Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Halogen bonding as a supramolecular dynamics catalyst
Halogen bonding as a supramolecular dynamics catalyst
The halogen bond is well known for its ability to assemble supramolecules. Here, using NMR experiments, the authors reveal the role of these bonds in dynamic processes, finding that the halogen bond directly catalyzes dynamical rotation in solid cocrystals by reducing the associated energy barrier.
- Patrick M. J. Szell
- , Scott Zablotny
- & David L. Bryce
-
Article
| Open Access Lignin-polysaccharide interactions in plant secondary cell walls revealed by solid-state NMR
Lignin-polysaccharide interactions in plant secondary cell walls revealed by solid-state NMR
The interactions of lignin with polysaccharides in plant secondary cell walls are not well understood. Here the authors employ solid-state NMR measurements to analyse intact stems of maize, Arabidopsis, switchgrass and rice and observe that lignin self-aggregates and forms highly hydrophobic microdomains that make extensive surface contacts to xylan.
- Xue Kang
- , Alex Kirui
- & Tuo Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Shifts in the selectivity filter dynamics cause modal gating in K+ channels
Shifts in the selectivity filter dynamics cause modal gating in K+ channels
Spontaneous activity shifts at constant experimental conditions are widespread among ion channels but the molecular origins are poorly understood. Here, using solid-state NMR and MD simulations, the authors reveal that modal gating shifts in K + channels are caused by large shifts in the channel dynamics which perturb the selectivity filter.
- Shehrazade Jekhmane
- , João Medeiros-Silva
- & Markus Weingarth
-
Article
| Open Access The structure of a β2-microglobulin fibril suggests a molecular basis for its amyloid polymorphism
The structure of a β2-microglobulin fibril suggests a molecular basis for its amyloid polymorphism
Impaired kidney function can lead to an increase of β2-microglobulin (β2m) serum levels, which can cause β2m aggregation and amyloid fibril formation. Here the authors combine cryo-EM and magic angle spinning NMR measurements to determine the structure of a β2m fibril and they also present the low resolution model of a β2m fibril with a different morphology.
- Matthew G. Iadanza
- , Robert Silvers
- & Sheena E. Radford
-
Article
| Open Access Cooperative mechanisms of oxygen vacancy stabilization and migration in the isolated tetrahedral anion Scheelite structure
Cooperative mechanisms of oxygen vacancy stabilization and migration in the isolated tetrahedral anion Scheelite structure
Fast oxide ion conductors are the key materials for some technological devices. Here the authors report the creation and stabilization of oxygen vacancies in BiVO4 Scheelite with isolated tetrahedral anion structures for improved ionic conducting performance and understanding of the conduction mechanism.
- Xiaoyan Yang
- , Alberto J. Fernández-Carrión
- & Xiaojun Kuang
-
Article
| Open Access RIP2 filament formation is required for NOD2 dependent NF-κB signalling
RIP2 filament formation is required for NOD2 dependent NF-κB signalling
Binding of bacterial peptidoglycan muramyl dipeptides induces NOD2 activation and signalling via the downstream adaptor kinase RIP2. Here the authors show that RIP2 forms filaments via its CARD domain, analyse the structure of the CARD filaments and demonstrate the requirement of RIP2 polymerisation for the activation of NF-κB by NOD2.
- Erika Pellegrini
- , Ambroise Desfosses
- & Stephen Cusack
-
Article
| Open Access Optimal control theory enables homonuclear decoupling without Bloch–Siegert shifts in NMR spectroscopy
Optimal control theory enables homonuclear decoupling without Bloch–Siegert shifts in NMR spectroscopy
Bloch–Siegert shifts prevent the accurate observation of resonance frequencies in NMR experiments. Here the authors present a method for homonuclear decoupling that avoids inducing Bloch–Siegert shifts and improves the sensitivity and resolution of HNCA experiments.
- Paul W. Coote
- , Scott A. Robson
- & Haribabu Arthanari
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of nuclear quantum effects and hydrogen bond symmetrisation in high pressure ice
Observation of nuclear quantum effects and hydrogen bond symmetrisation in high pressure ice
Hydrogen atoms in water ices, under pressures at which they might exist in ocean exoplanets and icy moons, exhibit dynamics that are still poorly understood. Here, 1H-NMR experiments approaching the Mbar range shed light on the symmetrisation of hydrogen bonds preceding and accompanying the transformation of ice VII into ice X.
- Thomas Meier
- , Sylvain Petitgirard
- & Leonid Dubrovinsky
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular architecture of fungal cell walls revealed by solid-state NMR
Molecular architecture of fungal cell walls revealed by solid-state NMR
Aspergillus fumigatus is a pathogenic fungus. Here the authors perform solid-state NMR measurements with intact Aspergillus cells, which provides insights into cell wall composition and dynamics and propose a structural model for fungal cell walls.
- Xue Kang
- , Alex Kirui
- & Tuo Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Scanning nuclear resonance imaging of a hyperfine-coupled quantum Hall system
Scanning nuclear resonance imaging of a hyperfine-coupled quantum Hall system
Exploring the hyperfine-coupled quantum Hall (QH) system facilitates the nuclear spintronic applications. Here the authors reveal the origin of the nonequilibrium QH phenomena by mapping the spatial distribution of nuclear and electron spin polarization in a GaAs quantum well with scanning probe incorporated nuclear resonance technique.
- Katsushi Hashimoto
- , Toru Tomimatsu
- & Yoshiro Hirayama
-
Article
| Open Access Minerals in the pre-settled coral Stylophora pistillata crystallize via protein and ion changes
Minerals in the pre-settled coral Stylophora pistillata crystallize via protein and ion changes
Coral biomineralization is an important example of natural mineralization and understanding the process will aid biomineralization research. Here, the authors identify the precipitation of amorphous calcium carbonate and small aragonite crystals in pre-settled larva of Stylophora pistillata.
- Anat Akiva
- , Maayan Neder
- & Tali Mass
-
Article
| Open Access A single NaK channel conformation is not enough for non-selective ion conduction
A single NaK channel conformation is not enough for non-selective ion conduction
NaK is a non-selective cation channel that conducts sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) equally well. Here authors use ssNMR and MD simulations to show that the selectivity filter of NaK adopts two conformations in the absence of ions, one of which is preferred by Na+ and the other by K+.
- Chaowei Shi
- , Yao He
- & Han Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of outer membrane protein G in lipid bilayers
Structure of outer membrane protein G in lipid bilayers
Porins, like OmpG, are embedded in the outer membrane of bacteria and facilitate uptake and secretion of nutrients and ions. Here the authors present a protocol for solid state NMR structure determination of proteins larger than 25 kDa and use it to structurally characterize membrane embedded OmpG.
- Joren S. Retel
- , Andrew J. Nieuwkoop
- & Hartmut Oschkinat
-
Article
| Open Access Quenching protein dynamics interferes with HIV capsid maturation
Quenching protein dynamics interferes with HIV capsid maturation
The process of HIV particle maturation involves complex molecular transitions. Here the authors combine NMR spectroscopy, cryo-EM, and molecular dynamics simulations to provide insight into the conformational equilibria in CA-SP1 assemblies relevant to HIV-1 maturation intermediates formation.
- Mingzhang Wang
- , Caitlin M. Quinn
- & Tatyana Polenova
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery and characterization of stable and toxic Tau/phospholipid oligomeric complexes
Discovery and characterization of stable and toxic Tau/phospholipid oligomeric complexes
The Alzheimer protein Tau interacts with biological membranes, but the role of these interactions in regulating Tau function in health and disease remains unexplored. Here, the authors report on the discovery and characterization of neurotoxic oligomeric protein/phospholipid complexes.
- Nadine Ait-Bouziad
- , Guohua Lv
- & Hilal A. Lashuel
-
Article
| Open Access Accessing the bottleneck in all-solid state batteries, lithium-ion transport over the solid-electrolyte-electrode interface
Accessing the bottleneck in all-solid state batteries, lithium-ion transport over the solid-electrolyte-electrode interface
The large impedance at the interface between electrode and electrolyte poses a challenge to the development of solid-state batteries. Here the authors utilize two-dimensional lithium-ion exchange-NMR to monitor the spontaneous lithium-ion transport, providing insight into the interface design.
- Chuang Yu
- , Swapna Ganapathy
- & Marnix Wagemaker
-
Article
| Open Access Species-dependent structural polymorphism of Y145Stop prion protein amyloid revealed by solid-state NMR spectroscopy
Species-dependent structural polymorphism of Y145Stop prion protein amyloid revealed by solid-state NMR spectroscopy
Prion diseases can be transmitted across species. Here the authors use solid-state NMR to study prion protein (PrP) amyloids from human, mouse and Syrian hamster and show that their structural differences are mainly governed by two residues, which helps to understand interspecies PrP propagation on a molecular level.
- Theint Theint
- , Philippe S. Nadaud
- & Christopher P. Jaroniec
-
Article
| Open Access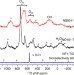 Distinguishing faceted oxide nanocrystals with 17O solid-state NMR spectroscopy
Distinguishing faceted oxide nanocrystals with 17O solid-state NMR spectroscopy
The exposed facets of oxide nanocrystals are key to their properties. Here, the authors use 17O solid-state NMR spectroscopy to discriminate between oxygen species on different facets of anatase titania nanocrystals, providing compelling evidence for the value of NMR spectroscopy in characterizing faceted oxides.
- Yuhong Li
- , Xin-Ping Wu
- & Luming Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Slow conformational exchange and overall rocking motion in ubiquitin protein crystals
Slow conformational exchange and overall rocking motion in ubiquitin protein crystals
X-ray crystallography is the main method for protein structure determination. Here the authors combine solid-state NMR measurements and molecular dynamics simulations and show that crystal packing alters the thermodynamics and kinetics of local conformational exchange as well as overall rocking motion of protein molecules in the crystal lattice.
- Vilius Kurauskas
- , Sergei A. Izmailov
- & Paul Schanda
-
Article
| Open Access Fibril polymorphism affects immobilized non-amyloid flanking domains of huntingtin exon1 rather than its polyglutamine core
Fibril polymorphism affects immobilized non-amyloid flanking domains of huntingtin exon1 rather than its polyglutamine core
Huntington's disease is caused by a polyglutamine stretch expansion in the first exon of huntingtin. Here, the authors use infrared spectroscopy and solid-state NMR and show that polymorphic huntingtin exon1 fibres differ in their flanking regions but not their core polyglutamine amyloid structures.
- Hsiang-Kai Lin
- , Jennifer C. Boatz
- & Patrick C. A. van der Wel
-
Article
| Open Access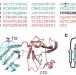 Cataract-associated P23T γD-crystallin retains a native-like fold in amorphous-looking aggregates formed at physiological pH
Cataract-associated P23T γD-crystallin retains a native-like fold in amorphous-looking aggregates formed at physiological pH
Aggregation of eye lens proteins leads to cataracts, a major cause of blindness. Here the authors use solid state NMR to probe the structure of γD-crystallin eye lens proteins aggregates, which are found to retain a native-like conformation.
- Jennifer C. Boatz
- , Matthew J. Whitley
- & Patrick C. A. van der Wel
-
Article
| Open Access Cholesterol-mediated allosteric regulation of the mitochondrial translocator protein structure
Cholesterol-mediated allosteric regulation of the mitochondrial translocator protein structure
The outer mitochondrial membrane translocator protein (TSPO) mediates several mitochondrial functions and binds cholesterol with a high affinity. Here the authors use solid-state NMR to show that cholesterol binding to TSPO results in allosteric changes that modulate TSPO oligomerization.
- Garima Jaipuria
- , Andrei Leonov
- & Markus Zweckstetter
-
Article
| Open Access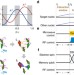 Delayed entanglement echo for individual control of a large number of nuclear spins
Delayed entanglement echo for individual control of a large number of nuclear spins
Single electrons of solid-state defects can be used to detect nearby nuclear spins, but so far only a few at a time have been resolved. Here the authors propose an approach based on delayed entanglement echo that demonstrates improved detection and manipulation capabilities of nuclear spins by an NV centre.
- Zhen-Yu Wang
- , Jorge Casanova
- & Martin B. Plenio
-
Article
| Open Access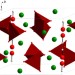 Interfacial Ca2+ environments in nanocrystalline apatites revealed by dynamic nuclear polarization enhanced 43Ca NMR spectroscopy
Interfacial Ca2+ environments in nanocrystalline apatites revealed by dynamic nuclear polarization enhanced 43Ca NMR spectroscopy
Solid-state NMR can in principle be used to study calcium environments in biomaterials such as bones/teeth, but43Ca lacks receptivity. Here the authors present an approach to acquire 43Ca data for hydroxyapatite at its natural isotopic abundance, distinguishing between core and surface Ca sites.
- Daniel Lee
- , César Leroy
- & Gaël De Paëpe
-
Article
| Open Access Folding of xylan onto cellulose fibrils in plant cell walls revealed by solid-state NMR
Folding of xylan onto cellulose fibrils in plant cell walls revealed by solid-state NMR
The polysaccharide xylan binds to cellulose microfibrils in the plant cell wall, but the nature of this interaction remains unclear. Here Simmonset al. show that while xylan forms a threefold helical screw in solution it forms a twofold screw to bind cellulose microfibrils in the plant cell wall.
- Thomas J. Simmons
- , Jenny C. Mortimer
- & Paul Dupree
-
Article
| Open Access Following lithiation fronts in paramagnetic electrodes with in situ magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging
Following lithiation fronts in paramagnetic electrodes with in situ magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging is a promising non-invasive approach to visualize paramagnetic materials in devices, but the short lifetime of signals currently limits its use. Here, the authors develop an approach which overcomes this hurdle to spectroscopically image lithiation fronts during battery operation.
- Mingxue Tang
- , Vincent Sarou-Kanian
- & Elodie Salager
-
Article
| Open Access Retinal orientation and interactions in rhodopsin reveal a two-stage trigger mechanism for activation
Retinal orientation and interactions in rhodopsin reveal a two-stage trigger mechanism for activation
Rhodopsin signalling is triggered by the light-induced isomerization of its 11-cisretinal chromophore. Here, the authors use NMR spectroscopy to define retinal orientation and interactions in the active metarhodopsin II intermediate, proposing a two-stage mechanism for rhodopsin activation.
- Naoki Kimata
- , Andreyah Pope
- & Steven O. Smith
-
Article
| Open Access In situ high-resolution structure of the baseplate antenna complex in Chlorobaculum tepidum
In situ high-resolution structure of the baseplate antenna complex in Chlorobaculum tepidum
The chlorosome of the photosynthetic bacterium C. tepidumharvests light and transfers the energy to the photosynthetic reaction centre. Here the authors determine the structure of the baseplate, a scaffolding super-structure, to show that the baseplate consists of rods of repeated CsmA dimers containing pigment molecules.
- Jakob Toudahl Nielsen
- , Natalia V. Kulminskaya
- & Niels Chr. Nielsen
-
Article
| Open Access Residue-specific structures and membrane locations of pH-low insertion peptide by solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance
Residue-specific structures and membrane locations of pH-low insertion peptide by solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance
The pH-low insertion peptides (pHLIPs) respond to environmental pH variations by forming transmembrane α-helices. Here, the authors present the residue-specific structures and membrane locations of pHLIPs at different pH levels to probe the mechanism of their pH-dependant membrane insertion.
- Nicolas S. Shu
- , Michael S. Chung
- & Wei Qiang
-
Article |
 High-resolution structure of the Shigella type-III secretion needle by solid-state NMR and cryo-electron microscopy
High-resolution structure of the Shigella type-III secretion needle by solid-state NMR and cryo-electron microscopy
Solving structures of large protein complexes remains a significant challenge for structural biologists. Demers et al. determine the atomic structure of a Shigellatype-III secretion system using a Rosetta-based modelling strategy that draws on both solid-state NMR and cryo-electron microscopy data sets.
- Jean-Philippe Demers
- , Birgit Habenstein
- & Nikolaos G. Sgourakis

 Integrated NMR and cryo-EM atomic-resolution structure determination of a half-megadalton enzyme complex
Integrated NMR and cryo-EM atomic-resolution structure determination of a half-megadalton enzyme complex