Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule diffusion and conformational dynamics by spatial integration of temporal fluctuations
Single-molecule diffusion and conformational dynamics by spatial integration of temporal fluctuations
Single-molecule localization and tracking technique is widely used to visualize molecular dynamics in life science, yet it fails to detect molecular conformation. Serag et al. address this limitation via spatial quantization of temporal fluctuations in the cumulative area occupied by molecules.
- Maged F. Serag
- , Maram Abadi
- & Satoshi Habuchi
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo single-molecule imaging identifies altered dynamics of calcium channels in dystrophin-mutant C. elegans
In vivo single-molecule imaging identifies altered dynamics of calcium channels in dystrophin-mutant C. elegans
Single molecule fluorescence microscopy is a powerful technique to study protein dynamics in cells, but it has not been applied to adult animals. The authors use complementation-activated light microscopy in C. elegansto discover that dystrophin regulates the diffusion properties of voltage-dependent calcium ion channels at the surface of body-wall muscle cells.
- Hong Zhan
- , Ramunas Stanciauskas
- & Fabien Pinaud
-
Article |
 Membrane curvature sensing by the C-terminal domain of complexin
Membrane curvature sensing by the C-terminal domain of complexin
Complexin binds to synaptic vesicles and inhibits spontaneous exocytosis. Here Snead et al. show that the high curvature of the vesicle membrane is important for membrane binding, and induces a conformational change that is important for complexin’s inhibitory function.
- David Snead
- , Rachel T. Wragg
- & David Eliezer
-
Article |
 Determination of collagen fibril size via absolute measurements of second-harmonic generation signals
Determination of collagen fibril size via absolute measurements of second-harmonic generation signals
Quantitative determination of collagen fibril size is important for investigating pathological disorders of the extracellular matrix. Here, the authors show that SHG microscopy is capable of measuring fibril diameter after calibration of SHG radiation using correlation to electron microscopy.
- Stéphane Bancelin
- , Carole Aimé
- & Marie-Claire Schanne-Klein
-
Article |
 Dynamic catch of a Thy-1–α5β1+syndecan-4 trimolecular complex
Dynamic catch of a Thy-1–α5β1+syndecan-4 trimolecular complex
Molecular details of the synergy between integrins and syndecans are poorly understood. Here, Fiore et al. show that syndecan-4 and α5β1integrin form a trimolecular complex with Thy-1 that exhibits ‘dynamic catch’ behaviour, in which force strengthens the synergistic binding and modulates signalling at the focal adhesion level.
- Vincent F. Fiore
- , Lining Ju
- & Thomas H. Barker
-
Article |
 Spontaneous transmembrane helix insertion thermodynamically mimics translocon-guided insertion
Spontaneous transmembrane helix insertion thermodynamically mimics translocon-guided insertion
Insertion of proteins into a membrane bilayer driven by the Sec translocon is aided by the attributes of the inserted peptides. Here, Ulmschneider et al.measure the free energies of various insertion events and suggest that the membrane interface plays an important role in translocon-guided TM helix insertion.
- Martin B. Ulmschneider
- , Jakob P. Ulmschneider
- & Stephen H. White
-
Article |
 Solution-state conformation and stoichiometry of yeast Sir3 heterochromatin fibres
Solution-state conformation and stoichiometry of yeast Sir3 heterochromatin fibres
Heterochromatin is a ‘repressed’ chromatin state involved in the generation of centromeres, the protection of telomeres and the maintenance of genome integrity. Here Swygert et al.show that Sir3 - a key factor in the formation of heterochromatin - promotes a chromatin structure distinct from the canonical 30 nm fibre.
- Sarah G. Swygert
- , Benjamin J. Manning
- & Craig L. Peterson
-
Article
| Open Access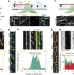 Actin–microtubule coordination at growing microtubule ends
Actin–microtubule coordination at growing microtubule ends
The structural cross-talk between components of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton remains poorly understood. Here the authors engineer an actin-binding microtubule tip-tracking protein that guides microtubule growth along actin bundles, and allows microtubule growing ends to pull and bundle actin filaments.
- Magdalena Preciado López
- , Florian Huber
- & Marileen Dogterom
-
Article |
 Molecular determinants of magnesium-dependent synaptic plasticity at electrical synapses formed by connexin36
Molecular determinants of magnesium-dependent synaptic plasticity at electrical synapses formed by connexin36
Electrical synaptic transmission is known to be modulated by intracellular magnesium. Here, Palacios-Prado et al.show that electrical synapses formed by connexin36 in the thalamic reticular nucleus are bidirectionally modulated by changes in magnesium concentration via pore-lining sensitive domains.
- Nicolás Palacios-Prado
- , Sandrine Chapuis
- & Feliksas F. Bukauskas
-
Article |
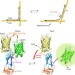 Documentation and localization of force-mediated filamin A domain perturbations in moving cells
Documentation and localization of force-mediated filamin A domain perturbations in moving cells
Biosensors designed to respond to mechanical force in cells have provided insights into the force landscape within a cell. Here, Nakamura et al. design a FRET probe in the actin crosslinking protein filamin A and show that it unfolds under force only in newly protruding regions of the cell.
- Fumihiko Nakamura
- , Mia Song
- & Thomas P. Stossel
-
Article |
 General rules for the arrangements and gating motions of pore-lining helices in homomeric ion channels
General rules for the arrangements and gating motions of pore-lining helices in homomeric ion channels
Rearrangements of the pore-lining helix (PLH) bundles of ion channels are central to their gating mechanisms. Here, Dai et al. use a modelling approach to define the general rules that govern the arrangements and gating motions of the PLHs in homomeric ion channels.
- Jian Dai
- & Huan-Xiang Zhou
-
Article |
 Force-dependent conformational switch of α-catenin controls vinculin binding
Force-dependent conformational switch of α-catenin controls vinculin binding
At cell–cell adhesions, α-catenin contains a cryptic vinculin-binding site. Here, Yao et al. demonstrate, using magnetic tweezers, that physiologically relevant forces unfurl α-catenin to reveal the vinculin-binding site, and allow the reversible binding of vinculin to mechanically reinforce the adhesion.
- Mingxi Yao
- , Wu Qiu
- & Jie Yan
-
Article |
 Cementing proteins provide extra mechanical stabilization to viral cages
Cementing proteins provide extra mechanical stabilization to viral cages
Some viruses possess ‘decoration’ proteins, such as gpD in lambda phage, that stabilize the viral particles in poorly understood ways. Here the authors show that gpD incorporation into lambda particles provides mechanical reinforcement and increased resistance to punctual deformations and collisions.
- M. Hernando-Pérez
- , S. Lambert
- & P. J. de Pablo
-
Article |
 IgGs are made for walking on bacterial and viral surfaces
IgGs are made for walking on bacterial and viral surfaces
Antibody–antigen recognition is one of the important aspects of immunity, but the nanomechanical process of this recognition is not fully understood. Here, using high-speed atomic force microscopy, the authors observe that on membranes containing a high density of immobile antigens antibodies move in a ‘random walking’ motion.
- Johannes Preiner
- , Noriyuki Kodera
- & Peter Hinterdorfer
-
Article
| Open Access Protruding knob-like proteins violate local symmetries in an icosahedral marine virus
Protruding knob-like proteins violate local symmetries in an icosahedral marine virus
Some viruses are spherical particles in which protein components are organized with well-defined icosahedral and local symmetries. Here, Gipson et al. describe a unique arrangement of proteins, breaking all expected local symmetries, in particles of a marine bacterial virus.
- Preeti Gipson
- , Matthew L. Baker
- & Wah Chiu
-
Article |
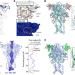 Relative motions between left flipper and dorsal fin domains favour P2X4 receptor activation
Relative motions between left flipper and dorsal fin domains favour P2X4 receptor activation
P2X receptors are ion channels that are controlled by the level of extracellular ATP. Here, Zhao et al.describe the coordinated allosteric changes in two protein domains that couple extracellular ATP-binding to channel gating and show that these changes are essential for the function of the proteins.
- Wen-Shan Zhao
- , Jin Wang
- & Ye Yu
-
Article |
 Interplay between trigger factor and other protein biogenesis factors on the ribosome
Interplay between trigger factor and other protein biogenesis factors on the ribosome
Ribosome-associated protein biogenesis factors act during protein synthesis to facilitate modification, targeting and folding of the nascent polypeptide. Here, Bornemann et al.establish the dynamic interplay between these factors, thus providing new insight into the early steps of protein biogenesis.
- Thomas Bornemann
- , Wolf Holtkamp
- & Wolfgang Wintermeyer
-
Article |
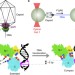 Evidence for an electrostatic mechanism of force generation by the bacteriophage T4 DNA packaging motor
Evidence for an electrostatic mechanism of force generation by the bacteriophage T4 DNA packaging motor
Viral DNA packaging motors must generate large forces to package the viral capsid. Here, Migliori et al.provide functional and computational evidence that electrostatic interactions between subdomains of the T4 packaging motor provide the driving force for DNA packaging.
- Amy D. Migliori
- , Nicholas Keller
- & Douglas E. Smith
-
Article |
 Coordinated DNA dynamics during the human telomerase catalytic cycle
Coordinated DNA dynamics during the human telomerase catalytic cycle
Telomerase reverse transcriptase extends the ends of linear chromosomes with the aid of an integral RNA subunit. Here, Parks and Stone characterize the translocation kinetics of telomerase identifying distinct steps important for the processivity of the enzyme.
- Joseph W. Parks
- & Michael D. Stone
-
Article |
 Correlated motions are a fundamental property of β-sheets
Correlated motions are a fundamental property of β-sheets
Functional changes in protein structures are involved in a large number of biochemical processes. Here, the authors perform a simulation study of known protein structures to show how β-sheets possess the ability to facilitate concerted backbone motions.
- R. Bryn Fenwick
- , Laura Orellana
- & Xavier Salvatella
-
Article |
 Targeting Mycobacterium tuberculosis nucleoid-associated protein HU with structure-based inhibitors
Targeting Mycobacterium tuberculosis nucleoid-associated protein HU with structure-based inhibitors
Histone-like HU proteins play roles in chromatin architecture and DNA-dependent processes in bacteria. Here, the authors describe the crystal structure of the DNA-binding domain of HU from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and show that the pathogen’s growth can be inhibited using HU-targeting small molecules.
- Tuhin Bhowmick
- , Soumitra Ghosh
- & Valakunja Nagaraja
-
Article |
 Physiological sodium concentrations enhance the iodide affinity of the Na+/I− symporter
Physiological sodium concentrations enhance the iodide affinity of the Na+/I− symporter
Thyroid hormone synthesis requires import of iodide ions through the Na+/I− symporter, however its affinity for iodide is surprisingly low. Using a statistical thermodynamics approach, Nicola et al. show that sodium ion binding enhances iodide affinity, revealing a mechanism for iodide transport.
- Juan P. Nicola
- , Nancy Carrasco
- & L. Mario Amzel
-
Article |
 Resolving the molecular mechanism of cadherin catch bond formation
Resolving the molecular mechanism of cadherin catch bond formation
Cadherins are calcium-dependent adhesion molecules that can form catch bonds, characterized by longer lifetimes at higher force. Here, Manibog et al. determine the mechanism of catch bond formation, whereby tension induces hydrogen bond formation between opposing extracellular domains in a calcium-dependent manner.
- Kristine Manibog
- , Hui Li
- & Sanjeevi Sivasankar
-
Article |
 Persistent super-diffusive motion of Escherichia coli chromosomal loci
Persistent super-diffusive motion of Escherichia coli chromosomal loci
In bacteria, chromosomal architecture exhibits spatial and temporal fluctuations, which affect cellular functions. Here, Javer et al. use high-resolution tracking of chromosomal loci in E. colito uncover rare events of unusually large and fast movements, providing new insight into bacterial chromosome dynamics.
- Avelino Javer
- , Nathan J. Kuwada
- & Marco Cosentino Lagomarsino
-
Article |
 Direct observation of the three regions in α-synuclein that determine its membrane-bound behaviour
Direct observation of the three regions in α-synuclein that determine its membrane-bound behaviour
α-synuclein is a protein whose aberrant aggregation is associated with Parkinson’s disease. Here, Fusco et al.characterize α-synuclein bound to lipid membranes using a combination of solution and solid-state NMR spectroscopy and provide insights into the molecular processes associated with the aggregation of this protein.
- Giuliana Fusco
- , Alfonso De Simone
- & Gianluigi Veglia
-
Article
| Open Access The full-length cell–cell fusogen EFF-1 is monomeric and upright on the membrane
The full-length cell–cell fusogen EFF-1 is monomeric and upright on the membrane
Cell–cell fusion in Caenorhabditis elegans is mediated by EFF-1 and AFF-1 proteins. Here, the authors present an electron cryomicroscopy 3D reconstruction of EFF-1 in the membrane, and combine snapshots of membrane fusion in vitrowith a recently reported crystal structure to propose a mechanism for the fusion process.
- Tzviya Zeev-Ben-Mordehai
- , Daven Vasishtan
- & Kay Grünewald
-
Article |
 Mid-range Ca2+ signalling mediated by functional coupling between store-operated Ca2+ entry and IP3-dependent Ca2+ release
Mid-range Ca2+ signalling mediated by functional coupling between store-operated Ca2+ entry and IP3-dependent Ca2+ release
It remains unclear how localized calcium influx activates distant effectors in the absence of a global Ca2+ rise. Courjaret and Machaca find that mid-range Ca2+ signalling is mediated by coupling between localized store-operated calcium entry and distal IP3-dependent Ca2+ release to activate Cl−channels.
- Raphaël Courjaret
- & Khaled Machaca
-
Article |
 KCNE1 divides the voltage sensor movement in KCNQ1/KCNE1 channels into two steps
KCNE1 divides the voltage sensor movement in KCNQ1/KCNE1 channels into two steps
The mechanism by which KCNEβ subunits slow the kinetics of KCNQ1 channels is controversial. Here, Barro-Soria et al.show that mutually independent voltage sensor movements underlie the initial activation delay, and a subsequent slower conformational change opens the channel.
- Rene Barro-Soria
- , Santiago Rebolledo
- & H. Peter Larsson
-
Article |
 Protein conformational dynamics dictate the binding affinity for a ligand
Protein conformational dynamics dictate the binding affinity for a ligand
The binding affinity of a protein for its ligand is governed by the rates of ligand association and dissociation. Here the authors show that intrinsic conformational dynamics of maltose binding protein dictate the ligand dissociation rate, and hence the affinity of the protein for maltose.
- Moon-Hyeong Seo
- , Jeongbin Park
- & Hak-Sung Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Protein accumulation in the endoplasmic reticulum as a non-equilibrium phase transition
Protein accumulation in the endoplasmic reticulum as a non-equilibrium phase transition
Misfolded protein accumulation is a hallmark of many neurodegenerative diseases. Here Budrikis et al. model protein aggregation in the endoplasmic reticulum and show that it is the result of a non-equilibrium phase transition caused by tipping the balance from the rates of protein production to degradation.
- Zoe Budrikis
- , Giulio Costantini
- & Stefano Zapperi
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular architecture and the structural basis for anion interaction in prestin and SLC26 transporters
Molecular architecture and the structural basis for anion interaction in prestin and SLC26 transporters
Prestin is an anion transporter-like protein in the mammalian inner ear that amplifies sound-induced vibration by voltage-driven structural rearrangements. Here, Gorbunov et al. show that this electromechanical activity is controlled by the binding of anions to a central cavity within the protein core.
- Dmitry Gorbunov
- , Mattia Sturlese
- & Dominik Oliver
-
Article |
 Catch-bond behaviour facilitates membrane tubulation by non-processive myosin 1b
Catch-bond behaviour facilitates membrane tubulation by non-processive myosin 1b
The non-processive motor protein myosin 1b is required for Golgi membrane tubulation. Using a minimal reconstituted system and theoretical analysis, Yamada et al.demonstrate that the mechanism of tubule extraction depends on the catch bond properties of myosin 1b.
- Ayako Yamada
- , Alexandre Mamane
- & Patricia Bassereau
-
Article |
 Molecular mechanism of Mg2+-dependent gating in CorA
Molecular mechanism of Mg2+-dependent gating in CorA
CorA is the major magnesium influx pathway in bacteria, but the mechanism for the uptake of magnesium by this system is not clear. Here, Dalmas et al.show that CorA is regulated by cytoplasmic magnesium levels, and determine the conformational changes required for the regulation by a negative feedback loop.
- Olivier Dalmas
- , Pornthep Sompornpisut
- & Eduardo Perozo
-
Article
| Open Access Timing of inorganic phosphate release modulates the catalytic activity of ATP-driven rotary motor protein
Timing of inorganic phosphate release modulates the catalytic activity of ATP-driven rotary motor protein
The F1-ATPase is a motor protein which exhibits rotary motion as a result of catalytic hydrolysis of ATP. Here, the authors investigate how the sequence of this reaction influences molecular rotation, showing that premature product release can result in protein inactivation.
- Rikiya Watanabe
- & Hiroyuki Noji
-
Article
| Open Access Tuning Piezo ion channels to detect molecular-scale movements relevant for fine touch
Tuning Piezo ion channels to detect molecular-scale movements relevant for fine touch
The stomatin domain protein STOML3 is required for the sensation of touch. Here, Poole et al.show that STOML3 enhances the activity of mechanosensitive Piezo1 and Piezo2 ion channels by reducing their activation thresholds, and that it achieves this through its stomatin domain.
- Kate Poole
- , Regina Herget
- & Gary R. Lewin
-
Article
| Open Access Self-recognition of the endothelium enables regulatory T-cell trafficking and defines the kinetics of immune regulation
Self-recognition of the endothelium enables regulatory T-cell trafficking and defines the kinetics of immune regulation
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) are important for the maintenance of self-tolerance and this requires their trafficking to the lymph nodes and target tissues. Here, the authors show that the recognition of self-antigens expressed by endothelial cells in target tissue is instrumental for efficient Treg recruitment in vivo.
- Hongmei Fu
- , Madhav Kishore
- & Federica M. Marelli-Berg
-
Article |
 Quantitative live-cell imaging reveals spatio-temporal dynamics and cytoplasmic assembly of the 26S proteasome
Quantitative live-cell imaging reveals spatio-temporal dynamics and cytoplasmic assembly of the 26S proteasome
The 26S proteasome is assembled in several steps, however the extent to which this assembly occurs before or after transport into the nucleus remains unclear. Pack et al.show that full assembly can occur in the cytoplasm, and that a concatameric form of the fully assembled complex is a substrate for nuclear import.
- Chan-Gi Pack
- , Haruka Yukii
- & Yasushi Saeki
-
Article |
 Activation pathway of Src kinase reveals intermediate states as targets for drug design
Activation pathway of Src kinase reveals intermediate states as targets for drug design
Activation of c-src kinase is associated with uncontrolled growth and metastasis of tumour cells. Shukla et al.model conformational changes in c-src during activation, and identify an allosteric site in an intermediate state that may provide a target for small molecule therapeutics.
- Diwakar Shukla
- , Yilin Meng
- & Vijay S. Pande
-
Article
| Open Access SILAC-based proteomic quantification of chemoattractant-induced cytoskeleton dynamics on a second to minute timescale
SILAC-based proteomic quantification of chemoattractant-induced cytoskeleton dynamics on a second to minute timescale
Actin-dependent motility is driven by the rapid changes in the recruitment of many different structural and regulatory proteins at the cell’s cortex. Sobczyk et al. characterize these changes in the cytoskeletal proteome on a second to minute timescale during chemotactic response in Dictyosteliumusing SILAC-based proteomics.
- Grzegorz J. Sobczyk
- , Jun Wang
- & Cornelis J. Weijer
-
Article |
 Radial symmetry in a chimeric glutamate receptor pore
Radial symmetry in a chimeric glutamate receptor pore
Crystallographic studies have shown that non-NMDA glutamate receptors exhibit fourfold symmetry in the transmembrane domain in the closed state; however, structural data regarding channel opening is lacking. Using chimeric receptors, Wilding et al.provide evidence that this fourfold symmetry is maintained in the open state.
- Timothy J. Wilding
- , Melany N. Lopez
- & James E. Huettner
-
Article
| Open Access X-ray refinement significantly underestimates the level of microscopic heterogeneity in biomolecular crystals
X-ray refinement significantly underestimates the level of microscopic heterogeneity in biomolecular crystals
The structural heterogeneity of a biomolecular crystal structure is typically captured using atomic B-factors, determined during structure refinement. Here, the authors use molecular dynamics to show that this strategy is flawed, and that crystallographic B-factors underestimate structural heterogeneity.
- Antonija Kuzmanic
- , Navraj S. Pannu
- & Bojan Zagrovic
-
Article
| Open Access Ligand-induced structural changes in the cyclic nucleotide-modulated potassium channel MloK1
Ligand-induced structural changes in the cyclic nucleotide-modulated potassium channel MloK1
The molecular determinants underlying ligand gating of cyclic nucleotide-modulated ion channels remain unclear. Kowal et al.determine the conformational changes underlying cAMP binding to the bacterial channel MloK1, and propose a mechanism for coupling of ligand gating and voltage sensing in eukaryotic HCN channels.
- Julia Kowal
- , Mohamed Chami
- & Henning Stahlberg
-
Article |
 Two potential therapeutic antibodies bind to a peptide segment of membrane-bound IgE in different conformations
Two potential therapeutic antibodies bind to a peptide segment of membrane-bound IgE in different conformations
Two antibodies targeting the CεmX domain of membrane-bound IgE on human B lymphocytes are being developed to treat allergy. Here, the authors map the antigenic epitopes of the two antibodies and show that they bind to different conformations of the same peptide region.
- Hsing-Mao Chu
- , Jon Wright
- & Carmay Lim
-
Article
| Open Access Actomyosin-dependent formation of the mechanosensitive talin–vinculin complex reinforces actin anchoring
Actomyosin-dependent formation of the mechanosensitive talin–vinculin complex reinforces actin anchoring
The interaction between focal adhesion proteins vinculin and talin is stimulated by mechanical stretching. Here the authors reconstitute actomyosin-dependent stretching of talin in vitro, and show that the resulting activation of vinculin reinforces anchoring of the adhesion complex to actin.
- Corina Ciobanasu
- , Bruno Faivre
- & Christophe Le Clainche
-
Article |
 Anisotropic energy flow and allosteric ligand binding in albumin
Anisotropic energy flow and allosteric ligand binding in albumin
Protein allosteric interactions involve a transfer of structural changes to a remote site. Here, the authors study the relationship between allosteric binding and energy flow, showing how the energy transport mechanism conveys binding energy to remote sites.
- Guifeng Li
- , Donny Magana
- & R. Brian Dyer
-
Article |
 Optical measurements of long-range protein vibrations
Optical measurements of long-range protein vibrations
Many biological processes rely on fluctuations in protein structure, but the characterization of extended structural motions is challenging. Here the authors use orientation-sensitive terahertz near-field microscopy to report the optical observation of long-range protein vibrational modes.
- Gheorghe Acbas
- , Katherine A. Niessen
- & A.G. Markelz
-
Article |
 Mia40 targets cysteines in a hydrophobic environment to direct oxidative protein folding in the mitochondria
Mia40 targets cysteines in a hydrophobic environment to direct oxidative protein folding in the mitochondria
Proteins containing multiple disulphide bonds fold more efficiently if these bonds are formed in a defined order. Koch et al.find that the mitochondrial thiol oxidase Mia40 achieves this by preferentially targeting cysteine residues within a hydrophobic context.
- Johanna R. Koch
- & Franz X. Schmid
-
Article |
 Kinetic modelling indicates that fast-translating codons can coordinate cotranslational protein folding by avoiding misfolded intermediates
Kinetic modelling indicates that fast-translating codons can coordinate cotranslational protein folding by avoiding misfolded intermediates
The speed of codon translation at the ribosome has a large bearing on the structure of the final protein, with faster rates thought to promote misfolding. Here the authors present a theoretical analysis suggesting that in some cases fast-translating codons may instead improve cotranslational folding.
- Edward P. O’Brien
- , Michele Vendruscolo
- & Christopher M. Dobson
-
Article |
 Binding of PHF1 Tudor to H3K36me3 enhances nucleosome accessibility
Binding of PHF1 Tudor to H3K36me3 enhances nucleosome accessibility
Binding of the Tudor domain of the PHD finger protein PHF1 to H3K36me3 inhibits Polycomb PRC2 complex methyltransferase activity. Here, Musselman et al.characterize this interaction in the context of the full nucleosome and show dual binding of the PHF1 Tudor domain to H3K36me3 and double-stranded DNA.
- Catherine A. Musselman
- , Matthew D. Gibson
- & Tatiana G. Kutateladze

 Constitutive phospholipid scramblase activity of a G protein-coupled receptor
Constitutive phospholipid scramblase activity of a G protein-coupled receptor