Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access A mechanistic model of tau amyloid aggregation based on direct observation of oligomers
A mechanistic model of tau amyloid aggregation based on direct observation of oligomers
Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by the aggregation of the Abeta peptide and the tau protein. Here the authors track the formation of wild-type or mutant tau oligomers through to large aggregates and gain insights into the molecular basis of how tau mutations cause disease by altering the aggregation pathway.
- Sarah L. Shammas
- , Gonzalo A. Garcia
- & David Klenerman
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time submillisecond single-molecule FRET dynamics of freely diffusing molecules with liposome tethering
Real-time submillisecond single-molecule FRET dynamics of freely diffusing molecules with liposome tethering
Single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer is widely used to probe biomolecular dynamics, but is limited by its temporal resolution. Here, Kim et al. push the limit to submillisecond for the duration of tens of milliseconds by tethering target molecules to liposomes in buffer solutions.
- Jae-Yeol Kim
- , Cheolhee Kim
- & Nam Ki Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanisms of splicing-dependent trans-synaptic adhesion by PTPδ–IL1RAPL1/IL-1RAcP for synaptic differentiation
Mechanisms of splicing-dependent trans-synaptic adhesion by PTPδ–IL1RAPL1/IL-1RAcP for synaptic differentiation
Synapse formation depends on trans-synaptic interactions between selective pairs of pre- and postsynaptic adhesion molecules. Here, the authors establish the basis for the splice isoform-dependent selectivity of receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase δ as it forms trans-synaptic contacts with IL1RAPL1 and IL-1RAcP.
- Atsushi Yamagata
- , Tomoyuki Yoshida
- & Shuya Fukai
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the Bacillus subtilis 70S ribosome reveals the basis for species-specific stalling
Structure of the Bacillus subtilis 70S ribosome reveals the basis for species-specific stalling
Ribosome stalling regulates gene expression by exposing otherwise inaccessible downstream ribosome-binding sites. Here the authors present a high-resolution Cryo-EM structure of the Bacillus subtilisMifM-stalled 70S ribosome to provide mechanistic insight into species-specific nascent peptide induced translational arrest.
- Daniel Sohmen
- , Shinobu Chiba
- & Daniel N. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structure of a mirror-image L-RNA aptamer (Spiegelmer) in complex with the natural L-protein target CCL2
Crystal structure of a mirror-image L-RNA aptamer (Spiegelmer) in complex with the natural L-protein target CCL2
Spiegelmers are ‘mirror image’ L-ribose oligonucleotides being developed as therapeutics. Here the authors present a crystal structure of the therapeutic L-aptamer NOX-E36 bound to the pro-inflammatory chemokine CLL2, providing insight into NOX-E36’s selectivity and mode of action.
- Dominik Oberthür
- , John Achenbach
- & Christian Betzel
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for the targeting of complement anaphylatoxin C5a using a mixed L-RNA/L-DNA aptamer
Structural basis for the targeting of complement anaphylatoxin C5a using a mixed L-RNA/L-DNA aptamer
Spiegelmers are mirror-image oligonucleotide aptamers designed for therapeutic use. Here the authors describe the crystal structure of the mixed L-RNA/L-DNA Spiegelmer NOX-D20 bound to complement component C5a, a key mediator of the innate immune response and clinical target in acute and chronic inflammatory disorders.
- Laure Yatime
- , Christian Maasch
- & Axel Vater
-
Article
| Open Access Reconstitution and structure of a bacterial Pnkp1–Rnl–Hen1 RNA repair complex
Reconstitution and structure of a bacterial Pnkp1–Rnl–Hen1 RNA repair complex
Bacterial ribotoxins target and cleave RNAs involved in translation, with target organism resistance being mediated by RNA repair systems. Here, Wang et al. identify, report the crystal structure, and characterize the activity of Pnkp1–Rnl–Hen1, a novel RNA repair complex from Capnocytophaga gingivalis.
- Pei Wang
- , Kiruthika Selvadurai
- & Raven H. Huang
-
Article
| Open Access CDK1 structures reveal conserved and unique features of the essential cell cycle CDK
CDK1 structures reveal conserved and unique features of the essential cell cycle CDK
Cyclin-dependent kinases are the principal drivers of cell cycle progression. Here the authors present several crystal structures of Cdk1 in complex with cyclin B and/or the assembly factors Cks1/2 and a small molecule inhibitor to reveal key features of this essential mitotic kinase.
- Nicholas R. Brown
- , Svitlana Korolchuk
- & Jane A. Endicott
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast myoglobin structural dynamics observed with an X-ray free-electron laser
Ultrafast myoglobin structural dynamics observed with an X-ray free-electron laser
Localized chemical events such as the breakage of a bond between a protein and a ligand may trigger a global protein conformational change. Here, the authors use an X-ray free-electron laser to track the motion of myoglobin in response to photoinduced ligand release, and observe a picosecond proteinquake.
- Matteo Levantino
- , Giorgio Schirò
- & Marco Cammarata
-
Article |
 Mechanical surface waves accompany action potential propagation
Mechanical surface waves accompany action potential propagation
Action potentials in neurons are accompanied by a mechanical displacement of the axonal membrane. Here, the authors present a model to describe these as surface waves which are driven by changes in charge separation, and compare their model to published experimental results from squid giant axons and garfish olfactory nerve bundles.
- Ahmed El Hady
- & Benjamin B. Machta
-
Article
| Open Access Non-canonical active site architecture of the radical SAM thiamin pyrimidine synthase
Non-canonical active site architecture of the radical SAM thiamin pyrimidine synthase
Most radical SAM enzymes use a [4Fe-4S] cluster to generate a 5′-deoxyadenosyl radical. Here the authors show the radical SAM thiamin pyrimidine synthase ThiC comprises an additional active site metal, probably representing an evolutionary link between the radical SAM and adenosylcobalamin-dependent enzyme superfamilies.
- Michael K. Fenwick
- , Angad P. Mehta
- & Steven E. Ealick
-
Article |
 Alternative splicing modulates Kv channel clustering through a molecular ball and chain mechanism
Alternative splicing modulates Kv channel clustering through a molecular ball and chain mechanism
Ion channel clustering at specific membrane sites plays a fundamental role in action potential transmission. Here, the authors show that alternative splice variants of the intrinsically disordered C-terminal segment of the Shaker Kv channel support distinct patterns of scaffold protein-mediated channel clustering.
- Nitzan Zandany
- , Shir Marciano
- & Ofer Yifrach
-
Article
| Open Access Synaptic GABA release prevents GABA transporter type-1 reversal during excessive network activity
Synaptic GABA release prevents GABA transporter type-1 reversal during excessive network activity
Membrane depolarization during increased neuronal activity as seen during epilepsy has been suggested to easily reverse neuronal GABA transporters. Here the authors use modelling and experimental data and challenge this view by showing that synaptic GABA release during excessive neuronal firing averts reversal of GABA uptake.
- Leonid Savtchenko
- , Maria Megalogeni
- & Ivan Pavlov
-
Article
| Open Access Translational diffusion of hydration water correlates with functional motions in folded and intrinsically disordered proteins
Translational diffusion of hydration water correlates with functional motions in folded and intrinsically disordered proteins
Hydration water plasticizes protein structures and is essential for their biological functions, such as enzymatic catalysis. Here, the authors use neutron scattering and molecular dynamics simulations to study hydration water at the dynamical transition of folded and disordered proteins.
- Giorgio Schirò
- , Yann Fichou
- & Martin Weik
-
Article |
 The insulin and IGF1 receptor kinase domains are functional dimers in the activated state
The insulin and IGF1 receptor kinase domains are functional dimers in the activated state
In contrast to most receptor tyrosine kinases, the insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors are preformed, disulfide-linked dimers. Here the authors show that, after the two kinase domains of IR and IGF1R undergo autophosphorylation, they form a specific dimer to phosphorylate downstream substrates.
- M. Zulema Cabail
- , Shiqing Li
- & W. Todd Miller
-
Article
| Open Access Supramolecular synergy in the boundary lubrication of synovial joints
Supramolecular synergy in the boundary lubrication of synovial joints
Interacting cartilage surfaces in synovial joints experience very low levels of friction, allowing unhindered mechanical motion. Here, the authors propose how a synergistic interaction of hyaluronan, lubricin and phospholipids, molecules that are ubiquitous in joints, may lead to this high level of lubrication.
- Jasmine Seror
- , Linyi Zhu
- & Jacob Klein
-
Article
| Open Access Abiotic ligation of DNA oligomers templated by their liquid crystal ordering
Abiotic ligation of DNA oligomers templated by their liquid crystal ordering
Some oligomers exhibit liquid-crystal-like ordering in concentrated aqueous solutions. Here, Fraccia et al. show that this kind of ordering can further facilitate DNA ligation in a way similar to a catalytic process that arises from a hierarchical self-assembly, namely liquid crystal autocatalysis.
- Tommaso P. Fraccia
- , Gregory P. Smith
- & Tommaso Bellini
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of CPV17 polyhedrin determined by the improved analysis of serial femtosecond crystallographic data
Structure of CPV17 polyhedrin determined by the improved analysis of serial femtosecond crystallographic data
Serial femtosecond crystallography and the use of X-ray free-electron lasers (XFEL) promise to revolutionize structural biology. Here, the authors describe refinements that reduce the redundancy required to obtain quality XFEL data and report a 1.75-Å structure—not obtainable by synchrotron radiation—using less than 6,000 crystals.
- Helen M. Ginn
- , Marc Messerschmidt
- & David I. Stuart
-
Article |
 Structure and function of lysosomal phospholipase A2 and lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase
Structure and function of lysosomal phospholipase A2 and lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase
Lysosomal phospholipase A2 (LPLA2) and lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) are important lipid metabolizing enzymes. Here the authors present crystal structures of LPLA2 and LCAT that reveal the unique architecture of this small family of enzymes involved in human physiology and disease.
- Alisa Glukhova
- , Vania Hinkovska-Galcheva
- & John J. G. Tesmer
-
Article |
 Action of the Hsp70 chaperone system observed with single proteins
Action of the Hsp70 chaperone system observed with single proteins
The bacterial Hsp70 chaperone system consists of DnaJ, DnaK and GrpE. To understand how these chaperones cooperate, Nunes et al. monitor refolding immunoglobulin domains using single-molecule force microscopy to demonstrate that the ‘holdase’ DnaJ can show foldase activity and suggest that GrpE can facilitate substrate release from DnaK.
- João M. Nunes
- , Manajit Mayer-Hartl
- & Daniel J. Müller
-
Article |
 Histone demethylase KDM5A is regulated by its reader domain through a positive-feedback mechanism
Histone demethylase KDM5A is regulated by its reader domain through a positive-feedback mechanism
Histone lysine methylation plays crucial roles in controlling gene expression. Here the authors demonstrate that the activity of the histone lysine demethylase KDM5A is regulated through a feedback mechanism involving communication between the histone tail-binding and catalytic domains.
- Idelisse Ortiz Torres
- , Kristopher M. Kuchenbecker
- & Danica Galonić Fujimori
-
Article |
 Undesired usage and the robust self-assembly of heterogeneous structures
Undesired usage and the robust self-assembly of heterogeneous structures
Biological and synthetic systems seek to assemble complex structures, such as protein or DNA assemblies, out of many distinct building blocks. Here, the authors show that the optimal supply of building blocks must account for the composition of undesired structures and not just the desired structure.
- Arvind Murugan
- , James Zou
- & Michael P. Brenner
-
Article |
 Complete architecture of the archaeal RNA polymerase open complex from single-molecule FRET and NPS
Complete architecture of the archaeal RNA polymerase open complex from single-molecule FRET and NPS
The archaeal RNA transcription machinery does not have a dedicated helicase factor. Here, the authors report the three-dimensional architecture of the open complex of DNA, RNA polymerase and its associated factors from M. jannaschii, providing a possible mechanism for promoter DNA melting.
- Julia Nagy
- , Dina Grohmann
- & Jens Michaelis
-
Article
| Open Access The ligand binding mechanism to purine nucleoside phosphorylase elucidated via molecular dynamics and machine learning
The ligand binding mechanism to purine nucleoside phosphorylase elucidated via molecular dynamics and machine learning
Understanding the dynamics of enzyme-substrate complexation provides an insight into potential drugs, but intermediate states are difficult to observe experimentally. Here, the authors use simulations and machine learning to analyse the binding of transition state inhibitors to purine nucleoside phosphorylase.
- Sergio Decherchi
- , Anna Berteotti
- & Andrea Cavalli
-
Article
| Open Access DNA sequencing using polymerase substrate-binding kinetics
DNA sequencing using polymerase substrate-binding kinetics
Next-generation sequencing technologies vary in performance, which is often measured by metrics such as sequencing speed, accuracy and read length. Here, the authors present a new sequencing by synthesis method that monitors polymerase binding to DNA, and suggest that this method has the potential to generate longer and faster reads.
- Michael John Robert Previte
- , Chunhong Zhou
- & Molly Min He
-
Article |
 Chromatin decompaction by the nucleosomal binding protein HMGN5 impairs nuclear sturdiness
Chromatin decompaction by the nucleosomal binding protein HMGN5 impairs nuclear sturdiness
Whether heterochromatin affects the physical properties of the nucleus is not known. Here, Furusawa et al. show that chromatin decompaction decreases the sturdiness of the nucleus in cultured cells and leads to lamina disruption and cardiac abnormalities in adult mice, suggesting a structural, non-genetic function for heterochromatin.
- Takashi Furusawa
- , Mark Rochman
- & Michael Bustin
-
Article
| Open Access A dynamically coupled allosteric network underlies binding cooperativity in Src kinase
A dynamically coupled allosteric network underlies binding cooperativity in Src kinase
Protein tyrosine kinases are subject to multiple regulatory mechanisms. Foda et al. show that reactants and products of the tyrosine kinase Src bind its catalytic domain with opposite cooperativity, and identify an allosteric network of dynamically coupled amino acids that underlie this behaviour.
- Zachariah H. Foda
- , Yibing Shan
- & Markus A. Seeliger
-
Article |
 Membrane tension and peripheral protein density mediate membrane shape transitions
Membrane tension and peripheral protein density mediate membrane shape transitions
An ultrafast mechanism of endocytosis was recently discovered, and proposed to be dependent on local reduction in membrane tension. Shi and Baumgart provide experimental support for this hypothesis by quantifying the impact of membrane tension on membrane tubulation by endocytic proteins, such as endophilin A1.
- Zheng Shi
- & Tobias Baumgart
-
Article
| Open Access Kinetic gating mechanism of DNA damage recognition by Rad4/XPC
Kinetic gating mechanism of DNA damage recognition by Rad4/XPC
XPC nucleotide excision repair factor is key to starting the repair of diverse helix-distorting DNA lesions caused by environmental insults. Here, the authors propose a kinetic gating mechanism whereby XPC recognizes DNA lesions by preferentially opening damaged sites while readily diffusing away from undamaged sites.
- Xuejing Chen
- , Yogambigai Velmurugu
- & Jung-Hyun Min
-
Article
| Open Access Slow unloading leads to DNA-bound β2-sliding clamp accumulation in live Escherichia coli cells
Slow unloading leads to DNA-bound β2-sliding clamp accumulation in live Escherichia coli cells
DNA replication is accomplished by the replisome, a multi-protein complex that comprises the sliding clamp. Here, Moolman et al. present quantitative and dynamic measurements of the number of β2-sliding clamps at the single-cell level in live E. colicells to shed light on key aspects of DNA replication.
- M. Charl Moolman
- , Sriram Tiruvadi Krishnan
- & Nynke H. Dekker
-
Article |
 Hydrogen bond rotations as a uniform structural tool for analyzing protein architecture
Hydrogen bond rotations as a uniform structural tool for analyzing protein architecture
Ramachandran plots are a convenient means of describing protein backbone conformation by depicting the distribution of Ca bond rotations. Here, the authors devise an alternative descriptor based on hydrogen bond rotations, and apply it to describe protein structures using a vocabulary of 30 hydrogen-bonding motifs.
- Robert C. Penner
- , Ebbe S. Andersen
- & Jørgen E. Andersen
-
Article |
 Translocation between PI(4,5)P2-poor and PI(4,5)P2-rich microdomains during store depletion determines STIM1 conformation and Orai1 gating
Translocation between PI(4,5)P2-poor and PI(4,5)P2-rich microdomains during store depletion determines STIM1 conformation and Orai1 gating
The Orai1 Ca2+ channel is activated by STIM1 in response to Ca2+ release from the ER. Here Maléth et al.show that Orai1 inactivation occurs by translocation to PI(4,5)P2-rich plasma membrane microdomains, which facilitates recruitment of SARAF, a negative regulator of STIM1 function.
- Jozsef Maléth
- , Seok Choi
- & Malini Ahuja
-
Article |
 A fully atomistic computer simulation study of cold denaturation of a β-hairpin
A fully atomistic computer simulation study of cold denaturation of a β-hairpin
Cold denaturation is the process by which globular proteins lose their structural integrity at sufficiently low temperatures. Here, the authors present an all-atom MD simulation of cold denaturation of the 16-mer hairpin peptide MrH1 using an explicit water model.
- Changwon Yang
- , Soonmin Jang
- & Youngshang Pak
-
Article |
 Cell dipole behaviour revealed by ECM sub-cellular geometry
Cell dipole behaviour revealed by ECM sub-cellular geometry
Cells probe and respond to their physical environment by exerting force on their surroundings. Here Mandal et al.grow cells in the same shape and area but on different adhesive patterns to show that they integrate information on extra-cellular matrix geometry at the whole-cell level.
- Kalpana Mandal
- , Irène Wang
- & Martial Balland
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrastable cellulosome-adhesion complex tightens under load
Ultrastable cellulosome-adhesion complex tightens under load
Cellulosomes are cell surface enzyme complexes that digest lignocellulosic biomass. Here, Schoeler et al.characterize the strength of the ligand–receptor anchoring complex and find that it represents one of the strongest interactions known, and is strengthened under applied force by a catch bond mechanism.
- Constantin Schoeler
- , Klara H. Malinowska
- & Michael A. Nash
-
Article |
 Cytoplasmic dynein transports cargos via load-sharing between the heads
Cytoplasmic dynein transports cargos via load-sharing between the heads
Dynein is a microtubule-based motor protein, but the mechanism of how it generates force is not clear. Here, Belyy et al. use an optical trapping approach to measure force and conclude that the two dynein heads function through a unique load sharing mechanism allowing them to work against forces greater than an individual head.
- Vladislav Belyy
- , Nathan L Hendel
- & Ahmet Yildiz
-
Article |
 Mechanistic insight into the interaction of BLM helicase with intra-strand G-quadruplex structures
Mechanistic insight into the interaction of BLM helicase with intra-strand G-quadruplex structures
G-quadruplexes (G4) DNA are DNA structures found throughout the genome previously shown to be bound with high specificity by the RecQ family helicase BLM. Here the authors describe how BLM interacts with G4 DNA in molecular details and propose an integrated model of the cooperative binding between BLM and G4 structures.
- Sujoy Chatterjee
- , Jennifer Zagelbaum
- & Eli Rothenberg
-
Article |
 In-line alignment and Mg2+ coordination at the cleavage site of the env22 twister ribozyme
In-line alignment and Mg2+ coordination at the cleavage site of the env22 twister ribozyme
Twisters ribozymes are a recently discovered class of non-coding, site-specific self-cleaving RNAs. Here Ren et al. describe a crystal structure of the env22twister ribozyme, propose an ion coordination and catalytic mechanism, and contrast their findings with those of two recently reported twister structures.
- Aiming Ren
- , Marija Košutić
- & Dinshaw J. Patel
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and function of a spectrin-like regulator of bacterial cytokinesis
Structure and function of a spectrin-like regulator of bacterial cytokinesis
EzrA regulates the polymerization of FtsZ, a tubulin-like protein and main component of the Z-ring, which drives cell division in bacteria. Here the authors describe the crystal structure of EzrA and demonstrate that it shares structural and functional properties with eukaryotic spectrins.
- Robert M. Cleverley
- , Jeffrey R. Barrett
- & Richard J. Lewis
-
Article |
 The SH2 domain of Abl kinases regulates kinase autophosphorylation by controlling activation loop accessibility
The SH2 domain of Abl kinases regulates kinase autophosphorylation by controlling activation loop accessibility
Abl is a cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase important for growth, whose hyper activation is associated with several types of cancers. Here, the authors use recombinant Abl protein to uncover the molecular mechanism underlying allosteric activation of Abl by its SH2 domain through the regulation of autophosphorylation.
- Allan Joaquim Lamontanara
- , Sandrine Georgeon
- & Oliver Hantschel
-
Article |
 High-resolution structure and mechanism of an F/V-hybrid rotor ring in a Na+-coupled ATP synthase
High-resolution structure and mechanism of an F/V-hybrid rotor ring in a Na+-coupled ATP synthase
Rotary ATPases exhibit similar architecture and mechanism but distinct physiological functions, operating either as ion pumps or ATP synthases. Here the authors report the structure and mechanism of the c-ring from the A. woodiiATP synthase, and suggest an evolutionary path between synthases and pumps through adaptations in this molecular rotor.
- Doreen Matthies
- , Wenchang Zhou
- & Thomas Meier
-
Article |
 Programmable energy landscapes for kinetic control of DNA strand displacement
Programmable energy landscapes for kinetic control of DNA strand displacement
The operation of DNA-based molecular devices often relies on toehold-mediated strand displacement. Here, the authors show how mismatches in base pairing can be used for the kinetic control of strand displacement, tuning the rate constant over three orders of magnitude.
- Robert R. F. Machinek
- , Thomas E. Ouldridge
- & Andrew J. Turberfield
-
Article |
 The molecular structure of the left-handed supra-molecular helix of eukaryotic polyribosomes
The molecular structure of the left-handed supra-molecular helix of eukaryotic polyribosomes
During translation, several ribosomes assemble on an mRNA strand to form polyribosomes. Here the authors describe—using cryo electron tomography—a compact state of the eukaryotic polysome where individual ribosomes contact each other and form a tight helical assembly that creates a continuous inner channel for the mRNA.
- Alexander G. Myasnikov
- , Zhanna A. Afonina
- & Bruno P. Klaholz
-
Article |
 Regulation of the NaV1.5 cytoplasmic domain by calmodulin
Regulation of the NaV1.5 cytoplasmic domain by calmodulin
Voltage-gated sodium channels (Nav) are transmembrane proteins that underlie action potentials in excitable tissues. Here, Gabelli et al. suggest a novel mechanism for the cytoplasmic control of switching from the inactivated to the non-inactivated form of the Nav1.5 channel that involves dimerization.
- Sandra B. Gabelli
- , Agedi Boto
- & L. Mario Amzel
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for ion selectivity revealed by high-resolution crystal structure of Mg2+ channel MgtE
Structural basis for ion selectivity revealed by high-resolution crystal structure of Mg2+ channel MgtE
MgtE is a magnesium ion-selective channel conserved in all domains of life that contributes to the maintenance of cellular Mg2+homeostasis. Here, the authors provide high-resolution crystal structures of MgtE combined with biochemical analyses that reveal the molecular basis for selectivity.
- Hironori Takeda
- , Motoyuki Hattori
- & Osamu Nureki
-
Article
| Open Access A critical base pair in k-turns that confers folding characteristics and correlates with biological function
A critical base pair in k-turns that confers folding characteristics and correlates with biological function
The k-turn is a widespread RNA element that adopts a kinked structure that mediates tertiary contacts and frequently binds specific proteins. Here, McPhee et al. show that the ability of a given k-turn to fold in the presence of metal ions alone—or to otherwise require protein binding—is attributable to a specific base pair.
- Scott A. McPhee
- , Lin Huang
- & David M. J. Lilley
-
Article |
 Kinetic modulation of a disordered protein domain by phosphorylation
Kinetic modulation of a disordered protein domain by phosphorylation
Protein phosphorylation is a frequent biological occurrence, but the way in which this process modulates the disordered states of proteins is poorly understood. Here, the authors present simulations of the effect of phosphorylation on the kinetics and energetics of a disordered protein.
- Nathaniel Stanley
- , Santiago Esteban-Martín
- & Gianni De Fabritiis
-
Article |
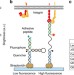 DNA-based digital tension probes reveal integrin forces during early cell adhesion
DNA-based digital tension probes reveal integrin forces during early cell adhesion
Imaging mechanical tension experienced by single adhesion molecules in living cells remains a significant challenge. Zhang et al.design fluorescent probes based on DNA hairpins that can be programmed to reversibly report specific force levels generated by individual integrin molecules in a digital manner.
- Yun Zhang
- , Chenghao Ge
- & Khalid Salaita
-
Article |
 Fine tuning of sub-millisecond conformational dynamics controls metabotropic glutamate receptors agonist efficacy
Fine tuning of sub-millisecond conformational dynamics controls metabotropic glutamate receptors agonist efficacy
Understanding the molecular basis of receptor activation requires characterizing the dynamic equilibrium of conformational states. Here the authors show that the metabotropic glutamate receptor oscillates between conformations on a sub-millisecond timescale, and agonists quantitatively shift the equilibrium towards the activated state based on their potency.
- Linnea Olofsson
- , Suren Felekyan
- & Emmanuel Margeat

 Molecular mechanism for USP7-mediated DNMT1 stabilization by acetylation
Molecular mechanism for USP7-mediated DNMT1 stabilization by acetylation