Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access UHRF1 suppresses retrotransposons and cooperates with PRMT5 and PIWI proteins in male germ cells
UHRF1 suppresses retrotransposons and cooperates with PRMT5 and PIWI proteins in male germ cells
Retrotransposons are silenced by an epigenetic mechanism and piRNA pathway in the mammalian germline. Here, the authors report that UHRF1 suppresses retrotransposons by interacting with PRMT5 and PIWI proteins during spermatogenesis.
- Juan Dong
- , Xiaoli Wang
- & Shuiqiao Yuan
-
Article
| Open Access Rare mutations in the complement regulatory gene CSMD1 are associated with male and female infertility
Rare mutations in the complement regulatory gene CSMD1 are associated with male and female infertility
Many molecular and physiological mechanisms in the regulation of fertility are shared between female and male mammals. Here, Lee et al. report an association of CNVs in CSMD1 with early idiopathic menopause in women and show that loss of Csmd1 leads to gonadal dysfunction in both male and female mice.
- Arthur S. Lee
- , Jannette Rusch
- & Donald F. Conrad
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular basis of egg coat cross-linking sheds light on ZP1-associated female infertility
Molecular basis of egg coat cross-linking sheds light on ZP1-associated female infertility
Glycoprotein ZP1 is a component of the oocyte’s zona pellucida (ZP), and mutations in human ZP1 are linked to female infertility. Here, using structure-function analysis, the authors suggest that filament cross-linking by ZP1 is required to form a stable ZP in human, and infertility mutations interfere with cross-linking.
- Kaoru Nishimura
- , Elisa Dioguardi
- & Luca Jovine
-
Article
| Open Access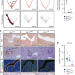 SOX17 regulates uterine epithelial–stromal cross-talk acting via a distal enhancer upstream of Ihh
SOX17 regulates uterine epithelial–stromal cross-talk acting via a distal enhancer upstream of Ihh
The transcription factor SOX17 is important for uterine gland formation, fertility, and embryo implantation in mouse. Here the authors show that SOX17 is upstream of Indian hedgehog to regulate mouse uterine receptivity, and their analysis of uterine tissue from endometriosis patients suggests the same function in humans.
- Xiaoqiu Wang
- , Xilong Li
- & Francesco J. DeMayo
-
Article
| Open Access SIRT1 mediates obesity- and nutrient-dependent perturbation of pubertal timing by epigenetically controlling Kiss1 expression
SIRT1 mediates obesity- and nutrient-dependent perturbation of pubertal timing by epigenetically controlling Kiss1 expression
The onset of mammalian puberty is sensitive to metabolic changes and nutritional status, but the mechanisms underlying this phenomenon are poorly understood. Here the authors show that the epigenetic regulator of transcription, SIRT1, mediates the effects of under and overnutrition on pubertal timing by controlling the expression of Kiss1 in hypothalamic neurons.
- M. J. Vazquez
- , C. A. Toro
- & M. Tena-Sempere
-
Article
| Open Access Mutations in CFAP43 and CFAP44 cause male infertility and flagellum defects in Trypanosoma and human
Mutations in CFAP43 and CFAP44 cause male infertility and flagellum defects in Trypanosoma and human
Asthenozoospermia is a major cause of male infertility, and multiple morphological abnormalities of the flagella (MMAF) is a particularly severe form. Here, using whole-exome sequencing of 78 MMAF patients, the authors identify mutations in two WDR proteins, CFAP43 and CFAP44, and confirm that these proteins are required for flagellogenesis in mouse and Trypanosoma brucei.
- Charles Coutton
- , Alexandra S. Vargas
- & Pierre F. Ray
-
Article
| Open Access Tridimensional visualization reveals direct communication between the embryo and glands critical for implantation
Tridimensional visualization reveals direct communication between the embryo and glands critical for implantation
Embryo implantation initiates the interaction of the blastocyst with the uterus and occurs within a specialised crypt formed by uterine epithelial cells. Here, using 3D imaging techniques of wild type and mutant uteri, the authors show that crypt formation occurs with preexisting glands of the uterus, opening communication between glands and the implanting embryo.
- Jia Yuan
- , Wenbo Deng
- & Sudhansu. K. Dey
-
Article
| Open Access Hypoxia and hypoxia inducible factor-1α are required for normal endometrial repair during menstruation
Hypoxia and hypoxia inducible factor-1α are required for normal endometrial repair during menstruation
About a quarter of pre-menopausal women will suffer from heavy menstrual bleeding in their lives. Here, Maybin and colleagues show hypoxia and subsequent activation of HIF-1α during menses are required for normal endometrial repair, and identify pharmacological stabilisation of HIF-1α as a potential therapeutic strategy for this debilitating condition.
- Jacqueline A. Maybin
- , Alison A. Murray
- & Hilary O. D. Critchley
-
Article
| Open Access The microbiota continuum along the female reproductive tract and its relation to uterine-related diseases
The microbiota continuum along the female reproductive tract and its relation to uterine-related diseases
Whether the female reproductive tract harbours distinct microbiomes beyond the vagina has been a matter of debate. Here, the authors show a subject-specific continuity in microbial communities at six sites along the female reproductive tract, indicative of a non-sterile environment.
- Chen Chen
- , Xiaolei Song
- & Huijue Jia
-
Article
| Open Access Common variants upstream of KDR encoding VEGFR2 and in TTC39B associate with endometriosis
Common variants upstream of KDR encoding VEGFR2 and in TTC39B associate with endometriosis
Endometriosis is a common gynaecological disease but the underlying pathogenesis is poorly understood, however there is a strong familial component. Here the authors conduct a genome wide association study and identify a novel susceptibility locus that correlates with disease severity.
- Valgerdur Steinthorsdottir
- , Gudmar Thorleifsson
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access Hypoxia causes transgenerational impairments in reproduction of fish
Hypoxia causes transgenerational impairments in reproduction of fish
Hypoxia has diverse effects on aquatic life. Wang et al.show that reproductive defects resulting from hypoxia are epigenetically heritable in Japanese rice fish, and that this intergenerational inheritance is accompanied by differential methylation and gene expression in sperm.
- Simon Yuan Wang
- , Karen Lau
- & Rudolf Shiu-Sun Wu
-
Article |
 Reduced selection and accumulation of deleterious mutations in genes exclusively expressed in men
Reduced selection and accumulation of deleterious mutations in genes exclusively expressed in men
Differential selection on sex-specific genes facilitates propagation of deleterious mutations. Here, the authors show that genes exclusively expressed in human testes harbour a greater number of deleterious mutations than genes expressed in both sexes, due to reduced selection in females.
- Moran Gershoni
- & Shmuel Pietrokovski
-
Article |
 Association analysis identifies new risk loci for non-obstructive azoospermia in Chinese men
Association analysis identifies new risk loci for non-obstructive azoospermia in Chinese men
Non-obstructive azoospermia (NOA) is a major cause of male infertility. Here, the authors provide insight into the genetic basis of NOA by identifying three new genetic risk loci in a genome-wide association study and reporting a fourth potential NOA susceptibility locus based on a Drosophilaknockdown experiment.
- Zhibin Hu
- , Zheng Li
- & Jiahao Sha
-
Article |
 Dependence of fertility on kisspeptin–Gpr54 signaling at the GnRH neuron
Dependence of fertility on kisspeptin–Gpr54 signaling at the GnRH neuron
The kisspeptin receptor GPR54 is implicated in the maintenance of mammalian fertility. Kirilov et al.study GPR54 mutant mice and identify a subset of neurons in the brain expressing gonadotropin-releasing hormone as the critical site for kisspeptin action.
- Milen Kirilov
- , Jenny Clarkson
- & Allan E. Herbison

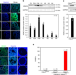 HDAC3 maintains oocyte meiosis arrest by repressing amphiregulin expression before the LH surge
HDAC3 maintains oocyte meiosis arrest by repressing amphiregulin expression before the LH surge