Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule visualization of dynamic transitions of pore-forming peptides among multiple transmembrane positions
Single-molecule visualization of dynamic transitions of pore-forming peptides among multiple transmembrane positions
Assessing protein localization within lipid membranes is problematic. Here, the authors describe a single molecule visualization method based on surface-induced fluorescence attenuation (SIFA) to determine the insertion depth and lateral diffusion of a peptide in a lipid bilayer.
- Ying Li
- , Zhenyu Qian
- & Ming Li
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional flow nanometry of biological nanoparticles for accurate determination of their size and emission intensity
Two-dimensional flow nanometry of biological nanoparticles for accurate determination of their size and emission intensity
Size and molecular composition of biological nanoparticles dictate their function, but cannot be simultaneously determined accurately. Here, Höök and others have subjected constrained biological nanoparticles on a lipid bilayer to hydrodynamic flow to quantify accurately both size and emission intensity.
- Stephan Block
- , Björn Johansson Fast
- & Fredrik Höök
-
Article
| Open Access Geometrical assembly of ultrastable protein templates for nanomaterials
Geometrical assembly of ultrastable protein templates for nanomaterials
Protein nanotechnology for the fabrication of protein-based nanoscale devices is gaining momentum but assembling well-defined three-dimensional shapes is still challenging. Here, the authors use an existing prefoldin assembled system to design a template for the construction of geometrically constrained structures.
- Dominic J. Glover
- , Lars Giger
- & Douglas S. Clark
-
Article
| Open Access Optical micromanipulation of nanoparticles and cells inside living zebrafish
Optical micromanipulation of nanoparticles and cells inside living zebrafish
Manipulating the interactions of cells with their environment is usually done with cells in vitro, which does not reflect the complex in vivosystem. Here the authors demonstrate micromanipulation of microparticles, bacteria and immune cells within live zebrafish using optical tweezers.
- Patrick Lie Johansen
- , Federico Fenaroli
- & Gerbrand Koster
-
Article
| Open Access Two-colour live-cell nanoscale imaging of intracellular targets
Two-colour live-cell nanoscale imaging of intracellular targets
The intracellular applications of STED microscopy are limited by the availability of dyes. Here the authors develop a two-colour labelling strategy based on SiR and ATTO590 dyes, and apply their strategy to image various subcellular membrane compartments.
- Francesca Bottanelli
- , Emil B. Kromann
- & Joerg Bewersdorf
-
Article
| Open Access Subnanometre enzyme mechanics probed by single-molecule force spectroscopy
Subnanometre enzyme mechanics probed by single-molecule force spectroscopy
Adenylate kinase catalyses the interconversion of adenosine phosphates, and plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular energy homeostasis. Here, the authors use single molecule optical tweezers to understand how the enzyme’s conformation dynamics modulates catalysis.
- Benjamin Pelz
- , Gabriel Žoldák
- & Matthias Rief
-
Article
| Open Access The mechanochemistry of copper reports on the directionality of unfolding in model cupredoxin proteins
The mechanochemistry of copper reports on the directionality of unfolding in model cupredoxin proteins
In metalloproteins, a metal cofactor participates in the formation of the correct fold. Here the authors demonstrate—using single molecule force spectroscopy and the native copper centre as an embedded internal reporter—that the blue-copper proteins azurin and plastocyanin unfold via two independent competing pathways under force.
- Amy E. M. Beedle
- , Ainhoa Lezamiz
- & Sergi Garcia-Manyes
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of erosion of nanostructured porous silicon drug carriers in neoplastic tissues
Mechanism of erosion of nanostructured porous silicon drug carriers in neoplastic tissues
The degradation of materials used in biological applications has an important bearing on their long term performance. Here, the authors show how porous silicon nanoparticle degradation can be accelerated in vivothrough the influence of local tissue pathology, likely influencing drug delivery performance.
- Adi Tzur-Balter
- , Zohar Shatsberg
- & Natalie Artzi
-
Article |
 Reconstitution of a nanomachine driving the assembly of proteins into bacterial outer membranes
Reconstitution of a nanomachine driving the assembly of proteins into bacterial outer membranes
The translocation and assembly module (TAM) is a nanomachine responsible for assembly of proteins into the outer membrane of pathogenic bacteria. Here, Shen et al.use magnetic contrast neutron reflectrometry to visualize movements within the TAM and insertion of a substrate protein into the lipid bilayer.
- Hsin-Hui Shen
- , Denisse L. Leyton
- & Trevor Lithgow
-
Article
| Open Access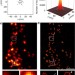 Quantitative super-resolution imaging of Bruchpilot distinguishes active zone states
Quantitative super-resolution imaging of Bruchpilot distinguishes active zone states
Complex molecular interactions occur in the active zone cytomatrix (CAZ) within the presynaptic terminal to regulate synaptic plasticity. Here, the authors use imaging techniques to show that the CAZ is composed of units containing on average 137 Bruchpilot proteins, many of which are arranged into clusters.
- Nadine Ehmann
- , Sebastian van de Linde
- & Robert J. Kittel

 Re-entrant DNA gels
Re-entrant DNA gels