Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Scarf enables a highly memory-efficient analysis of large-scale single-cell genomics data
Scarf enables a highly memory-efficient analysis of large-scale single-cell genomics data
As the scale of single-cell genomics experiments grows into the millions, the computational requirements to process this data are beyond the reach of many. Here the authors present Scarf, a modularly designed Python package that makes the analysis workflow highly memory efficient such that even the largest existing datasets can be analyzed on an average modern laptop.
- Parashar Dhapola
- , Johan Rodhe
- & Göran Karlsson
-
Article
| Open Access Climate windows of opportunity for plant expansion during the Phanerozoic
Climate windows of opportunity for plant expansion during the Phanerozoic
Climatic variables have played a significant role in plant evolution across the Phanerozoic. Here, the authors link climate with a new dynamic vegetation model to identify two windows of opportunity for plant biomass expansion, corresponding with the expansion of land plants and the angiosperm radiation.
- Khushboo Gurung
- , Katie J. Field
- & Benjamin J. W. Mills
-
Article
| Open Access Pan-African genome demonstrates how population-specific genome graphs improve high-throughput sequencing data analysis
Pan-African genome demonstrates how population-specific genome graphs improve high-throughput sequencing data analysis
Graph-based genome reference representations have seen significant development, motivated by the inadequacy of the current human genome reference to represent the diverse genetic information from different human populations and its inability to maintain the same level of accuracy for non-European ancestries. Here the authors present the case for iteratively augmenting tailored genome graphs for targeted populations and demonstrate this approach on the whole-genome samples of African ancestry.
- H. Serhat Tetikol
- , Deniz Turgut
- & Brandi N. Davis-Dusenbery
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time 3D analysis during electron tomography using tomviz
Real-time 3D analysis during electron tomography using tomviz
High-throughput electron tomography has been challenging due to time-consuming alignment and reconstruction. Here, the authors demonstrate real-time tomography with dynamic 3D tomographic visualization integrated in tomviz, an open-source 3D data analysis tool.
- Jonathan Schwartz
- , Chris Harris
- & Robert Hovden
-
Article
| Open Access Knowledge-graph-based cell-cell communication inference for spatially resolved transcriptomic data with SpaTalk
Knowledge-graph-based cell-cell communication inference for spatially resolved transcriptomic data with SpaTalk
Cell-cell communication is a vital feature involving numerous biological processes. Here, the authors develop SpaTalk, a cell-cell communication inference method using knowledge graph for spatially resolved transcriptomic data, providing valuable insights into spatial intercellular tissue dynamics.
- Xin Shao
- , Chengyu Li
- & Xiaohui Fan
-
Article
| Open Access TidyMass an object-oriented reproducible analysis framework for LC–MS data
TidyMass an object-oriented reproducible analysis framework for LC–MS data
Reproducibility, traceability, and transparency have been long-standing issues in metabolomics data analysis. Here, the authors present tidyMass, an R-based computational framework that allows designing traceable, shareable, and reproducible data processing and analysis workflows for untargeted metabolomics.
- Xiaotao Shen
- , Hong Yan
- & Michael P. Snyder
-
Article
| Open Access A density-based enrichment measure for assessing colocalization in single-molecule localization microscopy data
A density-based enrichment measure for assessing colocalization in single-molecule localization microscopy data
Full information gained from single-molecule localisation microscopy (SMLM) isn't exploited by current analysis tools. Here the authors report relative enrichment which uses a density-based colocalisation measure for both 2D and 3D SMLM data; they apply it to both simulated data and cultured neurons.
- Aske L. Ejdrup
- , Matthew D. Lycas
- & Ulrik Gether
-
Article
| Open Access Intratumor graph neural network recovers hidden prognostic value of multi-biomarker spatial heterogeneity
Intratumor graph neural network recovers hidden prognostic value of multi-biomarker spatial heterogeneity
Cancer prognosis using multiregion sampling is costly and not completely reliable due to the required biomarker homogenisation step. Here, the authors develop an intratumor graph neural network for prognosis in multiregion cancer samples based on in situ biomarkers and gene expression that does not need homogenisation.
- Lida Qiu
- , Deyong Kang
- & Haohua Tu
-
Article
| Open Access Accurate somatic variant detection using weakly supervised deep learning
Accurate somatic variant detection using weakly supervised deep learning
Deep learning could be applied to the challenge of somatic variant calling in cancer by making use of large-scale genomic data. Here, the authors develop VarNet, a weakly supervised deep learning model for somatic variant calling in cancer with robust performance across multiple cancer genomics datasets.
- Kiran Krishnamachari
- , Dylan Lu
- & Anders Jacobsen Skanderup
-
Article
| Open Access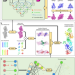 Model building of protein complexes from intermediate-resolution cryo-EM maps with deep learning-guided automatic assembly
Model building of protein complexes from intermediate-resolution cryo-EM maps with deep learning-guided automatic assembly
One challenge in cryo-EM is to build atomic models into intermediate resolution maps. Here, the authors present a deep learning-guided iterative assembling method by integrating AlphaFold, FFTbased fitting, and domain-based refinement.
- Jiahua He
- , Peicong Lin
- & Sheng-You Huang
-
Article
| Open Access dia-PASEF data analysis using FragPipe and DIA-NN for deep proteomics of low sample amounts
dia-PASEF data analysis using FragPipe and DIA-NN for deep proteomics of low sample amounts
The dia-PASEF technology uses ion mobility separation to reduce signal interferences and increase sensitivity of mass spectrometry-based proteomics. The authors present algorithms and a software solution, which boost proteomic depth in dia-PASEF experiments by up to 83% compared to previous work, and are specifically beneficial for fast proteomic experiments and those with low sample amounts.
- Vadim Demichev
- , Lukasz Szyrwiel
- & Markus Ralser
-
Article
| Open Access Mimicked synthetic ribosomal protein complex for benchmarking crosslinking mass spectrometry workflows
Mimicked synthetic ribosomal protein complex for benchmarking crosslinking mass spectrometry workflows
Cross-linking mass spectrometry is widely used to elucidate protein structures and interactions. Here, the authors generate an extensive peptide library to benchmark the most common cross-link search engines with frequently used cross-linking reagents in low and high complex sample systems.
- Manuel Matzinger
- , Adrian Vasiu
- & Karl Mechtler
-
Article
| Open Access Reconstruction of a catalogue of genome-scale metabolic models with enzymatic constraints using GECKO 2.0
Reconstruction of a catalogue of genome-scale metabolic models with enzymatic constraints using GECKO 2.0
Genome-scale metabolic models have been widely used for quantitative exploration of the relation between genotype and phenotype. Here the authors present GECKO 2, an automated framework for continuous and version controlled update of enzyme-constrained models of metabolism, producing an interesting catalogue of high-quality models for diverse yeasts, bacteria and human metabolism, aiming to facilitate their use in basic science, metabolic engineering and synthetic biology purposes.
- Iván Domenzain
- , Benjamín Sánchez
- & Jens Nielsen
-
Article
| Open Access Automated detection and segmentation of non-small cell lung cancer computed tomography images
Automated detection and segmentation of non-small cell lung cancer computed tomography images
Correct interpretation of computer tomography (CT) scans is important for the correct assessment of a patient’s disease but can be subjective and timely. Here, the authors develop a system that can automatically segment the non-small cell lung cancer on CT images of patients and show in an in silico trial that the method was faster and more reproducible than clinicians.
- Sergey P. Primakov
- , Abdalla Ibrahim
- & Philippe Lambin
-
Article
| Open Access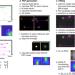 Global fitting for high-accuracy multi-channel single-molecule localization
Global fitting for high-accuracy multi-channel single-molecule localization
Multi-channel SMLM imaging is powerful. Here the authors report globLoc, a GPU-based global fitting algorithm, to extract maximum information from multichannel single molecule data; this gives improved localisation precision for biplane and 4Pi-SMLM and colour assignment in multi-colour astigmatic SMLM.
- Yiming Li
- , Wei Shi
- & Jonas Ries
-
Article
| Open Access SpotClean adjusts for spot swapping in spatial transcriptomics data
SpotClean adjusts for spot swapping in spatial transcriptomics data
Spatial transcriptomics experiments profile genome-wide gene expression at localized spots across a tissue. Here, the authors identify spot swapping, an artifact where RNA expressed at one tissue spot binds probes at another, and they propose SpotClean to adjust for it.
- Zijian Ni
- , Aman Prasad
- & Christina Kendziorski
-
Article
| Open Access A framework to efficiently describe and share reproducible DNA materials and construction protocols
A framework to efficiently describe and share reproducible DNA materials and construction protocols
DNA constructs and their annotated sequence maps have been rapidly accumulating with the advancement of DNA cloning, synthesis, and assembly methods. Here the authors introduce QUEEN, a framework to describe and share DNA materials and construction protocols.
- Hideto Mori
- & Nozomu Yachie
-
Article
| Open Access A rare variant analysis framework using public genotype summary counts to prioritize disease-predisposition genes
A rare variant analysis framework using public genotype summary counts to prioritize disease-predisposition genes
Sequencing studies in clinical and cancer genomics often utilize public data sets to identify genes enriched with pathogenic variants. Here, the authors propose a framework which controls for confounding factors that can bias the results in these studies.
- Wenan Chen
- , Shuoguo Wang
- & Gang Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Pytheas: a software package for the automated analysis of RNA sequences and modifications via tandem mass spectrometry
Pytheas: a software package for the automated analysis of RNA sequences and modifications via tandem mass spectrometry
RNA modifications represent a critical aspect of RNA biology that is not well suited to sequencing methods. Here, the authors provide a software tool for automated analysis of RNA tandem mass spectra with full support of modifications, isotope labelling, and control of false discovery rate.
- Luigi D’Ascenzo
- , Anna M. Popova
- & James R. Williamson
-
Article
| Open Access Kronos scRT: a uniform framework for single-cell replication timing analysis
Kronos scRT: a uniform framework for single-cell replication timing analysis
A scalable approach to explore DNA replication in single cells reveals that although aneuploidy does not have a major impact on the pattern of replication, different cell types and sub-populations display distinguished replication paths.
- Stefano Gnan
- , Joseph M. Josephides
- & Chun-Long Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Normalizing and denoising protein expression data from droplet-based single cell profiling
Normalizing and denoising protein expression data from droplet-based single cell profiling
Current single cell protein expression profiling approaches come with substantial measurement noise. Here the authors discover the sources of this noise and develop a denoising algorithm that improves data quality and downstream applications.
- Matthew P. Mulè
- , Andrew J. Martins
- & John S. Tsang
-
Article
| Open Access Designing highly multiplex PCR primer sets with Simulated Annealing Design using Dimer Likelihood Estimation (SADDLE)
Designing highly multiplex PCR primer sets with Simulated Annealing Design using Dimer Likelihood Estimation (SADDLE)
The design of highly multiplex PCR primers to amplify and enrich many different DNA sequences is increasing in biomedical importance as new mutations and pathogens are identified. The authors present and experimentally validate Simulated Annealing Design using Dimer Likelihood Estimation (SADDLE), a stochastic algorithm for design of highly multiplex PCR primer sets that minimize primer dimer formation.
- Nina G. Xie
- , Michael X. Wang
- & David Yu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Glyco-Decipher enables glycan database-independent peptide matching and in-depth characterization of site-specific N-glycosylation
Glyco-Decipher enables glycan database-independent peptide matching and in-depth characterization of site-specific N-glycosylation
Poor peptide fragmentation and unusual glycan structures limit mass spectrometry-based analysis of intact N-glycopeptides. Here, the authors develop Glyco-Decipher, a glycan-independent peptide search tool, to tackle these issues and improve the coverage of site-specific glycan analysis.
- Zheng Fang
- , Hongqiang Qin
- & Mingliang Ye
-
Article
| Open Access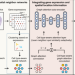 Deciphering spatial domains from spatially resolved transcriptomics with an adaptive graph attention auto-encoder
Deciphering spatial domains from spatially resolved transcriptomics with an adaptive graph attention auto-encoder
Breakthrough technologies for spatially resolved transcriptomics have enabled genome-wide profiling of gene expressions in captured locations. Here the authors integrate gene expressions and spatial locations to identify spatial domains using an adaptive graph attention auto-encoder.
- Kangning Dong
- & Shihua Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access cyCombine allows for robust integration of single-cell cytometry datasets within and across technologies
cyCombine allows for robust integration of single-cell cytometry datasets within and across technologies
Combining single-cell cytometry datasets increases the analytical flexibility and the statistical power of data analyses. Here, the authors present a method to robustly integrate cytometry data from different batches, experiments, or even different experimental techniques.
- Christina Bligaard Pedersen
- , Søren Helweg Dam
- & Lars Rønn Olsen
-
Article
| Open Access SHAPE-guided RNA structure homology search and motif discovery
SHAPE-guided RNA structure homology search and motif discovery
SHAPEwarp is a method that allows identifying structurally-similar RNAs by direct comparison of reactivity profiles derived from chemical probing experiments. Its application to viral genomes identified conserved RNA structure elements.
- Edoardo Morandi
- , Martijn J. van Hemert
- & Danny Incarnato
-
Article
| Open Access The landscape of receptor-mediated precision cancer combination therapy via a single-cell perspective
The landscape of receptor-mediated precision cancer combination therapy via a single-cell perspective
Intra-tumor heterogeneity is often associated with resistance to targeted therapy, requiring the design of combinatorial therapies. Here, based on tumor single-cell transcriptomic datasets, the authors develop a computational approach to identify optimal combinatorial treatments targeting membrane receptors for cancer therapy.
- Saba Ahmadi
- , Pattara Sukprasert
- & Eytan Ruppin
-
Article
| Open Access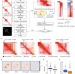 Stripenn detects architectural stripes from chromatin conformation data using computer vision
Stripenn detects architectural stripes from chromatin conformation data using computer vision
Chromosome conformation capture techniques have recently revealed features beyond chromatin loops such as architectural stripes. Here the authors present their stripe detection tool ‘Stripenn’ to detect and quantitate stripes from any type of chromatin conformation capture data. They show that architectural stripes are enriched at transcriptionally active and accessible genomic regions.
- Sora Yoon
- , Aditi Chandra
- & Golnaz Vahedi
-
Article
| Open Access DIAMetAlyzer allows automated false-discovery rate-controlled analysis for data-independent acquisition in metabolomics
DIAMetAlyzer allows automated false-discovery rate-controlled analysis for data-independent acquisition in metabolomics
The extraction of meaningful biological knowledge from high-throughput mass spectrometry data relies on limiting false discoveries to a manageable amount. Here the authors establish an automated, false discovery rate-controlled targeted analysis workflow for data-independent acquisition that enables a robust FDR estimation improving the comparability of results in the metabolomics field.
- Oliver Alka
- , Premy Shanthamoorthy
- & Hannes L. Röst
-
Article
| Open Access Fully-automated and ultra-fast cell-type identification using specific marker combinations from single-cell transcriptomic data
Fully-automated and ultra-fast cell-type identification using specific marker combinations from single-cell transcriptomic data
Cell types are typically identified in single cell transcriptomic data by manual annotation of cell clusters using established marker genes. Here the authors present a fully-automated computational platform that can quickly and accurately distinguish between cell types.
- Aleksandr Ianevski
- , Anil K. Giri
- & Tero Aittokallio
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell gene fusion detection by scFusion
Single-cell gene fusion detection by scFusion
Gene fusions are an important class of mutations in tumor genomes. Here, the authors develop a single-cell gene fusion detection method scFusion and demonstrate its applications in cancer single-cell studies.
- Zijie Jin
- , Wenjian Huang
- & Ruibin Xi
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-parameter photon-by-photon hidden Markov modeling
Multi-parameter photon-by-photon hidden Markov modeling
In this work, the authors demonstrate the application of multi-parameter photon-by-photon hidden Markov modeling (mpH2MM) on alternating laser excitation (ALEX)-based smFRET measurements. The utility of mpH2MM in identifying and quantifying dynamic biomolecular sub-populations is demonstrated in three different systems.
- Paul David Harris
- , Alessandra Narducci
- & Eitan Lerner
-
Article
| Open Access CytofIn enables integrated analysis of public mass cytometry datasets using generalized anchors
CytofIn enables integrated analysis of public mass cytometry datasets using generalized anchors
Challenges in batch normalization and data integration limit the comparison of existing mass cytometry datasets. Here, the authors report CytofIn that can integrate mass cytometry datasets from the public domain and reveal cellular features associated with immune oncology by analyzing five public cancer datasets.
- Yu-Chen Lo
- , Timothy J. Keyes
- & Kara L. Davis
-
Article
| Open Access A SIMPLI (Single-cell Identification from MultiPLexed Images) approach for spatially-resolved tissue phenotyping at single-cell resolution
A SIMPLI (Single-cell Identification from MultiPLexed Images) approach for spatially-resolved tissue phenotyping at single-cell resolution
Current high-dimension imaging data analysis methods are technology-specific and require multiple tools, restricting analytical scalability and result reproducibility. Here the authors present SIMPLI, a software that overcomes these limitations for single-cell and pixel analysis of multiplexed images at spatial resolution.
- Michele Bortolomeazzi
- , Lucia Montorsi
- & Francesca D. Ciccarelli
-
Article
| Open Access SMAP is a pipeline for sample matching in proteogenomics
SMAP is a pipeline for sample matching in proteogenomics
Sample mix-up is a potential problem in large-scale omic studies due to the complexity of sample processing. Here, the authors present a pipeline for sample matching in proteogenomics to verify sample identity and ensure data integrity.
- Ling Li
- , Mingming Niu
- & Xusheng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Polyply; a python suite for facilitating simulations of macromolecules and nanomaterials
Polyply; a python suite for facilitating simulations of macromolecules and nanomaterials
To facilitate the rational design of (nano)-materials and biomacromolecules by MD simulations, the authors present the polyply suite, featuring a graph matching algorithm and a random walk protocol for generating multi-scale polymeric topologies and initial coordinates.
- Fabian Grünewald
- , Riccardo Alessandri
- & Siewert J. Marrink
-
Article
| Open Access Association of mutation signature effectuating processes with mutation hotspots in driver genes and non-coding regions
Association of mutation signature effectuating processes with mutation hotspots in driver genes and non-coding regions
In cancer, associations between mutational signatures and driver mutations have been proposed but not fully explored. Here, the authors develop sigDriver to find associations between mutational signatures and mutation hotspots in order to predict coding and non-coding driver mutations in pan-cancer genomics data.
- John K. L. Wong
- , Christian Aichmüller
- & Marc Zapatka
-
Article
| Open Access Integrating gene expression and clinical data to identify drug repurposing candidates for hyperlipidemia and hypertension
Integrating gene expression and clinical data to identify drug repurposing candidates for hyperlipidemia and hypertension
Prioritizing drug repurposing candidates for downstream studies remains challenging. Here, the authors present a high-throughput approach to identify and validate drug repurposing candidates, integrating human gene expression, drug perturbation, and clinical data from publicly available resources.
- Patrick Wu
- , QiPing Feng
- & Wei-Qi Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Mini-batch optimization enables training of ODE models on large-scale datasets
Mini-batch optimization enables training of ODE models on large-scale datasets
Ordinary differential equation (ODE) models are widely used to understand multiple processes. Here the authors show how the concept of mini-batch optimization can be transferred from the field of Deep Learning to ODE modelling.
- Paul Stapor
- , Leonard Schmiester
- & Jan Hasenauer
-
Article
| Open Access RNA modifications detection by comparative Nanopore direct RNA sequencing
RNA modifications detection by comparative Nanopore direct RNA sequencing
Nanopore direct RNA Sequencing data contain information about the presence of RNA modifications, but their detection poses substantial challenges. Here the authors introduce Nanocompore, a new methodology for modification detection from Nanopore data.
- Adrien Leger
- , Paulo P. Amaral
- & Tony Kouzarides
-
Article
| Open Access Improved analyses of GWAS summary statistics by reducing data heterogeneity and errors
Improved analyses of GWAS summary statistics by reducing data heterogeneity and errors
Analyses of summary statistics from GWAS are subject to biases due to errors in the discovery GWAS or linkage disequilibrium reference data set or heterogeneity between data sets. Here, the authors propose a quality control method to be added to analysis of GWAS summary data that can reduce such biases.
- Wenhan Chen
- , Yang Wu
- & Jian Yang
-
Article
| Open Access DeepRank: a deep learning framework for data mining 3D protein-protein interfaces
DeepRank: a deep learning framework for data mining 3D protein-protein interfaces
The authors present DeepRank, a deep learning framework for the data mining of large sets of 3D protein-protein interfaces (PPI). They use DeepRank to address two challenges in structural biology: distinguishing biological versus crystallographic PPIs in crystal structures, and secondly the ranking of docking models.
- Nicolas Renaud
- , Cunliang Geng
- & Li C. Xue
-
Article
| Open Access Probabilistic inference of the genetic architecture underlying functional enrichment of complex traits
Probabilistic inference of the genetic architecture underlying functional enrichment of complex traits
Improving inference in large-scale genetic data linked to electronic medical record data requires the development of novel computationally efficient regression methods. Here, the authors develop a Bayesian approach for association analyses to improve SNP-heritability estimation, discovery, fine-mapping and genomic prediction.
- Marion Patxot
- , Daniel Trejo Banos
- & Matthew R. Robinson
-
Article
| Open Access Ensuring scientific reproducibility in bio-macromolecular modeling via extensive, automated benchmarks
Ensuring scientific reproducibility in bio-macromolecular modeling via extensive, automated benchmarks
Computational methods are becoming an increasingly important part of biological research. Using the Rosetta framework as an example, the authors demonstrate how community-driven development of computational methods can be done in a reproducible and reliable fashion.
- Julia Koehler Leman
- , Sergey Lyskov
- & Richard Bonneau
-
Article
| Open Access Jumper enables discontinuous transcript assembly in coronaviruses
Jumper enables discontinuous transcript assembly in coronaviruses
@melkebir @psashittal et al. develop a graph-based method for the assembly of discontinuous transcripts produced in Coronaviruses and other Nidovirales, enabling the discovery of transcriptional changes missed by existing methods.
- Palash Sashittal
- , Chuanyi Zhang
- & Mohammed El-Kebir
-
Article
| Open Access Accurate and scalable variant calling from single cell DNA sequencing data with ProSolo
Accurate and scalable variant calling from single cell DNA sequencing data with ProSolo
Obtaining accurate variant calls from multiple displacement amplified single cell DNA sequencing data needs dedicated models that account for amplification bias and copy errors. Here, the authors describe ProSolo, a model for calling single nucleotide variants with control over the false discovery rate.
- David Lähnemann
- , Johannes Köster
- & Alexander Schönhuth
-
Article
| Open Access Mesmerize is a dynamically adaptable user-friendly analysis platform for 2D and 3D calcium imaging data
Mesmerize is a dynamically adaptable user-friendly analysis platform for 2D and 3D calcium imaging data
Calcium imaging is valuable for understanding neuro and cell biology, but is challenging to analyze, organize, and access. Here, the authors present an efficient, expandable and user-friendly platform, which encapsulates the entire analysis process all to way to interactive visualizations.
- Kushal Kolar
- , Daniel Dondorp
- & Marios Chatzigeorgiou
-
Article
| Open Access Fast alignment and preprocessing of chromatin profiles with Chromap
Fast alignment and preprocessing of chromatin profiles with Chromap
As studies continue sequencing with deeper coverage, computational processing of these profiles has become increasingly resource consuming. Here the authors designed an efficient computational method called Chromap to align and preprocess high throughput sequencing data from chromatin profiling techniques, including ChIP-seq, Hi-C, or scATAC-seq, with a major decrease in runtime.
- Haowen Zhang
- , Li Song
- & Heng Li
-
Article
| Open Access Refining models of archaic admixture in Eurasia with ArchaicSeeker 2.0
Refining models of archaic admixture in Eurasia with ArchaicSeeker 2.0
Existing methods to identify the presence of DNA from other hominin species can be limited in the ability to accurately estimate introgression waves, or can only be applied to specific populations. Here, the authors have developed a generalizable method to identify introgression in multi-wave situations.
- Kai Yuan
- , Xumin Ni
- & Shuhua Xu

 Secure human action recognition by encrypted neural network inference
Secure human action recognition by encrypted neural network inference