Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling dispersion forces between small particles with artificially created random light fields
Controlling dispersion forces between small particles with artificially created random light fields
Natural dispersion forces acting between molecules and particles arise from electromagnetic fields generated by quantum and thermal fluctuations. Here, Brügger et al.show that isotropic dispersion forces between colloidal particles can be induced, controlled and tuned with artificial, fluctuating laser light fields.
- Georges Brügger
- , Luis S. Froufe-Pérez
- & Juan José Sáenz
-
Article
| Open Access Optoelectronic crystal of artificial atoms in strain-textured molybdenum disulphide
Optoelectronic crystal of artificial atoms in strain-textured molybdenum disulphide
Periodically strained monolayer molybdenum disulphide funnels photogenerated electron-hole pairs across an electric field induced by a spatially graded band gap, mimicking a crystal of artificial atoms. Here, the authors experimentally demonstrate the artificial crystal in strain-textured molybdenum disulphide.
- Hong Li
- , Alex W. Contryman
- & Xiaolin Zheng
-
Article |
 Spin transport and Hanle effect in silicon nanowires using graphene tunnel barriers
Spin transport and Hanle effect in silicon nanowires using graphene tunnel barriers
Graphene forms low-resistance tunnel barriers for spin injection from a ferromagnet into silicon. Here, the authors fabricate silicon nanowire non-local spin valves with graphene tunnel barriers, evidencing spin accumulation and transport via Hanle spin precession measurements.
- O. M. J. van ’t Erve
- , A. L. Friedman
- & B. T. Jonker
-
Article
| Open Access Pressure induced metallization with absence of structural transition in layered molybdenum diselenide
Pressure induced metallization with absence of structural transition in layered molybdenum diselenide
Controlling the properties of transition metal chalcogenides enables the study of new condensed-matter phenomena and the development of potential applications. Here, the authors continuously tune the crystal and electronic structure of molybdenum diselenide away from the pristine state using pressure.
- Zhao Zhao
- , Haijun Zhang
- & Wendy L. Mao
-
Article
| Open Access Valley polarization assisted spin polarization in two dimensions
Valley polarization assisted spin polarization in two dimensions
In the emerging field of valleytronics, the valley degree of freedom of electrons is exploited in addition to charge and spin for novel functionalities. Here, Renard et al.show how valley polarization can facilitate spin-polarization in a silicon-on-insulator quantum well.
- V. T. Renard
- , B. A. Piot
- & K. Takashina
-
Article
| Open Access A lead-halide perovskite molecular ferroelectric semiconductor
A lead-halide perovskite molecular ferroelectric semiconductor
Lead-halide perovskite compounds have seen a considerable interest for their optoelectronic properties. Here, the authors discover a ferroelectric halide perovskite compound as an alternative pathway towards designing semiconductor ferroelectrics.
- Wei-Qiang Liao
- , Yi Zhang
- & Ren-Gen Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access Electronic Raman scattering as an ultra-sensitive probe of strain effects in semiconductors
Electronic Raman scattering as an ultra-sensitive probe of strain effects in semiconductors
Engineering strain in semiconductor structures provides additional control over the optical and electronic properties, which is promising for device applications. Fluegel et al. show that electronic Raman scattering provides a route to sensitively measure the degree of strain in thin semiconductor layers.
- Brian Fluegel
- , Aleksej V. Mialitsin
- & Angelo Mascarenhas
-
Article
| Open Access Investigation of exotic stable calcium carbides using theory and experiment
Investigation of exotic stable calcium carbides using theory and experiment
Pressure causes profound changes in the properties of atoms and chemical bonding leading to unusual materials. Here, the authors investigate the Ca-C system and find that it becomes increasingly complex and develops a multitude of phases with various compositions and new structures at higher pressures.
- Yan-Ling Li
- , Sheng-Nan Wang
- & Timothy A. Strobel
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated digital inverters based on two-dimensional anisotropic ReS2 field-effect transistors
Integrated digital inverters based on two-dimensional anisotropic ReS2 field-effect transistors
Many two-dimensional materials exhibit isotropic properties, but anisotropy can extend the functionality of future devices. Here, the authors fabricate field-effect transistors from single and few-layer rhenium disulfide and observe an anisotropic ratio of three to one along the two principle axes
- Erfu Liu
- , Yajun Fu
- & Dingyu Xing
-
Article
| Open Access Rubrene crystal field-effect mobility modulation via conducting channel wrinkling
Rubrene crystal field-effect mobility modulation via conducting channel wrinkling
Building flexible electronic devices demands an understanding of how mechanical deformation affects the active materials. Here, the authors observe and quantify the effects of local strains generated by the wrinkling instability in the conducting channel of rubrene crystal thin-film transistors.
- Marcos A. Reyes-Martinez
- , Alfred J. Crosby
- & Alejandro L. Briseno
-
Article
| Open Access Three-terminal heterojunction bipolar transistor solar cell for high-efficiency photovoltaic conversion
Three-terminal heterojunction bipolar transistor solar cell for high-efficiency photovoltaic conversion
Multiple junction solar cells offer the means to high-efficiency photovoltaics but suffer from complicated manufacturing and packing. Here Martí et al., propose a three-terminal heterojuntion bipolar transistor solar cell that simplifies the structure reducing the number of layers while maintaining the efficiency.
- A. Martí
- & A. Luque
-
Article
| Open Access Patterning two-dimensional chalcogenide crystals of Bi2Se3 and In2Se3 and efficient photodetectors
Patterning two-dimensional chalcogenide crystals of Bi2Se3 and In2Se3 and efficient photodetectors
Two-dimensional chalcogenides offer great potential in electronics, but accurate control of their growth is difficult. Here, the authors combine microintaglio printing and van der Waals epitaxy to pattern various large-area arrays of single-crystal chalcogenides with remarkable properties.
- Wenshan Zheng
- , Tian Xie
- & Hailin Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient light emission from inorganic and organic semiconductor hybrid structures by energy-level tuning
Efficient light emission from inorganic and organic semiconductor hybrid structures by energy-level tuning
Hybrid inorganic-organic structures can overcome the limits of inorganic semiconductor light emitting devices but the energy level offset is an obstacle. Here, Schlesinger et al.lower the ZnO work function with an organometallic donor monolayer and enhance the radiative emission of the hybrid structure.
- R. Schlesinger
- , F. Bianchi
- & N. Koch
-
Article
| Open Access Probing long-range carrier-pair spin–spin interactions in a conjugated polymer by detuning of electrically detected spin beating
Probing long-range carrier-pair spin–spin interactions in a conjugated polymer by detuning of electrically detected spin beating
Interactions between weakly coupled pairs of electron spins are thought to play a role in biological magnetoreception and spin-dependent carrier dynamics in semiconductors. Here, the authors investigate such intrapair dipolar and exchange interactions in a polymer using electrically detected magnetic resonance experiments.
- Kipp J. van Schooten
- , Douglas L. Baird
- & Christoph Boehme
-
Article
| Open Access Direct electron injection into an oxide insulator using a cathode buffer layer
Direct electron injection into an oxide insulator using a cathode buffer layer
Carrier injection from a metallic electrode into an oxide insulator component is made difficult by the large energy level offset between the two. Here, the authors show that an intermediary zinc-oxide layer enables an Ohmic electrical contact between a metal and an oxide insulator layer.
- Eungkyu Lee
- , Jinwon Lee
- & Youn Sang Kim
-
Article |
 Transport properties of pristine few-layer black phosphorus by van der Waals passivation in an inert atmosphere
Transport properties of pristine few-layer black phosphorus by van der Waals passivation in an inert atmosphere
Ultrathin black phosphorus is a two-dimensional semiconductor with a finite band gap, unlike graphene, but it is known to degrade upon exposure to air. Here, the authors show that passivating few-layer samples of this material in an inert gas environment greatly improves the n-type charge transport.
- Rostislav A. Doganov
- , Eoin C. T. O’Farrell
- & Barbaros Özyilmaz
-
Article
| Open Access Liquid crystals for organic thin-film transistors
Liquid crystals for organic thin-film transistors
Polycrystalline thin films of small molecules hold promise for organic thin-film transistors because of their large charge mobility, but are currently limited by poor film homogeneity and thermal durability. Here, Iino et al. design an ordered liquid crystal phase to overcome these two problems.
- Hiroaki Iino
- , Takayuki Usui
- & Jun-ichi Hanna
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling band alignments by artificial interface dipoles at perovskite heterointerfaces
Controlling band alignments by artificial interface dipoles at perovskite heterointerfaces
Controlling the alignment of bands at oxide interfaces is crucial for developing them into useful devices. By inserting charges into the interface to generate dipoles, Yajima et al. show tuning of the band alignment between SrRuO3/Nb:SrTiO3by 1.7 eV.
- Takeaki Yajima
- , Yasuyuki Hikita
- & Harold Y. Hwang
-
Article
| Open Access Three-fold rotational defects in two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides
Three-fold rotational defects in two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides
Defects in a crystalline solid can have a dramatic effect on the material’s properties. Here, the authors demonstrate a class of defects in two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides mediated by chalcogen vacancies and inherently related to the crystal symmetry
- Yung-Chang Lin
- , Torbjörn Björkman
- & Kazu Suenaga
-
Article |
 Complementary spin-Hall and inverse spin-galvanic effect torques in a ferromagnet/semiconductor bilayer
Complementary spin-Hall and inverse spin-galvanic effect torques in a ferromagnet/semiconductor bilayer
Spin–orbit torques could enable a new generation of low-power electrically controlled memory devices. Here, the authors experimentally disentangle the spin-Hall effect and inverse spin-galvanic effect contributions to the relativistic spin torques in a room temperature Fe/(Ga,Mn)As bilayer.
- T. D. Skinner
- , K. Olejník
- & A. J. Ferguson
-
Article
| Open Access Strain-induced metal–semiconductor transition observed in atomic carbon chains
Strain-induced metal–semiconductor transition observed in atomic carbon chains
Previous studies have predicted that carbyne (a single chain of sp1carbon atoms) goes from being metallic to semiconducting under strain. Here, the authors measure the electronic properties of carbyne, confirming the prediction and showing that the conductivity is determined by strain and by the contacts.
- A. La Torre
- , A. Botello-Mendez
- & F. Banhart
-
Article
| Open Access Positioning and joining of organic single-crystalline wires
Positioning and joining of organic single-crystalline wires
Aligned, one-dimensional, single-crystal materials may allow on-demand photon/electron transfer. Here, the authors use a physical vapour transport technique to grow organic single-crystal wires with the guidance of pillar-structured substrates, and perform proof of concept waveguide experiments.
- Yuchen Wu
- , Jiangang Feng
- & Lei Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Giant oscillating thermopower at oxide interfaces
Giant oscillating thermopower at oxide interfaces
Electrons sitting in quantum wells at the interface between two oxides can localize in the disordered potential, completely changing their properties. Here, the authors observe unexpectedly large thermopower that oscillates upon carrier density modulation and ascribe it to strong electron-phonon coupling.
- Ilaria Pallecchi
- , Francesca Telesio
- & Daniele Marré
-
Article
| Open Access Ultimate thin vertical p–n junction composed of two-dimensional layered molybdenum disulfide
Ultimate thin vertical p–n junction composed of two-dimensional layered molybdenum disulfide
Molybdenum disulfide is a two-dimensional semiconducting material that has properties that make it useful for compact electronic devices. Here, the authors use molybdenum disulfide in an ultra-thin p–n junction that demonstrate ambipolar carrier transport and current rectification.
- Hua-Min Li
- , Daeyeong Lee
- & Won Jong Yoo
-
Article |
 A graphene field-effect transistor as a molecule-specific probe of DNA nucleobases
A graphene field-effect transistor as a molecule-specific probe of DNA nucleobases
The development of improved DNA sequencing technologies relies on the ability to distinguish each of the four DNA nucleobases separately. Here, the authors fabricate a graphene field-effect transistor able to experimentally observe individual DNA nucleobases.
- Nikolai Dontschuk
- , Alastair Stacey
- & Jiri Cervenka
-
Article |
 Semiconductor/relaxor 0–3 type composites without thermal depolarization in Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3-based lead-free piezoceramics
Semiconductor/relaxor 0–3 type composites without thermal depolarization in Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3-based lead-free piezoceramics
Piezoelectric materials are used as sensors or actuators in many devices. Here, the authors demonstrate that semiconducting ZnO particles embedded into a Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3-based matrix improve its piezoelectric properties, promising an alternative to presently used lead-based materials.
- Ji Zhang
- , Zhao Pan
- & Yan-Feng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access A high-mobility electronic system at an electrolyte-gated oxide surface
A high-mobility electronic system at an electrolyte-gated oxide surface
Electrolyte gating enables the accumulation of large carrier densities in two-dimensional electron systems. Here, the authors demonstrate that a few-atom thick layer of hexagonal boron nitride can dramatically improve carrier mobility in an electrolyte-gated system by limiting chemical reactions and disorder.
- Patrick Gallagher
- , Menyoung Lee
- & David Goldhaber-Gordon
-
Article |
 How intermolecular geometrical disorder affects the molecular doping of donor–acceptor copolymers
How intermolecular geometrical disorder affects the molecular doping of donor–acceptor copolymers
Doping of conjugated polymers is an important strategy for the development of organic electronics. Here, the authors study the spatial organization of dopants in donor–acceptor polymers, indicating that charge transfer is improved when the dopant and donor moiety are in close proximity.
- Daniele Di Nuzzo
- , Claudio Fontanesi
- & Enrico Da Como
-
Article |
 Phonon hydrodynamics in two-dimensional materials
Phonon hydrodynamics in two-dimensional materials
Heat flow in nanoscale structures varies dramatically from that in bulk materials. Here, the authors use density-functional perturbation theory and the Boltzmann transport equation to study heat conductivity in two dimensions, with applications to graphene, boron nitride, molybdenum disulphide, graphane and fluorographene.
- Andrea Cepellotti
- , Giorgia Fugallo
- & Nicola Marzari
-
Article |
 Optically switchable transistors by simple incorporation of photochromic systems into small-molecule semiconducting matrices
Optically switchable transistors by simple incorporation of photochromic systems into small-molecule semiconducting matrices
Organic thin-film transistors can be photomodulated by incorporating photochromic molecules, but the state-of-the-art suffers from poor charge transport. Here, the authors improve charge mobility by three orders of magnitude by blending small conjugated molecules into diarylethene.
- Mirella El Gemayel
- , Karl Börjesson
- & Paolo Samorì
-
Article
| Open Access Polaron pair mediated triplet generation in polymer/fullerene blends
Polaron pair mediated triplet generation in polymer/fullerene blends
The spin dynamics at organic donor–acceptor junctions is critical in determining charge generation and recombination in devices, but the detail is still unclear. Here, Dimitrov et al. observe singlet–triplet spin mixing at nanosecond timescales, which competes directly with free charge separation.
- Stoichko D. Dimitrov
- , Scot Wheeler
- & James R. Durrant
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible suspended gate organic thin-film transistors for ultra-sensitive pressure detection
Flexible suspended gate organic thin-film transistors for ultra-sensitive pressure detection
The development of wearable healthcare and intelligence systems require low-cost, large-area flexible electronic sensors. Here, Zang et al. report pressure sensors based on organic thin-film transistors in combination with a suspended-gate device geometry, which show high sensitivity up to 192 kPa−1.
- Yaping Zang
- , Fengjiao Zhang
- & Daoben Zhu
-
Article |
 Narrowband light detection via internal quantum efficiency manipulation of organic photodiodes
Narrowband light detection via internal quantum efficiency manipulation of organic photodiodes
There is a growing interest in the development of narrowband photodiodes for full-color imaging and visible-blind near-infrared detection. Armin et al.show a sub-100 nm response by tuning the spectral bandwidth through regulating the charge collection efficiency in a thick organic bulk heterojunction.
- Ardalan Armin
- , Ross D. Jansen-van Vuuren
- & Paul Meredith
-
Article |
 Observation of long-lived interlayer excitons in monolayer MoSe2–WSe2 heterostructures
Observation of long-lived interlayer excitons in monolayer MoSe2–WSe2 heterostructures
Monolayer transition metal dichalcogenide heterostructures with type II band alignment have generated wide interest in device physics at the two-dimensional limit. Here, Rivera et al. observe interlayer excitons in vertically stacked MoSe2–WSe2 heterostructures and demonstrate tunability of the energy and luminescence.
- Pasqual Rivera
- , John R. Schaibley
- & Xiaodong Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Suppression of nuclear spin bath fluctuations in self-assembled quantum dots induced by inhomogeneous strain
Suppression of nuclear spin bath fluctuations in self-assembled quantum dots induced by inhomogeneous strain
Decoherence of the nuclear spin bath causes decoherence of electron spin qubits in the solid state. Here, Chekhovich et al.use spin-echo measurements to demonstrate the suppression of nuclear spin fluctuations in semiconductor quantum dots via strain-induced quadrupolar interactions.
- E.A. Chekhovich
- , M. Hopkinson
- & A.I. Tartakovskii
-
Article
| Open Access Exploring atomic defects in molybdenum disulphide monolayers
Exploring atomic defects in molybdenum disulphide monolayers
Imperfections can greatly alter a material’s properties. Here, the authors investigate the influence of point defects on the electronic structure, charge-carrier mobility and optical absorption of molybdenum disulphide prepared by mechanical exfoliation, physical and chemical vapour deposition.
- Jinhua Hong
- , Zhixin Hu
- & Ze Zhang
-
Article |
 Hydrodynamic phonon transport in suspended graphene
Hydrodynamic phonon transport in suspended graphene
Hydrodynamic phonon transport occurs when phonons are able to drift over macroscopic distances, leading to the breakdown of Fourier’s law of heat conduction. Here, the authors predict that this regime occurs in suspended graphene at higher temperatures than bulk materials.
- Sangyeop Lee
- , David Broido
- & Gang Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Macroscopic rotation of photon polarization induced by a single spin
Macroscopic rotation of photon polarization induced by a single spin
The recently observed rotation of a photon's polarization by interaction with a single solid state spin has potential implications in quantum computing. Here, Arnold et al. demonstrate enhanced spin–photon coupling and polarization rotation via a coupled quantum dot/micropillar cavity system.
- Christophe Arnold
- , Justin Demory
- & Loïc Lanco
-
Article |
 Bandgap tunability at single-layer molybdenum disulphide grain boundaries
Bandgap tunability at single-layer molybdenum disulphide grain boundaries
Molybdenum disulphide is a two-dimensional material that, unlike graphene, has a nonzero bandgap. Here, the authors demonstrate that the bandgap of single-layer molybdenum disulphide grown on graphite by chemical vapour deposition changes with distance from the grain boundary
- Yu Li Huang
- , Yifeng Chen
- & Andrew T. S. Wee
-
Article |
 Massive band gap variation in layered oxides through cation ordering
Massive band gap variation in layered oxides through cation ordering
Understanding and controlling the electronic band gap of a material is vital for many electronic and optoelectronic applications. Towards this aim, this study shows how huge band gap variations can arise by manipulating the electrostatic interactions via cation ordering in correlated oxide materials.
- Prasanna V. Balachandran
- & James M. Rondinelli
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence for a small hole pocket in the Fermi surface of underdoped YBa2Cu3Oy
Evidence for a small hole pocket in the Fermi surface of underdoped YBa2Cu3Oy
Fully mapping the Fermi surface of a compound provides a clear picture of its fundamental properties. Through thermoelectric measurements of the underdoped cuprate YBa2Cu3Oy, this study shows evidence for a second Fermi pocket, consistent with charge–density–wave Fermi surface reconstruction.
- N. Doiron-Leyraud
- , S. Badoux
- & C. Proust
-
Article |
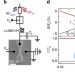 Probing the limits of gate-based charge sensing
Probing the limits of gate-based charge sensing
Reading out the state of quantum bits is an essential requirement that any quantum computer implementation must satisfy. Gonzalez-Zalba et al. now show that in situresonant gate-based detection can be a more sensitive approach than external electrometers while reducing the qubit architecture’s complexity.
- M. F. Gonzalez-Zalba
- , S. Barraud
- & A. C. Betz
-
Article |
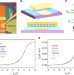 Probing the electron states and metal-insulator transition mechanisms in molybdenum disulphide vertical heterostructures
Probing the electron states and metal-insulator transition mechanisms in molybdenum disulphide vertical heterostructures
The mechanism that drives the metal to insulator transition in the two-dimensional material molybdenum disulphide is unknown. Here, the authors identify a percolation-type transition by studying the transport and capacitance properties of a metal-insulator-MoS2heterostructure.
- Xiaolong Chen
- , Zefei Wu
- & Ning Wang
-
Article
| Open Access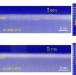 Engineering two-dimensional superconductivity and Rashba spin–orbit coupling in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 quantum wells by selective orbital occupancy
Engineering two-dimensional superconductivity and Rashba spin–orbit coupling in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 quantum wells by selective orbital occupancy
Two-dimensional electron gases at oxide interfaces induce exotic behaviours. By studying samples with different crystal orientation, Herranz et al.show that the extension and anisotropy of the oxide quantum well properties can be controlled through selective sub-band filling via orientational tuning.
- Gervasi Herranz
- , Gyanendra Singh
- & Josep Fontcuberta
-
Article |
 Exciton dynamics reveal aggregates with intermolecular order at hidden interfaces in solution-cast organic semiconducting films
Exciton dynamics reveal aggregates with intermolecular order at hidden interfaces in solution-cast organic semiconducting films
Grain boundaries between crystalline domains in solution-processed organic semiconductor thin films are believed to inhibit charge transport, but their structure is invisible to conventional characterization techniques. Wong et al. show the existence of nano-crystalline aggregates at domain interfaces.
- Cathy Y. Wong
- , Benjamin L. Cotts
- & Naomi S. Ginsberg
-
Article |
 Single-crystal field-effect transistors of new Cl2-NDI polymorph processed by sublimation in air
Single-crystal field-effect transistors of new Cl2-NDI polymorph processed by sublimation in air
Charge transport in organic semiconductors is highly sensitive to crystalline polymorphs. Here, He et al. manufacture the first n-channel single-crystal transistor via sublimation at ambient conditions and identify a new polymorphous phase that does not exist in its solution-processed counterpart.
- Tao He
- , Matthias Stolte
- & Frank Würthner
-
Article |
 Sub-10 nm rutile titanium dioxide nanoparticles for efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic hydrogen production
Sub-10 nm rutile titanium dioxide nanoparticles for efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic hydrogen production
Titanium dioxide is a promising photocatalyst for water splitting, although it suffers from low visible light activity. Here, the authors fabricate sub-10 nm rutile nanoparticles and investigate the role of surface/sub-surface defects in band-gap narrowing and enhanced charge-carrier separation.
- Landong Li
- , Junqing Yan
- & Naijia Guan
-
Article |
 Freezing-in orientational disorder induces crossover from thermally-activated to temperature-independent transport in organic semiconductors
Freezing-in orientational disorder induces crossover from thermally-activated to temperature-independent transport in organic semiconductors
The electronic properties of organic charge-transfer complexes are highly coupled to their crystallographic structures. Goetz et al.show that the librational motion can mediate a glass-like transition, resulting in a transition from temperature-activated to temperature-independent charge transport.
- K. P. Goetz
- , A. Fonari
- & O. D. Jurchescu
-
Article |
 Enhanced second-harmonic generation from metal-integrated semiconductor nanowires via highly confined whispering gallery modes
Enhanced second-harmonic generation from metal-integrated semiconductor nanowires via highly confined whispering gallery modes
Nanoscale light sources using nonlinearities are needed in many applications but their small size leads to very low efficiencies. Here, Ren et al.exploit the highly confined whispering gallery modes in metal-coated nanowires to achieve enhanced second-harmonic generation with minimal Ohmic losses.
- Ming-Liang Ren
- , Wenjing Liu
- & Ritesh Agarwal

 High-quality sandwiched black phosphorus heterostructure and its quantum oscillations
High-quality sandwiched black phosphorus heterostructure and its quantum oscillations