Featured
-
-
News & Views |
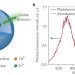 Upconversion goes broadband
Upconversion goes broadband
Upconversion nanoparticles that convert low-energy light into high-energy light hold promise for boosting solar-cell efficiency and enabling highly sensitive biological assays. But their spectral conversion under broadband excitation has been challenging, until now.
- Xiaoji Xie
- & Xiaogang Liu
-
Article |
 Polarized X-ray scattering reveals non-crystalline orientational ordering in organic films
Polarized X-ray scattering reveals non-crystalline orientational ordering in organic films
Molecular orientation, which critically influences the properties of organic materials, could until now only be characterized if the sample exhibited sufficient crystallinity. Resonant scattering of polarized soft X-rays by aromatic carbon bonds has now been used to probe non-crystalline ordering and molecular orientation in thin films with a resolution down to 20 nm.
- B. A. Collins
- , J. E. Cochran
- & H. Ade
-
Editorial |
 Solar energy's path towards competitiveness
Solar energy's path towards competitiveness
Progress in photovoltaic technology could soon mean grid parity for solar electricity. In this issue we highlight scientific as well as science-policy strategies aimed towards achieving this goal.
-
Interview |
 Solar's best shot
Solar's best shot
The funding approach taken by the US Department of Energy's SunShot programme, which aims to develop competitive solar technology, has proved very successful. Its director, R. Ramesh, explains why.
- Joerg Heber
-
Commentary |
 Photonic design principles for ultrahigh-efficiency photovoltaics
Photonic design principles for ultrahigh-efficiency photovoltaics
For decades, solar-cell efficiencies have remained below the thermodynamic limits. However, new approaches to light management that systematically minimize thermodynamic losses will enable ultrahigh efficiencies previously considered impossible.
- Albert Polman
- & Harry A. Atwater
-
Letter |
 Solution-processed small-molecule solar cells with 6.7% efficiency
Solution-processed small-molecule solar cells with 6.7% efficiency
Polymer-based bulk-heterojunction solar cells have shown some of the highest photoconversion efficiencies in organic photovoltaics, but polymer polydispersity impacts their performance. A small-molecule donor is now reported that enables the fabrication of bulk-heterojunction devices with low acceptor content and photoconversion efficiencies of up to 6.7%.
- Yanming Sun
- , Gregory C. Welch
- & Alan J. Heeger
-
Article |
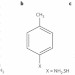 Molecular control of quantum-dot internal electric field and its application to CdSe-based solar cells
Molecular control of quantum-dot internal electric field and its application to CdSe-based solar cells
Inorganic nanocrystals are attractive materials for solar-cell applications. However, their performance is often limited by an insufficient alignment of internal energy levels. A tuning of these energy levels has now been achieved by attaching two different molecules to a single nanocrystal, which significantly alters its electronic and optoelectronic properties.
- Nir Yaacobi-Gross
- , Michal Soreni-Harari
- & Nir Tessler
-
Letter |
 Highly efficient Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells grown on flexible polymer films
Highly efficient Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells grown on flexible polymer films
The use of flexible polymer substrates not only reduces weight and fabrication costs of solar cells, but their bendability also enables new applications. A careful design of Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells grown on polymer substrates now solves earlier fabrication issues, leading to conversion efficiencies matching those grown on rigid substrates.
- Adrian Chirilă
- , Stephan Buecheler
- & Ayodhya N. Tiwari
-
Article |
 Efficiency enhancement in organic solar cells with ferroelectric polymers
Efficiency enhancement in organic solar cells with ferroelectric polymers
One of the key loss mechanisms in the operation of organic solar cells is the separation and extraction of the generated charge carriers from the active region. The use of a ferroelectric layer is now shown to create large internal electric fields, resulting in an enhanced carrier extraction and increased device efficiency.
- Yongbo Yuan
- , Timothy J. Reece
- & Jinsong Huang
-
News & Views |
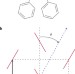 A little energy goes a long way
A little energy goes a long way
Excitons in a highly ordered organic semiconductor are found to diffuse over distances of a few micrometres. This may pave the way towards designing efficient excitonic solar cells.
- Carlos Silva
-
Article |
 Photon-enhanced thermionic emission for solar concentrator systems
Photon-enhanced thermionic emission for solar concentrator systems
The conversion of solar energy into electricity usually occurs either electrically or through thermal conversion. A new mechanism, photon-enhanced thermionic emission, which combines electric as well as thermal conversion mechanisms, is now shown to lead to enhanced conversion efficiencies that potentially could even exceed the theoretical limits of conventional photovoltaic cells.
- Jared W. Schwede
- , Igor Bargatin
- & Nicholas A. Melosh
-
Editorial |
 A small world full of opportunities
A small world full of opportunities
Light-concentration effects in photonic nanostructures, reviewed in this issue, promise new applications ranging from tumour therapy to catalysis and enhanced solar cells.
-
News & Views |
 More solar cells for less
More solar cells for less
A solar-cell design based on silicon microwires achieves efficient absorption of sunlight while using only 1% of the active material used in conventional designs.
- Jia Zhu
- & Yi Cui
-
Review Article |
 Plasmonics for improved photovoltaic devices
Plasmonics for improved photovoltaic devices
This review article surveys the potential of using plasmonic nanostructures to enhance the absorption of photovoltaic devices. As a result, the physical thickness of solar cells can be reduced, leading to new photovoltaic-device designs.
- Harry A. Atwater
- & Albert Polman
-
Letter |
 Enhanced absorption and carrier collection in Si wire arrays for photovoltaic applications
Enhanced absorption and carrier collection in Si wire arrays for photovoltaic applications
The use of silicon nanostructures in solar cells offers a number of benefits, such as the fact they can be used on flexible substrates. A silicon wire-array structure, containing reflecting nanoparticles for enhanced absorption, is now shown to achieve 96% peak absorption efficiency, capturing 85% of light with only 1% of the silicon used in comparable commercial cells.
- Michael D. Kelzenberg
- , Shannon W. Boettcher
- & Harry A. Atwater

 Photon management in two-dimensional disordered media
Photon management in two-dimensional disordered media