Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Cytochrome c lysine acetylation regulates cellular respiration and cell death in ischemic skeletal muscle
Cytochrome c lysine acetylation regulates cellular respiration and cell death in ischemic skeletal muscle
The authors report that acetylation of cytochrome c on K39 acts as a molecular switch in ischemic skeletal muscle, but not other tissues, to increase respiration and prevent apoptosis. This gives skeletal muscle robust resilience to ischemia and ischemia-reperfusion injury.
- Paul T. Morse
- , Gonzalo Pérez-Mejías
- & Maik Hüttemann
-
Article
| Open Access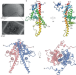 Atomic structure of a nudivirus occlusion body protein determined from a 70-year-old crystal sample
Atomic structure of a nudivirus occlusion body protein determined from a 70-year-old crystal sample
Viral occlusion bodies are robust protein crystals that encapsulate virions of some insect viruses. Here, the authors determine the nudivirus occlusion body structure and describe common principles of occlusion body structure.
- Jeremy R. Keown
- , Adam D. Crawshaw
- & Jonathan M. Grimes
-
Article
| Open Access Designed Rubredoxin miniature in a fully artificial electron chain triggered by visible light
Designed Rubredoxin miniature in a fully artificial electron chain triggered by visible light
Living organisms regulate their energy demand by managing electron trafficking in complex transport chains. Here, the authors pioneer a fully artificial electron chain triggered by visible light using designed proteins, unlocking possibilities in bioengineering.
- Marco Chino
- , Luigi Franklin Di Costanzo
- & Vincenzo Pavone
-
Article
| Open Access Regulation of BRCA1 stability through the tandem UBX domains of isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase 1
Regulation of BRCA1 stability through the tandem UBX domains of isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase 1
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases possess unique domains. In this study the structure of the vertebrate IARS1 and EARS1 complex reveals that vertebrate IARS1 protects the DNA repair factor BRCA1 from proteolytic degradation via its UBX-fold domain.
- Scisung Chung
- , Mi-Sun Kang
- & Yunje Cho
-
Article
| Open Access De novo determination of mosquitocidal Cry11Aa and Cry11Ba structures from naturally-occurring nanocrystals
De novo determination of mosquitocidal Cry11Aa and Cry11Ba structures from naturally-occurring nanocrystals
An environmentally safe means of mosquito control is the application of Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis, which produces a cocktail of four naturally crystalline proteins exclusively toxic to mosquito. Here the authors report the atomic-resolution structures of Bti Cry11Aa and related Btj Cry11Ba solved de novo through Serial Femtosecond Crystallography on naturally-occurring nanocrystals.
- Guillaume Tetreau
- , Michael R. Sawaya
- & Jacques-Philippe Colletier
-
Article
| Open Access Binding and structural basis of equine ACE2 to RBDs from SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2 and related coronaviruses
Binding and structural basis of equine ACE2 to RBDs from SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2 and related coronaviruses
This study documents equine ACE2 (eqACE2) binding to the RBDs of SARS-CoV-2 and related CoVs, revealing a mechanism of eqACE2 binding with RaTG13-RBD, SARS-CoV-2 prototype-RBD and Omicron BA.1-RBD.
- Zepeng Xu
- , Xinrui Kang
- & George Fu Gao
-
Article
| Open Access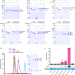 Structural basis for MTA1c-mediated DNA N6-adenine methylation
Structural basis for MTA1c-mediated DNA N6-adenine methylation
DNA N6-adenine methylation (6 mA) plays a crucial role in epigenetic regulation in eukaryotes. Here, the authors determined nine crystal structures of the ciliates 6 mA methyltransferase complexes, providing the molecular basis for understanding the functions of 6 mA.
- Jiyun Chen
- , Rong Hu
- & Liang Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Hypocrates is a genetically encoded fluorescent biosensor for (pseudo)hypohalous acids and their derivatives
Hypocrates is a genetically encoded fluorescent biosensor for (pseudo)hypohalous acids and their derivatives
There are a lack of tools to study the dynamics of (pseudo)hypohalous acids in live cells. Here the authors report a genetically encoded fluorescent biosensor, Hypocrates, for (pseudo)hypohalous acids and their derivatives which they use in cells and in a zebrafish tail fin injury model.
- Alexander I. Kostyuk
- , Maria-Armineh Tossounian
- & Vsevolod V. Belousov
-
Article
| Open Access MyD88 TIR domain higher-order assembly interactions revealed by microcrystal electron diffraction and serial femtosecond crystallography
MyD88 TIR domain higher-order assembly interactions revealed by microcrystal electron diffraction and serial femtosecond crystallography
MAL and MyD88 are downstream adaptors of Toll-like receptors (TLR) and the MAL TIR domain forms filaments in vitro, which in turn nucleate the assembly of crystalline arrays of the MyD88 TIR domain. Here, the authors present the structure of these MyD88 TIR crystalline arrays solved by both microcrystal electron diffraction and serial femtosecond crystallography, and they show with mutagenesis experiments that MyD88 interface residues are important for TLR4 signaling in vivo.
- Max T. B. Clabbers
- , Susannah Holmes
- & Thomas Ve
-
Article
| Open Access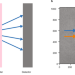 Effect of X-ray free-electron laser-induced shockwaves on haemoglobin microcrystals delivered in a liquid jet
Effect of X-ray free-electron laser-induced shockwaves on haemoglobin microcrystals delivered in a liquid jet
X-ray fee-electron lasers (XFELs) enable time-resolved crystallography experiments and the structure determination of proteins with little or no radiation damage. However currently it is unknown whether the designated 4.5 MHz maximum pulse rate for the European XFEL could lead to sample damage caused by shock waves from preceding pulses. Here, the authors address this question by performing a X-ray pump X-ray probe experiment on haemoglobin microcrystals at the Stanford XFEL facility that mimics the 4.5 MHz data collection mode and observe structural changes and a drop in diffraction data quality of the crystals.
- Marie Luise Grünbein
- , Alexander Gorel
- & Ilme Schlichting
-
Article
| Open Access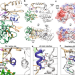 Granulovirus PK-1 kinase activity relies on a side-to-side dimerization mode centered on the regulatory αC helix
Granulovirus PK-1 kinase activity relies on a side-to-side dimerization mode centered on the regulatory αC helix
The viral Protein Kinase-1 (PK-1) phosphorylates the regulatory protein p6.9, which facilitates baculoviral genome release. Here, the authors combine X-ray crystallography with biophysical and biochemical analyses as well as molecular dynamics simulations to characterize Cydia pomenella granulovirus PK-1, which forms a dimer with a parallel side-to-side arrangement of the kinase domains and furthermore, they provide insights into its catalytic mechanism and evolutionary relationships with other kinases.
- Michael R. Oliver
- , Christopher R. Horne
- & James M. Murphy
-
Article
| Open Access The complex structure of GRL0617 and SARS-CoV-2 PLpro reveals a hot spot for antiviral drug discovery
The complex structure of GRL0617 and SARS-CoV-2 PLpro reveals a hot spot for antiviral drug discovery
The SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease (PLpro) is of interest as a drug target. Here, the authors identify GRL0617 as a PPI (protein–protein interaction) inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 PLpro that inhibits its deISGylating activity and present the mechanism of action of the compound through the GRL0617-bound PLpro crystal structure and NMR studies.
- Ziyang Fu
- , Bin Huang
- & Hao Huang
-
Article
| Open Access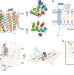 Structural insights into the mechanism of rhodopsin phosphodiesterase
Structural insights into the mechanism of rhodopsin phosphodiesterase
Rhodopsin phosphodiesterase (Rh-PDE) hydrolyzes both cAMP and cGMP in a light-dependent manner. Structural and functional analyses of the Rh-PDE from Salpingoeca rosetta reveal unusual rhodopsin topology comprising 8 transmembrane helices (TMs) and suggest that TM0 plays a crucial role in the enzymatic photoactivity.
- Tatsuya Ikuta
- , Wataru Shihoya
- & Osamu Nureki
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering and application of a biosensor with focused ligand specificity
Engineering and application of a biosensor with focused ligand specificity
Transcriptional biosensors represent powerful tools for the screening of vast strain libraries, but the broad ligand specificity of some transcriptional regulators (TRs) can prohibit such applications. Here authors present the engineering of a LysG-based biosensor with a focused ligand specificity to isolate L-histidine-producing strains.
- Dennis Della Corte
- , Hugo L. van Beek
- & Jan Marienhagen
-
Article
| Open Access Segmented flow generator for serial crystallography at the European X-ray free electron laser
Segmented flow generator for serial crystallography at the European X-ray free electron laser
Due to the pulsed nature of X-ray free electron laser (XFEL) instruments the majority of protein crystals, which are injected using continuous jet injection techniques are wasted. Here, the authors present a microfluidic device to deliver aqueous protein crystal laden droplets segmented with an immiscible oil and demonstrate that with this device an approx. 60% reduction in sample waste was achieved for data collection of 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonate 8-phosphate synthase crystals at the EuXFEL.
- Austin Echelmeier
- , Jorvani Cruz Villarreal
- & Alexandra Ros
-
Article
| Open Access Both Boceprevir and GC376 efficaciously inhibit SARS-CoV-2 by targeting its main protease
Both Boceprevir and GC376 efficaciously inhibit SARS-CoV-2 by targeting its main protease
Coronavirus main protease is essential for viral polyprotein processing and maturation. Here Fu et al. report efficient inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 replication using two inhibitors - Boceprevir and GC376 - targeting the active site of the main viral protease.
- Lifeng Fu
- , Fei Ye
- & George Fu Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Structural dynamics in proteins induced by and probed with X-ray free-electron laser pulses
Structural dynamics in proteins induced by and probed with X-ray free-electron laser pulses
The local X-ray-induced dynamics that occur in protein crystals during serial femtosecond crystallography (SFX) measurements at XFELs are not well understood. Here the authors performed a time-resolved X-ray pump X-ray probe SFX experiment, and they observe distinct structural changes in the disulfide bridges and peptide backbone of proteins; complementing theoretical approaches allow them to further characterize the details of the X-ray induced ionization and local structural dynamics.
- Karol Nass
- , Alexander Gorel
- & Ilme Schlichting
-
Article
| Open Access Serial femtosecond crystallography on in vivo-grown crystals drives elucidation of mosquitocidal Cyt1Aa bioactivation cascade
Serial femtosecond crystallography on in vivo-grown crystals drives elucidation of mosquitocidal Cyt1Aa bioactivation cascade
Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis (Bti) produces the naturally-crystalline proteinaceous toxin Cyt1Aa that is toxic to mosquito larvae. Here the authors grow recombinant nanocrystals of the Cyt1Aa protoxin in vivo and use serial femtosecond crystallography to determine its structure at different redox and pH conditions and by combining their structural data with further biochemical, toxicological and biophysical analyses provide mechanistic insights into the Cyt1Aa bioactivation cascade.
- Guillaume Tetreau
- , Anne-Sophie Banneville
- & Jacques-Philippe Colletier
-
Article
| Open Access Serial protein crystallography in an electron microscope
Serial protein crystallography in an electron microscope
For conventional three-dimensional microcrystal electron diffraction (3D ED/MicroED), a crystal is slowly rotated under an electron beam, leading to inevitable accumulation of radiation damage during data collection. In this work, the authors present a serial electron diffraction method, where still diffraction patterns from many protein nanocrystals are rapidly recorded and merged, which minimises radiation damage and only requires a slightly modified standard scanning transmission electron microscope.
- Robert Bücker
- , Pascal Hogan-Lamarre
- & R. J. Dwayne Miller
-
Article
| Open Access Photoswitching mechanism of a fluorescent protein revealed by time-resolved crystallography and transient absorption spectroscopy
Photoswitching mechanism of a fluorescent protein revealed by time-resolved crystallography and transient absorption spectroscopy
rsEGFP2 is a reversibly photoswitchable fluorescent protein used in super-resolution light microscopy. Here the authors present the structure of an rsEGFP2 ground-state intermediate after excited state-decay that was obtained by nanosecond time-resolved serial femtosecond crystallography at an X-ray free electron laser, and time-resolved absorption spectroscopy measurements complement their structural analysis.
- Joyce Woodhouse
- , Gabriela Nass Kovacs
- & Martin Weik
-
Article
| Open Access Membrane protein megahertz crystallography at the European XFEL
Membrane protein megahertz crystallography at the European XFEL
The European X-ray free-electron laser (EuXFEL) in Hamburg is the first XFEL with a megahertz repetition rate. Here the authors present the 2.9 Å structure of the large membrane protein complex Photosystem I from T. elongatus that was determined at the EuXFEL.
- Chris Gisriel
- , Jesse Coe
- & Nadia A. Zatsepin
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional view of ultrafast dynamics in photoexcited bacteriorhodopsin
Three-dimensional view of ultrafast dynamics in photoexcited bacteriorhodopsin
Bacteriorhodopsin (bR) is a light-driven proton pump. Here the authors combine time-resolved crystallography at a free-electron laser, ultrafast spectroscopy and quantum chemistry to study the structural changes following multiphoton photoexcitation of bR and find that they occur within 300 fs not only in the light-absorbing chromophore but also in the surrounding protein.
- Gabriela Nass Kovacs
- , Jacques-Philippe Colletier
- & Ilme Schlichting
-
Article
| Open Access Megahertz serial crystallography
Megahertz serial crystallography
The new European X-Ray Free-Electron Laser (EuXFEL) is the first XFEL that generates X-ray pulses with a megahertz inter-pulse spacing. Here the authors demonstrate that high-quality and damage-free protein structures can be obtained with the currently available 1.1 MHz repetition rate pulses using lysozyme as a test case and furthermore present a β-lactamase structure.
- Max O. Wiedorn
- , Dominik Oberthür
- & Anton Barty
-
Article
| Open Access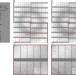 Megahertz data collection from protein microcrystals at an X-ray free-electron laser
Megahertz data collection from protein microcrystals at an X-ray free-electron laser
The European X-ray free-electron laser (EuXFEL) in Hamburg is the first megahertz (MHz) repetition rate XFEL. Here the authors use lysozyme crystals and microcrystals from jack bean proteins and demonstrate that damage-free high quality data can be collected at a MHz repetition rate.
- Marie Luise Grünbein
- , Johan Bielecki
- & Ilme Schlichting
-
Article
| Open Access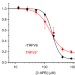 Structural bases of TRP channel TRPV6 allosteric modulation by 2-APB
Structural bases of TRP channel TRPV6 allosteric modulation by 2-APB
The transient receptor potential channel TRPV6 mediates calcium uptake in epithelia and its expression is increased in several cancer types. Here, authors present structures of TRPV6 bound to 2-APB, a TRPV6 inhibitor, and show that 2-APB induces TRPV6 channel closure by modulating protein–lipid interactions.
- Appu K. Singh
- , Kei Saotome
- & Alexander I. Sobolevsky
-
Article
| Open Access JMJD5 is a human arginyl C-3 hydroxylase
JMJD5 is a human arginyl C-3 hydroxylase
Jumonji-C domain containing protein 5 (JMJD5) is essential for animal development but its catalytic activity has remained elusive so far. Here the authors show that human JMJD5 is an arginyl-hydroxylase and present the cofactor, substrate and product bound JMJD5 crystal structures.
- Sarah E. Wilkins
- , Md. Saiful Islam
- & Rasheduzzaman Chowdhury
-
Article
| Open Access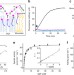 Structural insights into the committed step of bacterial phospholipid biosynthesis
Structural insights into the committed step of bacterial phospholipid biosynthesis
The first step in bacterial phospholipid biosynthesis is the acylation of glycerol 3-phosphate to form lysophosphatidic acid. Here, the authors present the high resolution crystal structure of the glycerol 3-phosphate acyltransferase PlsY, a membrane protein and give insights into its catalytical mechanism.
- Zhenjian Li
- , Yannan Tang
- & Dianfan Li
-
Article
| Open Access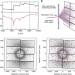 Multi-wavelength anomalous diffraction de novo phasing using a two-colour X-ray free-electron laser with wide tunability
Multi-wavelength anomalous diffraction de novo phasing using a two-colour X-ray free-electron laser with wide tunability
X-ray free-electron lasers produce bright femtosecond X-ray pulses. Here, the authors use a two-colour X-ray free-electron laser beam for simultaneous two-wavelength data collection and show that protein structures can be determined with multiple wavelength anomalous dispersion phasing, which is important for difficult-to-phase projects.
- Alexander Gorel
- , Koji Motomura
- & Ilme Schlichting
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and mechanistic characterization of an archaeal-like chaperonin from a thermophilic bacterium
Structural and mechanistic characterization of an archaeal-like chaperonin from a thermophilic bacterium
Chaperonins (CPNs) are ATP-dependent protein-folding machines. Here the authors present the open and closed crystal structures of a Group III CPN from the thermophilic bacterium Carboxydothermus hydrogenoformans, discuss its mechanism and structurally compare it with Group I and II CPNs.
- Young Jun An
- , Sara E. Rowland
- & Sun-Shin Cha
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structure of a multi-domain human smoothened receptor in complex with a super stabilizing ligand
Crystal structure of a multi-domain human smoothened receptor in complex with a super stabilizing ligand
Smoothened receptors (SMO) play a key role in the Hedgehog signalling pathway. Here the authors present the structure of a multi-domain human SMO with a rationally designed stabilizing ligand bound in the transmembrane domain of the receptor, and propose a model for SMO activation.
- Xianjun Zhang
- , Fei Zhao
- & Fei Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Inhibition of delta-secretase improves cognitive functions in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease
Inhibition of delta-secretase improves cognitive functions in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease
Delta-secretases are associated with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) as they cleave both amyloid precursor protein and tau. Here the authors develop a series of orally bioactive small molecule delta-secretase inhibitors and report its therapeutic effects in mouse models of AD.
- Zhentao Zhang
- , Obiamaka Obianyo
- & Keqiang Ye
-
Article
| Open Access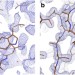 Selenium single-wavelength anomalous diffraction de novo phasing using an X-ray-free electron laser
Selenium single-wavelength anomalous diffraction de novo phasing using an X-ray-free electron laser
X-ray free electron lasers are increasingly available for use in macromolecular structure determination. Here, the authors describe the successful use of selenium single-wavelength anomalous diffraction data to calculate experimentally derived phases.
- Mark S. Hunter
- , Chun Hong Yoon
- & Sébastien Boutet

 Heterogeneity in M. tuberculosis β-lactamase inhibition by Sulbactam
Heterogeneity in M. tuberculosis β-lactamase inhibition by Sulbactam