Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Disulfide-activated protein kinase G Iα regulates cardiac diastolic relaxation and fine-tunes the Frank–Starling response
Disulfide-activated protein kinase G Iα regulates cardiac diastolic relaxation and fine-tunes the Frank–Starling response
The stroke volume of the heart increases in response to an increase in the blood volume filling the heart. Here the authors reveal that this coordinated process is mediated in part by oxidative activation of the protein kinase G Iα, which phosphorylates phospholamban to enhance diastolic relaxation in mice.
- Jenna Scotcher
- , Oleksandra Prysyazhna
- & Philip Eaton
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering prokaryotic channels for control of mammalian tissue excitability
Engineering prokaryotic channels for control of mammalian tissue excitability
Restoring lost excitability of injured tissue is a paramount of regenerative medicine. By using a combined expression of bacterial voltage-gated Na+ channel, Kir2.1, and connexin-43 in non-excitable human fibroblasts, here the authors generate excitable cells that rescue action potential conduction in an in vitromodel of cardiac fibrosis.
- Hung X. Nguyen
- , Robert D. Kirkton
- & Nenad Bursac
-
Article
| Open Access CaMKII induces permeability transition through Drp1 phosphorylation during chronic β-AR stimulation
CaMKII induces permeability transition through Drp1 phosphorylation during chronic β-AR stimulation
β-adrenergic receptor signaling induces mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) opening. Here, Xuet al. show that this effect is mediated by phosphorylation of mitochondrial fission protein Drp1 by CamKII, which increases the frequency of transient mPTP opening.
- Shangcheng Xu
- , Pei Wang
- & Wang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access NRK1 controls nicotinamide mononucleotide and nicotinamide riboside metabolism in mammalian cells
NRK1 controls nicotinamide mononucleotide and nicotinamide riboside metabolism in mammalian cells
Raising cellular levels of the metabolic cofactor NAD+ reverses key indicators of aging. Here, Ratajczak et al. show that cellular levels of NAD+ depend on the extracellular catalytic activity of NRK1, which processes two NAD+precursors, nicotinamide mononucleotide and nicotinamide riboside, in mice.
- Joanna Ratajczak
- , Magali Joffraud
- & Carles Cantó
-
Article
| Open Access Global and hepatocyte-specific ablation of Bmal1 induces hyperlipidaemia and enhances atherosclerosis
Global and hepatocyte-specific ablation of Bmal1 induces hyperlipidaemia and enhances atherosclerosis
Bmal1 is a key transcription factor that controls rhythmicity of diverse biological functions. Here, Pan et al. show that Bmal1 deficiency in mice increases lipoprotein secretion and reduces cholesterol excretion to bile, and decipher the molecular mechanisms underlying hyperlipidaemia and atherosclerosis promoted by the lack of Bmal1.
- Xiaoyue Pan
- , Christopher A. Bradfield
- & M. Mahmood Hussain
-
Article
| Open Access Nicotinamide riboside is uniquely and orally bioavailable in mice and humans
Nicotinamide riboside is uniquely and orally bioavailable in mice and humans
NAD+ is an important coenzyme that mediates cellular metabolism and defends against stresses due to age and overnutrition. Here the authors demonstrate unique bioavailability of the NAD+ precursor vitamin nicotinamide riboside (NR) in mice and humans, and show that NR safely elevates human NAD+.
- Samuel A. J. Trammell
- , Mark S. Schmidt
- & Charles Brenner
-
Article
| Open Access Endoglin integrates BMP and Wnt signalling to induce haematopoiesis through JDP2
Endoglin integrates BMP and Wnt signalling to induce haematopoiesis through JDP2
How both BMP and Wnt signalling pathways regulate lineage specification early in development is unclear. Here, the authors show that endoglin via Jdp2, an AP-1 family member, modulates BMP and Wnt signalling to commit mesodermal progenitors to a haematopoietic fate at the expense of the cardiac lineage.
- June Baik
- , Alessandro Magli
- & Rita C. R. Perlingeiro
-
Article
| Open Access Obesity-associated NLRC4 inflammasome activation drives breast cancer progression
Obesity-associated NLRC4 inflammasome activation drives breast cancer progression
Obesity is associated with higher breast cancer risk and poor prognosis. Here, the authors show that obesity promotes breast cancer through the recruitment of macrophages with activated NLRC4 inflammasome, which activate IL-1β production, resulting in VEGFA expression in adipocytes and angiogenesis.
- Ryan Kolb
- , Liem Phan
- & Weizhou Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Differential hepatic distribution of insulin receptor substrates causes selective insulin resistance in diabetes and obesity
Differential hepatic distribution of insulin receptor substrates causes selective insulin resistance in diabetes and obesity
Type 2 diabetes and obesity are associated with increased hepatic gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis, known as selective insulin resistance. Here Kubota et al. explain selective insulin resistance in the liver with the zonal distribution and selective insulin-mediated regulation of Irs1 and Irs2.
- Naoto Kubota
- , Tetsuya Kubota
- & Takashi Kadowaki
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide compendium and functional assessment of in vivo heart enhancers
Genome-wide compendium and functional assessment of in vivo heart enhancers
Identification of non-coding variants has outstripped our ability to annotate and interpret them. Dickel et al. present a compendium of over 80,000 putative human heart enhancers and demonstrate that two conserved enhancers are required for proper cardiac function in mice.
- Diane E. Dickel
- , Iros Barozzi
- & Len A. Pennacchio
-
Article
| Open Access Divergent effects of central melanocortin signalling on fat and sucrose preference in humans
Divergent effects of central melanocortin signalling on fat and sucrose preference in humans
Hypothalamic melanocortin-4-receptors (MC4R) regulate food preference in rodents, but their role in humans is unclear. Here, the authors perform food preference and liking tests in humans with MC4R mutations and find that they prefer fatty food more, but sweet food less, than people without MC4R mutations.
- Agatha A. van der Klaauw
- , Julia M. Keogh
- & I. Sadaf Farooqi
-
Article
| Open Access Neofunctionalization of zona pellucida proteins enhances freeze-prevention in the eggs of Antarctic notothenioids
Neofunctionalization of zona pellucida proteins enhances freeze-prevention in the eggs of Antarctic notothenioids
Despite subzero temperature of their surroundings, eggs of Antarctic notothenioid fishes do not freeze. This study shows the expansion of genes related to freezing temperature in notothenioid which also acquired of ice melting-promoting zona pellucida proteins with specific structural properties.
- Lixue Cao
- , Qiao Huang
- & Liangbiao Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Fhf2 gene deletion causes temperature-sensitive cardiac conduction failure
Fhf2 gene deletion causes temperature-sensitive cardiac conduction failure
Fever is a defence mechanism against infection, but it may also cause abnormal heart rhythm viaunknown mechanism. Here the authors identify FHF2 protein as a key regulator of myocardial excitability that protects the heart against conduction failure in response to an increase in body temperature.
- David S. Park
- , Akshay Shekhar
- & Glenn I. Fishman
-
Article
| Open Access A cholinergic-sympathetic pathway primes immunity in hypertension and mediates brain-to-spleen communication
A cholinergic-sympathetic pathway primes immunity in hypertension and mediates brain-to-spleen communication
Immune system participates in the development of high blood pressure. Here the authors show that cholinergic-sympathetic pathway mediated by the α7nAChR receptor and the activation of splenic T cells prime immunity during hypertension and that selective splenic denervation protects against the onset of hypertension in mice.
- Daniela Carnevale
- , Marialuisa Perrotta
- & Giuseppe Lembo
-
Article
| Open Access Platelet clearance via shear-induced unfolding of a membrane mechanoreceptor
Platelet clearance via shear-induced unfolding of a membrane mechanoreceptor
The platelets detect and respond to shear stress generated by blood flow. Here the authors show that the binding of the soluble von Willebrand factor to its receptor GPIba under physiological shear stress induces receptor's domain unfolding on the platelet and signalling into the platelet, leading to platelets clearance.
- Wei Deng
- , Yan Xu
- & Renhao Li
-
Article
| Open Access FHF-independent conduction of action potentials along the leak-resistant cerebellar granule cell axon
FHF-independent conduction of action potentials along the leak-resistant cerebellar granule cell axon
FHFs are known to regulate voltage-gated sodium channels (NaVs). Here, the authors compare the role of FHFs in cerebellar granule cell propagation, and find NaVs in the distal axon function independently of FHFs, allowing for faster inactivation rates and reducing energy demands during repetitive spiking.
- Katarzyna Dover
- , Christopher Marra
- & Mitchell Goldfarb
-
Article
| Open Access An imbalance between specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators and pro-inflammatory leukotrienes promotes instability of atherosclerotic plaques
An imbalance between specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators and pro-inflammatory leukotrienes promotes instability of atherosclerotic plaques
Atherosclerosis progression is linked to inflammatory processes in the blood vessel wall. Here, the authors show that, with the progression of atherosclerosis, the resolution of inflammation is impaired as the result of an imbalance between specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators and leukotrienes.
- Gabrielle Fredman
- , Jason Hellmann
- & Ira Tabas
-
Article
| Open Access Optogenetically enhanced pituitary corticotroph cell activity post-stress onset causes rapid organizing effects on behaviour
Optogenetically enhanced pituitary corticotroph cell activity post-stress onset causes rapid organizing effects on behaviour
Behavioural adaptations in response to stress are thought to be regulated by rapid neurotransmitter action, followed by slower hormonal signalling. Here, using optogenetic approaches, the authors find corticotroph cell populations are capable of rapidly modulating avoidance behaviours immediately after the onset of stress.
- Rodrigo J. De Marco
- , Theresa Thiemann
- & Soojin Ryu
-
Article
| Open Access The oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate activates the mTOR signalling pathway
The oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate activates the mTOR signalling pathway
Oncogenic mutations of isocitrate dehydrogenases 1 and 2 result in the production of the oncometabolite R-2-hydroxyglutarate. Here the authors show that the oncometabolite promotes mTOR activation in a PTEN/PI3K-independent manner by regulating DEPTOR stability via inhibition of KDM4A activity.
- Mélissa Carbonneau
- , Laurence M. Gagné
- & Frédérick A. Mallette
-
Article
| Open Access Multiple novel gene-by-environment interactions modify the effect of FTO variants on body mass index
Multiple novel gene-by-environment interactions modify the effect of FTO variants on body mass index
Common variants in the fat mass and obesity associated (FTO) gene are linked to body mass index (BMI). Using the latest UK Biobank data, this study shows novel gene x environment interactions between FTOand lifestyle factors, including frequency of alcohol consumption, sleep, and added dietary salt.
- Alexander I. Young
- , Fabian Wauthier
- & Peter Donnelly
-
Article
| Open Access Vascular microRNA-204 is remotely governed by the microbiome and impairs endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation by downregulating Sirtuin1
Vascular microRNA-204 is remotely governed by the microbiome and impairs endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation by downregulating Sirtuin1
Commensal bacteria, the vast majority of which reside in the gut, are involved in development of many diseases, including atherosclerotic vascular disease. Here the authors show that these bacteria remotely increase expression of vascular microRNA-204, which targets Sirt1 in the endothelium to impair endothelial function.
- Ajit Vikram
- , Young-Rae Kim
- & Kaikobad Irani
-
Article
| Open Access Nestin+ cells direct inflammatory cell migration in atherosclerosis
Nestin+ cells direct inflammatory cell migration in atherosclerosis
Bone marrow cells producing the intermediate filament nestin guide monocyte egress to the bloodstream in response to infection. Here, the authors show that nestin-producing stromal cells direct inflammatory cell migration in atherosclerosis, and that stromal Mcp1 is crucial in this process.
- Raquel del Toro
- , Raphael Chèvre
- & Simón Méndez-Ferrer
-
Article
| Open Access ORP4L is essential for T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell survival
ORP4L is essential for T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell survival
Lymphocytic leukaemia cells are characterized by high respiratory rates. Here, the authors report that the oxysterol-binding protein ORPL4 sustains mitochondrial respiration in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cells by regulating Ca2+release from the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Wenbin Zhong
- , Qing Yi
- & Daoguang Yan
-
Article
| Open Access MARCH1 regulates insulin sensitivity by controlling cell surface insulin receptor levels
MARCH1 regulates insulin sensitivity by controlling cell surface insulin receptor levels
Insulin receptor levels at the cell surface are reduced in insulin resistance, for reasons that are not fully understood. Here, the authors identify the E3 ubiquitin ligase MARCH1 as a direct regulator of basal insulin receptor surface levels and, therefore, insulin signalling.
- Arvindhan Nagarajan
- , Max C. Petersen
- & Narendra Wajapeyee
-
Article
| Open Access The aryl hydrocarbon receptor controls cyclin O to promote epithelial multiciliogenesis
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor controls cyclin O to promote epithelial multiciliogenesis
Epithelia are barriers against environmental insults and express the transcription factor aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR). Here the authors show that AhR regulates multiciliogenesis via cyclin O and Multicilin in a Notch-dependent manner and that this is blocked by toxic ligands.
- Matteo Villa
- , Stefania Crotta
- & Andreas Wack
-
Article
| Open Access MURC deficiency in smooth muscle attenuates pulmonary hypertension
MURC deficiency in smooth muscle attenuates pulmonary hypertension
MURC protein regulates the function of caveolae, the small invaginations of the plasma membrane in muscle cells. Here the authors show that by interacting with caveolin proteins, MURC affects RhoA/ROCK signalling and regulates proliferation and migration of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells, suggesting a new target in therapy of pulmonary hypertension.
- Naohiko Nakanishi
- , Takehiro Ogata
- & Tomomi Ueyama
-
Article
| Open Access β-arrestin-2 regulates NMDA receptor function in spinal lamina II neurons and duration of persistent pain
β-arrestin-2 regulates NMDA receptor function in spinal lamina II neurons and duration of persistent pain
The cellular mechanisms underlying acute pain transitions to chronic pain are poorly understood. Here the authors show that the scaffolding protein β-arrestin 2 contributes to these processes via desensitization of NMDA receptors in spinal neurons.
- Gang Chen
- , Rou-Gang Xie
- & Ru-Rong Ji
-
Article
| Open Access Endothelial cells are progenitors of cardiac pericytes and vascular smooth muscle cells
Endothelial cells are progenitors of cardiac pericytes and vascular smooth muscle cells
Pericytes and vascular smooth muscle cells are crucial for functional blood vessels, but the developmental sources of these cells are incompletely understood. Here, the authors show that endocardial endothelial cells give rise to cardiac mural cells, which are controlled by Wnt signalling.
- Qi Chen
- , Hui Zhang
- & Ralf H. Adams
-
Article
| Open Access Cell-permeable succinate prodrugs bypass mitochondrial complex I deficiency
Cell-permeable succinate prodrugs bypass mitochondrial complex I deficiency
Mitochondrial complex I deficiency is the most common respiratory chain defect in mitochondrial disease in children and currently there is no effective treatment. In this study, the authors show that succinate prodrugs can alleviate metabolic decompensation in Leigh syndrome patient fibroblasts.
- Johannes K. Ehinger
- , Sarah Piel
- & Eskil Elmér
-
Article
| Open Access A critical role for NF2 and the Hippo pathway in branching morphogenesis
A critical role for NF2 and the Hippo pathway in branching morphogenesis
Branching morphogenesis is essential for the formation of most epithelial organs. Here, the authors show that Neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2), the Hippo pathway kinases LATS1 and LATS2, and the transcriptional co-activators YAP and TAZ control tip identity, RET signalling and branching morphogenesis in the mouse kidney.
- Antoine Reginensi
- , Leonie Enderle
- & Helen McNeill
-
Article
| Open Access The transcriptional coregulator GRIP1 controls macrophage polarization and metabolic homeostasis
The transcriptional coregulator GRIP1 controls macrophage polarization and metabolic homeostasis
GRIP1 cooperates with the glucocorticoid receptor to repress inflammatory genes. Here the authors show that GRIP1 also controls macrophage polarization, by promoting KLF4-driven activation in response to IL-4, and that mice lacking GRIP1 in macrophages develop severe metabolic dysfunction on a high-fat diet.
- Maddalena Coppo
- , Yurii Chinenov
- & Inez Rogatsky
-
Article
| Open Access ANGPTL4 deficiency in haematopoietic cells promotes monocyte expansion and atherosclerosis progression
ANGPTL4 deficiency in haematopoietic cells promotes monocyte expansion and atherosclerosis progression
Angiopoietin-like 4 protein (ANGPTL4) is a regulator of lipoprotein metabolism whose role in atherosclerosis has been controversial. Here the authors show that ANGPTL4 deficiency in haematopoietic cells increases atherogenesis by promoting myeloid progenitor cell expansion and differentiation, foam cell formation and vascular inflammation.
- Binod Aryal
- , Noemi Rotllan
- & Carlos Fernández-Hernando
-
Article
| Open Access Lkb1 controls brown adipose tissue growth and thermogenesis by regulating the intracellular localization of CRTC3
Lkb1 controls brown adipose tissue growth and thermogenesis by regulating the intracellular localization of CRTC3
The kinase Lkb1 is expressed in various metabolic tissues and is known to regulate cellular and systemic energy homeostasis. Here, the authors delete Lkb1 specifically in mature adipocytes of mice to show that Lkb1 regulates brown adipose tissue expansion and expression of UCP1.
- Tizhong Shan
- , Yan Xiong
- & Shihuan Kuang
-
Article
| Open Access Healthy ageing of cloned sheep
Healthy ageing of cloned sheep
Since the birth of the first cloned animal, Dolly the sheep, concerns have been raised about potential long-term health consequences of cloning. Here the authors report on a cohort of 13 aged cloned sheep, including four created from the same cells as Dolly, and find they are healthy and seem to age normally.
- K. D. Sinclair
- , S. A. Corr
- & D. S. Gardner
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic lineage tracing defines myofibroblast origin and function in the injured heart
Genetic lineage tracing defines myofibroblast origin and function in the injured heart
The origin and fate of myofibroblasts, the cells responsible for cardiac remodelling and fibrosis, is controversial. Here the authors show that cardiac myofibroblasts express periostin, derive exclusively from tissue-resident fibroblasts, are necessary for scar formation after injury, and can revert back to a less-activated state upon injury resolution.
- Onur Kanisicak
- , Hadi Khalil
- & Jeffery D. Molkentin
-
Article
| Open Access Glycolytic regulation of cell rearrangement in angiogenesis
Glycolytic regulation of cell rearrangement in angiogenesis
Glycolytic regulator PFKFB3 is a key player in vessel sprouting. Here the authors develop a computational model predicting that PFKFB3 drives endothelial cell rearrangement during vessel sprouting by promoting filopodia formation and reducing intercellular adhesion, and empirically validate this prediction.
- Bert Cruys
- , Brian W. Wong
- & Peter Carmeliet
-
Article
| Open Access Regulation of post-Golgi LH3 trafficking is essential for collagen homeostasis
Regulation of post-Golgi LH3 trafficking is essential for collagen homeostasis
Lysine hydroxylation of procollagen precursors by LH3 is required for collagen fibril crosslinking and stabilization. Here the authors show that the trafficking protein VIPAR is required for correct sorting of LH3 into post-Golgi collagen carriers and for correct collagen modification and structure.
- Blerida Banushi
- , Federico Forneris
- & Paul Gissen
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and functional insights into IZUMO1 recognition by JUNO in mammalian fertilization
Structural and functional insights into IZUMO1 recognition by JUNO in mammalian fertilization
Sperm-egg fusion requires the interaction between IZUMO1 on the sperm and JUNO on the egg. Here, the authors report the crystal structure of mouse JUNO, and use it to explain its lack of binding to folate, along with in vivofunctional analyses.
- Kazuki Kato
- , Yuhkoh Satouh
- & Osamu Nureki
-
Article
| Open Access Septin 9 induces lipid droplets growth by a phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate and microtubule-dependent mechanism hijacked by HCV
Septin 9 induces lipid droplets growth by a phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate and microtubule-dependent mechanism hijacked by HCV
The accumulation of lipid droplets is often observed in hepatitis C virus infection, but the mechanism of their formation is not known. Here the authors show that septin 9 expression is increased in infected livers, and a septin 9/phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate signalling pathway regulates the growth of lipid droplets.
- Abdellah Akil
- , Juan Peng
- & Ama Gassama-Diagne
-
Article
| Open Access SREBP1c-CRY1 signalling represses hepatic glucose production by promoting FOXO1 degradation during refeeding
SREBP1c-CRY1 signalling represses hepatic glucose production by promoting FOXO1 degradation during refeeding
The clock protein Cry regulates hepatic glucose metabolism. Here the authors show that SREBP1c, activated by insulin signalling after feeding, directly regulates Cry transcription at specific circadian time points, and that Cry represses hepatic glucose production by promoting proteasomal degradation of Foxo1.
- Hagoon Jang
- , Gha Young Lee
- & Jae Bum Kim
-
Article
| Open Access TRPC5 channels participate in pressure-sensing in aortic baroreceptors
TRPC5 channels participate in pressure-sensing in aortic baroreceptors
The identity of mechanosensors within aortic baroreceptors that sense fluctuations in blood pressure is unclear. Here, Lau et al.show that a cation channel TRPC5 acts as a transducer of mechanical stimuli in aortic baroreceptor neurons in rodents.
- On-Chai Lau
- , Bing Shen
- & Xiaoqiang Yao
-
Article
| Open Access Critical role of RanBP2-mediated SUMOylation of Small Heterodimer Partner in maintaining bile acid homeostasis
Critical role of RanBP2-mediated SUMOylation of Small Heterodimer Partner in maintaining bile acid homeostasis
As signalling molecules, bile acids (BAs) can affect metabolism, but due to detergent-like properties, BA levels must be tightly regulated. Here, Kim et al.show that RanBP2, a nucleoporin, maintains BA homoeostasis through SUMOylation of Small Heterodimer Partner (SHP), an orphan nuclear receptor.
- Dong-Hyun Kim
- , Sanghoon Kwon
- & Jongsook Kim Kemper
-
Article
| Open Access Notch-independent RBPJ controls angiogenesis in the adult heart
Notch-independent RBPJ controls angiogenesis in the adult heart
Heart function after injury improves upon formation of new blood vessels. Here, the authors show that ablating a transcription factor RBPJ in the murine heart increases vascularization and maintains cardiac function after injury by increasing responsiveness to hypoxia, suggesting a new approach to treat heart injury.
- Ramón Díaz-Trelles
- , Maria Cecilia Scimia
- & Mark Mercola
-
Article
| Open Access Coronary vasculature patterning requires a novel endothelial ErbB2 holoreceptor
Coronary vasculature patterning requires a novel endothelial ErbB2 holoreceptor
Semaphorin ligands and cognate receptors are important in patterning the vasculature. Here, Aghajanian et al.report an unexpected role for ErbB2 in endothelial cells where it partners with Nrp1 to form a novel semaphoring holoreceptor required for embryonic vascular patterning.
- Haig Aghajanian
- , Young Kuk Cho
- & Jonathan A. Epstein
-
Article
| Open Access The genetic regulatory signature of type 2 diabetes in human skeletal muscle
The genetic regulatory signature of type 2 diabetes in human skeletal muscle
More than 90% of genetic variants associated with type 2 diabetes occur in non-coding regions. Scott et al. report genomes, epigenomes and transcriptomes of skeletal muscle from 271 participants with a range of glucose tolerances, revealing a genetic regulatory architecture enriched in muscle stretch/super enhancers.
- Laura J. Scott
- , Michael R. Erdos
- & Stephen C. J. Parker
-
Article
| Open Access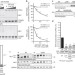 MLP and CARP are linked to chronic PKCα signalling in dilated cardiomyopathy
MLP and CARP are linked to chronic PKCα signalling in dilated cardiomyopathy
Altered function of the muscle LIM protein (MLP) causes dilated cardiomyopathy in mice and humans. Lange et al. explain the molecular role of MLP in the heart by showing that it affects the signalling complex at the intercalated discs of failing hearts that consists of PKCα, PLCβ1 and CARP by inhibiting PKCα auto-phosphorylation and function.
- Stephan Lange
- , Katja Gehmlich
- & Elisabeth Ehler
-
Article
| Open Access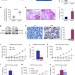 RETRACTED ARTICLE: SARI inhibits angiogenesis and tumour growth of human colon cancer through directly targeting ceruloplasmin
RETRACTED ARTICLE: SARI inhibits angiogenesis and tumour growth of human colon cancer through directly targeting ceruloplasmin
Ceruloplasmin has an important role in the stabilization and nuclear transport of HIF-1α, thus regulating VEGF expression. Here the authors show that the transcription factor SARI reduces colorectal cancer growth and angiogenesis in vivoby inducing the degradation of ceruloplasmin, thereby inhibiting the HIFα/VEGF axis.
- Lei Dai
- , Xueliang Cui
- & Hongxin Deng
-
Article
| Open Access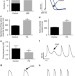 Cardiac sodium channel palmitoylation regulates channel availability and myocyte excitability with implications for arrhythmia generation
Cardiac sodium channel palmitoylation regulates channel availability and myocyte excitability with implications for arrhythmia generation
Cardiac voltage-gated sodium channels (Nav1.5) are crucial regulators of heart electric activity. Here the authors show that palmitoylation, a process of lipid modification of cysteine residues, modulates Nav1.5 function and affects cardiomyocyte excitability, representing a potential target in treating cardiac diseases.
- Zifan Pei
- , Yucheng Xiao
- & Theodore R. Cummins
-
Article
| Open Access The necroptosis-inducing kinase RIPK3 dampens adipose tissue inflammation and glucose intolerance
The necroptosis-inducing kinase RIPK3 dampens adipose tissue inflammation and glucose intolerance
The kinase RIPK3 initiates necroptosis, which has been reported to promote inflammation in various pathological conditions. Here, the authors show that genetic ablation of Ripk3results in adipocyte apoptosis and white adipose tissue inflammation in obese mice, which promotes glucose intolerance.
- Jérémie Gautheron
- , Mihael Vucur
- & Tom Luedde

 Thick filament mechano-sensing is a calcium-independent regulatory mechanism in skeletal muscle
Thick filament mechano-sensing is a calcium-independent regulatory mechanism in skeletal muscle