Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Rich complex behaviour of self-assembled nanoparticles far from equilibrium
Rich complex behaviour of self-assembled nanoparticles far from equilibrium
Unravelling the fundamental mechanisms of emergence of complex behaviour is key to understanding living systems. Here, the authors provide a simple experimental platform to investigate and control a rich set of complex phenomena, akin to those seen in living organisms, from a nonliving system of colloidal nanoparticles.
- Serim Ilday
- , Ghaith Makey
- & F. Ömer Ilday
-
Article
| Open Access Nonlinear dynamics and chaos in an optomechanical beam
Nonlinear dynamics and chaos in an optomechanical beam
In optomechanics, optical nonlinearities are usually regarded as detrimental and efforts are made to minimize their effects. Here, the authors study the complex dynamics, including chaos, arising from the coupling of such optical nonlinearities with the mechanical modes of a silicon nanobeam cavity.
- Daniel Navarro-Urrios
- , Néstor E. Capuj
- & Clivia M. Sotomayor-Torres
-
Article
| Open Access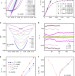 The yielding transition in amorphous solids under oscillatory shear deformation
The yielding transition in amorphous solids under oscillatory shear deformation
The onset of yielding can be difficult to define unambiguously for amorphous materials. Here the authors undertake computer simulations of model glasses of varying system sizes and show that, under oscillatory shear, they exhibit a sharp transition independent of preparation history.
- Premkumar Leishangthem
- , Anshul D. S. Parmar
- & Srikanth Sastry
-
Article
| Open Access Thinning sea ice weakens buttressing force of iceberg mélange and promotes calving
Thinning sea ice weakens buttressing force of iceberg mélange and promotes calving
Observed sea-ice loss near ice sheets has, in many cases, been accompanied by accelerated iceberg calving. Here, using a new model, the authors show that iceberg calving from glaciers can be suppressed by a mélange of sea ice and icebergs, with an increased likelihood of calving as sea ice thins.
- Alexander A. Robel
-
Article
| Open Access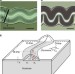 The shape of telephone cord blisters
The shape of telephone cord blisters
Telephone cord blisters constitute a well-known example of patterns generated following buckling in thin films. Here the authors develop an analytical approach that can model the sectional height profiles along the blisters that they measure experimentally and simulate numerically.
- Yong Ni
- , Senjiang Yu
- & Linghui He
-
Article
| Open Access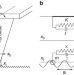 Imaging high-speed friction at the nanometer scale
Imaging high-speed friction at the nanometer scale
It has been a challenge to characterize microscopic origins of friction at high velocities. Here authors extend atomic force microscopy to develop a dynamic technique combining force sensitivity and spatial resolution and able to probe, at each image pixel, frictional forces at velocities up to several cm per second.
- Per-Anders Thorén
- , Astrid S. de Wijn
- & David B. Haviland
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic structure of active nematic shells
Dynamic structure of active nematic shells
In active matter, chemical energy is transformed into mechanical motion; theoretical descriptions of nematic liquids are useful in understanding such phenomena. Here, Zhang et al. model the dynamics of active nematic liquid crystals confined onto a spherical shell in systems that mimic cell motion.
- Rui Zhang
- , Ye Zhou
- & Juan J. de Pablo
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental characterization of extreme events of inertial dissipation in a turbulent swirling flow
Experimental characterization of extreme events of inertial dissipation in a turbulent swirling flow
The classical description of viscous turbulent flows is based on a formulation of Navier-Stokes equations which assumes its solutions to remain smooth at all times. Saw et al. characterize velocity fields in experimental turbulent flows at dissipative scale, and link the results to the singularities.
- E. -W. Saw
- , D. Kuzzay
- & B. Dubrulle
-
Article
| Open Access A stochastic model of randomly accelerated walkers for human mobility
A stochastic model of randomly accelerated walkers for human mobility
Many human mobility studies have shown empirically long-tailed distance distributions, which are usually associated to Lévy flights. Here, the authors show that the behavior of private vehicles could be misinterpreted as Lévy flights but is fully captured by a class of accelerated random walks.
- Riccardo Gallotti
- , Armando Bazzani
- & Marc Barthelemy
-
Article
| Open Access Strong nonlinear terahertz response induced by Dirac surface states in Bi2Se3 topological insulator
Strong nonlinear terahertz response induced by Dirac surface states in Bi2Se3 topological insulator
The terahertz response of topological insulator surface states, in which relativistic electrons are protected from backscattering, possesses potential optic and plasmonic applications. Here, the authors demonstrate a nonlinear absorption response of Bi2Se3to terahertz electric fields.
- Flavio Giorgianni
- , Enrica Chiadroni
- & Stefano Lupi
-
Article
| Open Access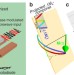 Nonlinear spin-wave excitations at low magnetic bias fields
Nonlinear spin-wave excitations at low magnetic bias fields
Nonlinear magnetization dynamics underlie the operation of important spintronic devices. Here, the authors study NiFe thin films via X-ray magnetic circular dichroism, to develop a model for nonlinear spin-wave excitation by ferromagnetic resonance under small applied magnetic fields.
- Hans G. Bauer
- , Peter Majchrak
- & Georg Woltersdorf
-
Article |
 Nonlinear spin-current enhancement enabled by spin-damping tuning
Nonlinear spin-current enhancement enabled by spin-damping tuning
Nonequilibrium magnons in a ferromagnetic insulator can generate spin current in an adjacent metal, with potential applications in spintronic devices. Here, Sakimura et al.demonstrate nonlinear enhancement of such effects via spin-damping tuning triggered by magnon-conserving scattering processes.
- Hiroto Sakimura
- , Takaharu Tashiro
- & Kazuya Ando
-
Article |
 Nonlinear phononics using atomically thin membranes
Nonlinear phononics using atomically thin membranes
Analogous to photonic crystals, phononic crystals can be used to engineer the acoustic properties of a system, however, creating nonlinear phononic crystals or nonlinear acoustic metamaterial is challenging. Here, Midtvedt et al.propose periodically pinned, atomically thin membranes as a nonlinear phononics platform.
- Daniel Midtvedt
- , Andreas Isacsson
- & Alexander Croy

 Efficient self-emulsification via cooling-heating cycles
Efficient self-emulsification via cooling-heating cycles