Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
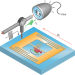 Single-electron spin resonance detection by microwave photon counting
Single-electron spin resonance detection by microwave photon counting
Spectroscopic measurements of individual rare-earth ion electron spins are performed by detecting their microwave fluorescence, with the method coming close to practical single-electron spin resonance at millikelvin temperatures.
- Z. Wang
- , L. Balembois
- & E. Flurin
-
Article |
 RNA conformational propensities determine cellular activity
RNA conformational propensities determine cellular activity
Systematic alteration of HIV-1 TAR RNA and quantitative determination of its propensity to bind to the Tat protein establish a key role role for a rare and short-lived RNA state in Tat-dependent transactivation in cells.
- Megan L. Ken
- , Rohit Roy
- & Hashim M. Al-Hashimi
-
Article
| Open Access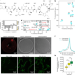 Teixobactin kills bacteria by a two-pronged attack on the cell envelope
Teixobactin kills bacteria by a two-pronged attack on the cell envelope
Using a combination of methods, the mechanism of the antibiotic teixobactin is revealed.
- Rhythm Shukla
- , Francesca Lavore
- & Markus Weingarth
-
Article |
 Structure of Tetrahymena telomerase-bound CST with polymerase α-primase
Structure of Tetrahymena telomerase-bound CST with polymerase α-primase
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of Tetrahymena thermophila telomerase-bound Ctc1–Stn1–Ten1 and DNA polymerase α–primase provide insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying telomere replication and maintenance.
- Yao He
- , He Song
- & Juli Feigon
-
Article |
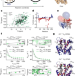 Structure determination of high-energy states in a dynamic protein ensemble
Structure determination of high-energy states in a dynamic protein ensemble
Combining NMR spectroscopy-derived pseudocontact shifts (PCSs) with Carr–Purcell–Meiboom–Gill (CPMG) relaxation dispersion enables protein structure determination of lowly populated high-energy states that are essential for macromolecular function.
- John B. Stiller
- , Renee Otten
- & Dorothee Kern
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing protein breathing motions associated with aromatic ring flipping
Visualizing protein breathing motions associated with aromatic ring flipping
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography capture how aromatic side chains can flip within the core of a protein via the generation of a local void volume.
- Laura Mariño Pérez
- , Francesco S. Ielasi
- & Malene Ringkjøbing Jensen
-
Article |
 Time-resolved structural analysis of an RNA-cleaving DNA catalyst
Time-resolved structural analysis of an RNA-cleaving DNA catalyst
Using high-resolution NMR characterization, the kinetics and dynamics of the catalytic function of a DNAzyme are shown.
- Jan Borggräfe
- , Julian Victor
- & Manuel Etzkorn
-
Article |
 Mechanisms of BRCA1–BARD1 nucleosome recognition and ubiquitylation
Mechanisms of BRCA1–BARD1 nucleosome recognition and ubiquitylation
The authors elucidate the mechanisms for the ubiquitylation specificity and recruitment of the ubiquitin ligase complex BRCA1–BARD1 to damaged DNA within chromatin to facilitate homologous recombination.
- Qi Hu
- , Maria Victoria Botuyan
- & Georges Mer
-
Article |
 HSP40 proteins use class-specific regulation to drive HSP70 functional diversity
HSP40 proteins use class-specific regulation to drive HSP70 functional diversity
The binding and activation of HSP70 by class B J-domain proteins is subject to an autoinhibitory regulatory mechanism that controls substrate targeting to HSP70 and is required for the disaggregation of amyloid fibres.
- Ofrah Faust
- , Meital Abayev-Avraham
- & Rina Rosenzweig
-
Article |
 Base-pair conformational switch modulates miR-34a targeting of Sirt1 mRNA
Base-pair conformational switch modulates miR-34a targeting of Sirt1 mRNA
Repression of a messenger RNA by a cognate microRNA depends not only on complementary base pairing, but also on the rearrangement of a single base pair, producing a conformation that fits better within the human Ago2 protein.
- Lorenzo Baronti
- , Ileana Guzzetti
- & Katja Petzold
-
Article |
 Atomic-scale imaging of a 27-nuclear-spin cluster using a quantum sensor
Atomic-scale imaging of a 27-nuclear-spin cluster using a quantum sensor
An individual electron is used as a quantum sensor to realize atomic-scale magnetic resonance imaging.
- M. H. Abobeih
- , J. Randall
- & T. H. Taminiau
-
Article |
 Regulation of α-synuclein by chaperones in mammalian cells
Regulation of α-synuclein by chaperones in mammalian cells
Chaperones interact with a canonical motif in α-synuclein, which can be prevented by phosphorylation of α-synuclein at Tyr39, whereas inhibition of this interaction leads to the localization of α-synuclein to the mitochondria and aggregate formation.
- Björn M. Burmann
- , Juan A. Gerez
- & Sebastian Hiller
-
Letter |
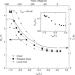 Constraints on the superconducting order parameter in Sr2RuO4 from oxygen-17 nuclear magnetic resonance
Constraints on the superconducting order parameter in Sr2RuO4 from oxygen-17 nuclear magnetic resonance
17O nuclear magnetic resonance measurements on Sr2RuO4 reveal a drop of the Knight shift in the superconducting state, contradicting previous work and imposing tight constraints on the order parameter symmetry of the system.
- A. Pustogow
- , Yongkang Luo
- & S. E. Brown
-
Letter |
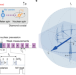 Tracking the precession of single nuclear spins by weak measurements
Tracking the precession of single nuclear spins by weak measurements
Periodic weak measurements of just a few carbon-13 nuclear spins in diamond demonstrate sensitive, high-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy at the molecular level.
- K. S. Cujia
- , J. M. Boss
- & C. L. Degen
-
Brief Communications Arising |
 Re-evaluating the p7 viroporin structure
Re-evaluating the p7 viroporin structure
- Benjamin P. Oestringer
- , Juan H. Bolivar
- & Jason R. Schnell
-
Article |
 Niobium tungsten oxides for high-rate lithium-ion energy storage
Niobium tungsten oxides for high-rate lithium-ion energy storage
Micrometre-sized particles of two niobium tungsten oxides have high volumetric capacities and rate performances, enabled by very high lithium-ion diffusion coefficients.
- Kent J. Griffith
- , Kamila M. Wiaderek
- & Clare P. Grey
-
Letter |
 High-resolution magnetic resonance spectroscopy using a solid-state spin sensor
High-resolution magnetic resonance spectroscopy using a solid-state spin sensor
High-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy at the scale of single cells is achieved by combining a magnetometer consisting of an ensemble of nitrogen–vacancy centres with a narrowband synchronized readout protocol.
- David R. Glenn
- , Dominik B. Bucher
- & Ronald L. Walsworth
-
Article |
 Extreme disorder in an ultrahigh-affinity protein complex
Extreme disorder in an ultrahigh-affinity protein complex
A high-affinity complex of histone H1 and prothymosin-α reveals an unexpected interaction mechanism, where the large opposite net charge enables the two proteins to remain highly disordered even in the complex.
- Alessandro Borgia
- , Madeleine B. Borgia
- & Benjamin Schuler
-
Article |
 Dynamic basis for dG•dT misincorporation via tautomerization and ionization
Dynamic basis for dG•dT misincorporation via tautomerization and ionization
A kinetic model is proposed to predict the probability of dG•dT misincorporation across different polymerases, and provides mechanisms for sequence-dependent misincorporation.
- Isaac J. Kimsey
- , Eric S. Szymanski
- & Hashim M. Al-Hashimi
-
Letter |
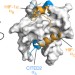 Hypersensitive termination of the hypoxic response by a disordered protein switch
Hypersensitive termination of the hypoxic response by a disordered protein switch
The intrinsically disordered CITED2 negative feedback regulator displaces the tightly bound hypoxia-inducible transcription factor HIF-1α from their common target TAZ1 through the formation of an intermediate ternary complex and thereby attenuates the hypoxic response.
- Rebecca B. Berlow
- , H. Jane Dyson
- & Peter E. Wright
-
Letter |
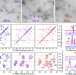 Structural variation in amyloid-β fibrils from Alzheimer's disease clinical subtypes
Structural variation in amyloid-β fibrils from Alzheimer's disease clinical subtypes
Structural differences in 40- and 42-residue-long amyloid-β fibrils seeded in vitro from the cortical tissue of patients with different clinical subtypes of Alzheimer’s disease suggest that different fibril structures form in different disease variants and with different peptide lengths.
- Wei Qiang
- , Wai-Ming Yau
- & Robert Tycko
-
Article |
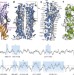 Structural basis for the antifolding activity of a molecular chaperone
Structural basis for the antifolding activity of a molecular chaperone
The solution structure of SecB, a molecular chaperone that exhibits strong antifolding activity, in complex with alkaline phosphatase and maltose-binding protein captured in their unfolded states.
- Chengdong Huang
- , Paolo Rossi
- & Charalampos G. Kalodimos
-
Letter |
 Activation of the A2A adenosine G-protein-coupled receptor by conformational selection
Activation of the A2A adenosine G-protein-coupled receptor by conformational selection
The adenosine A2A receptor, a class A G-protein-coupled receptor, exists as an ensemble of two inactive and two active states in equilibrium and is activated by conformational selection rather than induced fit.
- Libin Ye
- , Ned Van Eps
- & R. Scott Prosser
-
Letter |
 Architecture of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter
Architecture of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter
The structure of the core region of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) is determined by NMR and electron microscopy, revealing that MCU is a homo-pentamer with a specific transmembrane helix forming a hydrophilic pore across the membrane, and representing one of the largest membrane protein structures characterized by NMR spectroscopy.
- Kirill Oxenoid
- , Ying Dong
- & James J. Chou
-
Letter |
 Inhibiting fungal multidrug resistance by disrupting an activator–Mediator interaction
Inhibiting fungal multidrug resistance by disrupting an activator–Mediator interaction
A small molecule, inhibitor of a protein–protein interaction between the transcription factor Pdr1 and the Med15 subunit of Mediator in the fungal pathogen Candida glabrata, is identified and characterized here; the compound iKIX1 inhibits Pdr1-mediated gene activation and resensitizes drug-resistant C. glabrata to azole antifungals in vitro and in animal models of disseminated and urinary tract infection.
- Joy L. Nishikawa
- , Andras Boeszoermenyi
- & Haribabu Arthanari
-
Letter |
 Backbone NMR reveals allosteric signal transduction networks in the β1-adrenergic receptor
Backbone NMR reveals allosteric signal transduction networks in the β1-adrenergic receptor
Although several X-ray crystal structures of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) have been reported, relatively little is known about the conformational dynamics of these important membrane proteins; here, the authors used NMR spectroscopy to monitor the conformational changes that occur in the turkey β1-adrenergic receptor in the presence of antagonists, partial agonists, and full agonists.
- Shin Isogai
- , Xavier Deupi
- & Stephan Grzesiek
-
Article |
 Structural disorder of monomeric α-synuclein persists in mammalian cells
Structural disorder of monomeric α-synuclein persists in mammalian cells
Atomic resolution in-cell NMR and EPR spectroscopy show that the human amyloid protein α-synuclein remains disordered within all mammalian cells tested, including neurons, and identifies which parts of the protein dynamically interact or remain shielded from the cytoplasm, thus counteracting aggregation under physiological cell conditions.
- Francois-Xavier Theillet
- , Andres Binolfi
- & Philipp Selenko
-
Letter |
 Propagation of conformational changes during μ-opioid receptor activation
Propagation of conformational changes during μ-opioid receptor activation
NMR spectroscopy reveals the conformational changes of the μ-opioid receptor that are associated with receptor activation, helping to explain why the allosteric coupling between the agonist-binding pocket and the cytoplasmic G-protein-coupling interface of this receptor is relatively weak.
- Rémy Sounier
- , Camille Mas
- & Sébastien Granier
-
Letter |
 Synthesis and applications of RNAs with position-selective labelling and mosaic composition
Synthesis and applications of RNAs with position-selective labelling and mosaic composition
A hybrid solid–liquid phase transcription method and automated robotic platform synthesizes position-specific, fluorescence- or isotope-labelled RNA.
- Yu Liu
- , Erik Holmstrom
- & Yun-Xing Wang
-
Article |
 Visualizing transient Watson–Crick-like mispairs in DNA and RNA duplexes
Visualizing transient Watson–Crick-like mispairs in DNA and RNA duplexes
dG•dT and rG•rU ‘wobble’ mispairs in DNA and RNA transiently form base pairs with Watson–Crick geometry via tautomerization and ionization with probabilities that correlate with misincorporation probabilities during replication and translation.
- Isaac J. Kimsey
- , Katja Petzold
- & Hashim M. Al-Hashimi
-
Letter |
 A structure-based mechanism for tRNA and retroviral RNA remodelling during primer annealing
A structure-based mechanism for tRNA and retroviral RNA remodelling during primer annealing
To prime reverse transcription of Moloney murine leukaemia virus, a transfer RNA molecule must bind two regions of the retroviral RNA, the primer binding site (PBS) and primer activation signal within the U5-PBS; here, the NMR structures of the U5-PBS RNA and tRNA primer are solved, with and without the retroviral nucleocapsid protein, which remodels these regions.
- Sarah B. Miller
- , F. Zehra Yildiz
- & Victoria M. D’Souza
-
Article |
 Structural basis of the non-coding RNA RsmZ acting as a protein sponge
Structural basis of the non-coding RNA RsmZ acting as a protein sponge
A novel combined NMR and EPR spectroscopy approach reveals the structure and assembly mechanism of a 70-kDa bacterial ribonucleoprotein complex acting as a protein sponge in translational regulation.
- Olivier Duss
- , Erich Michel
- & Frédéric H.-T. Allain
-
Letter |
 Thermal maps of gases in heterogeneous reactions
Thermal maps of gases in heterogeneous reactions
A technique of NMR thermometry that relies on the inverse relationship between NMR linewidths and temperature can be used to map non-invasively the gas temperatures inside catalytic reactors, offering unprecedented capabilities for testing the approximations used in reactor modelling.
- Nanette N. Jarenwattananon
- , Stefan Glöggler
- & Louis-S. Bouchard
-
Outlook |
 Q&A: A man of many dimensions
Q&A: A man of many dimensions
Richard R. Ernst pioneered one- and two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), and talks to Stephanie Harris about why dimensions are important in life as well as in science.
-
Article |
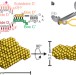 The structure of the box C/D enzyme reveals regulation of RNA methylation
The structure of the box C/D enzyme reveals regulation of RNA methylation
RNAs undergo many types of post-transcriptional modification, including methylation of ribosomal RNAs; here the structure of the archaeal box C/D ribonucleoprotein complex bound to substrate RNA is determined, showing that the two methylation guide sequences exist in different contexts and revealing sequential regulation of methylation at the two sites.
- Audrone Lapinaite
- , Bernd Simon
- & Teresa Carlomagno
-
Letter |
 Unusual architecture of the p7 channel from hepatitis C virus
Unusual architecture of the p7 channel from hepatitis C virus
The structure of the oligomeric hepatitis C virus viroporin p7 protein, solved by NMR spectroscopy, is reported; this protein can self-assemble into a channel complex that conducts cations and has a funnel-like channel architecture.
- Bo OuYang
- , Shiqi Xie
- & James J. Chou
-
Article |
 Visualizing transient low-populated structures of RNA
Visualizing transient low-populated structures of RNA
This study develops an NMR-based approach that can capture previously inaccessible, highly transient, low-populated ‘excited states’ in RNA; the localized rearrangements in base-pairing giving rise to these states are found to affect function by changing the exposure of residues required for a specific biological process.
- Elizabeth A. Dethoff
- , Katja Petzold
- & Hashim M. Al-Hashimi
-
Letter |
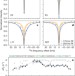 Atomic-resolution dynamics on the surface of amyloid-β protofibrils probed by solution NMR
Atomic-resolution dynamics on the surface of amyloid-β protofibrils probed by solution NMR
- Nicolas L. Fawzi
- , Jinfa Ying
- & G. Marius Clore
-
Letter |
 Mitochondrial uncoupling protein 2 structure determined by NMR molecular fragment searching
Mitochondrial uncoupling protein 2 structure determined by NMR molecular fragment searching
- Marcelo J. Berardi
- , William M. Shih
- & James J. Chou
-
Research Highlights |
NMR without the magnet
-
News Feature |
 Structural biology: Breaking the protein rules
Structural biology: Breaking the protein rules
If dogma dictates that proteins need a structure to function, then why do so many of them live in a state of disorder?
- Tanguy Chouard
-
News & Views |
 Unexpected interactions
Unexpected interactions
Unpaired electrons can exert effects that allow interatomic contacts in molecules to be detected more easily using nuclear magnetic resonance. One such effect reveals unusual interactions between certain atoms in a protein.
- Ivano Bertini
- & Claudio Luchinat
-
News & Views |
 Finding the wet spots
Finding the wet spots
The functions of proteins are critically coupled to their interplay with water, but determining the dynamics of most water molecules at protein surfaces hasn't been possible. A new spectroscopic method promises to change that.
- Vincent J. Hilser
-
Letter |
 Vernier templating and synthesis of a 12-porphyrin nano-ring
Vernier templating and synthesis of a 12-porphyrin nano-ring
Templates are widely used to arrange molecular components so they can be covalently linked into complex molecules that are not readily accessible by classical synthetic methods. But, as larger structures are targeted, the synthesis of the templates themselves becomes challenging. It is now shown that 'molecular Verniers' can solve this problem: using a template with six binding sites and molecular building blocks with four porphyrins acting as binding sites, a 12-porphyrin nano-ring with a diameter of 4.7 nm is created. The ease and efficiency of this synthesis establishes Vernier templating as a powerful new strategy for producing large monodisperse macromolecules.
- Melanie C. O’Sullivan
- , Johannes K. Sprafke
- & Harry L. Anderson
-
News & Views |
 Clear signals from surfaces
Clear signals from surfaces
Nuclear magnetic resonance is a versatile analytical technique, but acquiring well-resolved NMR spectra of chemical surfaces has been hard. The coming of age of a spectral enhancement method should change all that.
- Robert G. Griffin
-
Letter |
 The proteasome antechamber maintains substrates in an unfolded state
The proteasome antechamber maintains substrates in an unfolded state
The proteasome is a multi-protein complex that enzymatically degrades proteins. Proteolysis occurs in a barrel-shaped 20S core particle comprising three interconnected cavities, including a pair of antechambers in which substrates are held before degradation. These authors demonstrate that substrates interact actively with the antechamber walls and that the environment in this compartment is optimized to maintain the substrates in unfolded states so as to be accessible for hydrolysis.
- Amy M. Ruschak
- , Tomasz L. Religa
- & Lewis E. Kay
-
-
News Feature |
 Chemistry: Breaking the billion-hertz barrier
Chemistry: Breaking the billion-hertz barrier
Researchers in France have switched on the world's most powerful nuclear magnetic resonance instrument. Ananyo Bhattacharya asks whether it will attract new life to NMR spectroscopy.
- Ananyo Bhattacharya

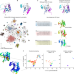 Predicting multiple conformations via sequence clustering and AlphaFold2
Predicting multiple conformations via sequence clustering and AlphaFold2