Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Endothelialization of arterial vascular grafts by circulating monocytes
Endothelialization of arterial vascular grafts by circulating monocytes
Acellular tissue engineered vessels functionalised with VEGF are coated with a layer of endothelial cells after in vivo implantation, but the source of the cells are unknown. Here the authors provide evidence that monocytes expressing VEGF receptors can transdifferentiate into endothelial cells via a macrophage intermediate.
- Randall J. Smith Jr.
- , Bita Nasiri
- & Stelios T. Andreadis
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular basis of ALK1-mediated signalling by BMP9/BMP10 and their prodomain-bound forms
Molecular basis of ALK1-mediated signalling by BMP9/BMP10 and their prodomain-bound forms
The molecular basis of activin receptor-like kinase 1 (ALK1)-mediated endothelial bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signalling is not fully understood. Here, the authors present crystal structures of the BMP10:ALK1 and prodomain-bound BMP9:ALK1 complexes, providing mechanistic insights into ALK1 signalling specificity.
- Richard M. Salmon
- , Jingxu Guo
- & Wei Li
-
Article
| Open Access Housing temperature influences exercise training adaptations in mice
Housing temperature influences exercise training adaptations in mice
Exercise has been shown to be an effective approach to ameliorate metabolic disease in mice housed at ambient temperatures, a condition of mild cold stress to mice. Here the authors show that molecular and metabolic adaptations to exercise are blunted when mice are housed in thermoneutral conditions.
- Steffen H. Raun
- , Carlos Henriquez-Olguín
- & Lykke Sylow
-
Article
| Open Access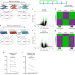 Transient non-integrative expression of nuclear reprogramming factors promotes multifaceted amelioration of aging in human cells
Transient non-integrative expression of nuclear reprogramming factors promotes multifaceted amelioration of aging in human cells
Aging involves gradual loss of tissue function, and transcription factor (TF) expression can ameliorate this in progeroid mice. Here the authors show that transient TF expression reverses age-associated epigenetic marks, inflammatory profiles and restores regenerative potential in naturally aged human cells.
- Tapash Jay Sarkar
- , Marco Quarta
- & Vittorio Sebastiano
-
Article
| Open Access Genomic analysis of male puberty timing highlights shared genetic basis with hair colour and lifespan
Genomic analysis of male puberty timing highlights shared genetic basis with hair colour and lifespan
Age at voice-breaking is used to determine puberty timing in men, recall of which is considered less accurate than age at first menarche in women. Here, the authors perform multi-trait GWAS for male puberty timing by including both age at voice breaking and age of first facial hair for improved phenotype definition and power.
- Ben Hollis
- , Felix R. Day
- & John R. B. Perry
-
Article
| Open Access Leptin receptor-expressing neuron Sh2b1 supports sympathetic nervous system and protects against obesity and metabolic disease
Leptin receptor-expressing neuron Sh2b1 supports sympathetic nervous system and protects against obesity and metabolic disease
Leptin regulates the sympathetic nervous system, energy expenditure and body weight through incompletely understood mechanisms. Here the authors report that Sh2b1 in leptin receptor positive neurons mediates the ability of leptin to stimulate sympathetic nerve activity in brown adipose tissue, body temperature and cold tolerance.
- Lin Jiang
- , Haoran Su
- & Liangyou Rui
-
Article
| Open Access FAM13A affects body fat distribution and adipocyte function
FAM13A affects body fat distribution and adipocyte function
Genetic variants in the FAM13A locus have been associated with anthropometric and glycemic traits. Here, using fine-mapping, in vitro knockdown studies in pre-adipocytes and in vivo knockout in mice, the authors show that FAM13A is involved in regulating fat distribution and metabolic traits.
- Mohsen Fathzadeh
- , Jiehan Li
- & Joshua W. Knowles
-
Article
| Open Access Olfactory specificity regulates lipid metabolism through neuroendocrine signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans
Olfactory specificity regulates lipid metabolism through neuroendocrine signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans
Olfaction is a key sensory modality with high diversity and olfactory defects has been associated with metabolic and neurodegenerative disorders. Here, the authors discovered that specific olfactory inputs actively regulate lipid metabolism in a dynamic and reversible manner.
- Ayse Sena Mutlu
- , Shihong Max Gao
- & Meng C. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access FGF6 and FGF9 regulate UCP1 expression independent of brown adipogenesis
FGF6 and FGF9 regulate UCP1 expression independent of brown adipogenesis
Uncoupling protein-1 (UCP1) plays a central role in energy dissipation in brown adipose tissue. Here the authors show that FGF6 and FGF9 induce UCP1 expression in adipocytes and preadipocytes, via modulation of a transcriptional network that is dissociated from brown adipogenesis.
- Farnaz Shamsi
- , Ruidan Xue
- & Yu-Hua Tseng
-
Article
| Open Access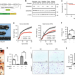 Grasp55−/− mice display impaired fat absorption and resistance to high-fat diet-induced obesity
Grasp55−/− mice display impaired fat absorption and resistance to high-fat diet-induced obesity
The physiological roles of the Golgi reassembly-stacking protein 55 (GRASP55/GORASP55) remain largely elusive. Here, the authors show that the Golgi-resident protein GRASP55 plays a crucial role in lipid homeostasis by regulating intestinal lipid uptake.
- Jiyoon Kim
- , Hyeyon Kim
- & Min Goo Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Quantification of the overall contribution of gene-environment interaction for obesity-related traits
Quantification of the overall contribution of gene-environment interaction for obesity-related traits
Most gene-by-environment interaction methods rely on the availability of the interacting environment. Here, the authors propose a robust maximum likelihood method for estimating the overall statistical interaction between a genetic risk score for a continuous outcome and all environmental variables.
- Jonathan Sulc
- , Ninon Mounier
- & Zoltán Kutalik
-
Article
| Open Access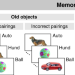 Sleep-dependent memory consolidation in infants protects new episodic memories from existing semantic memories
Sleep-dependent memory consolidation in infants protects new episodic memories from existing semantic memories
In infants, superiority of semantic over episodic memory formation has been postulated. Here, authors show that both types of memory coexist in one-year-olds, with consolidation during sleep affecting whether an experienced event is recognized as a detailed episode or as general semantic knowledge.
- Manuela Friedrich
- , Matthias Mölle
- & Jan Born
-
Article
| Open Access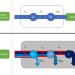 An analytical theory of balanced cellular growth
An analytical theory of balanced cellular growth
Genome-scale models of microbial metabolism largely ignore reaction kinetics. Here, the authors develop a general mathematical framework for modeling cellular growth with explicit non-linear reaction kinetics and use it to glean insights into the principles of cellular resource allocation and growth.
- Hugo Dourado
- & Martin J. Lercher
-
Article
| Open Access Adverse caregiving in infancy blunts neural processing of the mother
Adverse caregiving in infancy blunts neural processing of the mother
The roots of psychopathology take shape during adverse parent-infant interactions, shown through infant attachment quality. Using rodents, the authors show that blunted infant cortical processing of the mother determines attachment quality through a stress hormone-dependent mechanism.
- Maya Opendak
- , Emma Theisen
- & Regina M. Sullivan
-
Article
| Open Access Spectral cues are necessary to encode azimuthal auditory space in the mouse superior colliculus
Spectral cues are necessary to encode azimuthal auditory space in the mouse superior colliculus
Interaural timing and level differences had been considered the two important cues for horizontal sound localization. Here, the authors show that the third cue, spectral information, plays an essential role in the encoding of the azimuthal auditory map in the mouse superior colliculus.
- Shinya Ito
- , Yufei Si
- & Alan M. Litke
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo imaging of phosphocreatine with artificial neural networks
In vivo imaging of phosphocreatine with artificial neural networks
Phosphocreatine plays a vital role in cellular energetic homeostasis, but there are no routine diagnostic tests to noninvasively map the distribution with clinically relevant spatial resolution. Here, the authors develop and validate a noninvasive approach for quantifying and imaging phosphocreatine, without contrast agents, on widely available clinical MRI scanners with artificial neural networks.
- Lin Chen
- , Michael Schär
- & Jiadi Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Multiple network properties overcome random connectivity to enable stereotypic sensory responses
Multiple network properties overcome random connectivity to enable stereotypic sensory responses
Because of stochastic connections between some brain regions, an identified neuron can receive different inputs across individual animals and yet respond similarly to sensory stimuli. Here the authors reveal the network mechanisms that enable stereotypic sensory responses across individuals.
- Aarush Mohit Mittal
- , Diksha Gupta
- & Nitin Gupta
-
Article
| Open Access Collaborative interactions of heterogenous ribonucleoproteins contribute to transcriptional regulation of sterol metabolism in mice
Collaborative interactions of heterogenous ribonucleoproteins contribute to transcriptional regulation of sterol metabolism in mice
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs) play critical roles in the biogenesis, localization and transport of RNA. Here authors investigate a role for hnRNPs in sterol metabolism in mice and provide insights into their role in selective promoter activation.
- Zhengyi Zhang
- , An-Chieh Feng
- & Tamer Sallam
-
Article
| Open Access Alterations in promoter interaction landscape and transcriptional network underlying metabolic adaptation to diet
Alterations in promoter interaction landscape and transcriptional network underlying metabolic adaptation to diet
Metabolic adaptation to different diets results in changes to gene expression. Here, the authors characterise the chromatin landscape and transcriptional network in mice on a diet of high saturated fat, compared to a diet high in carbohydrate, finding a dramatic reprogramming of the liver transcriptional network.
- Yufeng Qin
- , Sara A. Grimm
- & Paul A. Wade
-
Article
| Open Access Histone demethylase JMJD1C is phosphorylated by mTOR to activate de novo lipogenesis
Histone demethylase JMJD1C is phosphorylated by mTOR to activate de novo lipogenesis
In response to insulin, liver cells increase de novo lipogenesis via the transcription factors USF-1 and SREBP. Here the authors show that USF-1 recruits JMJD1C, after its phosphorylation by mTOR, to lipogenic promoters where JMJD1C demethylates histone H3, contributing to lipogenesis by an epigenetic mechanism.
- Jose A. Viscarra
- , Yuhui Wang
- & Hei Sook Sul
-
Article
| Open Access Single cell analyses reveal contrasting life strategies of the two main nitrifiers in the ocean
Single cell analyses reveal contrasting life strategies of the two main nitrifiers in the ocean
Ammonia oxidizing archaea and Nitrospinae are the main known nitrifiers in the ocean, but the much greater abundance of the former is puzzling. Here, the authors show that differences in mortality, rather than thermodynamics, cell size or biomass yield, explain the discrepancy, without the need to invoke yet undiscovered, abundant nitrite oxidizers.
- Katharina Kitzinger
- , Hannah K. Marchant
- & Marcel M. M. Kuypers
-
Article
| Open Access Sexual-dimorphism in human immune system aging
Sexual-dimorphism in human immune system aging
Whether the immune system aging differs between men and women is barely known. Here the authors characterize gene expression, chromatin state and immune subset composition in the blood of healthy humans 22 to 93 years of age, uncovering shared as well as sex-unique alterations, and create a web resource to interactively explore the data.
- Eladio J. Márquez
- , Cheng-han Chung
- & Duygu Ucar
-
Article
| Open Access Liver governs adipose remodelling via extracellular vesicles in response to lipid overload
Liver governs adipose remodelling via extracellular vesicles in response to lipid overload
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) containing miRNAs or proteins can coordinate metabolic responses between tissues. Here the authors demonstrate that during lipid overload, the liver secretes miRNA-containing EVs through a Ggpps-Rab27 dependent mechanism, which controls adipose tissue lipid storage capacity.
- Yue Zhao
- , Meng-Fei Zhao
- & Chao-Jun Li
-
Article
| Open Access Nitric oxide orchestrates metabolic rewiring in M1 macrophages by targeting aconitase 2 and pyruvate dehydrogenase
Nitric oxide orchestrates metabolic rewiring in M1 macrophages by targeting aconitase 2 and pyruvate dehydrogenase
Production of inflammatory mediators by M1-polarized macrophages is thought to rely on suppression of mitochondrial metabolism in favor of glycolysis. Refining this concept, here the authors define metabolic targets of nitric oxide as responsible for the mitochondrial rewiring resulting from polarization.
- Erika M. Palmieri
- , Marieli Gonzalez-Cotto
- & Daniel W. McVicar
-
Article
| Open Access Loss of GFAT-1 feedback regulation activates the hexosamine pathway that modulates protein homeostasis
Loss of GFAT-1 feedback regulation activates the hexosamine pathway that modulates protein homeostasis
Mutations in the hexosamine pathway key enzyme glutamine fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase (GFAT-1) improve protein quality control and extend C. elegans lifespan. Here the authors present the crystal structures of full-length human GFAT-1 alone and with bound ligands and perform activity assays, which show that gain-of-function in the longevity-associated G451E variant is caused by a loss of feedback regulation.
- Sabine Ruegenberg
- , Moritz Horn
- & Martin S. Denzel
-
Article
| Open Access Endogenous FGF21-signaling controls paradoxical obesity resistance of UCP1-deficient mice
Endogenous FGF21-signaling controls paradoxical obesity resistance of UCP1-deficient mice
Brown adipose thermogenesis increases energy expenditure and relies on uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1), however, UCP1 knock-out mice show resistance to diet-induced obesity at room temperature. Here, the authors show that this resistance relies on FGF21-signaling, inducing the browning of white adipose tissue.
- Susanne Keipert
- , Dominik Lutter
- & Martin Jastroch
-
Comment
| Open Access Cellular adaptation to oxygen deficiency beyond the Nobel award
Cellular adaptation to oxygen deficiency beyond the Nobel award
Understanding the cellular adaptation to oxygen deficiency -hypoxia- has a profound impact on our knowledge of the pathogenesis of several diseases. The elucidation of the molecular machinery that regulates response to hypoxia has been awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
- José López-Barneo
- & M. Celeste Simon
-
Article
| Open Access Highly durable crack sensor integrated with silicone rubber cantilever for measuring cardiac contractility
Highly durable crack sensor integrated with silicone rubber cantilever for measuring cardiac contractility
Measuring cardiac contractility is challenging. Here, the authors encapsulated a crack-based sensor with polydimethylsiloxane, thereby endowing the sensor with the stability to measure cardiac contractility for up to 26 days as well as monitoring drug-induced cardiac toxicity in cell culture.
- Dong-Su Kim
- , Yong Whan Choi
- & Dong-Weon Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic deletion of mast cell serotonin synthesis prevents the development of obesity and insulin resistance
Genetic deletion of mast cell serotonin synthesis prevents the development of obesity and insulin resistance
Serotonin inhibits adipose tissue thermogenesis. Here the authors show that obese mice housed in thermoneutrality have increased mast cell serotonin synthesis, and that inhibiting this pathway through deletion of mast cell Tph1 increases white adipose tissue browning and protects against diet-induced obesity, insulin resistance and liver steatosis.
- Julian M. Yabut
- , Eric M. Desjardins
- & Gregory R. Steinberg
-
Article
| Open Access NPY mediates the rapid feeding and glucose metabolism regulatory functions of AgRP neurons
NPY mediates the rapid feeding and glucose metabolism regulatory functions of AgRP neurons
AgRP-expressing neurons regulate feeding, glucose homeostasis and locomotor activity, but the neurotransmitters that mediate these effects are unclear. Here the authors show that neuropeptide Y in these neurons regulates rapid feeding responses and insulin sensitivity, but not locomotor activity.
- Linda Engström Ruud
- , Mafalda M. A. Pereira
- & Jens C. Brüning
-
Article
| Open Access Non-canonical Wnt signalling regulates scarring in biliary disease via the planar cell polarity receptors
Non-canonical Wnt signalling regulates scarring in biliary disease via the planar cell polarity receptors
In fibrotic biliary disease, portal fibroblasts promote both biliary scarring and bile duct regeneration. Here, the authors report that the non-canonical Wnt-PCP signalling promotes bile duct scarring in mice, and inhibition of Wnt-ligands reduces the scarring without impairing regeneration.
- D. H. Wilson
- , E. J. Jarman
- & L. Boulter
-
Article
| Open Access The Medical Genome Reference Bank contains whole genome and phenotype data of 2570 healthy elderly
The Medical Genome Reference Bank contains whole genome and phenotype data of 2570 healthy elderly
Healthspan and healthy aging are areas of research with potential socioeconomic impact. Here, the authors present the Medical Genome Reference Bank (MGRB) which consist of over 4,000 individuals aged 70 years and older without a history of the major age-related diseases and report on results from whole-genome sequencing and association analyses.
- Mark Pinese
- , Paul Lacaze
- & David M. Thomas
-
Article
| Open Access Economic system justification predicts muted emotional responses to inequality
Economic system justification predicts muted emotional responses to inequality
Beliefs that justify the economic system buffer against the aversive emotional impact of inequality. Here the authors show that system-justifying economic ideology predicts dampened negativity, measured using self-reported and physiological responses, to manifestations of poverty and wealth.
- Shahrzad Goudarzi
- , Ruthie Pliskin
- & Eric D. Knowles
-
Article
| Open Access Distinctive phenotypes and functions of innate lymphoid cells in human decidua during early pregnancy
Distinctive phenotypes and functions of innate lymphoid cells in human decidua during early pregnancy
As an interface between maternal and fetal tissues, decidua hosts immune cells specialized in fostering a successful pregnancy. Here the authors carry out high-dimensional characterization of function, morphology and surface markers of human decidual innate lymphoid cells (ILCs), identifying subsets with features distinct from blood ILC.
- Oisín Huhn
- , Martin A. Ivarsson
- & Francesco Colucci
-
Article
| Open Access β4GALT1 controls β1 integrin function to govern thrombopoiesis and hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis
β4GALT1 controls β1 integrin function to govern thrombopoiesis and hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis
Mutations affecting sialylation and galactosylation affect megakaryocyte function and thrombopoiesis. Here the authors show that the enzyme β4GalT1 regulates thrombopoiesis and hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis by controlling beta-1 integrin function.
- Silvia Giannini
- , Melissa M. Lee-Sundlov
- & Karin M. Hoffmeister
-
Article
| Open Access A robust and efficient method for Mendelian randomization with hundreds of genetic variants
A robust and efficient method for Mendelian randomization with hundreds of genetic variants
Mendelian randomization (MR) is a method for inferring causal relationships between risk factors and outcomes via associated genetic variants. Here, Burgess et al. develop the contamination mixture method which yields robust MR results in the presence of invalid instrumental variables and groups variants by their effect estimates.
- Stephen Burgess
- , Christopher N Foley
- & Joanna M. M. Howson
-
Article
| Open Access A spontaneous mitonuclear epistasis converging on Rieske Fe-S protein exacerbates complex III deficiency in mice
A spontaneous mitonuclear epistasis converging on Rieske Fe-S protein exacerbates complex III deficiency in mice
A difference in the survival of respiratory chain complex III deficient Bcs1lp.S78G mice was observed between two congenic mouse strains. Here the authors show how in one of the strains the combined effects of a spontaneously arising non-pathogenic variant and the disease-causing Bcs1lp.S78G mutation exacerbate CIII deficiency and disease progression.
- Janne Purhonen
- , Vladislav Grigorjev
- & Jukka Kallijärvi
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanical sensing protein PIEZO1 regulates bone homeostasis via osteoblast-osteoclast crosstalk
Mechanical sensing protein PIEZO1 regulates bone homeostasis via osteoblast-osteoclast crosstalk
Mechanical forces induce bone remodeling, but how bone cells sense mechanical signaling is unclear. Here, the authors show that loss of the mechanotransduction channel Piezo1 in osteoblastic cells impairs osteoclast activity via YAP signaling and collagen expression, leading to reduced bone mass and spontaneous fractures.
- Lijun Wang
- , Xiuling You
- & Weiguo Zou
-
Article
| Open Access Sestrins are evolutionarily conserved mediators of exercise benefits
Sestrins are evolutionarily conserved mediators of exercise benefits
Exercise improves metabolic health and physical condition, particularly important for health in aged individuals. Here, the authors identify that Sestrins, proteins induced by exercise, are key mediators of the metabolic adaptation to exercise and increase endurance through the AKT and PGC1a axes.
- Myungjin Kim
- , Alyson Sujkowski
- & Jun Hee Lee
-
Article
| Open Access O-GlcNAc transferase inhibits visceral fat lipolysis and promotes diet-induced obesity
O-GlcNAc transferase inhibits visceral fat lipolysis and promotes diet-induced obesity
Post-translational O-linked β-N acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) modification acts as a nutrient-sensing mechanism. Here the authors report that O-GlcNAc transferase inhibits adipose tissue lipolysis via O-GlcNAcylation of the lipid droplet protein perilipin 1 and thus promotes diet-induced obesity.
- Yunfan Yang
- , Minnie Fu
- & Xiaoyong Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Astrocytes monitor cerebral perfusion and control systemic circulation to maintain brain blood flow
Astrocytes monitor cerebral perfusion and control systemic circulation to maintain brain blood flow
The brain receives 20% of cardiac output, but in accord with the current knowledge lacks a specialized sensor of its own blood flow. Here, the authors show that brain astrocytes detect drops in perfusion and trigger compensatory increases in arterial pressure and heart rate to preserve brain blood flow and oxygen delivery.
- Nephtali Marina
- , Isabel N. Christie
- & Alexander V. Gourine
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association and Mendelian randomisation analysis provide insights into the pathogenesis of heart failure
Genome-wide association and Mendelian randomisation analysis provide insights into the pathogenesis of heart failure
Heart failure is a complex syndrome that is associated with many different underlying risk factors. Here, to increase power, the authors jointly analyse cases of heart failure of different aetiologies in a genome-wide association study and identify 11 loci of which ten had not been previously reported.
- Sonia Shah
- , Albert Henry
- & R. Thomas Lumbers
-
Article
| Open Access DAF-16/FOXO requires Protein Phosphatase 4 to initiate transcription of stress resistance and longevity promoting genes
DAF-16/FOXO requires Protein Phosphatase 4 to initiate transcription of stress resistance and longevity promoting genes
The transcription factor DAF-16/FOXO mediates a wide variety of aging-preventive responses by driving the expression of stress resistance and longevity promoting genes. Here the authors show that transcriptional initiation at many DAF-16/FOXO target genes requires the dephosphorylation of SPT-5 by Protein Phosphatase 4.
- Ilke Sen
- , Xin Zhou
- & Christian G. Riedel
-
Article
| Open Access Generating ring-shaped engineered heart tissues from ventricular and atrial human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes
Generating ring-shaped engineered heart tissues from ventricular and atrial human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes
The cellular composition of previous engineered heart tissue is often heterogeneous. Here, the authors create chamber-specific human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes to form both ventricular and atrial cells before embedding in collagen-based matrix to form ring-shaped engineered heart tissue.
- Idit Goldfracht
- , Stephanie Protze
- & Lior Gepstein
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of osteoclast-osteoblast coupling factors in humans reveals links between bone and energy metabolism
Identification of osteoclast-osteoblast coupling factors in humans reveals links between bone and energy metabolism
Anti-resorptive bone therapies also inhibit bone formation, as osteoclasts secrete factors that stimulate bone formation by osteoblasts. Here, the authors identify osteoclast-secreted factors that couple bone resorption to bone formation in healthy subjects, and show that osteoclast-derived DPP4 may be a factor coupling bone resorption to energy metabolism.
- Megan M. Weivoda
- , Chee Kian Chew
- & Sundeep Khosla
-
Review Article
| Open Access Mitochondrial TCA cycle metabolites control physiology and disease
Mitochondrial TCA cycle metabolites control physiology and disease
Mitochondrial metabolites contribute to more than biosynthesis, and it is clear that they influence multiple cellular functions in a variety of ways. Here, Martínez-Reyes and Chandel review key metabolites and describe their effects on processes involved in physiology and disease including chromatin dynamics, immunity, and hypoxia.
- Inmaculada Martínez-Reyes
- & Navdeep S. Chandel
-
Article
| Open Access Mitochondrial oxidative capacity and NAD+ biosynthesis are reduced in human sarcopenia across ethnicities
Mitochondrial oxidative capacity and NAD+ biosynthesis are reduced in human sarcopenia across ethnicities
Sarcopenia is the loss of muscle mass and strength associated with physical disability during ageing. Here, the authors analyse muscle biopsies from 119 patients with sarcopenia and age-matched controls of different ethnic groups and find transcriptional signatures indicating mitochondrial dysfunction, associated with reduced mitochondria numbers and lower NAD+ levels in older individuals with sarcopenia.
- Eugenia Migliavacca
- , Stacey K. H. Tay
- & Jerome N. Feige
-
Article
| Open Access Edematous severe acute malnutrition is characterized by hypomethylation of DNA
Edematous severe acute malnutrition is characterized by hypomethylation of DNA
The edematous form of severe acute childhood malnutrition (ESAM) presents with more severe multi-organ dysfunction than non-edematous SAM (NESAM). Here the authors assess genome-wide DNA methylation in buccal cells of SAM children and find that ESAM is characterized by hypomethylation at genes associated with disorders of nutrition and metabolism, including fatty liver and diabetes.
- Katharina V. Schulze
- , Shanker Swaminathan
- & Neil A. Hanchard
-
Article
| Open Access Helix 8 is the essential structural motif of mechanosensitive GPCRs
Helix 8 is the essential structural motif of mechanosensitive GPCRs
GPCRs are versatile cellular sensors for chemical stimuli but the molecular mechanisms underlying mechanically induced GPCR activation have remained elusive. Here authors identify the C-terminal helix 8 (H8) as the essential structural motif endowing H1R and other GPCRs with mechanosensitivity.
- Serap Erdogmus
- , Ursula Storch
- & Michael Mederos y Schnitzler

 Genome-wide association study identifies 143 loci associated with 25 hydroxyvitamin D concentration
Genome-wide association study identifies 143 loci associated with 25 hydroxyvitamin D concentration