Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting locations of cryptic pockets from single protein structures using the PocketMiner graph neural network
Predicting locations of cryptic pockets from single protein structures using the PocketMiner graph neural network
Cryptic pockets enable targeting of proteins currently considered undruggable because they lack pockets in their ground state structures. Here, the authors develop a graph neural network that accurately predicts cryptic pockets in static structures by training using molecular simulation data alone.
- Artur Meller
- , Michael Ward
- & Gregory R. Bowman
-
Article
| Open Access Structural details of a Class B GPCR-arrestin complex revealed by genetically encoded crosslinkers in living cells
Structural details of a Class B GPCR-arrestin complex revealed by genetically encoded crosslinkers in living cells
The conformation of GPCR-arrestin complexes at the cell membrane, despite available structures, remains uncertain. This work reveals structure and dynamics of the PTH1R-arrestin2 complex, including flexible regions, in live cells.
- Yasmin Aydin
- , Thore Böttke
- & Irene Coin
-
Article
| Open Access Evaluating native-like structures of RNA-protein complexes through the deep learning method
Evaluating native-like structures of RNA-protein complexes through the deep learning method
RNA-protein docking is a very challenging area. Here, the authors develop a deep-learning based method, DRPScore, to evaluate RNA-protein complexes. DRPScore is robust and consistently performs better than existing methods on representative testing sets.
- Chengwei Zeng
- , Yiren Jian
- & Yunjie Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Network of hotspot interactions cluster tau amyloid folds
Network of hotspot interactions cluster tau amyloid folds
The authors developed a computational approach to probe the stability of amyloid fibrils and discover networks of hotspot interactions. Understanding the mechanisms of amyloid folding will help identify novel methods to treat protein (mis)folding diseases.
- Vishruth Mullapudi
- , Jaime Vaquer-Alicea
- & Lukasz A. Joachimiak
-
Article
| Open Access Histone variant H2A.Z modulates nucleosome dynamics to promote DNA accessibility
Histone variant H2A.Z modulates nucleosome dynamics to promote DNA accessibility
Here the authors show that H2A.Z histone variant incorporation reduces the nucleosomal barrier for transcription. Furthermore their simulations reveal that H2A.Z facilitates spontaneous DNA unwrapping from the histone octamer and enhances nucleosome gaping.
- Shuxiang Li
- , Tiejun Wei
- & Anna R. Panchenko
-
Article
| Open Access Direct generation of protein conformational ensembles via machine learning
Direct generation of protein conformational ensembles via machine learning
Computational methods to study protein structural dynamics are a powerful tool in life sciences but are computationally expensive. Here, the authors show that machine learning can be used to efficiently generate protein conformational ensembles and test their method on intrinsically disordered peptides.
- Giacomo Janson
- , Gilberto Valdes-Garcia
- & Michael Feig
-
Article
| Open Access The SPOC domain is a phosphoserine binding module that bridges transcription machinery with co- and post-transcriptional regulators
The SPOC domain is a phosphoserine binding module that bridges transcription machinery with co- and post-transcriptional regulators
Here the authors establish the SPOC domain as a universal reader of the RNA Pol II CTD code and a versatile reader of phosphoserine marks found in co- and post-transcriptional regulators such as m6A writer and reader proteins.
- Lisa-Marie Appel
- , Vedran Franke
- & Dea Slade
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing the transiently populated closed-state of human HSP90 ATP binding domain
Visualizing the transiently populated closed-state of human HSP90 ATP binding domain
To refold client proteins, HSP90 chaperone undergoes large structural rearrangements. Here the authors use NMR and molecular simulation and reveal structure and dynamics of a key functionally relevant metastable state of human HSP90α N-terminal domain.
- Faustine Henot
- , Elisa Rioual
- & Jerome Boisbouvier
-
Article
| Open Access Sampling of structure and sequence space of small protein folds
Sampling of structure and sequence space of small protein folds
In this work the authors provide a computational workflow for the parallel, from scratch, design of proteins to rapidly explore the shape diversity of protein folds.
- Thomas W. Linsky
- , Kyle Noble
- & Eva-Maria Strauch
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical space docking enables large-scale structure-based virtual screening to discover ROCK1 kinase inhibitors
Chemical space docking enables large-scale structure-based virtual screening to discover ROCK1 kinase inhibitors
Virtual screening of huge libraries is successful in identifying drug leads. Here, the authors describe a computational strategy, Chemical Space Docking, which combines docking with a reaction-based search of compounds, thereby enabling the exploration of billions of compounds and beyond.
- Paul Beroza
- , James J. Crawford
- & Christian Lemmen
-
Article
| Open Access Small molecules targeting the disordered transactivation domain of the androgen receptor induce the formation of collapsed helical states
Small molecules targeting the disordered transactivation domain of the androgen receptor induce the formation of collapsed helical states
In this work the authors report atomically detailed computer simulations revealing the binding mechanisms of small molecule drugs to an intrinsically disordered region of the androgen receptor, a castration-resistant prostate cancer drug target.
- Jiaqi Zhu
- , Xavier Salvatella
- & Paul Robustelli
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for recognition of antihistamine drug by human histamine receptor
Structural basis for recognition of antihistamine drug by human histamine receptor
Crystal structure of human histamine receptor H3R bound to an antagonist PF-03654746 reveals the unexpected binding modes of the antagonist and allosteric cholesterol, which could facilitate the structure-based design of novel antihistamines.
- Xueqian Peng
- , Linlin Yang
- & Haitao Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting the structure of large protein complexes using AlphaFold and Monte Carlo tree search
Predicting the structure of large protein complexes using AlphaFold and Monte Carlo tree search
The accuracy of AlphaFold decreases with the number of protein chains and the available GPU memory limits the size of protein complexes that can be predicted. Here, the authors show that complexes with 10–30 chains can be assembled from predicted subcomponents using Monte Carlo tree search.
- Patrick Bryant
- , Gabriele Pozzati
- & Arne Elofsson
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting the structural basis of targeted protein degradation by integrating molecular dynamics simulations with structural mass spectrometry
Predicting the structural basis of targeted protein degradation by integrating molecular dynamics simulations with structural mass spectrometry
The formation of ternary degrader-protein complexes is a key step in the targeted degradation of proteins of interest. Here, the authors explore the structure and dynamics of such complexes applying high-performance computer simulations augmented with experimental data.
- Tom Dixon
- , Derek MacPherson
- & Jesus A. Izaguirre
-
Article
| Open Access Evolutionary origin of vertebrate OCT4/POU5 functions in supporting pluripotency
Evolutionary origin of vertebrate OCT4/POU5 functions in supporting pluripotency
By constructing an evolutionary trajectory of the cyclostome-gnathostome Pou5 gene family and comparing the structural and phenotypic protein variations, the authors uncover the origin of functional characteristics for the pluripotency factor Oct4.
- Woranop Sukparangsi
- , Elena Morganti
- & Joshua M. Brickman
-
Article
| Open Access A multi-adenylate cyclase regulator at the flagellar tip controls African trypanosome transmission
A multi-adenylate cyclase regulator at the flagellar tip controls African trypanosome transmission
Trypanosomes can sense signal molecules and coordinate their movement in response to such signals, a phenomenon termed social motility (SoMo). Here, Bachmaier et al show that cyclic AMP response protein 3 (CARP3) localization to the flagellar tip and its interaction with a number of different adenylate cyclases is essential for migration to tsetse fly salivary glands and for SoMo, therewith linking SoMo and cAMP signaling to trypanosome transmission.
- Sabine Bachmaier
- , Giacomo Giacomelli
- & Michael Boshart
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into the pSer/pThr dependent regulation of the SHP2 tyrosine phosphatase in insulin and CD28 signaling
Structural insights into the pSer/pThr dependent regulation of the SHP2 tyrosine phosphatase in insulin and CD28 signaling
SHP2 is an important human tyrosine phosphatase with key roles in cancer, immune responses and insulin signaling. Here, the authors explore its substrate recognition mechanism in molecular detail and uncover a complex regulatory mechanism for this enzyme that marks specific target sites for dephosphorylation.
- András Zeke
- , Tamás Takács
- & Attila Reményi
-
Article
| Open Access The clinical drug candidate anle138b binds in a cavity of lipidic α-synuclein fibrils
The clinical drug candidate anle138b binds in a cavity of lipidic α-synuclein fibrils
Understanding how small molecules bind to pathological aggregates is of importance for therapeutic and diagnostic development in diseases such as Parkinson’s Disease. Here, the authors reveal a binding site of anle138b to lipid-induced α-synuclein fibrils.
- Leif Antonschmidt
- , Dirk Matthes
- & Loren B. Andreas
-
Article
| Open Access Proton-driven alternating access in a spinster lipid transporter
Proton-driven alternating access in a spinster lipid transporter
The Spns lipid transporters use ion gradients to drive substrate transport, including bioactive sphingolipids. Here, Dastvan et al. investigated how binding of protons powers the conformational changes that enable broad transport by a bacterial Spns.
- Reza Dastvan
- , Ali Rasouli
- & Emad Tajkhorshid
-
Article
| Open Access ABCA1 is an extracellular phospholipid translocase
ABCA1 is an extracellular phospholipid translocase
ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) drives phospholipid (PL) from the plasma membrane into extracellular apolipoprotein A-I, for the production of high density lipoprotein (HDL). Here, the authors use simulations to assess the mechanism of ABCA1 function and show that ABCA1 extracts lipid from the outer face of the plasma membrane.
- Jere P. Segrest
- , Chongren Tang
- & Jay W. Heinecke
-
Article
| Open Access G protein coupling and activation of the metabotropic GABAB heterodimer
G protein coupling and activation of the metabotropic GABAB heterodimer
Despite its crucial role in the central nervous system, little is known about the activation mechanism of GABAB receptor. Here, the authors predict that the inactive G protein induces conformational changes of the receptor to form an intermediate state.
- Moon Young Yang
- , Soo-Kyung Kim
- & William A. Goddard III
-
Article
| Open Access Cross-validation of distance measurements in proteins by PELDOR/DEER and single-molecule FRET
Cross-validation of distance measurements in proteins by PELDOR/DEER and single-molecule FRET
Pulsed electron-electron double resonance spectroscopy (PELDOR/DEER) and single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer spectroscopy (smFRET) are used to determine conformational changes and probe distances in biological macromolecules. Here the authors compare the methods on a large set of samples.
- Martin F. Peter
- , Christian Gebhardt
- & Gregor Hagelueken
-
Article
| Open Access Protein shape sampled by ion mobility mass spectrometry consistently improves protein structure prediction
Protein shape sampled by ion mobility mass spectrometry consistently improves protein structure prediction
Collision cross sections (CCS) from ion mobility mass spectrometry provide information about protein shape and size. Here, the authors develop an algorithm to predict CCS and integrate experimental ion mobility data into Rosetta-based molecular modelling to predict protein structures from sequence.
- SM Bargeen Alam Turzo
- , Justin T. Seffernick
- & Steffen Lindert
-
Article
| Open Access Length-dependent motions of SARS-CoV-2 frameshifting RNA pseudoknot and alternative conformations suggest avenues for frameshifting suppression
Length-dependent motions of SARS-CoV-2 frameshifting RNA pseudoknot and alternative conformations suggest avenues for frameshifting suppression
Modeling the SARS-CoV-2 frameshifting RNA element (FSE), a drug target against Covid-19, the authors analyze the dynamics of three FSE conformations at different lengths to propose a conformational transition pathway and describe anti-viral strategies.
- Shuting Yan
- , Qiyao Zhu
- & Tamar Schlick
-
Article
| Open Access Selective activation of Gαob by an adenosine A1 receptor agonist elicits analgesia without cardiorespiratory depression
Selective activation of Gαob by an adenosine A1 receptor agonist elicits analgesia without cardiorespiratory depression
Wall et al. describe the selective activation of an adenosine A1 receptor-mediated intracellular pathway that provides potent analgesia in the absence of sedation or cardiorespiratory depression, paving the way for novel medicines based on the far-reaching concept of selective Gα agonism.
- Mark J. Wall
- , Emily Hill
- & Bruno G. Frenguelli
-
Article
| Open Access Elasticity of podosome actin networks produces nanonewton protrusive forces
Elasticity of podosome actin networks produces nanonewton protrusive forces
Actin filaments generate force in diverse contexts, although how they can produce nanonewtons of force is unclear. Here, the authors apply cryo-electron tomography, quantitative analysis, and modelling to reveal the podosome core is a dense, spring-loaded, actin network storing elastic energy.
- Marion Jasnin
- , Jordan Hervy
- & Renaud Poincloux
-
Article
| Open Access A litmus test for classifying recognition mechanisms of transiently binding proteins
A litmus test for classifying recognition mechanisms of transiently binding proteins
The authors provide a litmus test for the recognition mechanism of transiently binding proteins based on nuclear magnetic resonance and find a conformational selection binding mechanism through concentration-dependent kinetics of ubiquitin and SH3.
- Kalyan S. Chakrabarti
- , Simon Olsson
- & Christian Griesinger
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and electrophysiological basis for the modulation of KCNQ1 channel currents by ML277
Structural and electrophysiological basis for the modulation of KCNQ1 channel currents by ML277
KCNQ1 channels are active in heart, brain and gut. Functional loss causes epilepsy and sudden arrhythmic death. Here, authors describe a key activator drug binding site, explaining isoform and drug selectivity, and point the way for new drug design.
- Katrien Willegems
- , Jodene Eldstrom
- & David Fedida
-
Article
| Open Access Computational identification of HCV neutralizing antibodies with a common HCDR3 disulfide bond motif in the antibody repertoires of infected individuals
Computational identification of HCV neutralizing antibodies with a common HCDR3 disulfide bond motif in the antibody repertoires of infected individuals
Identifying determinants of broadly neutralizing antibodies against hepatitis C virus (HCV) may guide HCV vaccine design. Here, the authors discover new anti-HCV antibodies using computational screening and analyze the amino acid composition and sequence-structure relationships in this antibody family.
- Nina G. Bozhanova
- , Andrew I. Flyak
- & Jens Meiler
-
Article
| Open Access The pocketome of G-protein-coupled receptors reveals previously untargeted allosteric sites
The pocketome of G-protein-coupled receptors reveals previously untargeted allosteric sites
G-protein-coupled receptors bind endogenous ligands at sites that are frequently highly conserved. Here, authors computationally describe alternative allosteric pockets, several of which have not been targeted by synthetic ligands before.
- Janik B. Hedderich
- , Margherita Persechino
- & Peter Kolb
-
Article
| Open Access Magic angle spinning NMR structure of human cofilin-2 assembled on actin filaments reveals isoform-specific conformation and binding mode
Magic angle spinning NMR structure of human cofilin-2 assembled on actin filaments reveals isoform-specific conformation and binding mode
Despite their relevance as regulators of actin severing and filament disassembly, few structural insights into the mechanism of cofilin-isoform-specific severing activity are reported. Here, the authors provide structural insights towards actin severing activity by human cofilin-2 obtained by MAS NMR and all-atom MD simulations. The results reveal an isoform-specific binding mode unique to CFL2 that may be related to its potent severing properties in-vivo.
- Jodi Kraus
- , Ryan W. Russell
- & Tatyana Polenova
-
Article
| Open Access Functional control of a 0.5 MDa TET aminopeptidase by a flexible loop revealed by MAS NMR
Functional control of a 0.5 MDa TET aminopeptidase by a flexible loop revealed by MAS NMR
Motion is key to enzymatic catalysis. Gauto et al. show that a flexible loop region is crucial for the function of an aminopeptidase and show that magic-angle spinning NMR provides atomic-level quantitative insights in this very large complex.
- Diego F. Gauto
- , Pavel Macek
- & Paul Schanda
-
Article
| Open Access Activation of the essential kinase PDK1 by phosphoinositide-driven trans-autophosphorylation
Activation of the essential kinase PDK1 by phosphoinositide-driven trans-autophosphorylation
The essential protein kinase PDK1 is activated by phospoinositide-mediated dimerization and trans-autophosphorylation. Here, the authors show that in the absence of PIP3 or PI(3,4)P2 phosphoinositides, PDK1 is maintained in an inactive, autoinhibited conformation in the cytosol.
- Aleksandra Levina
- , Kaelin D. Fleming
- & Thomas A. Leonard
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping the sequence specificity of heterotypic amyloid interactions enables the identification of aggregation modifiers
Mapping the sequence specificity of heterotypic amyloid interactions enables the identification of aggregation modifiers
In this work, Louros et al. uncover a rule book for interactions of amyloids with other proteins. This grammar was shown to promote cellular spreading of tau aggregates in cells, but can also be harvested to develop structure-based aggregation blockers.
- Nikolaos Louros
- , Meine Ramakers
- & Joost Schymkowitz
-
Article
| Open Access Host receptor-targeted therapeutic approach to counter pathogenic New World mammarenavirus infections
Host receptor-targeted therapeutic approach to counter pathogenic New World mammarenavirus infections
Five New World mammarenaviruses (NWMs) enter cells via binding to human transferrin receptor 1 (hTfR1). Here, Hickerson et al. show that hTfR1 targeting antibodies partially protect hTfR1-transgenic mice from lethal NWM challenge via competition of anti-hTfR1 antibody and viral glycoprotein for hTfR1.
- Brady T. Hickerson
- , Tracy R. Daniels-Wells
- & Brian B. Gowen
-
Article
| Open Access Ion currents through Kir potassium channels are gated by anionic lipids
Ion currents through Kir potassium channels are gated by anionic lipids
The Kir potassium channels are known to operate and gate without a major conformational change. Here, the authors identify the permeation gate of Kir channels as a steric plug within the conduction pathway, describing how tightly associated anionic lipids pushing into fenestrations in the pore walls engage with the plug to operate the gate.
- Ruitao Jin
- , Sitong He
- & Jacqueline M. Gulbis
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights in cell-type specific evolution of intra-host diversity by SARS-CoV-2
Structural insights in cell-type specific evolution of intra-host diversity by SARS-CoV-2
BriSΔ, a SARS-CoV-2 variant from clinical isolate hCoV/England/02/2020, comprises a deletion in a spike cleavage site. The structure and molecular dynamics of this spike provides mechanistic insights into how the deletion modulates virus infectivity.
- Kapil Gupta
- , Christine Toelzer
- & Imre Berger
-
Article
| Open Access Harnessing protein folding neural networks for peptide–protein docking
Harnessing protein folding neural networks for peptide–protein docking
AlphaFold2 has originally been developed to provide highly accurate predictions of protein monomer structures. Here, the authors present a simple adaptation of AlphaFold2 that enables structural modeling of peptide–protein complexes, and explore the underlying mechanisms and limitations of this approach.
- Tomer Tsaban
- , Julia K. Varga
- & Ora Schueler-Furman
-
Article
| Open Access DeepRank: a deep learning framework for data mining 3D protein-protein interfaces
DeepRank: a deep learning framework for data mining 3D protein-protein interfaces
The authors present DeepRank, a deep learning framework for the data mining of large sets of 3D protein-protein interfaces (PPI). They use DeepRank to address two challenges in structural biology: distinguishing biological versus crystallographic PPIs in crystal structures, and secondly the ranking of docking models.
- Nicolas Renaud
- , Cunliang Geng
- & Li C. Xue
-
Article
| Open Access Kinetic and structural mechanism for DNA unwinding by a non-hexameric helicase
Kinetic and structural mechanism for DNA unwinding by a non-hexameric helicase
UvrD is a model helicase from the non-hexameric Superfamily 1. Here, the authors use optical tweezers to measure directly the stepwise translocation of UvrD along a DNA hairpin, and propose a mechanism in which UvrD moves one base pair at a time, but sequesters the nascent single strands, releasing them after a variable number of ATP hydrolysis cycles.
- Sean P. Carney
- , Wen Ma
- & Yann R. Chemla
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of Rad26-assisted rescue of stalled RNA polymerase II in transcription-coupled repair
Mechanism of Rad26-assisted rescue of stalled RNA polymerase II in transcription-coupled repair
Here the authors provide models of RNA polymerase II bound to the yeast CSB ortholog Rad26 in different nucleotide states; explain how Rad26 domain motions help the polymerase progress past DNA lesions; and interpret the effects of CSB-associated disease mutations.
- Chunli Yan
- , Thomas Dodd
- & Ivaylo Ivanov
-
Article
| Open Access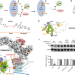 Development of a BCL-xL and BCL-2 dual degrader with improved anti-leukemic activity,
Development of a BCL-xL and BCL-2 dual degrader with improved anti-leukemic activity,
Simultaneous targeting of BCL-xL and BCL-2 is an attractive approach for cancer treatment. Based on information gained by computational structure modelling, the authors develop a PROTAC that induces degradation of both BCL-xL and BCL-2 and effectively targets BCL-xL/2-dependent leukaemia cells.
- Dongwen Lv
- , Pratik Pal
- & Daohong Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping protein interactions in the active TOM-TIM23 supercomplex
Mapping protein interactions in the active TOM-TIM23 supercomplex
The TOM and TIM23 complexes facilitate the transport of nuclear-encoded proteins into the mitochondrial matrix. Here, the authors use a stalled client protein to purify the translocation supercomplex and gain insight into the TOM-TIM23 interface and the mechanism of protein handover from the TOM to the TIM23 complex.
- Ridhima Gomkale
- , Andreas Linden
- & Peter Rehling
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and function relationship of OqxB efflux pump from Klebsiella pneumoniae
Structure and function relationship of OqxB efflux pump from Klebsiella pneumoniae
OqxB is an RND (Resistance-Nodulation-Division) transporter that contributes to the antibiotic resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Here, the authors report structural and functional characterization of OqxB, with insights into its substrate binding pocket and the role in fluoroquinolone resistance.
- Nagakumar Bharatham
- , Purnendu Bhowmik
- & Satoshi Murakami
-
Article
| Open Access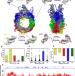 Binding of regulatory proteins to nucleosomes is modulated by dynamic histone tails
Binding of regulatory proteins to nucleosomes is modulated by dynamic histone tails
The intrinsic disorder of histone tails poses challenges in their characterization. Here the authors apply extensive molecular dynamics simulations of the full nucleosome to show reversible binding to DNA with specific binding modes of different types of histone tails, where charge-altering modifications suppress tail-DNA interactions and may boost interactions between nucleosomes and nucleosome-binding proteins.
- Yunhui Peng
- , Shuxiang Li
- & Anna R. Panchenko
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for ALK2/BMPR2 receptor complex signaling through kinase domain oligomerization
Structural basis for ALK2/BMPR2 receptor complex signaling through kinase domain oligomerization
Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) receptors are single pass transmembrane serine/threonine kinases that form tetrameric complexes comprised of two type I and two type II BMP receptors. Here the authors characterize a structure of an active type I/type II kinase tetramer providing insight into molecular mechanism driving ligand-induced signaling.
- Christopher Agnew
- , Pelin Ayaz
- & Natalia Jura
-
Article
| Open Access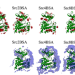 Reduced efficacy of a Src kinase inhibitor in crowded protein solution
Reduced efficacy of a Src kinase inhibitor in crowded protein solution
The intracellular compartment is a crowded environment. Here, the authors use molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to assess inhibitor binding to c-Src kinase and show how ligand binding pathways differ in crowded and dilute protein solutions, highlighting the role of c-Src Tyr82 sidechain.
- Kento Kasahara
- , Suyong Re
- & Yuji Sugita
-
Article
| Open Access Residue 6.43 defines receptor function in class F GPCRs
Residue 6.43 defines receptor function in class F GPCRs
The class Frizzled of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) consist of ten Frizzled (FZD1-10) subtypes and Smoothened (SMO). Here the Schulte laboratory demonstrates that FZDs differ substantially from SMO in receptor activation-associated conformational changes, while SMO manifests a preference for a straight TM6, the TM6 of FZDs is kinked upon activation.
- Ainoleena Turku
- , Hannes Schihada
- & Gunnar Schulte
-
Article
| Open Access Distinct EH domains of the endocytic TPLATE complex confer lipid and protein binding
Distinct EH domains of the endocytic TPLATE complex confer lipid and protein binding
AtEH/Pan1 proteins contain two N-terminal Eps15 homology (EH) domains and are subunits of the endocytic TPLATE complex present in plants. Here, the authors combine X-ray crystallography, NMR and MD simulations with biochemical and in planta analysis to characterize the two AtEH1/Pan1 EH domains and reveal their structural differences and complementary functional roles.
- Klaas Yperman
- , Anna C. Papageorgiou
- & Daniel Van Damme

 FTD-tau S320F mutation stabilizes local structure and allosterically promotes amyloid motif-dependent aggregation
FTD-tau S320F mutation stabilizes local structure and allosterically promotes amyloid motif-dependent aggregation