Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access SPOP mutation induces DNA methylation via stabilizing GLP/G9a
SPOP mutation induces DNA methylation via stabilizing GLP/G9a
The molecular mechanism underlying the DNA hypermethylation phenotype observed in the SPOP-mutant prostate cancers is unclear. Here, the authors show that mutant SPOP induces global aberrant DNA methylation patterns through GLP/G9a and renders prostate cancer cells susceptible to DNA demethylating agents.
- Jianong Zhang
- , Kun Gao
- & Haojie Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Inhibition of CK1ε potentiates the therapeutic efficacy of CDK4/6 inhibitor in breast cancer
Inhibition of CK1ε potentiates the therapeutic efficacy of CDK4/6 inhibitor in breast cancer
Acquisition of CDK4/6i resistance represents a major clinical challenge. Here, the authors report that inhibition of CK1ε can prevent acquisition of CDK4/6i resistance, potentiating the therapeutic efficacy of CDK4/6i in human breast cancer.
- Fabin Dang
- , Li Nie
- & Wenyi Wei
-
Article
| Open Access The E3 ubiquitin ligase component, Cereblon, is an evolutionarily conserved regulator of Wnt signaling
The E3 ubiquitin ligase component, Cereblon, is an evolutionarily conserved regulator of Wnt signaling
Cereblon (CRBN) is an E3 ubiquitin ligase substrate receptor that is involved in cancer cell death, although its regulation is poorly understood. Here, the authors show that Wnt ligand increases CRBN-dependent protein degradation and demonstrate CRBN’s importance in physiological Wnt signaling.
- Chen Shen
- , Anmada Nayak
- & David J. Robbins
-
Article
| Open Access Reconstitution defines the roles of p62, NBR1 and TAX1BP1 in ubiquitin condensate formation and autophagy initiation
Reconstitution defines the roles of p62, NBR1 and TAX1BP1 in ubiquitin condensate formation and autophagy initiation
Misfolded proteins are ubquitinated and subsequently condensed by cargo receptors for selective autophagy. Here, the authors use in vitro reconstitution to elegantly dissect how the receptors p62/SQSTM1, NBR1 and TAX1BP1 contribute to p62-ubiquitin condensate formation and degradation by autophagy.
- Eleonora Turco
- , Adriana Savova
- & Sascha Martens
-
Article
| Open Access PARylation prevents the proteasomal degradation of topoisomerase I DNA-protein crosslinks and induces their deubiquitylation
PARylation prevents the proteasomal degradation of topoisomerase I DNA-protein crosslinks and induces their deubiquitylation
TOP1 resolves DNA supercoils by forming cleavage complexes (TOP1cc) that are trapped by TOP1 inhibitors. Here the authors provide insights into the mechanistic understanding of TOP1cc PARylation, showing that inhibition of PARG results in stabilization of TOP1cc PARylation that blocks the proteasomal degradation of TOP1cc.
- Yilun Sun
- , Jiji Chen
- & Yves Pommier
-
Article
| Open Access MARCH8 inhibits influenza A virus infection by targeting viral M2 protein for ubiquitination-dependent degradation in lysosomes
MARCH8 inhibits influenza A virus infection by targeting viral M2 protein for ubiquitination-dependent degradation in lysosomes
The membrane-associated RING-CH (MARCH) proteins are E3 ligases regulating stability of plasma membrane (PM) proteins. Here, Liu et al. show that MARCH8 suppresses Influenza A virus infection in vitro and in vivo through redirecting M2 protein from the PM to lysosomes for degradation.
- Xiaoman Liu
- , Fengwen Xu
- & Fei Guo
-
Article
| Open Access UBE4B, a microRNA-9 target gene, promotes autophagy-mediated Tau degradation
UBE4B, a microRNA-9 target gene, promotes autophagy-mediated Tau degradation
Hyperphosphorylated Tau accumulation promotes neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Here, the authors screen a miRNA library in Drosophila and identify a conserved ubiquitin ligase that directs Tau for autophagic degradation, uncovering a potential target to treat Tau-mediated neurodegeneration.
- Manivannan Subramanian
- , Seung Jae Hyeon
- & Kweon Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of the human LONP1 protease reveal regulatory steps involved in protease activation
Structures of the human LONP1 protease reveal regulatory steps involved in protease activation
The human mitochondrial protease LONP1 is an AAA+ ATP-dependent quality control protease. Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structures of human LONP1 in three distinct states and provide insights into the mechanism and regulation of this important protease.
- Mia Shin
- , Edmond R. Watson
- & Gabriel C. Lander
-
Article
| Open Access Selective inhibition of cullin 3 neddylation through covalent targeting DCN1 protects mice from acetaminophen-induced liver toxicity
Selective inhibition of cullin 3 neddylation through covalent targeting DCN1 protects mice from acetaminophen-induced liver toxicity
Activation of cullin-RING ligases can be inhibited by targeting DCN1, but selective DCN1 inhibitors with in vivo activity are lacking. Here, the authors develop covalent DCN1 inhibitors that selectively and potently inhibit cullin-3 activation and downstream functions in cells and in mice.
- Haibin Zhou
- , Jianfeng Lu
- & Shaomeng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access MAEA is an E3 ubiquitin ligase promoting autophagy and maintenance of haematopoietic stem cells
MAEA is an E3 ubiquitin ligase promoting autophagy and maintenance of haematopoietic stem cells
Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are metabolically quiescent, with balanced myeloid and lymphoid potential. Here the authors show that MAEA is required in HSCs for ubiquitination and downregulation of surface cytokine receptors via autophagy; MAEA loss leads to impaired HSC quiescence and a myeloproliferative disorder.
- Qiaozhi Wei
- , Sandra Pinho
- & Paul S. Frenette
-
Article
| Open Access IP6-assisted CSN-COP1 competition regulates a CRL4-ETV5 proteolytic checkpoint to safeguard glucose-induced insulin secretion
IP6-assisted CSN-COP1 competition regulates a CRL4-ETV5 proteolytic checkpoint to safeguard glucose-induced insulin secretion
Mediators of insulin signalling are targets of cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases (CRL) that mediate protein degradation, but the role of protein degradation in insulin signalling is incompletely understood. Here, the authors identified a glucose-responsive CRL4-COP1-ETV5 proteolytic axis that promotes insulin secretion, and is inhibited under hypoglycemia.
- Hong Lin
- , Yuan Yan
- & Feng Rao
-
Article
| Open Access A slowly cleaved viral signal peptide acts as a protein-integral immune evasion domain
A slowly cleaved viral signal peptide acts as a protein-integral immune evasion domain
Glycoprotein US9 of human cytomegalovirus downregulates the activating immune ligand MICA*008 to avoid NK cell activation. Here, Seidel et al. show that the signal peptide of US9 is cleaved unusually slowly, causing MICA*008 to be retained in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and degraded via the ER quality control system.
- Einat Seidel
- , Liat Dassa
- & Ofer Mandelboim
-
Article
| Open Access Proteasomal degradation of the tumour suppressor FBW7 requires branched ubiquitylation by TRIP12
Proteasomal degradation of the tumour suppressor FBW7 requires branched ubiquitylation by TRIP12
The tumor suppressor FBW7 is a substrate adaptor for the E3 ubiquitin ligase complex SKP1-CUL1-F-box (SCF) and itself a target for ubiquitylation. Here, the authors show that TRIP12 mediates branched K11-linked ubiquitylation of FBW7, to regulate its stability and thus abundance of a subset of SCFFBW7 substrates.
- Omar M. Khan
- , Jorge Almagro
- & Axel Behrens
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping specificity, cleavage entropy, allosteric changes and substrates of blood proteases in a high-throughput screen
Mapping specificity, cleavage entropy, allosteric changes and substrates of blood proteases in a high-throughput screen
Characterizing proteases in their native environment is still challenging. Here, the authors develop a proteomics workflow for analyzing protease-specific peptides from cell lysates in 96-well format, providing mechanistic insights into blood proteases and enabling the prediction of protease substrates.
- Federico Uliana
- , Matej Vizovišek
- & Ruedi Aebersold
-
Article
| Open Access Antagonistic control of myofiber size and muscle protein quality control by the ubiquitin ligase UBR4 during aging
Antagonistic control of myofiber size and muscle protein quality control by the ubiquitin ligase UBR4 during aging
Sarcopenia is the age-associated functional decline and atrophy of muscle fibers, and it has been proposed that it might be counteracted by inducing myofiber hypertrophy. Here, the authors show that expression levels of the ubiquitin ligase UBR4 are increased with ageing, and that whilst its genetic ablation rescues muscle atrophy, it is also associated with reduced protein quality and impaired force production in Drosophila and mouse models.
- Liam C. Hunt
- , Bronwen Schadeberg
- & Fabio Demontis
-
Article
| Open Access VPS34 K29/K48 branched ubiquitination governed by UBE3C and TRABID regulates autophagy, proteostasis and liver metabolism
VPS34 K29/K48 branched ubiquitination governed by UBE3C and TRABID regulates autophagy, proteostasis and liver metabolism
Autophagy and the ubiquitin–proteasome system (UPS) are cellular quality control processes, but their coordination remains unclear. Here, the authors show that branched ubiquitination of VPS34 functions as a switch between UPS and autophagy and has an important role in lipid metabolism in the liver.
- Yu-Hsuan Chen
- , Tzu-Yu Huang
- & Ruey-Hwa Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Maintenance of type 2 glycolytic myofibers with age by Mib1-Actn3 axis
Maintenance of type 2 glycolytic myofibers with age by Mib1-Actn3 axis
Muscle atrophy is associated with ageing, but the underlying molecular mechanisms are not well understood. Here, they authors show that ablation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase Mib1 is important for myofibre maintenance via a mechanism that involves targeting and degradation of Actn3, and that Mib1 ablation in mice induces muscle atrophy which can be rescued by knockown of Actn3 expression.
- Ji-Yun Seo
- , Jong-Seol Kang
- & Young-Yun Kong
-
Article
| Open Access 20S proteasomes secreted by the malaria parasite promote its growth
20S proteasomes secreted by the malaria parasite promote its growth
Plasmodium falciparum secretes extracellular vesicles (EVs) while growing inside red blood cells (RBCs). Here the authors show that these EVs contain assembled and functional 20S proteasome complexes that remodel the cytoskeleton of naïve human RBCs, priming the RBCs for parasite invasion.
- Elya Dekel
- , Dana Yaffe
- & Neta Regev-Rudzki
-
Article
| Open Access Mutant-selective degradation by BRAF-targeting PROTACs
Mutant-selective degradation by BRAF-targeting PROTACs
Hundreds of BRAF mutations have been identified in patients with cancer but currently approved drugs only target BRAF V600 mutants. Here, the authors develop a vemurafenib-based PROTAC that induces degradation of all classes of BRAF mutants without affecting wild-type RAF proteins.
- Shanique Alabi
- , Saul Jaime-Figueroa
- & Craig M. Crews
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM of mammalian PA28αβ-iCP immunoproteasome reveals a distinct mechanism of proteasome activation by PA28αβ
Cryo-EM of mammalian PA28αβ-iCP immunoproteasome reveals a distinct mechanism of proteasome activation by PA28αβ
The proteasome activator PA28αβ affects MHC class I antigen presentation by associating with immunoproteasome core particles (iCPs). Cryo-EM structures of the mammalian PA28αβ -iCP immunoproteasome and free iCP, combined with cross-linking data, reveal the complex architecture and suggest a distinct immunoproteasome activation mechanism.
- Jinhuan Chen
- , Yifan Wang
- & Yao Cong
-
Article
| Open Access Microthermal-induced subcellular-targeted protein damage in cells on plasmonic nanosilver-modified surfaces evokes a two-phase HSP-p97/VCP response
Microthermal-induced subcellular-targeted protein damage in cells on plasmonic nanosilver-modified surfaces evokes a two-phase HSP-p97/VCP response
Existing methods for inflicting cellular heat shock are limited by the time delay in achieving the desired temperature and the spatial precision that can be achieved. Here the authors report a method to induce focused thermal protein damage using plasmonic silver nanoparticles.
- Martin Mistrik
- , Zdenek Skrott
- & Jiri Bartek
-
Article
| Open Access Functional cooperativity between the trigger factor chaperone and the ClpXP proteolytic complex
Functional cooperativity between the trigger factor chaperone and the ClpXP proteolytic complex
ClpXP is the main ATP-dependent proteolytic complex in bacteria, is essential for maintaining cellular protein homeostasis and is also critical for bacterial pathogenesis. Here, the authors establish a functional link between ClpXP and trigger actor, a chaperone involved in the early stages of protein folding.
- Kamran Rizzolo
- , Angela Yeou Hsiung Yu
- & Walid A. Houry
-
Article
| Open Access RETRACTED ARTICLE:The Arabidopsis NOT4A E3 ligase promotes PGR3 expression and regulates chloroplast translation
RETRACTED ARTICLE:The Arabidopsis NOT4A E3 ligase promotes PGR3 expression and regulates chloroplast translation
NOT4 proteins associate with ribosomes and are required for co-translational quality control in yeast and animals. Here, Bailey et al. show that Arabidopsis NOT4A positively regulates the expression of the nuclear encoded pentatricopeptide repeat (PPR) protein PGR3 and is required for ribosome biogenesis and mRNA translation in the chloroplast.
- Mark Bailey
- , Aiste Ivanauskaite
- & Daniel J. Gibbs
-
Article
| Open Access p62/SQSTM1-droplet serves as a platform for autophagosome formation and anti-oxidative stress response
p62/SQSTM1-droplet serves as a platform for autophagosome formation and anti-oxidative stress response
Liquid-liquid phase separation of p62/SQSTM1 has been previously described, although the significance in vivo remains unclear. Here the authors show p62 droplets contain ubiquitin, autophagy-related proteins and Keap1 to serve as platform of not only autophagosome formation but also Nrf2 activation.
- Shun Kageyama
- , Sigurdur Runar Gudmundsson
- & Masaaki Komatsu
-
Article
| Open Access Conformational maps of human 20S proteasomes reveal PA28- and immuno-dependent inter-ring crosstalks
Conformational maps of human 20S proteasomes reveal PA28- and immuno-dependent inter-ring crosstalks
Immune cells express immunoproteasomes (i20S), which bind to specialized regulators, contain different catalytic subunits and generate immunogenic peptides. HDX-MS—based assessment of the differences between the conformational dynamics of standard and i20s reveals specific, allosteric changes in i20S and upon regulator binding.
- Jean Lesne
- , Marie Locard-Paulet
- & Julien Marcoux
-
Article
| Open Access The Hsp70-Hsp90 co-chaperone Hop/Stip1 shifts the proteostatic balance from folding towards degradation
The Hsp70-Hsp90 co-chaperone Hop/Stip1 shifts the proteostatic balance from folding towards degradation
Hop, also known as Stip1 or Sti1, facilitates substrate transfer between the Hsp70 and Hsp90 molecular chaperones. Characterization of proteostasis-related pathways in STIP1 knock-out cell lines reveals that in eukaryotes Stip1 modulates the balance between protein folding and degradation.
- Kaushik Bhattacharya
- , Lorenz Weidenauer
- & Didier Picard
-
Article
| Open Access The auxin-inducible degron 2 technology provides sharp degradation control in yeast, mammalian cells, and mice
The auxin-inducible degron 2 technology provides sharp degradation control in yeast, mammalian cells, and mice
Auxin-inducible degron systems can be leaky and require high doses of auxin. Here the authors establish AID2 which uses an OsTIR1 mutant and the ligand 5-Ph-IAA to overcome these problems and establish AID-mediated target depletion in mice.
- Aisha Yesbolatova
- , Yuichiro Saito
- & Masato T. Kanemaki
-
Article
| Open Access Wipi3 is essential for alternative autophagy and its loss causes neurodegeneration
Wipi3 is essential for alternative autophagy and its loss causes neurodegeneration
Unlike canonical macroautophagy, alternative autophagy does not require the factors Atg5 and Atg7. Here, the authors show that Wipi3 is essential for alternative autophagy, but not for canonical autophagy, and that Wipi3 functions to maintain neuronal cells via mechanisms different from those of canonical autophagy.
- Hirofumi Yamaguchi
- , Shinya Honda
- & Shigeomi Shimizu
-
Article
| Open Access Cathepsin D deficiency in mammary epithelium transiently stalls breast cancer by interference with mTORC1 signaling
Cathepsin D deficiency in mammary epithelium transiently stalls breast cancer by interference with mTORC1 signaling
The lysosomal aspartic protease Cathepsin D (CTSD) is associated with breast cancer progression. Here the authors show that selective inactivation of CTSD in mammary epithelium delays tumor onset due to impaired mTORC1 signaling, but resumes malignant growth due to compensatory oncogenic pathways
- Stephanie Ketterer
- , Julia Mitschke
- & Thomas Reinheckel
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for substrate recognition and chemical inhibition of oncogenic MAGE ubiquitin ligases
Structural basis for substrate recognition and chemical inhibition of oncogenic MAGE ubiquitin ligases
Testis-restricted melanoma antigen (MAGE) proteins function as substrate adapters for E3 ubiquitin ligases. Biochemical and structural analyses of MAGE-A11 provide insight into the substrate binding mode of MAGE proteins and enable discovery of potent, cytotoxic inhibitors of MAGE-A11:substrate interaction.
- Seung Wook Yang
- , Xin Huang
- & Patrick Ryan Potts
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid and direct control of target protein levels with VHL-recruiting dTAG molecules
Rapid and direct control of target protein levels with VHL-recruiting dTAG molecules
The dTAG system is used to rapidly deplete tagged target proteins in vitro and in vivo, but there are context- and protein-specific differences in its effectiveness. Here, the authors develop a second generation dTAG molecule that can degrade previously recalcitrant target proteins in cells and mice.
- Behnam Nabet
- , Fleur M. Ferguson
- & Nathanael S. Gray
-
Article
| Open Access A phospho-switch controls RNF43-mediated degradation of Wnt receptors to suppress tumorigenesis
A phospho-switch controls RNF43-mediated degradation of Wnt receptors to suppress tumorigenesis
RNF43 is frequently mutated in cancers and negatively regulates Wnt signalling. Here, the authors report that RNF43 phosphorylation at a serine triplet is required for the negative regulation of Wnt signalling and that the phosphorylation of RNF43 suppresses cancer-associated oncogenic RNF43 mutants.
- Tadasuke Tsukiyama
- , Juqi Zou
- & Shigetsugu Hatakeyama
-
Article
| Open Access Structural bases of IMiD selectivity that emerges by 5-hydroxythalidomide
Structural bases of IMiD selectivity that emerges by 5-hydroxythalidomide
5-hydroxythalidomide is a primary thalidomide metabolite generated by the cytochrome P450 isozymes. The reported data, including crystal structure of the 5-hydroxythalidomide-mediated complex of CRBN with SALL4, elucidate how additional hydroxy group of the metabolite enhances the interaction of CRBN with the neosubstrate SALL4.
- Hirotake Furihata
- , Satoshi Yamanaka
- & Takuya Miyakawa
-
Article
| Open Access Epsin-mediated degradation of IP3R1 fuels atherosclerosis
Epsin-mediated degradation of IP3R1 fuels atherosclerosis
Endothelial cell (EC) dysfunction and inflammation contribute to plaque destabilization in atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of thrombotic events. Here, the authors show that epsin promotes EC inflammation via a mechanism involving IP3R1 degradation, and that deletion of epsin in the endothelium prevents EC dysfunctoin and atherosclerosis in mice.
- Yunzhou Dong
- , Yang Lee
- & Hong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access A deubiquitylase with an unusually high-affinity ubiquitin-binding domain from the scrub typhus pathogen Orientia tsutsugamushi
A deubiquitylase with an unusually high-affinity ubiquitin-binding domain from the scrub typhus pathogen Orientia tsutsugamushi
Many pathogens manipulate ubiquitin-mediated signaling to evade host cell defense. Here, the authors characterize the structure and enzymatic activity of a deubiquitylase domain from the causative pathogen of scrub typhus, providing evidence for a distinct mechanism of ubiquitin chain selectivity.
- Jason M. Berk
- , Christopher Lim
- & Mark Hochstrasser
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for DNA damage-induced phosphoregulation of MDM2 RING domain
Structural basis for DNA damage-induced phosphoregulation of MDM2 RING domain
p53 is an important tumor suppressor protein which is regulated by the E3 ubiquitin ligase MDM2. Here the authors reveal that DNA damage-induced Ser429 phosphorylation of MDM2 serve to boost the activity of MDM2 homodimer by stabilizing the active E2–ubiquitin complex and promote its self-destruction to enable rapid p53 stabilization.
- Helge M. Magnussen
- , Syed F. Ahmed
- & Danny T. Huang
-
Article
| Open Access A masked initiation region in retinoblastoma protein regulates its proteasomal degradation
A masked initiation region in retinoblastoma protein regulates its proteasomal degradation
Human papilloma virus (HPV) E7 protein destabilizes the retinoblastoma protein (Rb) by inducing its ubiquitination in cervical cancer cells, however proteasomal degradation requires cleavage of Rb after Lys 810 and so far it has been unclear how Rb cleavage contributes to its degradation. Here, the authors combine cell based and in vitro assays and show that calpain cleavage exposes a region in Rb that is recognized by the proteasome, leading to rapid proteolysis of Rb, whereas the proteasome cannot initiate degradation efficiently on full-length Rb.
- Takuya Tomita
- , Jon M. Huibregtse
- & Andreas Matouschek
-
Article
| Open Access A salvage pathway maintains highly functional respiratory complex I
A salvage pathway maintains highly functional respiratory complex I
Maintenance and quality control of the mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes responsible for bulk energy production are unclear. Here, the authors show that the mitochondrial protease ClpXP is required for the rapid turnover of the core N-module of respiratory complex I, which happens independently of other modules in the complex.
- Karolina Szczepanowska
- , Katharina Senft
- & Aleksandra Trifunovic
-
Article
| Open Access FAM111A protects replication forks from protein obstacles via its trypsin-like domain
FAM111A protects replication forks from protein obstacles via its trypsin-like domain
DNA-protein crosslinks represent obstacles on genomic DNA that can hamper progression of replication forks. Here, the authors reveal that FAM111A, a PCNA-interacting protein, plays part in mitigating the effect of protein obstacles on replication forks.
- Yusuke Kojima
- , Yuka Machida
- & Yuichi J. Machida
-
Article
| Open Access TEX264 coordinates p97- and SPRTN-mediated resolution of topoisomerase 1-DNA adducts
TEX264 coordinates p97- and SPRTN-mediated resolution of topoisomerase 1-DNA adducts
Eukaryotic topoisomerase 1 (TOP1) regulates DNA topology to ensure efficient DNA replication and transcription. Here, the authors reveal insights into the molecular resolution of topoisomerase 1-DNA adducts by TEX264, p97 and SPRTN.
- John Fielden
- , Katherine Wiseman
- & Kristijan Ramadan
-
Article
| Open Access Cross-talks of glycosylphosphatidylinositol biosynthesis with glycosphingolipid biosynthesis and ER-associated degradation
Cross-talks of glycosylphosphatidylinositol biosynthesis with glycosphingolipid biosynthesis and ER-associated degradation
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchors are found on many cell surface proteins but their biosynthesis is not fully understood. Here, the authors identify genes involved in GPI galactosylation and reveal functional connections between GPI processing, glycosphingolipid biosynthesis and ER-associated degradation.
- Yicheng Wang
- , Yusuke Maeda
- & Taroh Kinoshita
-
Article
| Open Access The proteasome 19S cap and its ubiquitin receptors provide a versatile recognition platform for substrates
The proteasome 19S cap and its ubiquitin receptors provide a versatile recognition platform for substrates
Ubiquitylated proteins are degraded by the proteasome and the three proteasome subunits Rpn10, Rpn13 and Rpn1 recognize ubiquitin chains. Here the authors employ biochemical and kinetic assays and characterise the ubiquitin chain type specificities of these three ubiquitin receptors.
- Kirby Martinez-Fonts
- , Caroline Davis
- & Andreas Matouschek
-
Article
| Open Access Golgi organization is regulated by proteasomal degradation
Golgi organization is regulated by proteasomal degradation
Correct Golgi assembly is important to cellular homeostasis but regulation of its structure under stress remains unclear. Here, the authors identify stress-induced degradation of GM130 by Golgi-localized 26S proteasomes, leading to Golgi dispersal.
- Avital Eisenberg-Lerner
- , Ron Benyair
- & Yifat Merbl
-
Article
| Open Access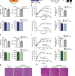 Sestrin prevents atrophy of disused and aging muscles by integrating anabolic and catabolic signals
Sestrin prevents atrophy of disused and aging muscles by integrating anabolic and catabolic signals
Ageing is associated with muscle atrophy, which negatively impacts quality of life. Here the authors show that expression of sestrins decreases during inactivity and that their overexpression prevents atrophy in mice via modulation of autophagy and protein degradation.
- Jessica Segalés
- , Eusebio Perdiguero
- & Pura Muñoz-Cánoves
-
Article
| Open Access SKP2 attenuates autophagy through Beclin1-ubiquitination and its inhibition reduces MERS-Coronavirus infection
SKP2 attenuates autophagy through Beclin1-ubiquitination and its inhibition reduces MERS-Coronavirus infection
Here, Gassen et al. show that S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (SKP2) is responsible for lysine-48-linked poly-ubiquitination of beclin 1, resulting in its proteasomal degradation, and that inhibition of SKP2 enhances autophagy and reduces replication of MERS coronavirus.
- Nils C. Gassen
- , Daniela Niemeyer
- & Theo Rein
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into ubiquitin recognition and Ufd1 interaction of Npl4
Structural insights into ubiquitin recognition and Ufd1 interaction of Npl4
The Lys48-linked polyubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation in yeast depends on Cdc48 and its cofactors Ufd1 and Npl4. Here, the authors present crystal structures of Npl4 bound to Lys48-linked diubiquitin and the Npl4-binding motif of Ufd1, providing insights into the reaction mechanism of the Cdc48- Ufd1/Npl4 complex.
- Yusuke Sato
- , Hikaru Tsuchiya
- & Shuya Fukai
-
Article
| Open Access Nestin regulates cellular redox homeostasis in lung cancer through the Keap1–Nrf2 feedback loop
Nestin regulates cellular redox homeostasis in lung cancer through the Keap1–Nrf2 feedback loop
Loss of Nestin sensitizes non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) to oxidative stress. Here, the authors report a feedback loop between Nestin and Nrf2 wherein Nestin competes with Nrf2 for Keap1 binding, preventing Nrf2 degradation, and show the Nestin–Keap1–Nrf2 axis to regulate redox homeostasis in NSCLC.
- Jiancheng Wang
- , Qiying Lu
- & Andy Peng Xiang
-
Article
| Open Access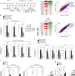 HCMV-encoded US7 and US8 act as antagonists of innate immunity by distinctively targeting TLR-signaling pathways
HCMV-encoded US7 and US8 act as antagonists of innate immunity by distinctively targeting TLR-signaling pathways
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) has evolved several mechanisms to evade the host immune response. Here, Park et al. show that HCMV-encoded US7 and US8 proteins bind TLR3 and TLR4 and facilitate TLR degradation by distinct mechanisms, including ER-associated and lysosomal degradation.
- Areum Park
- , Eun A. Ra
- & Boyoun Park
-
Article
| Open Access USP7 inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling through promoting stabilization of Axin
USP7 inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling through promoting stabilization of Axin
Axin is a scaffolding protein known for its role in Wnt signalling that can be marked with a variety of post-translational modifications. Here, Cong et al. demonstrate that USP7 de-ubiquinates Axin and that canonical Wnt signaling output can be increased with USP7 inhibitors.
- Lei Ji
- , Bo Lu
- & Feng Cong

 The 20S as a stand-alone proteasome in cells can degrade the ubiquitin tag
The 20S as a stand-alone proteasome in cells can degrade the ubiquitin tag