into the molecular basis of EndoE’s substrate specificity and catalytic mechanism.
- Mikel García-Alija
- , Jonathan J. Du
- & Marcelo E. Guerin
-
Article
| Open Access A multi-factor trafficking site on the spliceosome remodeling enzyme BRR2 recruits C9ORF78 to regulate alternative splicing
A multi-factor trafficking site on the spliceosome remodeling enzyme BRR2 recruits C9ORF78 to regulate alternative splicing
Bergfort et al. use biochemistry, cryoEM, structure-guided mutagenesis, transcriptomics and proteomics to reveal how the intrinsically unstructured C9ORF78 protein binds BRR2 and PRPF8, regulating cassette exons and alternative 3’-splice sites.
- Alexandra Bergfort
- , Marco Preußner
- & Markus C. Wahl
-
Article
| Open Access Leveraging the multivalent p53 peptide-MdmX interaction to guide the improvement of small molecule inhibitors
Leveraging the multivalent p53 peptide-MdmX interaction to guide the improvement of small molecule inhibitors
Peptide fragments derived from the interfaces of protein-protein interactions (PPIs) provide useful templates for designing small molecule PPI inhibitors. Here, the authors utilize the multivalency of an MdmX-binding p53 peptide to develop a weak inhibitor of MdmX into potent Mdm2/MdmX inhibitors.
- Xiyao Cheng
- , Rong Chen
- & Zhengding Su
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and assembly of the S-layer in C. difficile
Structure and assembly of the S-layer in C. difficile
The S-layer is a two-dimensional protein array that covers the cell surface of many bacteria and archaea. Here, the authors use high-resolution X-ray crystallography and electron microscopy to provide detailed insights into S-layer organisation and assembly for the bacterial pathogen Clostridioides difficile.
- Paola Lanzoni-Mangutchi
- , Oishik Banerji
- & Paula S. Salgado
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding self-assembly at molecular level enables controlled design of DNA G-wires of different properties
Understanding self-assembly at molecular level enables controlled design of DNA G-wires of different properties
G-wire structures have potential applications in bio-nanotechnology, however, this is limited by a lack of understanding about the assembly process and structures formed. Here, the authors use nuclear magnetic resonance and molecular dynamic simulations to understand the guiding principles of G-wire assembly.
- Daša Pavc
- , Nerea Sebastian
- & Primož Šket
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of translesion DNA synthesis polymerase ζ with a base pair mismatch
Cryo-EM structure of translesion DNA synthesis polymerase ζ with a base pair mismatch
The structure of mismatched DNA-Polζ ternary complex provides a basis for understanding what makes Polζ adept at extending DNA synthesis past mismatched base pairs.
- Radhika Malik
- , Robert E. Johnson
- & Aneel K. Aggarwal
-
Article
| Open Access Inhibition of SRP-dependent protein secretion by the bacterial alarmone (p)ppGpp
Inhibition of SRP-dependent protein secretion by the bacterial alarmone (p)ppGpp
Bacterial responses to nutrient limitation and other stress conditions are often modulated by the nucleotide-based second messenger (p)ppGpp. Here, the authors show that (p)ppGpp inhibits the SRP membrane-protein insertion and secretion pathway by binding to GTPases Ffh and FtsY.
- Laura Czech
- , Christopher-Nils Mais
- & Gert Bange
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular recognition of formylpeptides and diverse agonists by the formylpeptide receptors FPR1 and FPR2
Molecular recognition of formylpeptides and diverse agonists by the formylpeptide receptors FPR1 and FPR2
Zhuang et al. report four cryo-EM structures of formylpeptide receptors FPR1 and FPR2 coupled with Gi protein and diverse agonists, revealing how FPRs as pattern recognition receptors recognize formylpeptides and synthetic agonists and a distinctive receptor activation mechanism.
- Youwen Zhuang
- , Lei Wang
- & Cheng Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into multiplexed pharmacological actions of tirzepatide and peptide 20 at the GIP, GLP-1 or glucagon receptors
Structural insights into multiplexed pharmacological actions of tirzepatide and peptide 20 at the GIP, GLP-1 or glucagon receptors
Multi-targeting agonists at GIPR, GLP-1R or GCGR are pursued vigorously. Here, the authors report cryo-EM structures of tirzepatide-bound GIPR and GLP-1R, peptide 20-bound GIPR, GLP-1R and GCGR, revealing the molecular basis of their multiplexed pharmacological actions.
- Fenghui Zhao
- , Qingtong Zhou
- & Ming-Wei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access A mechanism of origin licensing control through autoinhibition of S. cerevisiae ORC·DNA·Cdc6
A mechanism of origin licensing control through autoinhibition of S. cerevisiae ORC·DNA·Cdc6
Cryo-EM structures of S. cerevisiae ORC bound to DNA and Cdc6 reveal an autoinhibited conformation and suggest a mechanism of origin licensing control in response to CDK phosphorylation.
- Jan Marten Schmidt
- , Ran Yang
- & Franziska Bleichert
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of adenylyl cyclase 9 activation
Structural basis of adenylyl cyclase 9 activation
Adenylyl cyclases (ACs) generate the second messenger cAMP and play an important role in cellular signaling. Here, the authors use cryo-EM to trace the conformational changes resulting from binding to partial and full activators to one of these enzymes, AC9.
- Chao Qi
- , Pia Lavriha
- & Volodymyr M. Korkhov
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence for a trap-and-flip mechanism in a proton-dependent lipid transporter
Evidence for a trap-and-flip mechanism in a proton-dependent lipid transporter
LtaA catalyzes glycolipid translocation by a ‘trap-and-flip’ mechanism, pointing to a shared mechanistic model among MFS lipid transporters. Asymmetric lateral openings allow access of the entire lipid substrate to the amphipathic central cavity.
- Elisabeth Lambert
- , Ahmad Reza Mehdipour
- & Camilo Perez
-
Article
| Open Access High-pH structure of EmrE reveals the mechanism of proton-coupled substrate transport
High-pH structure of EmrE reveals the mechanism of proton-coupled substrate transport
EmrE transporter effluxes cationic substrates across lipid membranes in a pH-coupled manner. Here, the authors solve the structure of ligand-bound EmrE at high pH by NMR, with insights into the transport mechanism.
- Alexander A. Shcherbakov
- , Peyton J. Spreacker
- & Mei Hong
-
Article
| Open Access Development and characterization of functional antibodies targeting NMDA receptors
Development and characterization of functional antibodies targeting NMDA receptors
Selective targeting individual subtypes of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) is a desirable therapeutic strategy for neurological disorders. Here, the authors report identification of a functional antibody that specifically targets and allosterically down-regulates ion channel activity of the GluN1—GluN2B NMDAR subtype.
- Nami Tajima
- , Noriko Simorowski
- & Hiro Furukawa
-
Article
| Open Access A late-stage assembly checkpoint of the human mitochondrial ribosome large subunit
A late-stage assembly checkpoint of the human mitochondrial ribosome large subunit
Rebelo-Guiomar et al. unveil late stage assembly intermediates of the human mitochondrial ribosome by inactivating the methyltransferase MRM2 in cells. Absence of MRM2 impairs organismal homeostasis, while its catalytic activity is dispensable for mitoribosomal biogenesis.
- Pedro Rebelo-Guiomar
- , Simone Pellegrino
- & Michal Minczuk
-
Article
| Open Access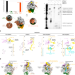 Structural snapshots of La Crosse virus polymerase reveal the mechanisms underlying Peribunyaviridae replication and transcription
Structural snapshots of La Crosse virus polymerase reveal the mechanisms underlying Peribunyaviridae replication and transcription
La Crosse is a human life threatening virus belonging to the Bunyavirales order. The structure of its polymerase solved in seven key active states by cryo-electron microscopy reveals the molecular mechanisms of viral RNA replication and transcription.
- Benoît Arragain
- , Quentin Durieux Trouilleton
- & Hélène Malet
-
Article
| Open Access HSL1 and BAM1/2 impact epidermal cell development by sensing distinct signaling peptides
HSL1 and BAM1/2 impact epidermal cell development by sensing distinct signaling peptides
HAESA and HSL2 are receptors for IDA/IDL-family signaling peptides in plants. Here the authors show that HSL1, previously shown to recognize CLE9, preferentially binds IDA/IDL peptides and regulates leaf epidermal patterning independently of CLE peptides.
- Andra-Octavia Roman
- , Pedro Jimenez-Sandoval
- & Julia Santiago
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant recognition of ACE2 receptor and broadly neutralizing antibodies
Structural basis for SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant recognition of ACE2 receptor and broadly neutralizing antibodies
Here the authors reveal conformational dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Delta spike and its complex with ACE2 receptor or broadly neutralizing Mab 8D3 by cryo-EM, shedding new insights into mechanisms of receptor recognition and antibody neutralization for the Delta variant.
- Yifan Wang
- , Caixuan Liu
- & Yao Cong
-
Article
| Open Access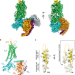 Structural basis of neuropeptide Y signaling through Y1 receptor
Structural basis of neuropeptide Y signaling through Y1 receptor
The human neuropeptide Y (NPY) acts through G-protein coupled receptors and is involved in food intake, stress response, anxiety, and memory retention. Here, the authors show that, unlike in other neuropeptides, both the N-terminal and the C-terminal regions of NPY interact with the NPY receptor 1.
- Chaehee Park
- , Jinuk Kim
- & Hee-Jung Choi
-
Article
| Open Access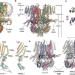 Structural insights into the Venus flytrap mechanosensitive ion channel Flycatcher1
Structural insights into the Venus flytrap mechanosensitive ion channel Flycatcher1
Flycatcher1 (FLYC1) is a candidate mechanosensitive channel involved in Venus flytrap touch-induced prey capture. Here, the authors report structural and functional details of FLYC1, with insights into gating conformational transitions.
- Sebastian Jojoa-Cruz
- , Kei Saotome
- & Andrew B. Ward
-
Article
| Open Access Allosteric control of Ubp6 and the proteasome via a bidirectional switch
Allosteric control of Ubp6 and the proteasome via a bidirectional switch
The interplay of the proteasome and deubiquitinase Ubp6 is crucial for the degradation of ubiquitylated substrates. Here, the authors provide structural insights into the allosteric mechanism by which the activities of both Ubp6 and the proteasome are regulated.
- Ka Ying Sharon Hung
- , Sven Klumpe
- & Daniel Finley
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of highly flexible intracellular domain of human α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Structures of highly flexible intracellular domain of human α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
The intracellular domain (ICD) of Cys-loop receptors mediates many of their functions, but no complete structure of a Cys-loop receptor ICD is available to date. Here, the authors combine NMR and ESR spectroscopy to determine the full-length ICD structures of the human α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7nAChR).
- Vasyl Bondarenko
- , Marta M. Wells
- & Pei Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Defining molecular glues with a dual-nanobody cannabidiol sensor
Defining molecular glues with a dual-nanobody cannabidiol sensor
Molecular glue has been used as a broad term describing a class of protein interaction-promoting compounds. Here, the authors outline two unifying thermodynamic features to formally define molecular glues and guide their prospective discovery.
- Shiyun Cao
- , Shoukai Kang
- & Ning Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and biochemical rationale for enhanced spike protein fitness in delta and kappa SARS-CoV-2 variants
Structural and biochemical rationale for enhanced spike protein fitness in delta and kappa SARS-CoV-2 variants
Saville, Mannar et al. provide a structural basis for enhanced antibody evasion and ACE2 binding by the Delta SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. They further identify a head-to-head dimer-of-trimers cryoEM reconstruction unique to the Kappa variant spike.
- James W. Saville
- , Dhiraj Mannar
- & Sriram Subramaniam
-
Article
| Open Access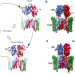 Mechanisms underlying TARP modulation of the GluA1/2-γ8 AMPA receptor
Mechanisms underlying TARP modulation of the GluA1/2-γ8 AMPA receptor
AMPA glutamate receptors, mediate the majority of excitatory signaling in the brain. Here the authors show how the auxiliary subunit TARP-γ8 shapes gating kinetics, ion conductance and rectification properties of the heteromeric GluA1/2 AMPA receptor.
- Beatriz Herguedas
- , Bianka K. Kohegyi
- & Ingo H. Greger
-
Article
| Open Access Differential activation mechanisms of lipid GPCRs by lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine 1-phosphate
Differential activation mechanisms of lipid GPCRs by lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine 1-phosphate
Liu et al. report structures of human sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor 1 (S1P1) in complex with Gi and S1P or the multiple sclerosis (MS) drug Siponimod, as well as human lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) receptor 1 (LPA1) in complex with Gi and LPA, revealing distinct conformations of the lysophospholipids interacting with their cognate GPCRs.
- Shian Liu
- , Navid Paknejad
- & Xin-Yun Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Neutralizing antibodies induced in immunized macaques recognize the CD4-binding site on an occluded-open HIV-1 envelope trimer
Neutralizing antibodies induced in immunized macaques recognize the CD4-binding site on an occluded-open HIV-1 envelope trimer
Neutralizing antibodies (bNAbs) against HIV-1 are exclusively directed against the viral envelope protein (Env) and mainly target Env in a closed, prefusion state. Here, Yang et al. structurally characterize two heterologously-neutralizing CD4-binding site (CD4bs) antibodies isolated from sequentially immunized macaques, and show that these antibodies recognize the CD4bs on Env trimers in an „occluded-open‟ conformation between closed, as targeted by bNAbs, and fully-open, as recognized by CD4.
- Zhi Yang
- , Kim-Marie A. Dam
- & Pamela J. Bjorkman
-
Article
| Open Access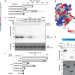 Tousled-like kinase 2 targets ASF1 histone chaperones through client mimicry
Tousled-like kinase 2 targets ASF1 histone chaperones through client mimicry
Tousled-like kinase 2 (TLK2) phosphorylates ASF1 histone chaperones to promote nucleosome assembly in S phase. Here, the authors show that TLK2 targets ASF1 by simulating its client protein histone H3, exploiting a primordial protein interaction surface for regulatory control.
- Bertrand Simon
- , Hua Jane Lou
- & David A. Calderwood
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structures of human bradykinin receptor-Gq proteins complexes
Cryo-EM structures of human bradykinin receptor-Gq proteins complexes
Type 2 bradykinin receptor (B2R) is essential in vasodilation and cardioprotection. Here the authors present two cryo-EM structures of human B2R-Gq in complex with bradykinin and kallidin to elucidate the mechanisms for ligand binding, receptor activation, and Gq proteins coupling.
- Jinkang Shen
- , Dongqi Zhang
- & Haitao Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access An archaellum filament composed of two alternating subunits
An archaellum filament composed of two alternating subunits
The archaellum is a molecular machine used by archaea to swim, consisting of an intracellular motor that drives the rotation of an extracellular filament composed of multiple copies of proteins named archaellins. Here, the authors use electron cryo-microscopy to elucidate the structure of an archaellum, and find that the filament is composed of two alternating archaellins.
- Lavinia Gambelli
- , Michail N. Isupov
- & Bertram Daum
-
Article
| Open Access Induction of tier-2 neutralizing antibodies in mice with a DNA-encoded HIV envelope native like trimer
Induction of tier-2 neutralizing antibodies in mice with a DNA-encoded HIV envelope native like trimer
HIV envelope is a target for vaccine development, but induction of broadly neutralizing antibodies has been difficult. Here, the authors show that electroporation with a synthetic DNA vaccine construct allows in vivo production of HIV envelope native like trimers to induce autologous tier-2 neutralizing antibodies targeting a C3/V5 epitope in mice.
- Ziyang Xu
- , Susanne Walker
- & Daniel W. Kulp
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular mechanism of Arp2/3 complex inhibition by Arpin
Molecular mechanism of Arp2/3 complex inhibition by Arpin
The Arp2/3 complex inhibitor Arpin controls cell migration by interrupting a feedback loop involving Rac-WAVE-Arp2/3 complex Here, the authors use structural, biochemical, and cellular studies to reveal Arpin’s mechanism of inhibition.
- Fred E. Fregoso
- , Trevor van Eeuwen
- & Roberto Dominguez
-
Article
| Open Access Gut microbiome of the largest living rodent harbors unprecedented enzymatic systems to degrade plant polysaccharides
Gut microbiome of the largest living rodent harbors unprecedented enzymatic systems to degrade plant polysaccharides
Here, Cabral et al., perform a multi-omics analysis of the gut microbiome of capybara, the largest living rodent, unveiling enzymatic mechanisms for the breakdown of lignocellulosic biomass, and report two undescribed families of carbohydrate-active enzymes.
- Lucelia Cabral
- , Gabriela F. Persinoti
- & Mario T. Murakami
-
Article
| Open Access A dual mechanism of action of AT-527 against SARS-CoV-2 polymerase
A dual mechanism of action of AT-527 against SARS-CoV-2 polymerase
The drug AT-527 targets the SARS-CoV-2 replication machinery. Here the authors use Cryo-EM to show how AT-527 inhibits SARS-CoV-2 polymerase by acting as an immediate RNA chain terminator and stably binding in a NiRAN active-site pocket; impeding an essential nucleotide-transfer activity.
- Ashleigh Shannon
- , Véronique Fattorini
- & Bruno Canard
-
Article
| Open Access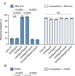 PplD is a de-N-acetylase of the cell wall linkage unit of streptococcal rhamnopolysaccharides
PplD is a de-N-acetylase of the cell wall linkage unit of streptococcal rhamnopolysaccharides
The cell wall of the bacterial pathogen Group A Streptococcus is decorated with a polysaccharide termed GAC, which is a target for vaccine development. Here, Rush et al. characterize the linkage between GAC and peptidoglycan, and identify a protein that deacetylates the linkage and thus protects the pathogen against host cationic antimicrobial proteins.
- Jeffrey S. Rush
- , Prakash Parajuli
- & Natalia Korotkova
-
Article
| Open Access Adaptation to genome decay in the structure of the smallest eukaryotic ribosome
Adaptation to genome decay in the structure of the smallest eukaryotic ribosome
Many parasitic organisms contain molecular structures that are drastically smaller than analogous structures in non-parasitic organisms. Here the authors describe a cryo-EM structure of the ribosome from E. cuniculi that reveals that it compensated rRNA truncations by evolving the ability to use small molecules as ribosomal building blocks.
- David Nicholson
- , Marco Salamina
- & Sergey V. Melnikov
-
Article
| Open Access Catalytic trajectory of a dimeric nonribosomal peptide synthetase subunit with an inserted epimerase domain
Catalytic trajectory of a dimeric nonribosomal peptide synthetase subunit with an inserted epimerase domain
The catalytic domains in nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) are responsible for a choreography of events that elongates substrates into natural products. Here, the authors present cryo-EM structures of a siderophore-producing dimeric NRPS elongation module in multiple distinct conformations, which provides insight into the mechanisms of catalytic trajectory.
- Jialiang Wang
- , Dandan Li
- & Zhijun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Host receptor-targeted therapeutic approach to counter pathogenic New World mammarenavirus infections
Host receptor-targeted therapeutic approach to counter pathogenic New World mammarenavirus infections
Five New World mammarenaviruses (NWMs) enter cells via binding to human transferrin receptor 1 (hTfR1). Here, Hickerson et al. show that hTfR1 targeting antibodies partially protect hTfR1-transgenic mice from lethal NWM challenge via competition of anti-hTfR1 antibody and viral glycoprotein for hTfR1.
- Brady T. Hickerson
- , Tracy R. Daniels-Wells
- & Brian B. Gowen
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of Vibrio collagenase VhaC provides insight into the mechanism of bacterial collagenolysis
Structure of Vibrio collagenase VhaC provides insight into the mechanism of bacterial collagenolysis
The collagenolytic mechanism of Vibrio collagenase, a virulence factor, remains unclear. Here, the authors report the structure of Vibrio collagenase VhaC and propose the mechanism for collagen recognition and degradation, providing new insight into bacterial collagenolysis.
- Yan Wang
- , Peng Wang
- & Yu-Zhong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access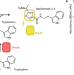 Structures and function of a tailoring oxidase in complex with a nonribosomal peptide synthetase module
Structures and function of a tailoring oxidase in complex with a nonribosomal peptide synthetase module
Nonribosomal peptide synthetases work with additional enzymes to synthesise secondary metabolites and therapeutics. Here, the authors explore bacillamide D synthesis and show the oxidase action is done while the intermediate is attached to the synthetase and replicate this with an oxidase bound synthetase for bioengineering applications.
- Camille Marie Fortinez
- , Kristjan Bloudoff
- & T. Martin Schmeing
-
Article
| Open Access Multiple conformations of trimeric spikes visualized on a non-enveloped virus
Multiple conformations of trimeric spikes visualized on a non-enveloped virus
Zhang and Cui et al. present in situ cryoEM structures of the trimeric spike of cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus in both open and close conformations, and demonstrate that spike detachment from the capsid is triggered by the presence of SAM and ATP.
- Yinong Zhang
- , Yanxiang Cui
- & Z. Hong Zhou

 Improved prediction of protein-protein interactions using AlphaFold2
Improved prediction of protein-protein interactions using AlphaFold2