Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 THP9 enhances seed protein content and nitrogen-use efficiency in maize
THP9 enhances seed protein content and nitrogen-use efficiency in maize
Genetic analyses of teosinte, the wild ancestor of maize, identify a locus (THP9) that is associated with high seed protein content and increased nitrogen-use efficiency, suggesting that THP9 could have applications in crop breeding.
- Yongcai Huang
- , Haihai Wang
- & Yongrui Wu
-
Article
| Open Access An oxygen-sensing mechanism for angiosperm adaptation to altitude
An oxygen-sensing mechanism for angiosperm adaptation to altitude
Plants have adapted to grow at specific altitudes by regulating chlorophyll synthesis in response to ambient oxygen concentration, calibrated by altitude-dependent activity of GROUP VII ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR.
- Mohamad Abbas
- , Gunjan Sharma
- & Michael J. Holdsworth
-
Article
| Open Access A chickpea genetic variation map based on the sequencing of 3,366 genomes
A chickpea genetic variation map based on the sequencing of 3,366 genomes
Whole-genome sequencing of 3,171 cultivated and 195 wild chickpea accessions is used to construct a chickpea pan-genome, providing insight into chickpea evolution and enabling breeding strategies that could improve crop productivity.
- Rajeev K. Varshney
- , Manish Roorkiwal
- & Xin Liu
-
Article |
 Fine-root traits in the global spectrum of plant form and function
Fine-root traits in the global spectrum of plant form and function
The authors analyse the coordination and trade-off of the aboveground and fine-root traits of vascular plants using global trait databases.
- Carlos P. Carmona
- , C. Guillermo Bueno
- & Riin Tamme
-
Article |
 Genomic basis of geographical adaptation to soil nitrogen in rice
Genomic basis of geographical adaptation to soil nitrogen in rice
OsTCP19 is a modulator of the tillering response to nitrogen in rice, and introgression of an allele of OsTCP19 associated with a high tillering response into modern rice cultivars markedly improves their nitrogen-use efficiency.
- Yongqiang Liu
- , Hongru Wang
- & Chengcai Chu
-
Article |
 A prion-like domain in ELF3 functions as a thermosensor in Arabidopsis
A prion-like domain in ELF3 functions as a thermosensor in Arabidopsis
The adaptability of the plant Arabidopsis thaliana to different temperatures is regulated by the ability of its ELF3 protein to undergo liquid–liquid phase separation, in a manner that is dependent on the protein’s prion-like domain.
- Jae-Hoon Jung
- , Antonio D. Barbosa
- & Philip A. Wigge
-
Article |
 The strength and pattern of natural selection on gene expression in rice
The strength and pattern of natural selection on gene expression in rice
Phenotypic selection analysis is used to estimate the type and strength of selection that acts on more than 15,000 transcripts in rice (Oryza sativa), which provides insight into the adaptive evolutionary role of selection on gene expression.
- Simon C. Groen
- , Irina Ćalić
- & Michael D. Purugganan
-
Article |
 Modulating plant growth–metabolism coordination for sustainable agriculture
Modulating plant growth–metabolism coordination for sustainable agriculture
The balance of DELLA and GRF4 proteins in plants ensures the co-regulation of growth with metabolism and tipping this balance towards GRF4 leads to higher efficiency of nitrogen use.
- Shan Li
- , Yonghang Tian
- & Xiangdong Fu
-
Article
| Open Access Genomic variation in 3,010 diverse accessions of Asian cultivated rice
Genomic variation in 3,010 diverse accessions of Asian cultivated rice
Analyses of genetic variation and population structure based on over 3,000 cultivated rice (Oryza sativa) genomes reveal subpopulations that correlate with geographic location and patterns of introgression consistent with multiple rice domestication events.
- Wensheng Wang
- , Ramil Mauleon
- & Hei Leung
-
Article
| Open Access Genomics of the origin and evolution of Citrus
Genomics of the origin and evolution of Citrus
The origin, evolution and domestication of Citrus and the genealogy of the most important wild and cultivated citrus varieties.
- Guohong Albert Wu
- , Javier Terol
- & Manuel Talon
-
Article
| Open Access A chromosome conformation capture ordered sequence of the barley genome
A chromosome conformation capture ordered sequence of the barley genome
The International Barley Genome Sequencing Consortium reports sequencing and assembly of a reference genome for barley, Hordeum vulgare.
- Martin Mascher
- , Heidrun Gundlach
- & Nils Stein
-
Article |
 Genomic architecture of heterosis for yield traits in rice
Genomic architecture of heterosis for yield traits in rice
Insights into the genomic architecture of heterosis for grain yield in rice are presented, and further mapping of grain yield loci resolves candidate genes that could be useful for breeding.
- Xuehui Huang
- , Shihua Yang
- & Bin Han
-
Letter |
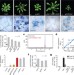 Natural allelic variation underlying a major fitness trade-off in Arabidopsis thaliana
Natural allelic variation underlying a major fitness trade-off in Arabidopsis thaliana
Here, a combination of forward genetics and genome-wide association analyses has been used to show that variation at a single genetic locus in Arabidopsis thaliana underlies phenotypic variation in vegetative growth as well as resistance to infection. The strong enhancement of resistance mediated by one of the alleles at this locus explains the allele's persistence in natural populations throughout the world, even though it drastically reduces the production of new leaves.
- Marco Todesco
- , Sureshkumar Balasubramanian
- & Detlef Weigel
-
Letter |
 Genome-wide association study of 107 phenotypes in Arabidopsis thaliana inbred lines
Genome-wide association study of 107 phenotypes in Arabidopsis thaliana inbred lines
Here, large-scale genome-wide association studies were carried out with the naturally occurring inbred lines of Arabidopsis thaliana, which can be genotyped once and phenotyped repeatedly. The results range from significant associations, usually corresponding to single genes, to findings that are more difficult to interpret, because confounding by complex genetics and population structure makes it hard to distinguish true associations from false.
- Susanna Atwell
- , Yu S. Huang
- & Magnus Nordborg

 The giant diploid faba genome unlocks variation in a global protein crop
The giant diploid faba genome unlocks variation in a global protein crop