Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access OptoDyCE as an automated system for high-throughput all-optical dynamic cardiac electrophysiology
OptoDyCE as an automated system for high-throughput all-optical dynamic cardiac electrophysiology
The efficiency of preclinical drug testing and characterization of cellular function can be improved through the use of optogenetic tools. Here Klimas et al. present and validate OptoDyCE, a fully automated system for all-optical high-throughput cardiac electrophysiology.
- Aleksandra Klimas
- , Christina M. Ambrosi
- & Emilia Entcheva
-
Article
| Open Access Arrhythmia risk stratification of patients after myocardial infarction using personalized heart models
Arrhythmia risk stratification of patients after myocardial infarction using personalized heart models
Sudden arrhythmic death is a leading cause of mortality, however approaches to identify at-risk patients are of low sensitivity and specificity. Here, the authors develop a personalized approach to assess arrhythmia risk in post-infarction patients based on cardiac imaging and computational modelling that significantly outperforms existing clinical metrics.
- Hermenegild J. Arevalo
- , Fijoy Vadakkumpadan
- & Natalia A. Trayanova
-
Article
| Open Access Myoscape controls cardiac calcium cycling and contractility via regulation of L-type calcium channel surface expression
Myoscape controls cardiac calcium cycling and contractility via regulation of L-type calcium channel surface expression
Heart failure is a major public health issue but due to our poor disease understanding the current therapies are symptomatic. Here the authors identify Myoscape as a novel cardiac protein regulating membrane localization of the L-type calcium channel and heart's contractile force, thus promising new therapeutic avenues for heart failure.
- Matthias Eden
- , Benjamin Meder
- & Norbert Frey
-
Article
| Open Access Exosomal microRNA miR-92a concentration in serum reflects human brown fat activity
Exosomal microRNA miR-92a concentration in serum reflects human brown fat activity
Exosomes are RNA-containing lipid vesicles with roles in inter-tissue crosstalk. Here the authors show that exosome release from brown adipocytes is increased upon thermogenic activation, both in vitro and in vivo, and demonstrate that serum levels of exosomal miR-92 reflect brown fat activity in humans.
- Yong Chen
- , Joschka J. Buyel
- & Alexander Pfeifer
-
Article
| Open Access The obesity-induced transcriptional regulator TRIP-Br2 mediates visceral fat endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced inflammation
The obesity-induced transcriptional regulator TRIP-Br2 mediates visceral fat endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced inflammation
Visceral and subcutaneous fat are associated with different metabolic risk, but mediators of such depot specific effects are not very well known. Here the authors identify the transcriptional regulator, TRIP-Br2, as a regulator of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-induced inflammatory responses specifically in visceral fat.
- Guifen Qiang
- , Hyerim Whang Kong
- & Chong Wee Liew
-
Article
| Open Access Adipose tissue mTORC2 regulates ChREBP-driven de novo lipogenesis and hepatic glucose metabolism
Adipose tissue mTORC2 regulates ChREBP-driven de novo lipogenesis and hepatic glucose metabolism
The kinase mTOR controls anabolic metabolism. Here, the authors create fat-specific mTORC2 knockout mice using the Adiponectin-Cre driver and show mTORC2 signalling is important for systemic metabolic homeostasis by controlling adipocyte de novolipogenesis and glucose uptake.
- Yuefeng Tang
- , Martina Wallace
- & David A. Guertin
-
Article
| Open Access A two decade dementia incidence comparison from the Cognitive Function and Ageing Studies I and II
A two decade dementia incidence comparison from the Cognitive Function and Ageing Studies I and II
Future dramatic rises in dementia are widely reported, assuming no change in incidence. Matthews and colleagues report that, in contrast to such statements, age-specific incidence has dropped over 20 years, with overall incidence of dementia remaining stable in a large multi-site population study from England.
- F. E. Matthews
- , B. C. M. Stephan
- & G. Forster
-
Article
| Open Access ZBTB20 is required for anterior pituitary development and lactotrope specification
ZBTB20 is required for anterior pituitary development and lactotrope specification
The pituitary is a complex structure with the anterior lobe containing five specialized cell types secreting different hormones. Here Cao et al. unravel a role for ZBTB20 in pituitary development and specifically in lactrotrope specification.
- Dongmei Cao
- , Xianhua Ma
- & Weiping J. Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Prostacyclin-producing human mesenchymal cells target H19 lncRNA to augment endogenous progenitor function in hindlimb ischaemia
Prostacyclin-producing human mesenchymal cells target H19 lncRNA to augment endogenous progenitor function in hindlimb ischaemia
Human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSC) expressing paracrine factors may enhance therapeutic benefits when transplanted. Here, the authors show that hMSCs stably expressing prostacyclin enhance host regeneration and muscle mass gain in a mouse hindlimb ischaemia model, mediated by the long noncoding RNA H19.
- Yuxiao Deng
- , Zhongwei Yang
- & Qi Liu
-
Article
| Open Access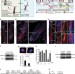 Signalling couples hair follicle stem cell quiescence with reduced histone H3 K4/K9/K27me3 for proper tissue homeostasis
Signalling couples hair follicle stem cell quiescence with reduced histone H3 K4/K9/K27me3 for proper tissue homeostasis
Changes in global histone trimethylation have been linked to embryonic but not adult stem cell plasticity. Here, Lee et al. find H3 K4/K9/K27me3 levels actively reduced in adult mouse skin and hair follicle stem cells during quiescence (catagen) and link this to active bone morphogen protein signalling.
- Jayhun Lee
- , Sangjo Kang
- & Tudorita Tumbar
-
Article
| Open Access ASK1 signalling regulates brown and beige adipocyte function
ASK1 signalling regulates brown and beige adipocyte function
The protein kinase ASK1 has been linked to cellular stress responses. Here the authors show that ASK1 also regulates gene expression and activity of beige and brown adipocytes, and demonstrate adipocyte ASK1 has a physiological role in regulating thermogenesis in mice.
- Kazuki Hattori
- , Isao Naguro
- & Hidenori Ichijo
-
Article
| Open Access Blood-based biomarkers of age-associated epigenetic changes in human islets associate with insulin secretion and diabetes
Blood-based biomarkers of age-associated epigenetic changes in human islets associate with insulin secretion and diabetes
Aging is associated with impaired pancreatic islet function, increased risk of type 2 diabetes, and changes in DNA methylation. Here the authors find blood-based biomarkers that reflect age-associated DNA methylation changes in human pancreatic islets associated with insulin secretion and diabetes.
- Karl Bacos
- , Linn Gillberg
- & Charlotte Ling
-
Article
| Open Access Variants near CHRNA3/5 and APOE have age- and sex-related effects on human lifespan
Variants near CHRNA3/5 and APOE have age- and sex-related effects on human lifespan
Understanding the genetic influences on human aging requires a large number of subjects for a study of sufficient power. Here, Jim Wilson and colleagues use information on parental ages at death to show that common variants near the genes for apolipoprotein E and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha 5 are associated with longer lifespan.
- Peter K. Joshi
- , Krista Fischer
- & James F. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access The plasma membrane calcium ATPase 4 signalling in cardiac fibroblasts mediates cardiomyocyte hypertrophy
The plasma membrane calcium ATPase 4 signalling in cardiac fibroblasts mediates cardiomyocyte hypertrophy
Restricting hypertrophic heart growth in response to pathologic overload is an unmet therapeutic need. Here, the authors show that blocking Ca2+signaling controlled by the transport protein PMCA4 in cardiac fibroblasts enhances secretion of a potent Wnt signaling inhibitor, sFRP2, and prevents the development of pathologic cardiac hypertrophy in mice.
- Tamer M. A. Mohamed
- , Riham Abou-Leisa
- & Delvac Oceandy
-
Article
| Open Access Defects in TRPM7 channel function deregulate thrombopoiesis through altered cellular Mg2+ homeostasis and cytoskeletal architecture
Defects in TRPM7 channel function deregulate thrombopoiesis through altered cellular Mg2+ homeostasis and cytoskeletal architecture
Although Mg2+is vital for platelet activation and aggregation, its regulation in these cells is still largely unknown. Here, the authors show that TRPM7, a cation channel and a protein kinase, regulates thrombopoiesis and platelet size by affecting the cytoskeleton of these cells in mice and humans.
- Simon Stritt
- , Paquita Nurden
- & Attila Braun
-
Article
| Open Access Fish optimize sensing and respiration during undulatory swimming
Fish optimize sensing and respiration during undulatory swimming
Head movements of swimming fishes are thought to exist only because of recoil of the oscillating tail. Here, Akanyeti et al. show that by controlling the timing of head movements, fish can improve their swimming efficiency while simultaneously optimizing sensing and respiration.
- O. Akanyeti
- , P. J. M. Thornycroft
- & J. C. Liao
-
Article
| Open Access Rotational manipulation of single cells and organisms using acoustic waves
Rotational manipulation of single cells and organisms using acoustic waves
The precise rotational manipulation of single cells is technically challenging and relies on the optical, magnetic and electrical properties of the biospecimen. Here the authors develop an acoustic-based, on-chip manipulation method that can rotate single microparticles, cells and organisms.
- Daniel Ahmed
- , Adem Ozcelik
- & Tony Jun Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic link between renal birth defects and congenital heart disease
Genetic link between renal birth defects and congenital heart disease
Using forward genetic screen in fetal mice, Gregory Pazour and colleagues describe mutants affecting kidney/urinary tract development. The authors also show that mutants that cause kidney defects overlaps with those leading to congenital heart defects, thus linking renal anomalies and congenital heart disease.
- Jovenal T. San Agustin
- , Nikolai Klena
- & Gregory J. Pazour
-
Article
| Open Access Mondo complexes regulate TFEB via TOR inhibition to promote longevity in response to gonadal signals
Mondo complexes regulate TFEB via TOR inhibition to promote longevity in response to gonadal signals
Removal of the C. elegans germline substantially increases organismal lifespan. Here, Nakamura et al. show that the transcription factors MML-1 and MXL-2 coordinate this process in that they reduce TOR signalling and increase autophagy by regulating activity of HLH-30.
- Shuhei Nakamura
- , Özlem Karalay
- & Adam Antebi
-
Article
| Open Access G6PD protects from oxidative damage and improves healthspan in mice
G6PD protects from oxidative damage and improves healthspan in mice
The enzyme G6PD generates the reductive metabolite NADPH, which has antioxidant effects, but has also been linked to tumour growth. Here the authors generate mice that modestly overexpress G6PD and report increased lifespan in females, and no negative effects on tumour formation in various genetic models.
- Sandrina Nóbrega-Pereira
- , Pablo J. Fernandez-Marcos
- & Manuel Serrano
-
Article
| Open Access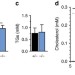 CCC- and WASH-mediated endosomal sorting of LDLR is required for normal clearance of circulating LDL
CCC- and WASH-mediated endosomal sorting of LDLR is required for normal clearance of circulating LDL
Low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) is crucial for cholesterol homeostasis. Here, the authors show that components of the CCC-protein complex, CCDC22 and COMMD1, facilitate the endosomal sorting of LDLR and that mutations in these genes cause hypercholesterolemia in dogs and mice, providing new insights into regulation of cholesterol homeostasis.
- Paulina Bartuzi
- , Daniel D. Billadeau
- & Bart van de Sluis
-
Article
| Open Access The Gq signalling pathway inhibits brown and beige adipose tissue
The Gq signalling pathway inhibits brown and beige adipose tissue
Brown and beige adipose tissues contribute to organismal energy expenditure by generating heat. Here, Klepac et al. survey G protein-coupled receptors in brown fat and show that Gq-coupled receptors inhibit expression of thermogenic proteins in mice and in human adipocytes.
- Katarina Klepac
- , Ana Kilić
- & Alexander Pfeifer
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of allosteric and synergistic activation of AMPK by furan-2-phosphonic derivative C2 binding
Structural basis of allosteric and synergistic activation of AMPK by furan-2-phosphonic derivative C2 binding
AMPK regulates the metabolism and so drugs that activate AMPK might have potential for the treatment of metabolic disease. Here, the authors report the structure of AMPK bound to an activating compound, revealing two binding sites and indicating that dual therapy might be a good drug strategy.
- Christopher G. Langendorf
- , Kevin R. W. Ngoei
- & Bruce E. Kemp
-
Article
| Open Access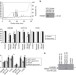 The HMGB1 protein induces a metabolic type of tumour cell death by blocking aerobic respiration
The HMGB1 protein induces a metabolic type of tumour cell death by blocking aerobic respiration
HMBG1 is a protein expressed in natural killer cells and is important in immunosurveillance. In this study, the authors show that HMGB1 binds to and inhibits PKM2, resulting in a block in aerobic glycolysis and ultimately cell death.
- Georg Gdynia
- , Sven W. Sauer
- & Wilfried Roth
-
Article
| Open Access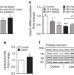 Hypothalamic leptin action is mediated by histone deacetylase 5
Hypothalamic leptin action is mediated by histone deacetylase 5
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) regulate energy metabolism in peripheral tissues, but whether HDACs expressed in the brain influence systemic metabolism is unknown. Here the authors show that hypothalamic HDAC5 expression is affected by the diet and HDAC5 regulates leptin sensitivity by deacetylating STAT3.
- Dhiraj G. Kabra
- , Katrin Pfuhlmann
- & Paul T. Pfluger
-
Article
| Open Access Rationally engineered Troponin C modulates in vivo cardiac function and performance in health and disease
Rationally engineered Troponin C modulates in vivo cardiac function and performance in health and disease
Heart contraction, which is decreased in disease, is determined by Ca2+binding to troponin C. Here, the authors combine a protein engineering approach with gene therapy to modulate heart contractility in mice with the use of rationally designed Troponin C variants, suggesting a new therapy for diseased hearts.
- Vikram Shettigar
- , Bo Zhang
- & Jonathan P. Davis
-
Article
| Open Access Human oocyte developmental potential is predicted by mechanical properties within hours after fertilization
Human oocyte developmental potential is predicted by mechanical properties within hours after fertilization
Reliable assessments of oocyte developmental potential are lacking, making it difficult to select the best quality embryos for transfer after in vitrofertilization. Here, the authors show that a non-invasive measurement of viscoelastic properties predicts developmental potential in both humans and mice.
- Livia Z. Yanez
- , Jinnuo Han
- & David B. Camarillo
-
Article
| Open Access Repositioning tolcapone as a potent inhibitor of transthyretin amyloidogenesis and associated cellular toxicity
Repositioning tolcapone as a potent inhibitor of transthyretin amyloidogenesis and associated cellular toxicity
Misfolding of transthyretin can cause amyloid aggregation disorders that can be treated by stabilizing the tetrameric form with tafamidis. Here the authors show that tolcapone, a drug already FDA-approved for Parkinson disease, has strong transthyretin stabilizing function and might be a superior therapeutic option for CNS amyloidosis as it can cross the blood brain barrier.
- Ricardo Sant'Anna
- , Pablo Gallego
- & Salvador Ventura
-
Article
| Open Access Tenomodulin promotes human adipocyte differentiation and beneficial visceral adipose tissue expansion
Tenomodulin promotes human adipocyte differentiation and beneficial visceral adipose tissue expansion
Expansion of visceral adipose tissue is usually associated with insulin resistance and metabolic disease. Here, the authors show that the membrane protein TNMD is upregulated in visceral fat of insulin resistant obese individuals and promotes healthy adipose tissue expansion through increasing adipogenesis.
- Ozlem Senol-Cosar
- , Rachel J. Roth Flach
- & Michael P. Czech
-
Article
| Open Access Endothelial Dicer promotes atherosclerosis and vascular inflammation by miRNA-103-mediated suppression of KLF4
Endothelial Dicer promotes atherosclerosis and vascular inflammation by miRNA-103-mediated suppression of KLF4
The RNAse III endonuclease Dicer is crucial for processing of pre-miRNAs in health and disease. Here the authors show that endothelial Dicer promotes atherosclerosis by increasing miR-103 levels leading to suppression of the anti-inflammatory transcription factor KLF4, thus suggesting a novel approach to treat this disease.
- Petra Hartmann
- , Zhe Zhou
- & Andreas Schober
-
Article
| Open Access PKR is not obligatory for high-fat diet-induced obesity and its associated metabolic and inflammatory complications
PKR is not obligatory for high-fat diet-induced obesity and its associated metabolic and inflammatory complications
Protein kinase R (PKR) has been suggested to act as a mediator of ER stress and inflammation in obesity. Here, Lancaster et al. find that genetic loss of PKR does not alter the development of obesity, and suggest that the use of littermate controls may explain differences in mouse knockout phenotypes.
- G. I. Lancaster
- , H. L. Kammoun
- & M. A. Febbraio
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-scale study reveals reduced metabolic adaptability in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Genome-scale study reveals reduced metabolic adaptability in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a risk factor for other types of liver diseases. Here, the authors integrate transcriptomic and metabolomic data from patients with NAFLD with a genome-scale metabolic model to paint a comprehensive picture of liver function in NAFLD.
- Tuulia Hyötyläinen
- , Livnat Jerby
- & Matej Orešič
-
Article
| Open Access New loci for body fat percentage reveal link between adiposity and cardiometabolic disease risk
New loci for body fat percentage reveal link between adiposity and cardiometabolic disease risk
A genome-wide association meta-analysis study here shows novel genetic loci to be associated to body fat percentage, and describes cross-phenotype association that further demonstrate a close relationship between adiposity and cardiovascular disease risk.
- Yingchang Lu
- , Felix R. Day
- & Ruth J. F. Loos
-
Article
| Open Access MDM2 E3 ligase-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of HDAC1 in vascular calcification
MDM2 E3 ligase-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of HDAC1 in vascular calcification
Vascular calcification (VC) increases morbidity and mortality in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Here, Kwon et al.show that calcification stimuli induce MDM2- mediated ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of HDAC1, suggesting a possible therapeutic strategy for treatment of VC patients.
- Duk-Hwa Kwon
- , Gwang Hyeon Eom
- & Hyun Kook
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide meta-analysis uncovers novel loci influencing circulating leptin levels
Genome-wide meta-analysis uncovers novel loci influencing circulating leptin levels
This meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies four genetic loci associated with circulating leptin levels independent of adiposity. Examination in mouse adipose tissue explants provides functional support for the leptin-associated loci.
- Tuomas O. Kilpeläinen
- , Jayne F. Martin Carli
- & Ruth J. F. Loos
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association study and targeted metabolomics identifies sex-specific association of CPS1 with coronary artery disease
Genome-wide association study and targeted metabolomics identifies sex-specific association of CPS1 with coronary artery disease
Dietary choline metabolites, such as trimethylamine N-oxide and betaine, have been associated with coronary artery disease (CAD). Here, Hartiala et al. identify two genetic loci for betaine levels on chromosomes 2q34 and 5q14.1 and find that the 2q34 locus was also associated with other pathway intermediates, and decreased risk of CAD in women.
- Jaana A. Hartiala
- , W. H. Wilson Tang
- & Hooman Allayee
-
Article
| Open Access Arrhythmogenesis in Timothy Syndrome is associated with defects in Ca2+-dependent inactivation
Arrhythmogenesis in Timothy Syndrome is associated with defects in Ca2+-dependent inactivation
Timothy Syndrome (TS) is a multisystem disorder caused by two mutations leading to dysfunction of the CaV1.2 channel. Here, Dick et al. uncover a major and mechanistically divergent effect of both mutations on Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent inactivation of CaV1.2 channels, suggesting genetic variant-tailored therapy for TS treatment.
- Ivy E. Dick
- , Rosy Joshi-Mukherjee
- & David T. Yue
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association studies in the Japanese population identify seven novel loci for type 2 diabetes
Genome-wide association studies in the Japanese population identify seven novel loci for type 2 diabetes
Here, Imamuraet al. conduct meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies to identify novel susceptibility loci for type 2 diabetes (T2D) in the Japanese population. By doing so, this study shows that both ethnicity-specific and ethnically-shared genetic loci can contribute to T2D risk.
- Minako Imamura
- , Atsushi Takahashi
- & Takashi Kadowaki
-
Article
| Open Access A mouse model for a partially inactive obesity-associated human MC3R variant
A mouse model for a partially inactive obesity-associated human MC3R variant
The melanocortin receptor, MC3R, regulates organismal energy homeostasis. Here, Lee et al. create knock-in mice with the a mutated version of the human MC3R receptor found in obese children, and show these mice have more fat and smaller bone, yet are by and large metabolically healthy.
- Bonggi Lee
- , Jashin Koo
- & Jack A. Yanovski
-
Article
| Open Access p38γ and δ promote heart hypertrophy by targeting the mTOR-inhibitory protein DEPTOR for degradation
p38γ and δ promote heart hypertrophy by targeting the mTOR-inhibitory protein DEPTOR for degradation
mTOR signalling pathway is a critical regulator of cardiac hypertrophy. Here the authors show that two kinases, p38γ and p38δ, control heart growth by promoting mTOR activity via phosphorylation and consequent proteasome degradation of mTOR inhibitor DEPTOR, extending our knowledge of cardiac hypertrophy regulation.
- Bárbara González-Terán
- , Juan Antonio López
- & Guadalupe Sabio
-
Article
| Open Access D25V apolipoprotein C-III variant causes dominant hereditary systemic amyloidosis and confers cardiovascular protective lipoprotein profile
D25V apolipoprotein C-III variant causes dominant hereditary systemic amyloidosis and confers cardiovascular protective lipoprotein profile
Decrease in Apolipoprotein C-III (ApoC-III) yields a cardioprotective lipoprotein profile. Here, Valleix et al.reveal a novel ApoC-III variant conferring low plasma ApoC-III concentration and cardioprotection despite renal insufficiency, and, unexpectedly, causing dominant hereditary systemic amyloidosis due to its fibrillogenic nature.
- Sophie Valleix
- , Guglielmo Verona
- & Vittorio Bellotti
-
Article
| Open Access New observations on maternal age effect on germline de novo mutations
New observations on maternal age effect on germline de novo mutations
The study of germline mutations has been greatly enhanced by massive parallel sequencing technologies. Here the authors use deep sequencing data from nearly 700 parent-child trios to show maternal age has a small but significant correlation with the number of de novomutations in the offspring.
- Wendy S. W. Wong
- , Benjamin D. Solomon
- & John E. Niederhuber
-
Article
| Open Access Autonomous beating rate adaptation in human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes
Autonomous beating rate adaptation in human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes
The use of stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes for heart repair is hampered by their immature structural and contractile properties that may cause arrhythmia. Here, Eng et al.show that electrical conditioning of human cardiomyocytes in 3D culture can enhance connectivity and provide resistance to arrhythmia.
- George Eng
- , Benjamin W. Lee
- & Gordana Vunjak-Novakovic
-
Article
| Open Access Functional anterior pituitary generated in self-organizing culture of human embryonic stem cells
Functional anterior pituitary generated in self-organizing culture of human embryonic stem cells
It is difficult to generate functional human anterior pituitary tissues in vitro. Here, Ozone et al. generate human anterior pituitary from embryonic stem cells by recapitulating in vivodevelopment, and demonstrate this tissue secretes hormones and rescues hypopituitarism when grafted into mice.
- Chikafumi Ozone
- , Hidetaka Suga
- & Yoshiki Sasai
-
Article
| Open Access Periprostatic adipocytes act as a driving force for prostate cancer progression in obesity
Periprostatic adipocytes act as a driving force for prostate cancer progression in obesity
Obesity is associated with an elevated risk of prostate cancer. Here, the authors show that periprostatic adipose tissue promotes the migration and local invasion of prostate cancer cells by secreting the chemokine, CCL7, and that this process is enhanced in the context of obesity.
- Victor Laurent
- , Adrien Guérard
- & Catherine Muller
-
Article
| Open Access A role of stochastic phenotype switching in generating mosaic endothelial cell heterogeneity
A role of stochastic phenotype switching in generating mosaic endothelial cell heterogeneity
Spontaneous phenotypic heterogeneity confers a population-level advantage to cells that are exposed to fluctuating environments. Here the authors show that the endothelium of some organs displays a dynamic mosaicism in expression of Von Willebrand factor, suggesting bet hedging as a strategy for adaptive homeostasis.
- Lei Yuan
- , Gary C. Chan
- & William C. Aird
-
Article
| Open Access Sequence variants in the PTCH1 gene associate with spine bone mineral density and osteoporotic fractures
Sequence variants in the PTCH1 gene associate with spine bone mineral density and osteoporotic fractures
Bone mineral density (BMD) is the best predictor of osteoporotic fracture risk. Here, the authors perform a genome wide association study in Icelanders and people of European and East-Asian descent, and identify a new allele in intron 15 of the PTCH1gene that associates with reduced BMD.
- Unnur Styrkarsdottir
- , Gudmar Thorleifsson
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access A shear gradient-activated microfluidic device for automated monitoring of whole blood haemostasis and platelet function
A shear gradient-activated microfluidic device for automated monitoring of whole blood haemostasis and platelet function
The current hemostasis assays are unable to predict thrombotic or bleeding risk in clinics. Here, Jain et al. present a novel microfluidic device mimicking stenosed arterioles that determines clotting times in vitroand in extracorporeal circuits, offering a simple and reliable monitoring of blood homeostasis and platelet function.
- Abhishek Jain
- , Amanda Graveline
- & Donald E. Ingber
-
Article
| Open Access Human pancreatic beta-like cells converted from fibroblasts
Human pancreatic beta-like cells converted from fibroblasts
Insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells, generatedin vitro, could lead to new anti-diabetic therapies. Here, Zhu et al. convert human fibroblasts into endodermal progenitors that differentiate in vitrointo glucose-responsive beta-like cells that, following transplantation in mice, protect from diabetes.
- Saiyong Zhu
- , Holger A. Russ
- & Sheng Ding

 HIF-1α-PDK1 axis-induced active glycolysis plays an essential role in macrophage migratory capacity
HIF-1α-PDK1 axis-induced active glycolysis plays an essential role in macrophage migratory capacity