Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Inferring HIV-1 transmission networks and sources of epidemic spread in Africa with deep-sequence phylogenetic analysis
Inferring HIV-1 transmission networks and sources of epidemic spread in Africa with deep-sequence phylogenetic analysis
Here, Ratmann et al. show how viral deep sequencing data can be used to reconstruct HIV-1 transmission networks and to infer the direction of transmission in these networks.
- Oliver Ratmann
- , M. Kate Grabowski
- & Jennifer Wagman
-
Review Article
| Open Access Systematic benchmarking of omics computational tools
Systematic benchmarking of omics computational tools
Benchmarking studies are important for comprehensively understanding and evaluating different computational omics methods. Here, the authors review practices from 25 recent studies and propose principles to improve the quality of benchmarking studies.
- Serghei Mangul
- , Lana S. Martin
- & Jonathan Flint
-
Article
| Open Access Accurate autocorrelation modeling substantially improves fMRI reliability
Accurate autocorrelation modeling substantially improves fMRI reliability
There has been recent controversy over the validity of commonly-used software packages for functional MRI (fMRI) data analysis. Here, the authors compare the performance of three leading packages (AFNI, FSL, SPM) in terms of temporal autocorrelation modeling, a key statistical step in fMRI analysis.
- Wiktor Olszowy
- , John Aston
- & Guy B. Williams
-
Article
| Open Access The use of technical replication for detection of low-level somatic mutations in next-generation sequencing
The use of technical replication for detection of low-level somatic mutations in next-generation sequencing
Somatic mutations of low allele frequencies are often difficult to detect. Here, the authors develop RePlow, a computational method that leverages technical replication for detecting low-level somatic mutations using next-generation sequencing.
- Junho Kim
- , Dachan Kim
- & Sangwoo Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Microbial abundance, activity and population genomic profiling with mOTUs2
Microbial abundance, activity and population genomic profiling with mOTUs2
Metagenomic analysis based on universal phylogenetic marker gene (MG)-based operational taxonomic units (mOTUs) is a useful strategy, especially for microbial species without reference genomes. Here, the authors develop mOTUs2, an updated and functionally extended profiling tool for microbial abundance, activity and population profiling.
- Alessio Milanese
- , Daniel R Mende
- & Shinichi Sunagawa
-
Article
| Open Access Exploring the landscape of focal amplifications in cancer using AmpliconArchitect
Exploring the landscape of focal amplifications in cancer using AmpliconArchitect
Focal amplifications are prevalent in many cancer genomes. Here, the authors present AmpliconArchitect (AA), a computational tool for reconstructing their architecture, and reveal an extrachromosomal origin for focal amplifications, including hybrid human-virus elements in HPV-mediated cancers.
- Viraj Deshpande
- , Jens Luebeck
- & Vineet Bafna
-
Article
| Open Access Transcriptomic meta-signatures identified in Anopheles gambiae populations reveal previously undetected insecticide resistance mechanisms
Transcriptomic meta-signatures identified in Anopheles gambiae populations reveal previously undetected insecticide resistance mechanisms
Increasing insecticide resistance of mosquitoes represents a public health threat, and underlying mechanisms are poorly understood. Here, Ingham et al. identify putative insecticide resistance genes in Anopheles gambiae populations across Africa and develop a web-based application that maps their expression.
- V. A. Ingham
- , S. Wagstaff
- & H. Ranson
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchical and programmable one-pot synthesis of oligosaccharides
Hierarchical and programmable one-pot synthesis of oligosaccharides
The software Optimer has aided the programmable one-pot oligosaccharide synthesis with a library of 50 Building BLocks (BBLs). Here, the authors expanded Optimer's validated and virtual libraries of BBLs and developed Auto-CHO, a software which allows the one-pot programmable synthesis of more complex glycans.
- Cheng-Wei Cheng
- , Yixuan Zhou
- & Chi-Huey Wong
-
Article
| Open Access A web server for comparative analysis of single-cell RNA-seq data
A web server for comparative analysis of single-cell RNA-seq data
Publicly available single cell RNA-seq datasets represent valuable resources for comparative and meta-analysis. Here, the authors develop scQuery, a web server integrating over 500 different studies with over 300 unique cell types for comparative analysis of existing and new scRNA-seq data.
- Amir Alavi
- , Matthew Ruffalo
- & Ziv Bar-Joseph
-
Article
| Open Access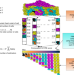 Discovery of rare cells from voluminous single cell expression data
Discovery of rare cells from voluminous single cell expression data
Algorithms designed to find rare cells in single cell RNA-seq data sets cannot cope with data sets containing tens of thousands of cells. Here the authors present Finder of Rare Entities (FiRE), an algorithm that uses the Sketching technique to assign a rareness score to every expression profile in large RNA-seq data sets.
- Aashi Jindal
- , Prashant Gupta
- & Debarka Sengupta
-
Article
| Open Access A computational framework to study sub-cellular RNA localization
A computational framework to study sub-cellular RNA localization
Automated analysis of RNA localisation in smFISH data has been elusive. Here, the authors simulate and use a large dataset of images to design and validate a framework for highly accurate classification of sub-cellular RNA localisation patterns from smFISH experiments.
- Aubin Samacoits
- , Racha Chouaib
- & Florian Mueller
-
Article
| Open Access Large-scale genome-wide enrichment analyses identify new trait-associated genes and pathways across 31 human phenotypes
Large-scale genome-wide enrichment analyses identify new trait-associated genes and pathways across 31 human phenotypes
In genome-wide association studies, variant-level associations are hard to identify and can be difficult to interpret biologically. Here, the authors develop a new model-based enrichment analysis method, and apply it to identify new associated genes, pathways and tissues across 31 human phenotypes.
- Xiang Zhu
- & Matthew Stephens
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic force microscopy methodology and AFMech Suite software for nanomechanics on heterogeneous soft materials
Atomic force microscopy methodology and AFMech Suite software for nanomechanics on heterogeneous soft materials
Atomic force microscopy is an indispensable method in characterizing soft materials but the complexity of biological samples makes reproducible measurements difficult. Here the authors use a 3-step method to investigate biological specimens in which vertical and lateral heterogeneity hinders a precise quantitative characterization.
- Massimiliano Galluzzi
- , Guanlin Tang
- & Florian J. Stadler
-
Article
| Open Access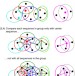 Clustering huge protein sequence sets in linear time
Clustering huge protein sequence sets in linear time
Billions of metagenomic and genomic sequences fill up public datasets, which makes similarity clustering an important and time-critical analysis step. Here, the authors develop Linclust, an algorithm with linear time complexity that can cluster over a billion sequences within hours on a single server.
- Martin Steinegger
- & Johannes Söding
-
Article
| Open Access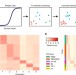 Unsupervised clustering and epigenetic classification of single cells
Unsupervised clustering and epigenetic classification of single cells
Single cell ATAC-seq (scATAC-seq) data reveals cellular level epigenetic heterogeneity but its application in delineating distinct subpopulations is still challenging. Here, the authors develop scABC, a statistical method for unsupervised clustering of scATAC-seq data and identification of open chromatin regions specific to cell identity.
- Mahdi Zamanighomi
- , Zhixiang Lin
- & Wing Hung Wong
-
Article
| Open Access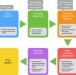 Allelic decomposition and exact genotyping of highly polymorphic and structurally variant genes
Allelic decomposition and exact genotyping of highly polymorphic and structurally variant genes
Many genes of functional and clinical significance are highly polymorphic and experience structural alterations. Here, Numanagić et al. develop Aldy, a computational tool for resolving the copy number and the sequence content of each copy of a gene by analyzing whole or targeted genome sequencing data.
- Ibrahim Numanagić
- , Salem Malikić
- & S. Cenk Sahinalp
-
Article
| Open Access CellCycleTRACER accounts for cell cycle and volume in mass cytometry data
CellCycleTRACER accounts for cell cycle and volume in mass cytometry data
Mass cytometry is a powerful method of single cell analysis, but potential confounding effects of cell cycle and cell volume are not taken into account. Here the authors present a combined experimental and computational method to correct for these effects and reveal features of TNFα stimulation that are otherwise masked.
- Maria Anna Rapsomaniki
- , Xiao-Kang Lun
- & María Rodríguez Martínez
-
Article
| Open Access A general and flexible method for signal extraction from single-cell RNA-seq data
A general and flexible method for signal extraction from single-cell RNA-seq data
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data provides information on transcriptomic heterogeneity within cell populations. Here, Risso et al develop ZINB-WaVE for low-dimensional representations of scRNA-seq data that account for zero inflation, over-dispersion, and the count nature of the data.
- Davide Risso
- , Fanny Perraudeau
- & Jean-Philippe Vert
-
Article
| Open Access Deconvoluting interrelationships between concentrations and chemical shifts in urine provides a powerful analysis tool
Deconvoluting interrelationships between concentrations and chemical shifts in urine provides a powerful analysis tool
The NMR chemical shifts of a substance in urine strongly depend on the composition of the mixture itself, and this makes automatic assignment for quantification very difficult. Here the authors show the chemical shifts of signals and the concentration of NMR-invisible inorganic ions in urine, are predictable.
- Panteleimon G. Takis
- , Hartmut Schäfer
- & Claudio Luchinat
-
Article
| Open Access PLATO software provides analytic framework for investigating complexity beyond genome-wide association studies
PLATO software provides analytic framework for investigating complexity beyond genome-wide association studies
Centralized infrastructure to support analyses involving complexity beyond genome-wide association studies is broadly needed. Here, Ritchie and colleagues develop PLATO, a software tool to process and integrate various methods for this task.
- Molly A. Hall
- , John Wallace
- & Marylyn D. Ritchie
-
Article
| Open Access On the performance of pre-microRNA detection algorithms
On the performance of pre-microRNA detection algorithms
As the experimental discovery of microRNAs (miRNAs) is cumbersome, computational tools have been developed for the prediction of pre-miRNAs. Here the authors develop a framework to assess the performance of existing and novel pre-miRNA prediction tools and provide guidelines for selecting an appropriate approach for a given data set.
- Müşerref Duygu Saçar Demirci
- , Jan Baumbach
- & Jens Allmer
-
Article
| Open Access Reconstructing cell cycle pseudo time-series via single-cell transcriptome data
Reconstructing cell cycle pseudo time-series via single-cell transcriptome data
In single-cell RNA sequencing data of heterogeneous cell populations, cell cycle stage of individual cells would often be informative. Here, the authors introduce a computational model to reconstruct a pseudo-time series from single cell transcriptome data, identify the cell cycle stages, identify candidate cell cycle-regulated genes and recover the methylome changes during the cell cycle.
- Zehua Liu
- , Huazhe Lou
- & Ting Chen
-
Article
| Open Access A BaSiC tool for background and shading correction of optical microscopy images
A BaSiC tool for background and shading correction of optical microscopy images
Accurate quantification of bioimaging data is often confounded by uneven illumination (shading) in space and background variation in time. Here the authors present BaSiC, a Fiji plugin solving both issues. It requires fewer input images and is more robust to artefacts than existing shading correction tools.
- Tingying Peng
- , Kurt Thorn
- & Nassir Navab
-
Article
| Open Access Smooth 2D manifold extraction from 3D image stack
Smooth 2D manifold extraction from 3D image stack
Maximum Intensity Projection is a common tool to represent 3D biological imaging data in a 2D space, but it creates artefacts. Here the authors develop Smooth Manifold Extraction, an ImageJ/Fiji plugin, to preserve local spatial relationships when extracting the content of a 3D volume to a 2D space.
- Asm Shihavuddin
- , Sreetama Basu
- & Auguste Genovesio
-
Article
| Open Access A complete tool set for molecular QTL discovery and analysis
A complete tool set for molecular QTL discovery and analysis
Analysis of molecular quantitative trait loci (molQTL) can help interpret genome-wide association studies and requires efficient approaches to correct for multiple testing. This study describes a bioinformatics toolkit called QTLtool that can handle large data sets and quickly perform multiple types of molQTL analyses.
- Olivier Delaneau
- , Halit Ongen
- & Emmanouil T. Dermitzakis
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative 3D analysis of complex single border cell behaviors in coordinated collective cell migration
Quantitative 3D analysis of complex single border cell behaviors in coordinated collective cell migration
Quantifying cell behavioursin vivo is essential to understanding the mechanisms of collective cell migration. Here the authors present an image analysis toolkit, CCMToolKit, to describe and characterize various modes of coordinated cell movements accompanying collective cell migration in Drosophilaborder cells.
- Adam Cliffe
- , David P. Doupé
- & Weimiao Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Comparative survey of the relative impact of mRNA features on local ribosome profiling read density
Comparative survey of the relative impact of mRNA features on local ribosome profiling read density
Ribosome profiling data can suffer from uneven coverage which hampers estimation of elongation rates. Connor et al.present an enhanced data smoothing method for Ribo-seq data and highlight significant variability in sequence determinants of ribosome density in publicly available data sets.
- Patrick B. F. O’Connor
- , Dmitry E. Andreev
- & Pavel V. Baranov
-
Article
| Open Access Determining crystal structures through crowdsourcing and coursework
Determining crystal structures through crowdsourcing and coursework
Building crystal structures into the electron density is an important step in protein structure solution. Here, the authors recruit online game players, students, and experienced crystallographers to compete in a competition to solve a new structure, and find that crowdsourcing model-building works.
- Scott Horowitz
- , Brian Koepnick
- & James C. A. Bardwell
-
Article
| Open Access Rare variant phasing and haplotypic expression from RNA sequencing with phASER
Rare variant phasing and haplotypic expression from RNA sequencing with phASER
Genome interpretation and analysis of allelic activity requires appropriate haplotype phasing. Here the authors present phASER, a fast and accurate method for variant phrasing from RNA-seq and genome sequencing data.
- Stephane E. Castel
- , Pejman Mohammadi
- & Tuuli Lappalainen
-
Article
| Open Access Fast live-cell conventional fluorophore nanoscopy with ImageJ through super-resolution radial fluctuations
Fast live-cell conventional fluorophore nanoscopy with ImageJ through super-resolution radial fluctuations
Super-resolution fluorescent imaging typically makes use of intense phototoxic illumination. Here the authors achieve live-cell super-resolution imaging using low-illumination standard microscopes with the aid of a new analytical approach called Super-Resolution Radial Fluctuations (SRRF), provided as an ImageJ plugin.
- Nils Gustafsson
- , Siân Culley
- & Ricardo Henriques
-
Article
| Open Access Environmental change makes robust ecological networks fragile
Environmental change makes robust ecological networks fragile
Despite their complexity, ecological networks appear robust to species loss. Here, Strona and Lafferty use artificial life simulations and real-world data to show that such robustness applies to stable conditions, but can collapse when the environment changes.
- Giovanni Strona
- & Kevin D. Lafferty
-
Article
| Open Access aMAP is a validated pipeline for registration and segmentation of high-resolution mouse brain data
aMAP is a validated pipeline for registration and segmentation of high-resolution mouse brain data
Anatomical segmentation of high-resolution 3D microscopy datasets is necessary to map large samples at cellular resolution. Here the authors present a pipeline for automated mouse atlas propagation (aMAP) to segment fluorescence images of the adult mouse brain and validate it against human segmentations.
- Christian J. Niedworok
- , Alexander P. Y. Brown
- & Troy W. Margrie
-
Article
| Open Access An interactive web-based application for Comprehensive Analysis of RNAi-screen Data
An interactive web-based application for Comprehensive Analysis of RNAi-screen Data
Analysis of RNAi screens is a multi-step process requiring the sequential use of several unrelated resources. Here the authors generate an online resource integrating RNAi analytic tools and filters into a seamless workflow, which improves the specificity, selectivity and reproducibility of the results.
- Bhaskar Dutta
- , Alaleh Azhir
- & Iain D. C. Fraser
-
Article
| Open Access An exact arithmetic toolbox for a consistent and reproducible structural analysis of metabolic network models
An exact arithmetic toolbox for a consistent and reproducible structural analysis of metabolic network models
Current tools to analyse constraint-based models of metabolic networks have limited accuracy due to their use of floating-point arithmetic. Here the authors present MONGOOSE, a new computational tool that analyses such models in exact arithmetic, providing improved accuracy and reproducibility.
- Leonid Chindelevitch
- , Jason Trigg
- & Bonnie Berger

 Precise segmentation of densely interweaving neuron clusters using G-Cut
Precise segmentation of densely interweaving neuron clusters using G-Cut