Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional bicontinuous nanoporous materials by vapor phase dealloying
Three-dimensional bicontinuous nanoporous materials by vapor phase dealloying
Conventional dealloying methods to produce bicontinuous open nanoporous structures for catalysis are limited to very few alloys and produce chemical waste. Here, the authors develop a green process, vapor-phase dealloying, to selectively remove high partial vapor pressure components and create nanoporosity in a wide range of alloys.
- Zhen Lu
- , Cheng Li
- & Mingwei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access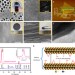 MXene molecular sieving membranes for highly efficient gas separation
MXene molecular sieving membranes for highly efficient gas separation
Two-dimensional materials show great potential for membrane technologies, but their disordered channels hinder their molecular sieving performance. Here, Wang, Gogotsi and colleagues design a MXene membrane with ordered nanochannels that exhibits an excellent H2/CO2 gas separation performance.
- Li Ding
- , Yanying Wei
- & Yury Gogotsi
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrathin graphene oxide-based hollow fiber membranes with brush-like CO2-philic agent for highly efficient CO2 capture
Ultrathin graphene oxide-based hollow fiber membranes with brush-like CO2-philic agent for highly efficient CO2 capture
Membrane separation technologies show promise for CO2 capture, but typically suffer from a trade-off between permeance and selectivity. Here, the authors produce hollow fiber membranes coated with graphene oxide and a CO2-philic agent that can efficiently separate CO2 from flue gas under wet conditions.
- Fanglei Zhou
- , Huynh Ngoc Tien
- & Miao Yu
-
Article
| Open Access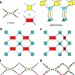 Redox-switchable breathing behavior in tetrathiafulvalene-based metal–organic frameworks
Redox-switchable breathing behavior in tetrathiafulvalene-based metal–organic frameworks
Modulating the adsorption behaviours of metal-organic frameworks using external stimuli is desirable, but challenging to achieve. Here, Zhou and colleagues design an indium-based MOF in which tetrathiafulvalene ligands undergo reversible redox reactions that alter the framework breathing behaviour.
- Jian Su
- , Shuai Yuan
- & Hong-Cai Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access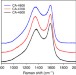 Oxygen-rich microporous carbons with exceptional hydrogen storage capacity
Oxygen-rich microporous carbons with exceptional hydrogen storage capacity
Hydrogen is attractive as a clean fuel for motor vehicles and porous carbons represent promising hydrogen storage materials. Here, Mokaya and colleagues incorporate oxygen-rich functional groups into porous carbons with high microporosity, showing that such materials exhibit significantly enhanced H2 storage capacity.
- L. Scott Blankenship
- , Norah Balahmar
- & Robert Mokaya
-
Article
| Open Access Inflating hollow nanocrystals through a repeated Kirkendall cavitation process
Inflating hollow nanocrystals through a repeated Kirkendall cavitation process
Owing to their unique properties, hollow metal nanocrystals demonstrate greater catalytic promise than their solid counterparts. Here the authors produce hollow and inflated palladium nanocrystals with thin shells via a repeated Kirkendall cavitation process, and demonstrate their activity for formic acid oxidation.
- He Tianou
- , Weicong Wang
- & Yadong Yin
-
Article
| Open Access Multifunctional nanocomposite hollow fiber membranes by solvent transfer induced phase separation
Multifunctional nanocomposite hollow fiber membranes by solvent transfer induced phase separation
Coating porous membranes with nanoparticles can enhance their separation and antifouling properties, but methods to do so remain complex. Here, Lee and colleagues use solvent transfer-induced phase separation to prepare nanoparticle-functionalized hollow fiber membranes from bicontinuous interfacially jammed emulsion gels.
- Martin F. Haase
- , Harim Jeon
- & Daeyeon Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchical self-entangled carbon nanotube tube networks
Hierarchical self-entangled carbon nanotube tube networks
Low-dimensional nanomaterials are crucial conducting components of stretchable electronics, but their mechanical reinforcement remains challenging. Here, the authors infiltrate carbon nanotubes into a porous ceramic network to produce a 3D nanofelted self-entangled assembly with high conductivity and mechanical stability.
- Fabian Schütt
- , Stefano Signetti
- & Rainer Adelung
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogen substituted graphdiyne as carbon-rich flexible electrode for lithium and sodium ion batteries
Hydrogen substituted graphdiyne as carbon-rich flexible electrode for lithium and sodium ion batteries
Flexible batteries have been used to power wearable smart electronics and implantable medical devices. Here, the authors report a carbon-rich flexible hydrogen substituted graphdiyne electrode exhibiting superior electrochemical performance in lithium and sodium ion batteries.
- Jianjiang He
- , Ning Wang
- & Yuliang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrathin two-dimensional porous organic nanosheets with molecular rotors for chemical sensing
Ultrathin two-dimensional porous organic nanosheets with molecular rotors for chemical sensing
Molecular rotors that fluoresce upon restriction are useful components in functional materials. Here, the authors incorporate molecular rotors into 2D porous organic nanosheets, creating sensitive and selective fluorescent sensors for volatile organic compounds and metal ions.
- Jinqiao Dong
- , Kang Zhang
- & Dan Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering the internal surfaces of three-dimensional nanoporous catalysts by surfactant-modified dealloying
Engineering the internal surfaces of three-dimensional nanoporous catalysts by surfactant-modified dealloying
Tuning the ratio of facets in materials can affect catalytic activity but methods to achieve this can be difficult to control. Here, using surfactants during dealloying, the authors prepare nanoporous gold with controlled facet ratios and show how it can significantly improve electrocatalytic activity.
- Zhili Wang
- , Pan Liu
- & Mingwei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access A three-dimensional view of structural changes caused by deactivation of fluid catalytic cracking catalysts
A three-dimensional view of structural changes caused by deactivation of fluid catalytic cracking catalysts
Catalyst deactivation in fluid catalytic cracking processes is unavoidably associated with structural changes. Here, the authors visualize the deactivation of zeolite catalysts by ptychography and other imaging techniques, showing pronounced amorphization of the outer layer of the catalyst particles.
- J. Ihli
- , R. R. Jacob
- & J. A. van Bokhoven
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible supercapacitor electrodes based on real metal-like cellulose papers
Flexible supercapacitor electrodes based on real metal-like cellulose papers
With ligand-mediated layer-by-layer assembly between metal nanoparticles and small organic molecules, the authors prepare metallic paper electrodes for supercapacitors with high power and energy densities. This approach could be extended to various electrodes for portable/wearable electronics.
- Yongmin Ko
- , Minseong Kwon
- & Jinhan Cho
-
Article
| Open Access A rechargeable iodine-carbon battery that exploits ion intercalation and iodine redox chemistry
A rechargeable iodine-carbon battery that exploits ion intercalation and iodine redox chemistry
Carbon-based electrodes able to intercalate Li+ and Na+ ions have been exploited for high performing energy storage devices. Here, the authors combine the ion intercalation properties of porous graphitic carbons with the redox chemistry of iodine to produce iodine–carbon batteries with high reversible capacities.
- Ke Lu
- , Ziyu Hu
- & Jintao Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Thermally-drawn fibers with spatially-selective porous domains
Thermally-drawn fibers with spatially-selective porous domains
Porous polymer fibers show great potential for a range of applications, but their simple structures typically limit their functionality. Here, the authors combine a thermal drawing process with polymer solution phase separation to fabricate porous multimaterial fibers with complex internal architectures.
- Benjamin Grena
- , Jean-Baptiste Alayrac
- & Yoel Fink
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of ordered carbonaceous frameworks from organic crystals
Synthesis of ordered carbonaceous frameworks from organic crystals
Carbon-based materials are promising alternatives to noble metal catalysts, but their structures are typically disordered and difficult to control. Here, the authors obtain ordered carbonaceous frameworks with advantageous electrocatalytic properties via the carbonization of nickel-containing porphyrin dimer networks.
- Hirotomo Nishihara
- , Tetsuya Hirota
- & Fumito Tani
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchical porous carbons with layer-by-layer motif architectures from confined soft-template self-assembly in layered materials
Hierarchical porous carbons with layer-by-layer motif architectures from confined soft-template self-assembly in layered materials
2D nanomaterials are promising capacitive energy storage materials, but their tendency to restack hinders electrolyte transport. Here, Yamauchi and colleagues introduce 2D ordered mesoporous carbons in between MXene layers, and metal removal affords all-carbon porous 2D–2D heterostructures in which restacking is prevented.
- Jie Wang
- , Jing Tang
- & Yusuke Yamauchi
-
Article
| Open Access Temperature-regulated guest admission and release in microporous materials
Temperature-regulated guest admission and release in microporous materials
Regulating guest access and release in porous materials remains an important goal. Here, May and colleagues elucidate the mechanism by which guest admission can be temperature-regulated in typical microporous materials, and experimentally exploit this process to achieve appreciable and reversible hydrogen storage.
- Gang (Kevin) Li
- , Jin Shang
- & Eric F. May
-
Article
| Open Access The controlled disassembly of mesostructured perovskites as an avenue to fabricating high performance nanohybrid catalysts
The controlled disassembly of mesostructured perovskites as an avenue to fabricating high performance nanohybrid catalysts
Disassembly of three-dimensionally ordered materials generates nanoparticles with new structural and physicochemical properties. Here the authors show a fragmentation strategy applied to a perovskite material leading to nanostructures with improved catalytic activity in the methane combustion.
- Yuan Wang
- , Hamidreza Arandiyan
- & Rose Amal
-
Article
| Open Access Ion-specific ice recrystallization provides a facile approach for the fabrication of porous materials
Ion-specific ice recrystallization provides a facile approach for the fabrication of porous materials
Ice recrystallization is important for a range of research fields, both applied and fundamental, however the effect of ions on this process is not well known. Here the authors discover an ion-specific Hofmeister type effect on ice recrystallization, using this phenomenon to prepare porous materials with tuneable pore sizes.
- Shuwang Wu
- , Chongqin Zhu
- & Jianjun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Solid-state synthesis of ordered mesoporous carbon catalysts via a mechanochemical assembly through coordination cross-linking
Solid-state synthesis of ordered mesoporous carbon catalysts via a mechanochemical assembly through coordination cross-linking
Ordered mesoporous carbons have shown promise in a range of applications, but sustainable methods to achieve their large scale production are lacking. Here, Dai and coworkers produce OMCs via the mechanochemical assembly of non-toxic polyphenol-metal complexes and triblock copolymers, followed by pyrolysis.
- Pengfei Zhang
- , Li Wang
- & Sheng Dai
-
Article
| Open Access Bio-inspired Murray materials for mass transfer and activity
Bio-inspired Murray materials for mass transfer and activity
Plant and animal tissues have evolved to contain hierarchical networks of pores that maximize mass transfer and exchange. Here the authors fabricate bio-inspired materials with multi-scale macro–meso–micropores and show their enhanced performances as photocatalysts, gas sensors and Li-ion battery electrodes.
- Xianfeng Zheng
- , Guofang Shen
- & Bao-Lian Su
-
Article
| Open Access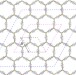 Adsorbate-induced lattice deformation in IRMOF-74 series
Adsorbate-induced lattice deformation in IRMOF-74 series
IRMOF-74 materials have thus far been thought to undergo only simple crystal lattice expansion upon gas adsorption. Here, Smit and co-workers demonstrate that these MOFs undergo a unique complex deformation upon argon uptake, changing how we view the fundamentals of adsorption in this series.
- Sudi Jawahery
- , Cory M. Simon
- & Berend Smit
-
Article
| Open Access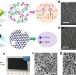 Synthesis of single-crystal-like nanoporous carbon membranes and their application in overall water splitting
Synthesis of single-crystal-like nanoporous carbon membranes and their application in overall water splitting
Hierarchical, nanoporous graphitic membranes are synthetically challenging yet attractive materials, due to their structural integrity. Here, the authors fabricate freestanding, porous carbon membranes with single-crystal-like graphitic order which serve as water splitting electrocatalysts upon cobalt doping.
- Hong Wang
- , Shixiong Min
- & Tom Wu
-
Article
| Open Access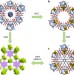 An ultra-tunable platform for molecular engineering of high-performance crystalline porous materials
An ultra-tunable platform for molecular engineering of high-performance crystalline porous materials
Synthetic design of crystalline porous materials is important for applications such as catalysis and adsorption. Here, the authors demonstrate a platform for the development of crystalline porous materials with a variety of organic ligands and metallic clusters, and control of their gas sorption properties.
- Quan-Guo Zhai
- , Xianhui Bu
- & Pingyun Feng
-
Article
| Open Access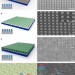 Ordered fragmentation of oxide thin films at submicron scale
Ordered fragmentation of oxide thin films at submicron scale
Fracture and related processes are typically considered detrimental, but have also attracted interest in more constructive roles. Here authors demonstrate ordered fragmentation at submicron scales of a metal oxide/hydroxide thin film by introducing preferential sites for fracture on the underlying substrate.
- L. Guo
- , Y. Ren
- & S. Y. Chiam
-
Article
| Open Access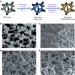 Efficient hydrogen evolution by ternary molybdenum sulfoselenide particles on self-standing porous nickel diselenide foam
Efficient hydrogen evolution by ternary molybdenum sulfoselenide particles on self-standing porous nickel diselenide foam
There is on-going research into efficient noble metal-free materials for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Here, the authors prepare ternary molybdenum sulfoselenide particles supported on three-dimensional porous nickel selenide foam, and demonstrate the high efficiency of the hydrogen evolving composite.
- Haiqing Zhou
- , Fang Yu
- & Zhifeng Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional protonic conductivity in porous organic cage solids
Three-dimensional protonic conductivity in porous organic cage solids
Proton conduction is a fundamental process for fuel cell development, but three-dimensional proton conduction in crystalline porous solids is rare. Here, the authors report organic molecular cages in which the structure imposes three-dimensional proton conductivity competing with metal-organic frameworks.
- Ming Liu
- , Linjiang Chen
- & Andrew I. Cooper
-
Article
| Open Access Epoxide-functionalization of polyethyleneimine for synthesis of stable carbon dioxide adsorbent in temperature swing adsorption
Epoxide-functionalization of polyethyleneimine for synthesis of stable carbon dioxide adsorbent in temperature swing adsorption
Carbon dioxide capture technologies have been implemented as a strategy to alleviate the environmental costs of CO2 emissions. Here, the authors synthesize a functionalized-polyethyleneimine/silica adsorbent for post-combustion CO2 capture that exhibits a large CO2capacity and long-term stability.
- Woosung Choi
- , Kyungmin Min
- & Minkee Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Asymmetric synthesis using chiral-encoded metal
Asymmetric synthesis using chiral-encoded metal
Chiral compounds are extremely important as they can be used in medicine, agriculture and biotechnology. Here, Kuhn and co-workers use a mesoporous metal structure encoded with chiral information in order to induce asymmetry in electrochemical synthesis of mandelic acid.
- Thittaya Yutthalekha
- , Chularat Wattanakit
- & Alexander Kuhn
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional porous carbon composites containing high sulfur nanoparticle content for high-performance lithium–sulfur batteries
Three-dimensional porous carbon composites containing high sulfur nanoparticle content for high-performance lithium–sulfur batteries
Lithium–sulfur batteries have high theoretical capacities but their performance is limited by poor conductivity and low stability. Here, the authors fabricate three-dimensional porous graphitic carbon composites containing sulfur nanoparticles and probe the effect of sulfur content on battery performance.
- Guoxing Li
- , Jinhua Sun
- & Jianxin Geng
-
Article
| Open Access Active porous transition towards spatiotemporal control of molecular flow in a crystal membrane
Active porous transition towards spatiotemporal control of molecular flow in a crystal membrane
Valve functionality is an essential tool for flow regulation in microfluidic systems. Here, the authors employ porous crystals which undergo mechanical reorientation of their internal subnanometer channels in order to manipulate spatiotemporal flow.
- Yuichi Takasaki
- & Satoshi Takamizawa
-
Article
| Open Access Sponge-like nanoporous single crystals of gold
Sponge-like nanoporous single crystals of gold
Naturally occurring single crystals can exhibit various intricate porous morphologies. Here, the authors are able to grow nanoporous single crystals of gold following solidification of a eutectic composition melt that forms as a result of the dewetting of nanometric thin films.
- Maria Koifman Khristosov
- , Leonid Bloch
- & Boaz Pokroy
-
Article
| Open Access Inward lithium-ion breathing of hierarchically porous silicon anodes
Inward lithium-ion breathing of hierarchically porous silicon anodes
Porous silicon is highly promising as an anode material in lithium ion batteries, but its volume change upon lithiation has deleterious effects upon efficiency. Here, the authors demonstrate porous shell/hollow core Si nanospheres which exhibit negligible outward expansion and maintain performance.
- Qiangfeng Xiao
- , Meng Gu
- & Mei Cai
-
Article
| Open Access Mesoporous MnCeOx solid solutions for low temperature and selective oxidation of hydrocarbons
Mesoporous MnCeOx solid solutions for low temperature and selective oxidation of hydrocarbons
Precious metal free catalysts for aerobic oxidation of hydrocarbons are industrially useful materials. Here, the authors report a mesoporous maganese-cerium oxide solid solution that is highly active for the selective oxidation of C-H bonds in hydrocarbons under mild conditions.
- Pengfei Zhang
- , Hanfeng Lu
- & Sheng Dai
-
Article
| Open Access Atomistic understandings of reduced graphene oxide as an ultrathin-film nanoporous membrane for separations
Atomistic understandings of reduced graphene oxide as an ultrathin-film nanoporous membrane for separations
Ultrathin-film nanoporous membranes promise low-cost and high-performance separation for applications such as water desalination and the purification of natural gas. Here, the authors adopt a molecular dynamics approach to assess the potential of reduced grapheme oxide as such a material.
- Li-Chiang Lin
- & Jeffrey C. Grossman
-
Article
| Open Access Coordination templated [2+2+2] cyclotrimerization in a porous coordination framework
Coordination templated [2+2+2] cyclotrimerization in a porous coordination framework
Nanospace defined by unsaturated metal coordination sites opens up the possibility of controlling and templating chemical reactivity. Here, the authors show that a Fe(III) dicarboxylate framework with triangularly arranged metal sites can direct the [2+2+2] cyclisation of nitriles, alkynes and alkenes.
- Yong-Sheng Wei
- , Mei Zhang
- & Xiao-Ming Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Uphill diffusion and overshooting in the adsorption of binary mixtures in nanoporous solids
Uphill diffusion and overshooting in the adsorption of binary mixtures in nanoporous solids
During the transient adsorption of a binary mixture in a nanoporous host, the concentration of one component may temporarily exceed its equilibrium value, with molecules diffusing in the direction of increasing concentration. Here, the authors use microimaging to examine this process in a real system.
- Alexander Lauerer
- , Tomas Binder
- & Jörg Kärger
-
Article
| Open Access A porous metal-organic framework with ultrahigh acetylene uptake capacity under ambient conditions
A porous metal-organic framework with ultrahigh acetylene uptake capacity under ambient conditions
The efficient storage of high-energy gaseous fuels is problematic due to the risk of explosion. Here, the authors design and employ a metal-organic framework composed of Cu(II) and an octacarboxylate ligand, which is able to store acetylene in high density but at atmospheric pressure.
- Jiandong Pang
- , Feilong Jiang
- & Maochun Hong
-
Article
| Open Access Facile synthesis of ultrahigh-surface-area hollow carbon nanospheres for enhanced adsorption and energy storage
Facile synthesis of ultrahigh-surface-area hollow carbon nanospheres for enhanced adsorption and energy storage
Well-defined, large surface area nanostructures are promising functional materials but can be difficult to fabricate. Here the authors show how to prepare ultrahigh-surface-area hollow carbon nanospheres, via a controlled carbonization route, and assess their organic vapour adsorption and electrochemical performance.
- Fei Xu
- , Zhiwei Tang
- & Dingcai Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Microporous metal–organic framework with dual functionalities for highly efficient removal of acetylene from ethylene/acetylene mixtures
Microporous metal–organic framework with dual functionalities for highly efficient removal of acetylene from ethylene/acetylene mixtures
The removal of acetylene from ethylene/acetylene mixtures is an industrially important but challenging task. Here the authors report a microporous metal–organic framework with optimized pore/cage space design and chemical functionalization, capable of removing acetylene from low concentration mixtures.
- Tong-Liang Hu
- , Hailong Wang
- & Banglin Chen
-
Article |
 Self-templated chemically stable hollow spherical covalent organic framework
Self-templated chemically stable hollow spherical covalent organic framework
Hollow, spherical nano/microstructures are potentially useful for energy and drug delivery applications. Here, the authors show that these structures can be fabricated from covalent organic frameworks, and exploit their chemical stability and mesoporous structures for enzyme encapsulation.
- Sharath Kandambeth
- , V. Venkatesh
- & Rahul Banerjee
-
Article
| Open Access Porous molybdenum carbide nano-octahedrons synthesized via confined carburization in metal-organic frameworks for efficient hydrogen production
Porous molybdenum carbide nano-octahedrons synthesized via confined carburization in metal-organic frameworks for efficient hydrogen production
There is extensive research into non-platinum electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution. Here, the authors report a molybdenum carbide catalyst, prepared via the carburization of a copper metal-organic framework host/molybdenum-based polyoxometalates guest system, and demonstrate its catalytic activity.
- Hao Bin Wu
- , Bao Yu Xia
- & Xiong Wen (David) Lou
-
Article |
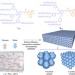 Mesoporous monoliths of inverse bicontinuous cubic phases of block copolymer bilayers
Mesoporous monoliths of inverse bicontinuous cubic phases of block copolymer bilayers
Solution self-assembly of block copolymers is one approach for creating porous materials with highly organized bicontinuous mesoporous networks. Here, the authors use copolymers with branched hydrophilic blocks to fabricate mesoporous monoliths with large-pore networks weaved in crystalline lattices.
- Chiyoung Park
- , Yunju La
- & Kyoung Taek Kim
-
Article |
 Self-catalysed aerobic oxidization of organic linker in porous crystal for on-demand regulation of sorption behaviours
Self-catalysed aerobic oxidization of organic linker in porous crystal for on-demand regulation of sorption behaviours
Controlling and selectively altering the structure of materials opens up the possibility of modulating their physical properties. Here, the authors report a method for altering the properties of a coordination polymer, where the metal centres active molecular oxygen to oxidize the organic ligand.
- Pei-Qin Liao
- , Ai-Xin Zhu
- & Xiao-Ming Chen
-
Article |
 Transparent air filter for high-efficiency PM2.5 capture
Transparent air filter for high-efficiency PM2.5 capture
Particulate matter pollution is a public health concern in industrialized and urban areas. Here, the authors control the surface chemistry and microstructure of filtration materials to fabricate effective and transparent air filters for the capture of PM2.5pollutants.
- Chong Liu
- , Po-Chun Hsu
- & Yi Cui
-
Article
| Open Access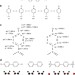 Porous coordination polymers with ubiquitous and biocompatible metals and a neutral bridging ligand
Porous coordination polymers with ubiquitous and biocompatible metals and a neutral bridging ligand
Inexpensive porous materials synthesized from Group II metals may be useful for industrial applications. Here, the authors demonstrate that neutral bridging ligands can be used for the synthesis of magnesium(II) and calcium(II) porous coordination polymers.
- Shin-ichiro Noro
- , Junya Mizutani
- & Takayoshi Nakamura
-
Article |
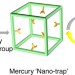 Mercury nano-trap for effective and efficient removal of mercury(II) from aqueous solution
Mercury nano-trap for effective and efficient removal of mercury(II) from aqueous solution
Decontamination of mercury pollution from fresh water is a serious environmental issue. Here, the authors report a porous organic polymer-based nano-trap, functionalized with mercury chelating groups, capable of efficient and rapid mercury removal from aqueous media.
- Baiyan Li
- , Yiming Zhang
- & Shengqian Ma
-
Article |
 A general and scalable synthesis approach to porous graphene
A general and scalable synthesis approach to porous graphene
Scalable routes towards porous graphene are useful for developing materials for mass transfer applications. Here, the authors report the fabrication of porous graphene with controllable pore size and nitrogen content via the carbothermal reaction of graphene and (poly)oxometallates.
- Ding Zhou
- , Yi Cui
- & Bao-Hang Han

 Facile storage and release of white phosphorus and yellow arsenic
Facile storage and release of white phosphorus and yellow arsenic