Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access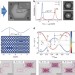 Dynamic acousto-optic control of a strongly coupled photonic molecule
Dynamic acousto-optic control of a strongly coupled photonic molecule
Dynamic control of components is required for large-scale quantum photonic networks. Here, Kapfingeret al. show dynamic control of the interaction between two coupled photonic crystal nanocavities forming a photonic molecule. Tuning is achieved by using an electrically generated radio frequency surface acoustic wave.
- Stephan Kapfinger
- , Thorsten Reichert
- & Hubert J. Krenner
-
Article
| Open Access Nanophotonic coherent light–matter interfaces based on rare-earth-doped crystals
Nanophotonic coherent light–matter interfaces based on rare-earth-doped crystals
Quantum light–matter interfaces connecting stationary qubits to photons are fundamental elements of future quantum optical networks. Here, the authors report a quantum interface based on highly coherent rare-earth ions—the solid-state qubits—coupled to a nanophotonic cavity fabricated in the host crystal.
- Tian Zhong
- , Jonathan M. Kindem
- & Andrei Faraon
-
Article
| Open Access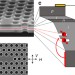 Spin–cavity interactions between a quantum dot molecule and a photonic crystal cavity
Spin–cavity interactions between a quantum dot molecule and a photonic crystal cavity
Optical cavities enhance light–matter interactions, and have been used to strongly couple a photon to a single spin. Here, the authors take this a step further by coupling a photon to a two-spin system by embedding an indium arsenide quantum-dot molecule in a photonic crystal cavity.
- Patrick M. Vora
- , Allan S. Bracker
- & Daniel Gammon
-
Article
| Open Access Photonic sensing of organic solvents through geometric study of dynamic reflection spectrum
Photonic sensing of organic solvents through geometric study of dynamic reflection spectrum
Photonic sensing is a method for detecting individual chemical species, but can fail when they are sufficiently similar in physical properties. Here, the authors report a method that can distinguish even very closely related species, such as homologues and chemical isomers.
- Yuqi Zhang
- , Qianqian Fu
- & Jianping Ge
-
Article
| Open Access Reconfigurable photonic crystals enabled by pressure-responsive shape-memory polymers
Reconfigurable photonic crystals enabled by pressure-responsive shape-memory polymers
Smart shape-memory polymers based on pressure stimuli have potential biomedical and aerospace applications but are largely unexplored. Here, Fang et al.present a reconfigurable photonic crystal that is reprogrammed at ambient conditions by a pressure-responsive shape-memory polymer.
- Yin Fang
- , Yongliang Ni
- & Peng Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Fast and bright spontaneous emission of Er3+ ions in metallic nanocavity
Fast and bright spontaneous emission of Er3+ ions in metallic nanocavity
The Purcell effect predicts a spontaneous emission rate enhancement of several orders of magnitude, but experimental demonstrations have been much lower. Here, Song et al. show emission enhancement of Er3+ions in a metallic nanocavity with a 170 Purcell factor at room temperature and 55% extraction efficiency.
- Jung-Hwan Song
- , Jisu Kim
- & Yong-Hee Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Photonic crystals cause active colour change in chameleons
Photonic crystals cause active colour change in chameleons
Colour change in many vertebrates originates from pigment dispersion or aggregation. Here, Teyssier et al. show that chameleons rapidly shift colour through a physical mechanism involving a lattice of nanocrystals in dermal iridophores, a second and deeper iridophore layer strongly reflects near-infrared light.
- Jérémie Teyssier
- , Suzanne V. Saenko
- & Michel C. Milinkovitch
-
Article |
 Optically switchable transistors by simple incorporation of photochromic systems into small-molecule semiconducting matrices
Optically switchable transistors by simple incorporation of photochromic systems into small-molecule semiconducting matrices
Organic thin-film transistors can be photomodulated by incorporating photochromic molecules, but the state-of-the-art suffers from poor charge transport. Here, the authors improve charge mobility by three orders of magnitude by blending small conjugated molecules into diarylethene.
- Mirella El Gemayel
- , Karl Börjesson
- & Paolo Samorì
-
Article |
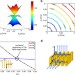 Dirac leaky-wave antennas for continuous beam scanning from photonic crystals
Dirac leaky-wave antennas for continuous beam scanning from photonic crystals
Directive and scannable radiation patterns beyond the microwave region are desirable but leaky-wave antennas in the terahertz and optical range are unavailable. Here, Memarian and Eleftheriades demonstrate continuously scanned leaky-wave radiation from the interface of a photonic crystal with a Dirac-type dispersion.
- Mohammad Memarian
- & George V. Eleftheriades
-
Article
| Open Access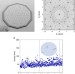 Photonic quasi-crystal terahertz lasers
Photonic quasi-crystal terahertz lasers
Various vertical surface emitting, terahertz quantum-cascade lasers have been proposed recently but these suffer from power cancellations in the far-field and limited extraction efficiencies. Here, Vitiello et al.circumvent these issues using two-dimensional photonic quasi-crystalline resonators.
- Miriam Serena Vitiello
- , Michele Nobile
- & A. Giles Davies
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamically controlling the emission of single excitons in photonic crystal cavities
Dynamically controlling the emission of single excitons in photonic crystal cavities
Controlling the coherent evolution of cavity quantum electrodynamics systems is key for future quantum networks. Here Pagliano et al.demonstrate dynamic control of the coupling of a single exciton to a photonic micro-resonator using electrical tuning of the exciton energy in a photonic crystal cavity diode.
- Francesco Pagliano
- , YongJin Cho
- & Andrea Fiore
-
Article
| Open Access Ultralow mode-volume photonic crystal nanobeam cavities for high-efficiency coupling to individual carbon nanotube emitters
Ultralow mode-volume photonic crystal nanobeam cavities for high-efficiency coupling to individual carbon nanotube emitters
Efficient coupling to photonic structures is essential to exploit the emission properties of carbon nanotubes (CNTs). Here, Miura et al.demonstrate spontaneous emission coupling efficiency exceeding 85% from a single CNT to a silicon photonic crystal nanobeam cavity with an ultralow mode-volume.
- R. Miura
- , S. Imamura
- & Y. K. Kato
-
Article |
 Slow-light-enhanced gain in active photonic crystal waveguides
Slow-light-enhanced gain in active photonic crystal waveguides
Slow-light propagation provides the means to enhance and control light–matter interactions and it has been predicted to increase the gain coefficient of active waveguides. Here, Ek et al.experimentally demonstrate that the gain of a material can be enhanced using slow-light effects in photonic crystals.
- Sara Ek
- , Per Lunnemann
- & Jesper Mork
-
Article |
 Mechano-actuated ultrafast full-colour switching in layered photonic hydrogels
Mechano-actuated ultrafast full-colour switching in layered photonic hydrogels
Photonic crystals used for many optical devices are the materials made of nanoscaled periodic structures that diffract light. Yue et al. design and fabricate a soft mechanochromic hydrogel that exhibits a fast colour switching rate at 0.1 ms in a full-colour band.
- Youfeng Yue
- , Takayuki Kurokawa
- & Jian Ping Gong
-
Article
| Open Access Rydberg atoms in hollow-core photonic crystal fibres
Rydberg atoms in hollow-core photonic crystal fibres
Rydberg atoms are appealing for sensing, atomic and quantum information studies, if they can be suitably integrated with optical devices. Towards this end, Epple et al. show that caesium-filled kagome-lattice hollow-core photonic crystal fibres provide a platform for fibre-based spectroscopy of Rydberg states.
- G. Epple
- , K. S. Kleinbach
- & R. Löw
-
Article
| Open Access Lamb-Dicke spectroscopy of atoms in a hollow-core photonic crystal fibre
Lamb-Dicke spectroscopy of atoms in a hollow-core photonic crystal fibre
Atoms lose coherence via interactions with each other and the walls of their environment, which degrades the performance of atomic systems. As a route to minimize such effects, Okaba et al.use kagome-lattice hollow-core photonic crystal fibres to confine atoms, preventing them interacting with the wall.
- Shoichi Okaba
- , Tetsushi Takano
- & Hidetoshi Katori
-
Article |
 Atom–light interactions in photonic crystals
Atom–light interactions in photonic crystals
The use of photonic crystals to trap atoms on a chip offers unique possibilities for atom–light interactions. Advancing towards this goal, the authors realize photonic crystal waveguides where the electronic transition frequencies of localized caesium atoms are aligned with the band edges of the waveguides.
- A. Goban
- , C.-L. Hung
- & H.J. Kimble
-
Article |
 Integrated optical auto-correlator based on third-harmonic generation in a silicon photonic crystal waveguide
Integrated optical auto-correlator based on third-harmonic generation in a silicon photonic crystal waveguide
The characterization of short light pulses is important for performance management in applications such as telecommunications and spectroscopy. Here, Monat et al. demonstrate a photonic crystal waveguide that, based on third-harmonic generation, delivers such auto-correlator functionality on a silicon chip.
- Christelle Monat
- , Christian Grillet
- & David J. Moss
-
Article |
 Monodisperse silicon nanocavities and photonic crystals with magnetic response in the optical region
Monodisperse silicon nanocavities and photonic crystals with magnetic response in the optical region
Metamaterials offer optical functionality, such as cloaking, that is impossible to achieve with natural bulk materials. Here, Shi and colleagues fabricate colloidal metamaterials made from silicon whose magneto-optical response considerably exceeds that of related bulk materials.
- Lei Shi
- , Justin T Harris
- & Francisco Meseguer
-
Article
| Open Access All optical reconfiguration of optomechanical filters
All optical reconfiguration of optomechanical filters
Nanoscale optomechanical systems offer a route to using optical forces for a range of devices based on photonic structures. Deotareet al. present a reconfigurable optical filter based on coupled silicon photonic crystal nanobeam cavities that can overcome thermo-optic effects at high frequencies.
- Parag B. Deotare
- , Irfan Bulu
- & Marko Loncar

 Phase diagram for the transition from photonic crystals to dielectric metamaterials
Phase diagram for the transition from photonic crystals to dielectric metamaterials