Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Enabling accurate and early detection of recently emerged SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in wastewater
Enabling accurate and early detection of recently emerged SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in wastewater
Sapoval et al. introduce QuaID, a bioinformatics tool for SARS-CoV-2 variant detection based on quasi-unique mutations. QuaID leverages all mutations, including insertions and deletions, and provides precise detection of variants early in their spread.
- Nicolae Sapoval
- , Yunxi Liu
- & Todd J. Treangen
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial analysis with SPIAT and spaSim to characterize and simulate tissue microenvironments
Spatial analysis with SPIAT and spaSim to characterize and simulate tissue microenvironments
Spatial proteomic data serve to provide cell-level location information for the extraction of biological features from tissues, but analyzing such data can be difficult. Here the authors report the development of SPIAT for data analyses and spaSim for simulation and validation of methods to help bridge the gap between the technology and its translation.
- Yuzhou Feng
- , Tianpei Yang
- & Anna S. Trigos
-
Article
| Open Access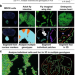 The PECAn image and statistical analysis pipeline identifies Minute cell competition genes and features
The PECAn image and statistical analysis pipeline identifies Minute cell competition genes and features
The 3D nature of clones makes sample image analysis challenging. Here the authors report PECAn, a pipeline for image processing and statistical analysis of complex multi-genotype 3D images, and apply this to the study of Minute cell competition in drosophila.
- Michael E. Baumgartner
- , Paul F. Langton
- & Eugenia Piddini
-
Article
| Open Access MetaTiME integrates single-cell gene expression to characterize the meta-components of the tumor immune microenvironment
MetaTiME integrates single-cell gene expression to characterize the meta-components of the tumor immune microenvironment
Integration and comparison of multiple single cell sequencing datasets can be used to compare different studies. Here the authors propose MetaTiME which compares the gene expression of single cells from the tumour microenvironment across different tumours and uses transportable labels and metacomponents to annotate cell types and states.
- Yi Zhang
- , Guanjue Xiang
- & Clifford A. Meyer
-
Article
| Open Access NetBID2 provides comprehensive hidden driver analysis
NetBID2 provides comprehensive hidden driver analysis
It’s challenging to capture “hidden” drivers that may not be genetically-altered or differentially-expressed from omics data. Here the authors developed NetBID2, a comprehensive network-based toolbox with versatile features, enabling the integration of multi-omics data to expose such hidden drivers.
- Xinran Dong
- , Liang Ding
- & Jiyang Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Optical neural network via loose neuron array and functional learning
Optical neural network via loose neuron array and functional learning
Here the authors have realized a programmable incoherent optical neural network that delivers light-speed, high-bandwidth, and power-efficient neural network inference via processing parallel visible light signals in the free space.
- Yuchi Huo
- , Hujun Bao
- & Sung-Eui Yoon
-
Article
| Open Access DeMAG predicts the effects of variants in clinically actionable genes by integrating structural and evolutionary epistatic features
DeMAG predicts the effects of variants in clinically actionable genes by integrating structural and evolutionary epistatic features
Interpretation of rare genetic variants remains challenging. Here, the authors develop a supervised variant effect predictor for use in clinically actionable genes which incorporates evolutionary and structural relationships between residues and has balanced specificity and sensitivity.
- Federica Luppino
- , Ivan A. Adzhubei
- & Agnes Toth-Petroczy
-
Article
| Open Access PepQuery2 democratizes public MS proteomics data for rapid peptide searching
PepQuery2 democratizes public MS proteomics data for rapid peptide searching
Billions of MS/MS spectra are available in public proteomics data repositories, but their usage has been limited to informatics experts. Here, the authors provide a solution to democratize these data for rapid peptide searching and demonstrate utilities in a wide range of biological applications
- Bo Wen
- & Bing Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Performance efficient macromolecular mechanics via sub-nanometer shape based coarse graining
Performance efficient macromolecular mechanics via sub-nanometer shape based coarse graining
Here the authors report SBCG2 an update to the neural network based, Shape-Based Coarse Graining (SBCG) approach for creating coarse grained molecular topologies with atomistic detail. They show how SBCG2 can reduce the computational costs of simulating very large assemblies like the HIV-1 capsid allowing simulation on commodity hardware.
- Alexander J. Bryer
- , Juan S. Rey
- & Juan R. Perilla
-
Article
| Open Access Cellcano: supervised cell type identification for single cell ATAC-seq data
Cellcano: supervised cell type identification for single cell ATAC-seq data
Accurately annotating cell types is a fundamental step in single-cell omics data analysis. Here, the authors develop a computational method called Cellcano based on a two-round supervised learning algorithm to identify cell types for scATAC-seq data and perform benchmarking to demonstrate its accuracy, robustness and computational efficiency.
- Wenjing Ma
- , Jiaying Lu
- & Hao Wu
-
Article
| Open Access The CellPhe toolkit for cell phenotyping using time-lapse imaging and pattern recognition
The CellPhe toolkit for cell phenotyping using time-lapse imaging and pattern recognition
Approaches for temporal analysis and quantitative characterisation of single cell morphology and dynamics remain in high demand. Here authors present CellPhe, a pattern recognition toolkit for the unbiased characterisation of cellular phenotypes within time-lapse videos.
- Laura Wiggins
- , Alice Lord
- & Julie Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access Comparative analysis of dimension reduction methods for cytometry by time-of-flight data
Comparative analysis of dimension reduction methods for cytometry by time-of-flight data
Dimension reduction (DR) is a key step of Cytometry by Time-of-Flight (CyTOF) data analysis. Here, the authors benchmark 21 DR methods on 110 real and 425 synthetic CyTOF samples, finding a high level of complementarity between the methods, and providing a comprehensive set of user guidelines.
- Kaiwen Wang
- , Yuqiu Yang
- & Tao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access A mass spectrum-oriented computational method for ion mobility-resolved untargeted metabolomics
A mass spectrum-oriented computational method for ion mobility-resolved untargeted metabolomics
The high dimensionality of ion mobility (IM)-resolved metabolomics data presents a great challenge to data processing. Here, authors develop a mass spectrum-oriented bottom-up assembly algorithm and the end-to-end computational framework Met4DX for IM-resolved metabolomics.
- Mingdu Luo
- , Yandong Yin
- & Zheng-Jiang Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access MS2Query: reliable and scalable MS2 mass spectra-based analogue search
MS2Query: reliable and scalable MS2 mass spectra-based analogue search
The authors develop a machine learning approach to find structurally related chemicals in mass spectral libraries. Their method boosts the annotation rate and aids in assessing novelty in metabolomics datasets.
- Niek F. de Jonge
- , Joris J. R. Louwen
- & Justin J. J. van der Hooft
-
Article
| Open Access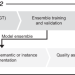 Deep learning-enabled segmentation of ambiguous bioimages with deepflash2
Deep learning-enabled segmentation of ambiguous bioimages with deepflash2
The signal-to-noise ratio in bioimages is often low, which is problematic for segmentation. Here the authors report a deep learning method, deepflash2, to facilitate the segmentation of ambiguous bioimages through multi-expert annotations and integrated quality assurance.
- Matthias Griebel
- , Dennis Segebarth
- & Christoph M. Flath
-
Article
| Open Access Pan-cancer classification of single cells in the tumour microenvironment
Pan-cancer classification of single cells in the tumour microenvironment
The accuracy and granularity of classifying cell types in the tumour microenvironment (TME) from single-cell RNA-seq data is impacted by heterogeneity among cancer cells and similarities among functionally related immune cells. Here, the authors develop scATOMIC, a tumour and TME cell type classifier based on a hierarchical approach that can be applied to pan-cancer datasets.
- Ido Nofech-Mozes
- , David Soave
- & Sagi Abelson
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated analysis of genomic and transcriptomic data for the discovery of splice-associated variants in cancer
Integrated analysis of genomic and transcriptomic data for the discovery of splice-associated variants in cancer
Analysing the regulatory consequences of mutations and splice variants at large scale in cancer requires efficient computational tools. Here, the authors develop RegTools, a software package that can identify splice-associated variants from large-scale genomics and transcriptomics data with efficiency and flexibility.
- Kelsy C. Cotto
- , Yang-Yang Feng
- & Malachi Griffith
-
Article
| Open Access Interoperable slide microscopy viewer and annotation tool for imaging data science and computational pathology
Interoperable slide microscopy viewer and annotation tool for imaging data science and computational pathology
There is a lack of standardisation in slide microscopy imaging data. Here the authors report Slim, an open-source, web-based slide microscopy viewer implementing the Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) standard to achieve interoperability with a range of existing medical imaging systems.
- Chris Gorman
- , Davide Punzo
- & Markus D. Herrmann
-
Article
| Open Access Robust automated backbone triple resonance NMR assignments of proteins using Bayesian-based simulated annealing
Robust automated backbone triple resonance NMR assignments of proteins using Bayesian-based simulated annealing
The authors present BARASA, an approach to assign backbone triple resonance spectra of proteins that augments traditional approaches with a Bayesian statistical analysis of the observed chemical shifts. The algorithm employs a simulated annealing engine to establish a consensus set of resonance assignments and is tested against systems ranging in size to over 450 amino acids including examples of intrinsically disordered proteins.
- Anthony C. Bishop
- , Glorisé Torres-Montalvo
- & A. Joshua Wand
-
Article
| Open Access Determining protein structures in cellular lamella at pseudo-atomic resolution by GisSPA
Determining protein structures in cellular lamella at pseudo-atomic resolution by GisSPA
High-resolution in situ protein structure can be solved by cryo-ET, which requires several days of data collection. Here Cheng et al. report GisSPA, a program that may enable determining sub-4 Å resolution structures on cellular lamellae within one day of data collection.
- Jing Cheng
- , Tong Liu
- & Xinzheng Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Towards routine chromosome-scale haplotype-resolved reconstruction in cancer genomics
Towards routine chromosome-scale haplotype-resolved reconstruction in cancer genomics
The precise inference of structural variants (SVs) requires suitable sequencing technologies and computational tools. Here, in order to analyse SVs with haplotype resolution, the author applies high-resolution long-read sequencing and long-range Hi-C to a melanoma cell line and develops an efficient graph-based computational framework, pstools.
- Shilpa Garg
-
Article
| Open Access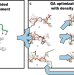 Automatic and accurate ligand structure determination guided by cryo-electron microscopy maps
Automatic and accurate ligand structure determination guided by cryo-electron microscopy maps
As cryo-EM becomes commonplace in drug discovery, tools for automating small molecule structure determination are needed. Here, authors show a map-guided ligand modeling approach to building ligand structures at resolutions common in cryo-EM.
- Andrew Muenks
- , Samantha Zepeda
- & Frank DiMaio
-
Article
| Open Access Batch alignment of single-cell transcriptomics data using deep metric learning
Batch alignment of single-cell transcriptomics data using deep metric learning
The increasing scale of single-cell RNA-seq studies presents new challenge for integrating datasets from different batches. Here, the authors develop scDML, a tool that simultaneously removes batch effects, improves clustering performance, recovers true cell types, and scales well to large datasets.
- Xiaokang Yu
- , Xinyi Xu
- & Xiangjie Li
-
Article
| Open Access Direct generation of protein conformational ensembles via machine learning
Direct generation of protein conformational ensembles via machine learning
Computational methods to study protein structural dynamics are a powerful tool in life sciences but are computationally expensive. Here, the authors show that machine learning can be used to efficiently generate protein conformational ensembles and test their method on intrinsically disordered peptides.
- Giacomo Janson
- , Gilberto Valdes-Garcia
- & Michael Feig
-
Article
| Open Access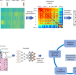 Cartography of Genomic Interactions Enables Deep Analysis of Single-Cell Expression Data
Cartography of Genomic Interactions Enables Deep Analysis of Single-Cell Expression Data
Existing genomic data analysis methods tend to not take full advantage of underlying biological characteristics. Here, the authors leverage the inherent interactions of scRNA-seq data and develop a cartography strategy to contrive the data into a spatially configured genomap for accurate deep pattern discovery.
- Md Tauhidul Islam
- & Lei Xing
-
Article
| Open Access DNA-Aeon provides flexible arithmetic coding for constraint adherence and error correction in DNA storage
DNA-Aeon provides flexible arithmetic coding for constraint adherence and error correction in DNA storage
The extensive information capacity of DNA makes it an attractive alternative to traditional data storage. DNA-Aeon is a DNA data storage solution that can correct all error types commonly observed in DNA storage, while encoding data into sequences that meet user-defined constraints such as GC content, homopolymer length, and no undesired motifs.
- Marius Welzel
- , Peter Michael Schwarz
- & Dominik Heider
-
Article
| Open Access Estimation of cell lineages in tumors from spatial transcriptomics data
Estimation of cell lineages in tumors from spatial transcriptomics data
Cell type deconvolution in tumor spatial transcriptomics (ST) data remains challenging. Here, the authors develop Spatial Cellular Estimator for Tumors (SpaCET) to infer cell types and intercellular interactions from ST data in cancer across different platforms, with improved performance over similar methods.
- Beibei Ru
- , Jinlin Huang
- & Peng Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access scMoMaT jointly performs single cell mosaic integration and multi-modal bio-marker detection
scMoMaT jointly performs single cell mosaic integration and multi-modal bio-marker detection
Many methods for single cell data integration have been developed, though mosaic integration remains challenging. Here the authors present scMoMaT, a mosaic integration method for single cell multi-modality data from multiple batches, that jointly learns cell representations and marker features across modalities for different cell clusters, to interpret the cell clusters from different modalities.
- Ziqi Zhang
- , Haoran Sun
- & Xiuwei Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access 3D RNA-scaffolded wireframe origami
3D RNA-scaffolded wireframe origami
Hybrid nucleic acid origami has potential for biomedical delivery of mRNA and fabrication of artificial ribozymes. Here, the authors use chemical footprinting and cryo-electron microscopy to reveal insights into nucleic acid origami used to fold messenger and ribosomal RNA into 3D polyhedral structures.
- Molly F. Parsons
- , Matthew F. Allan
- & Mark Bathe
-
Article
| Open Access Annotation of natural product compound families using molecular networking topology and structural similarity fingerprinting
Annotation of natural product compound families using molecular networking topology and structural similarity fingerprinting
Comparing experimental mass spectra to reference spectra can enable natural product identification, but these spectral libraries are often incomplete and not universally applicable. Here, the authors present SNAP-MS, a tool that allows assigning compound families without experimental or calculated reference spectra.
- Nicholas J. Morehouse
- , Trevor N. Clark
- & Roger G. Linington
-
Article
| Open Access Probabilistic embedding, clustering, and alignment for integrating spatial transcriptomics data with PRECAST
Probabilistic embedding, clustering, and alignment for integrating spatial transcriptomics data with PRECAST
Methods that perform data integration are needed to analyse spatial transcriptomics data from multiple tissue slides. Here, the authors present PRECAST, an efficient data integration method for multiple spatial transcriptomics datasets with complex batch or biological effects between slides.
- Wei Liu
- , Xu Liao
- & Jin Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Deciphering the exact breakpoints of structural variations using long sequencing reads with DeBreak
Deciphering the exact breakpoints of structural variations using long sequencing reads with DeBreak
Long-read sequencing is promising for the detection of structural variants (SVs), which requires algorithms with high sensitivity and precision. Here, the authors develop DeBreak, an algorithm for comprehensive and accurate SV detection in long-read sequencing data across different platforms, which outperforms other SV callers.
- Yu Chen
- , Amy Y. Wang
- & Zechen Chong
-
Article
| Open Access Transformer for one stop interpretable cell type annotation
Transformer for one stop interpretable cell type annotation
Developing computational tools for interpretable cell type annotation in scRNA-seq data remains challenging. Here the authors propose a Transformer-based model for interpretable annotation transfer using biologically understandable entities, and demonstrate its performance on large or atlas datasets.
- Jiawei Chen
- , Hao Xu
- & Jing-Dong J. Han
-
Article
| Open Access Benchmarking tools for detecting longitudinal differential expression in proteomics data allows establishing a robust reproducibility optimization regression approach
Benchmarking tools for detecting longitudinal differential expression in proteomics data allows establishing a robust reproducibility optimization regression approach
Longitudinal proteomics holds great promise for biomarker discovery, but the data interpretation has remained a challenge. Here, the authors evaluate several tools to detect longitudinal differential expression in proteomics data and introduce RolDE, a robust reproducibility optimization approach.
- Tommi Välikangas
- , Tomi Suomi
- & Laura L. Elo
-
Article
| Open Access Combining genome-wide association studies highlight novel loci involved in human facial variation
Combining genome-wide association studies highlight novel loci involved in human facial variation
Combining multiple related traits can increase power in genetic association studies. Here, the authors develop a method to integrate GWAS statistics for multiple traits and apply it to find genetic loci affecting human facial variation.
- Ziyi Xiong
- , Xingjian Gao
- & Fan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Extending resolution within a single imaging frame
Extending resolution within a single imaging frame
The presented Mean-Shift Super Resolution (MSSR) algorithm can extend spatial resolution within a single microscopy image. Its applicability extends across a wide range of experimental and instrumental configurations and it is compatible with other super-resolution microscopy approaches.
- Esley Torres-García
- , Raúl Pinto-Cámara
- & Adán Guerrero
-
Article
| Open Access Muscle5: High-accuracy alignment ensembles enable unbiased assessments of sequence homology and phylogeny
Muscle5: High-accuracy alignment ensembles enable unbiased assessments of sequence homology and phylogeny
Multiple sequence alignments are widely used to predict protein structure, function, and phylogeny, but are uncertain with more diverged sequences. Muscle5 generates ensembles of alternative high-accurate alignments, enabling novel confidence estimates in alignments, trees, and other inferences.
- Robert C. Edgar
-
Article
| Open Access A flexible cross-platform single-cell data processing pipeline
A flexible cross-platform single-cell data processing pipeline
As the throughput of single-cell RNA-seq studies increases, there is a need for tools that can make the data analysis steps more streamlined and convenient. Here, the authors develop UniverSC, a tool that unifies single-cell RNA-seq analysis workflows and also facilitates their use for non-experts.
- Kai Battenberg
- , S. Thomas Kelly
- & Aki Minoda
-
Article
| Open Access dcHiC detects differential compartments across multiple Hi-C datasets
dcHiC detects differential compartments across multiple Hi-C datasets
The organisation of mammalian genomes plays a role in many biological processes. Here the authors report dcHiC, a tool which uses a multivariate distance measure to identify changes in compartmentalisation among multiple genome-wide chromatin contact maps, and apply this to different human and mouse datasets.
- Abhijit Chakraborty
- , Jeffrey G. Wang
- & Ferhat Ay
-
Article
| Open Access Metabolite annotation from knowns to unknowns through knowledge-guided multi-layer metabolic networking
Metabolite annotation from knowns to unknowns through knowledge-guided multi-layer metabolic networking
Unknown metabolite annotation is a grand challenge in untargeted metabolomics. Here, the authors develop knowledge-guided multi-layer networking (KGMN) to enable global metabolite annotation from knowns to unknowns in untargeted metabolomics.
- Zhiwei Zhou
- , Mingdu Luo
- & Zheng-Jiang Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access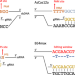 A comprehensive Bioconductor ecosystem for the design of CRISPR guide RNAs across nucleases and technologies
A comprehensive Bioconductor ecosystem for the design of CRISPR guide RNAs across nucleases and technologies
The success of CRISPR experiments relies on the choice of gRNA. Here the authors report crisprVerse, which enables efficient gRNA design and annotation for methods including CRISPRko, CRISPRa, CRISPRi, CRISPRbe and CRISPRkd, enabled for RNA- and DNA-targeting nucleases, including Cas9, Cas12 and Cas13.
- Luke Hoberecht
- , Pirunthan Perampalam
- & Jean-Philippe Fortin
-
Article
| Open Access Deep transfer learning of cancer drug responses by integrating bulk and single-cell RNA-seq data
Deep transfer learning of cancer drug responses by integrating bulk and single-cell RNA-seq data
Single-cell RNA-seq data provide the opportunity to predict drug response in cancer while considering intratumour heterogeneity. Here, the authors develop a deep transfer learning framework - scDEAL - to predict single-cell drug responses in cancer by integrating single-cell and bulk RNA-seq data.
- Junyi Chen
- , Xiaoying Wang
- & Qin Ma
-
Article
| Open Access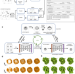 Isotropic reconstruction for electron tomography with deep learning
Isotropic reconstruction for electron tomography with deep learning
Cryogenic electron tomography suffers from anisotropic resolution due to the missing-wedge problem. Here, the authors present IsoNet, a neural network that learn the feature representation from similar structures in the tomogram and recover the missing information for isotropic tomogram reconstruction.
- Yun-Tao Liu
- , Heng Zhang
- & Z. Hong Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Technology readiness levels for machine learning systems
Technology readiness levels for machine learning systems
The development of machine learning systems has to ensure their robustness and reliability. The authors introduce a framework that defines a principled process of machine learning system formation, from research to production, for various domains and data scenarios.
- Alexander Lavin
- , Ciarán M. Gilligan-Lee
- & Yarin Gal
-
Article
| Open Access Alignment of single-cell trajectory trees with CAPITAL
Alignment of single-cell trajectory trees with CAPITAL
Global alignment of complex cell state trajectories between single-cell datasets remains challenging. Here, the authors present a computational method called CAPITAL to compare branching trajectories, and demonstrate that this method achieves accurate and robust alignments.
- Reiichi Sugihara
- , Yuki Kato
- & Yukio Kawahara
-
Article
| Open Access Cost-effective methylome sequencing of cell-free DNA for accurately detecting and locating cancer
Cost-effective methylome sequencing of cell-free DNA for accurately detecting and locating cancer
Early cancer detection by cell-free DNA (cfDNA) is challenged by the low amount of tumour DNA in cfDNA, tumour heterogeneity and the small patient cohorts. Here, the authors develop a method, cfMethyl-Seq, for cost-effective methylome profiling of cfDNA and for detecting and locating cancer.
- Mary L. Stackpole
- , Weihua Zeng
- & Xianghong Jasmine Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Autonomous optimization of non-aqueous Li-ion battery electrolytes via robotic experimentation and machine learning coupling
Autonomous optimization of non-aqueous Li-ion battery electrolytes via robotic experimentation and machine learning coupling
Human-operated optimization of non-aqueous Li-ion battery liquid electrolytes is a time-consuming process. Here, the authors propose an automated workflow that couples robotic experiments with machine learning to optimize liquid electrolyte formulations without human intervention.
- Adarsh Dave
- , Jared Mitchell
- & Venkatasubramanian Viswanathan
-
Article
| Open Access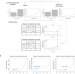 Batch effects removal for microbiome data via conditional quantile regression
Batch effects removal for microbiome data via conditional quantile regression
Here, the authors present ConQuR, a conditional quantile regression method that removes microbiome batch effects through non-parametric modeling of complex microbial read counts, while preserving the signals of interest.
- Wodan Ling
- , Jiuyao Lu
- & Michael C. Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Robust data storage in DNA by de Bruijn graph-based de novo strand assembly
Robust data storage in DNA by de Bruijn graph-based de novo strand assembly
DNA data storage is a rapidly developing technology with great potential due to its high density, long-term durability, and low maintenance cost. Here the authors present a strand assembly algorithm (DBGPS) using de Bruijn graph and greedy path search.
- Lifu Song
- , Feng Geng
- & Ying-Jin Yuan

 Linear time complexity de novo long read genome assembly with GoldRush
Linear time complexity de novo long read genome assembly with GoldRush