Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of a non-axisymmetric mode in laboratory experiments searching for standard magnetorotational instability
Identification of a non-axisymmetric mode in laboratory experiments searching for standard magnetorotational instability
Magnetohydrodynamic instabilities are related to different characteristics and behavior of fluids. Here the authors report an experiment and simulation combined study of a global non-axisymmetric MHD instability that exists at sufficiently large rotation rates and intermediate magnetic field strengths.
- Yin Wang
- , Erik P. Gilson
- & Hantao Ji
-
Article
| Open Access Data-driven load profiles and the dynamics of residential electricity consumption
Data-driven load profiles and the dynamics of residential electricity consumption
In modern power grids, knowing the required electric power demand and its variations is necessary to balance demand and supply. The authors propose a data-driven approach to create high-resolution load profiles and characterize their fluctuations, based on recorded data of electricity consumption.
- Mehrnaz Anvari
- , Elisavet Proedrou
- & Marc Timme
-
Article
| Open Access Unjamming and emergent nonreciprocity in active ploughing through a compressible viscoelastic fluid
Unjamming and emergent nonreciprocity in active ploughing through a compressible viscoelastic fluid
The field of dense active matter has been the fount of many intriguing phenomena. Here, authors show that nonreciprocal interactions can emerge between active particles due to a dynamical feedback between their motility and the corresponding slow remodelling of a dense passive compressible medium.
- Jyoti Prasad Banerjee
- , Rituparno Mandal
- & Madan Rao
-
Article
| Open Access Robust prediction of force chains in jammed solids using graph neural networks
Robust prediction of force chains in jammed solids using graph neural networks
The emergence of correlated and self-organized linear structures, known as force chains, is relevant for granular materials, foams, emulsions, and extreme active matter. The authors develop a machine learning-based approach to predict force chain formation in jammed disordered solids under deformation.
- Rituparno Mandal
- , Corneel Casert
- & Peter Sollich
-
Article
| Open Access Confinement anisotropy drives polar organization of two DNA molecules interacting in a nanoscale cavity
Confinement anisotropy drives polar organization of two DNA molecules interacting in a nanoscale cavity
A nanofluidic model system is used to explore how polymer interactions between large dsDNA molecules can give rise to self-organizing behavior in compartments with controlled anisotropy. The reported findings may help explain the observed non-uniform distribution of plasmids in E. coli.
- Zezhou Liu
- , Xavier Capaldi
- & Walter Reisner
-
Article
| Open Access Overload wave-memory induces amnesia of a self-propelled particle
Overload wave-memory induces amnesia of a self-propelled particle
Memory and information storage play an important role in biological systems, however challenging to implement in synthetic active matter. The authors show that the wave field, propelling the particle, acts as a memory repository, and an excess of memory leads to a memory-less particle dynamics.
- Maxime Hubert
- , Stéphane Perrard
- & Matthieu Labousse
-
Article
| Open Access Forecasting the evolution of fast-changing transportation networks using machine learning
Forecasting the evolution of fast-changing transportation networks using machine learning
Transportation networks undergo permanent changes influenced by a variety of human-induced and natural factors. The authors propose here a machine learning framework for prediction of connections removal that could be useful in building scenarios for transportation infrastructure needs.
- Weihua Lei
- , Luiz G. A. Alves
- & Luís A. Nunes Amaral
-
Article
| Open Access Local bifurcation with spin-transfer torque in superparamagnetic tunnel junctions
Local bifurcation with spin-transfer torque in superparamagnetic tunnel junctions
There has been much interest in using the probabilistic switching of magnetic tunnel junctions in unconventional computing, but to do so requires a detailed understanding of this switching. Here, Funatsu et al rigorously determine the switching exponents in superparamagnetic tunnel junctions.
- Takuya Funatsu
- , Shun Kanai
- & Hideo Ohno
-
Article
| Open Access Energy-selective confinement of fusion-born alpha particles during internal relaxations in a tokamak plasma
Energy-selective confinement of fusion-born alpha particles during internal relaxations in a tokamak plasma
Confining plasma for fusion requires controlling many parameters. Here the authors report the existence of a narrow parameter space for the simultaneous confinement of energetic alpha particles and removal of slowed-down helium ash in a magnetically confined fusion plasma by using kinetic-magnetohydrodynamic hybrid simulations.
- A. Bierwage
- , K. Shinohara
- & S. Ide
-
Article
| Open Access Recovery of neural dynamics criticality in personalized whole-brain models of stroke
Recovery of neural dynamics criticality in personalized whole-brain models of stroke
The authors investigate the influence of brain injury (strokes) on the criticality of neural dynamics using directly measured connectomes and whole-brain models. They show that lesions engender a sub-critical state that recovers over time in parallel with behavior.
- Rodrigo P. Rocha
- , Loren Koçillari
- & Maurizio Corbetta
-
Article
| Open Access Influence maximization in Boolean networks
Influence maximization in Boolean networks
Boolean networks modelling various biological processes are characterized by nonlinear reversible dynamics that makes their control challenging. The authors introduce extended concepts of influence and control, typically considered in the study of spreading processes, for Boolean dynamics.
- Thomas Parmer
- , Luis M. Rocha
- & Filippo Radicchi
-
Article
| Open Access Topological invariant and anomalous edge modes of strongly nonlinear systems
Topological invariant and anomalous edge modes of strongly nonlinear systems
Topological phases are challenging to identify in systems with general, strong nonlinearities. Here, the authors establish the analytic methodology that defines the topological invariant of nonlinear normal modes. Strongly nonlinear topological boundary modes are guaranteed by the nontrivial topological index.
- Di Zhou
- , D. Zeb Rocklin
- & Yugui Yao
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent response of the electronic system driven by non-interfering laser pulses
Coherent response of the electronic system driven by non-interfering laser pulses
Light–matter interaction is expected to be isotropic in free-electron-like materials. Here, by using time- and phase-resolved photoemission, the authors observe signatures of an anisotropic interaction on a noble metal surface, that can only be accounted for by optical transition dipoles with a fixed orientation.
- Tobias Eul
- , Eva Prinz
- & Benjamin Stadtmüller
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental realization of one dimensional helium
Experimental realization of one dimensional helium
Helium isotopes are interesting platforms for testing the quantum properties of fluids. Here the authors demonstrate quantum one-dimensional behaviour of helium (4He) confined in nanopores by using neutron scattering.
- Adrian Del Maestro
- , Nathan S. Nichols
- & Paul E. Sokol
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-scale turbulence simulation suggesting improvement of electron heated plasma confinement
Multi-scale turbulence simulation suggesting improvement of electron heated plasma confinement
Understanding the transport of the particles and fuel in the fusion plasma is fundamentally important. Here the authors report a cross-link interaction between electron- and ion-scale turbulences in plasma in terms of trapped electron mode and electron temperature gradient modes and their implication to fusion plasma.
- Shinya Maeyama
- , Tomo-Hiko Watanabe
- & Akihiro Ishizawa
-
Article
| Open Access Relative, local and global dimension in complex networks
Relative, local and global dimension in complex networks
Defining the dimension in bounded, inhomogeneous or discrete physical systems may be challenging. The authors introduce here a dynamics-based notion of dimension by analysing diffusive processes in space, relevant for non-ideal physical systems and networks.
- Robert Peach
- , Alexis Arnaudon
- & Mauricio Barahona
-
Article
| Open Access From subcritical behavior to a correlation-induced transition in rumor models
From subcritical behavior to a correlation-induced transition in rumor models
Rumors and information spreading emerge naturally from human-to-human interaction and have a growing impact on people’s lives due to increasing and faster access to information, whether trustworthy or not. The authors study the Maki–Thompson rumor model and its variation, revealing a phase transition and providing insights into the nature of this transition.
- Guilherme Ferraz de Arruda
- , Lucas G. S. Jeub
- & Yamir Moreno
-
Article
| Open Access Full reconstruction of simplicial complexes from binary contagion and Ising data
Full reconstruction of simplicial complexes from binary contagion and Ising data
Data-driven recovery of topology is challenging for networks beyond pairwise interactions. The authors propose a framework to reconstruct complex networks with higher-order interactions from time series, focusing on networks with 2-simplexes where social contagion and Ising dynamics generate binary data.
- Huan Wang
- , Chuang Ma
- & Hai-Feng Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Non-selective distribution of infectious disease prevention may outperform risk-based targeting
Non-selective distribution of infectious disease prevention may outperform risk-based targeting
Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) is an effective HIV prevention measure but identifying those most at risk to target for treatment is challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate that non-selective PrEP distribution outperforms targeted strategies when use is not consistent, and/or prevalence of untreated HIV is high.
- Benjamin Steinegger
- , Iacopo Iacopini
- & Eugenio Valdano
-
Article
| Open Access A topological fluctuation theorem
A topological fluctuation theorem
While topology is crucial in complex systems, stochastic thermodynamics uncovers universal constraints for non-equilibrium fluctuations. The authors combine these two areas and formulate a fluctuation theorem for the heat dissipated along closed loops in vortex force fields, which is found to be topologically protected.
- Benoît Mahault
- , Evelyn Tang
- & Ramin Golestanian
-
Article
| Open Access Oscillatory rheotaxis of artificial swimmers in microchannels
Oscillatory rheotaxis of artificial swimmers in microchannels
Biological and artificial microswimmers often navigate channels under external flow, where in many biomicroswimmers the active upstream motion is oscillatory. Here the authors demonstrate that regular, controllable, and reproducible oscillatory rheotaxis can be observed in artificial microswimmers.
- Ranabir Dey
- , Carola M. Buness
- & Corinna C. Maass
-
Article
| Open Access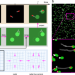 Rectification and confinement of photokinetic bacteria in an optical feedback loop
Rectification and confinement of photokinetic bacteria in an optical feedback loop
Light can be used to precisely modulate the speed of active particles in space and time. Here, the authors rectify and confine bacteria using an optical feedback loop that couples bacteria topast configurations.
- Helena Massana-Cid
- , Claudio Maggi
- & Roberto Di Leonardo
-
Article
| Open Access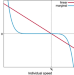 Marginal speed confinement resolves the conflict between correlation and control in collective behaviour
Marginal speed confinement resolves the conflict between correlation and control in collective behaviour
Bird flocks are known to adjust the orientation and speed of individual birds giving rise to correlations that extend across very large groups. The authors show that marginal control provides an explanation of scale-free correlations of speed fluctuations in natural bird flocks of any sizes.
- Andrea Cavagna
- , Antonio Culla
- & Pablo Villegas
-
Article
| Open Access Beating Carnot efficiency with periodically driven chiral conductors
Beating Carnot efficiency with periodically driven chiral conductors
The power generated by an ideal thermal machine cannot exceed the Carnot limit in classical physics. Here, Ryu et al., demonstrate that a periodically driven quantum chiral conductor can exhibit efficiencies beyond the Carnot limit while the second law of thermodynamics is preserved.
- Sungguen Ryu
- , Rosa López
- & David Sánchez
-
Article
| Open Access Synchronization in electric power networks with inherent heterogeneity up to 100% inverter-based renewable generation
Synchronization in electric power networks with inherent heterogeneity up to 100% inverter-based renewable generation
Modern power grids undergo a transition due to the integration of renewable energy generation technologies that bring heterogeneity in the grid. The authors study the synchronization and stability of power grids with heterogeneous inertia and damping factors, and demonstrate power feasibility of operating a system consisting of only renewable generation technologies with enhanced stability.
- Amirhossein Sajadi
- , Rick Wallace Kenyon
- & Bri-Mathias Hodge
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of Bloch oscillations dominated by effective anyonic particle statistics
Observation of Bloch oscillations dominated by effective anyonic particle statistics
Electric circuits represent a versatile platform for simulations of exotic phenomena that are difficult to realize is condensed matter systems. Here the authors simulate particle statistics-dependent Bloch oscillations with electric circuits and observe features predicted for a model of anyons on a 1D lattice.
- Weixuan Zhang
- , Hao Yuan
- & Xiangdong Zhang
-
-
Article
| Open Access Spontaneous chiral symmetry breaking in a random driven chemical system
Spontaneous chiral symmetry breaking in a random driven chemical system
“A hallmark of living systems is their homochirality, the selection of specific mirror symmetry in their molecules. Here, the authors show that chiral symmetry can be spontaneously broken in complex, random chemical systems via exploitation of environmental energy sources – a possible mechanism for the emergence of homochirality in life.”
- William D. Piñeros
- & Tsvi Tlusty
-
Article
| Open Access Microrobot collectives with reconfigurable morphologies, behaviors, and functions
Microrobot collectives with reconfigurable morphologies, behaviors, and functions
Reconfigurability at the micro-scale is rare. Here, authors present a versatile magnetic microrobot collective that reconfigures on-demand among miscellaneous behaviors that allow for exploration, navigation, and interaction with diverse environments.
- Gaurav Gardi
- , Steven Ceron
- & Metin Sitti
-
Article
| Open Access Generic self-stabilization mechanism for biomolecular adhesions under load
Generic self-stabilization mechanism for biomolecular adhesions under load
Cellular adhesions have the remarkable property that they adapt their stability to the applied mechanical load. Here, authors describe a generic physical mechanism that explains self-stabilization of idealized adhesion systems under shear.
- Andrea Braeutigam
- , Ahmet Nihat Simsek
- & Benedikt Sabass
-
Article
| Open Access Simulating a chemically fueled molecular motor with nonequilibrium molecular dynamics
Simulating a chemically fueled molecular motor with nonequilibrium molecular dynamics
Molecular motors move in response to an imbalance between concentrations of fuel and waste molecules. Here, the authors simulate such non-equilibrium conditions to characterize a model motor’s performance and mechanism of operation.
- Alex Albaugh
- & Todd R. Gingrich
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular communications in complex systems of dynamic supramolecular polymers
Molecular communications in complex systems of dynamic supramolecular polymers
The dynamic structure of supramolecular polymers is challenging to determine both in experiments and in simulations. Here the authors use coarse-grained molecular models to provide a comprehensive analysis of the molecular communication in these complex molecular systems.
- Martina Crippa
- , Claudio Perego
- & Giovanni M. Pavan
-
Article
| Open Access Electrically tunable collective motion of dissipative solitons in chiral nematic films
Electrically tunable collective motion of dissipative solitons in chiral nematic films
Understanding of the collective motion seen in biological systems is crucial for development of autonomous robots and swarm computing. The authors introduce an experimental platform with liquid crystal driven by external electric field, that mimics the collective motion of living systems.
- Yuan Shen
- & Ingo Dierking
-
Article
| Open Access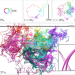 The statistical geometry of material loops in turbulence
The statistical geometry of material loops in turbulence
Turbulent flows are observed in atmosphere, ocean, and technology, with turbulent mixing due to stretching and folding of material elements. The authors analyze a geometric perspective of this process and uncover statistical properties of an ensemble of material loops in a turbulent environment.
- Lukas Bentkamp
- , Theodore D. Drivas
- & Michael Wilczek
-
Article
| Open Access Dislocation avalanches are like earthquakes on the micron scale
Dislocation avalanches are like earthquakes on the micron scale
Metallic microsamples deform in a sequence of abrupt strain bursts. Here, the authors demonstrate by analysing the elastic waves emitted by these bursts that this intermittent process resembles earthquakes in several aspects, although on completely different spatial and temporal scales.
- Péter Dusán Ispánovity
- , Dávid Ugi
- & István Groma
-
Article
| Open Access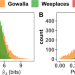 Contrasting social and non-social sources of predictability in human mobility
Contrasting social and non-social sources of predictability in human mobility
Information about an individual’s mobility can leave traces embedded in the social network. The authors show that such traces are also present beyond the social network. Simple colocation contains predictive information about one’s mobility patterns even when the colocators have no social links. In the aggregate, non-social information can sometimes meet or exceed social information.
- Zexun Chen
- , Sean Kelty
- & Gourab Ghoshal
-
Article
| Open Access A metafluid with multistable density and internal energy states
A metafluid with multistable density and internal energy states
Investigating and tailoring the thermodynamic properties of different fluids is crucial to many applied fields such as energy and refrigeration cycles. Here, authors use multistable, gas filled, particles suspension to enhance the macro-properties of thermodynamic fluids.
- Ofek Peretz
- , Ezra Ben Abu
- & Amir D. Gat
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamics of ranking
Dynamics of ranking
Ranking lists are relevant to various areas of nature and society, however their evolution with the elements changing rank in time remained unexplored. The authors uncover a mechanism of ranking dynamics induced by the flux governing the arrival of new elements in the list, for improved predictability of ranking models.
- Gerardo Iñiguez
- , Carlos Pineda
- & Albert-László Barabási
-
Article
| Open Access Photonic heat transport in three terminal superconducting circuit
Photonic heat transport in three terminal superconducting circuit
Quantum heat transport devices are currently intensively studied. Here, the authors report the photonic heat transport modulated by superconducting qubit in a three-terminal device. Flux dependent heat power correlates with microwave measurements.
- Azat Gubaydullin
- , George Thomas
- & Jukka P. Pekola
-
Article
| Open Access Transition from simple to complex contagion in collective decision-making
Transition from simple to complex contagion in collective decision-making
In consensus-based collective dynamics, the occurrence of simple and complex contagions shapes system behavior. The authors analyze a transition from simple to complex contagions in collective decision-making processes based on consensus, and demonstrate it with a swarm robotic system.
- Nikolaj Horsevad
- , David Mateo
- & Roland Bouffanais
-
Article
| Open Access Universality, criticality and complexity of information propagation in social media
Universality, criticality and complexity of information propagation in social media
The authors identify characteristic patterns that describe the propagation of information in online social media platforms. They show that, depending on the topic, the information flows can spread as simple or complex contagion processes, operating at a critical regime.
- Daniele Notarmuzi
- , Claudio Castellano
- & Filippo Radicchi
-
Article
| Open Access Recovery coupling in multilayer networks
Recovery coupling in multilayer networks
Infrastructure and power systems are often represented as multilayer structures of interdependent networks. Danziger and Barabási demonstrate the presence of recovery coupling in such systems, where the recovery of an element in one network requires resources from nodes and links in another network.
- Michael M. Danziger
- & Albert-László Barabási
-
Article
| Open Access Hyperuniformity and phase enrichment in vortex and rotor assemblies
Hyperuniformity and phase enrichment in vortex and rotor assemblies
Rotor-like dynamics is observed in many natural systems, from the rotor proteins in cellular membranes to atmospheric models. Here, the authors uncover geometrical conservation laws that limit distribution of driven rotors in a membrane or a soap film and allow to predict their structural states.
- Naomi Oppenheimer
- , David B. Stein
- & Michael J. Shelley
-
Perspective
| Open Access Sculpting tissues by phase transitions
Sculpting tissues by phase transitions
Many biological processes require changes in the physical properties of cells and their surroundings. Here, Lenne and Trivedi discuss recent findings in biological systems in terms of phase transitions in inert physical systems from both theoretical and experimental perspectives.
- Pierre-François Lenne
- & Vikas Trivedi
-
Article
| Open Access Assessing the impact of SARS-CoV-2 prevention measures in Austrian schools using agent-based simulations and cluster tracing data
Assessing the impact of SARS-CoV-2 prevention measures in Austrian schools using agent-based simulations and cluster tracing data
How to safely maintain open schools during a pandemic is still controversial. Here, the authors aim to identify those measures that effectively control the spread of SARS-CoV-2 in Austrian schools, with an agent-based mathematical model.
- Jana Lasser
- , Johannes Sorger
- & Peter Klimek
-
Article
| Open Access Onset of criticality in hyper-auxetic polymer networks
Onset of criticality in hyper-auxetic polymer networks
Auxetic materials are characterized by a negative Poisson’s ratio - they become thicker when stretched. Here, authors reach the limit of auxetic behavior, known as hyper-auxetic, in polymer networks, hitting an unconventional mechanical critical point.
- Andrea Ninarello
- , José Ruiz-Franco
- & Emanuela Zaccarelli
-
Article
| Open Access The shape of memory in temporal networks
The shape of memory in temporal networks
The evolution of networks with structure changing in time is dependent on their past states and relevant to diffusion and spreading processes. The authors show that temporal network’s memory is described by multidimensional patterns at a microscopic scale, and cannot be reduced to a scalar quantity.
- Oliver E. Williams
- , Lucas Lacasa
- & Vito Latora
-
Article
| Open Access AI Pontryagin or how artificial neural networks learn to control dynamical systems
AI Pontryagin or how artificial neural networks learn to control dynamical systems
Optimal control of complex dynamical systems can be challenging due to cost constraints and analytical intractability. The authors propose a machine-learning-based control framework able to learn control signals and force complex high-dimensional dynamical systems towards a desired target state.
- Lucas Böttcher
- , Nino Antulov-Fantulin
- & Thomas Asikis
-
Matters Arising
| Open AccessReply to: On the difficulty of achieving differential privacy in practice: user-level guarantees in aggregate location data
- Aleix Bassolas
- , Hugo Barbosa-Filho
- & Jose J. Ramasco

 Confinement-induced accumulation and de-mixing of microscopic active-passive mixtures
Confinement-induced accumulation and de-mixing of microscopic active-passive mixtures Universality out of order
Universality out of order