Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access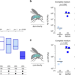 Metabolic cross-feeding in imbalanced diets allows gut microbes to improve reproduction and alter host behaviour
Metabolic cross-feeding in imbalanced diets allows gut microbes to improve reproduction and alter host behaviour
In the fly Drosophila melanogaster commensal bacteria and dietary essential amino acids control food choice behavior. Here, by using chemically defined diets and metabolomics, the authors show that Acetobacter pomorum (Ap) and Lactobacilli plantarum (Lp) engage in a mutualistic metabolic relationship to overcome detrimental diets, and identify Ap as the bacterium altering the host’s feeding decisions.
- Sílvia F. Henriques
- , Darshan B. Dhakan
- & Carlos Ribeiro
-
Article
| Open Access The Rad53CHK1/CHK2-Spt21NPAT and Tel1ATM axes couple glucose tolerance to histone dosage and subtelomeric silencing
The Rad53CHK1/CHK2-Spt21NPAT and Tel1ATM axes couple glucose tolerance to histone dosage and subtelomeric silencing
The relationship between DNA damage response (DDR) and regulation of the tolerance to glucose restriction is currently unclear. Here the authors reveal that maintaining a physiological level of histones by Rad53-Spt21 is necessary for glucose tolerance via multiple parallel pathways, including derepression of subtelomeric genes and acetyl-coA regulation by histone acetylation.
- Christopher Bruhn
- , Arta Ajazi
- & Marco Foiani
-
Article
| Open Access Triacylglycerol synthesis enhances macrophage inflammatory function
Triacylglycerol synthesis enhances macrophage inflammatory function
As macrophages switch to a proinflammatory gylcolytic state they start to generate triglyceride-rich lipid droplets, but what function these droplets have in this context is not clear. Here the authors show that this triglyceride synthesis is requisite for prostaglandin E2 production and subsequent inflammatory activation.
- Angela Castoldi
- , Lauar B. Monteiro
- & Edward J. Pearce
-
Article
| Open Access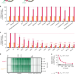 The natural function of the malaria parasite’s chloroquine resistance transporter
The natural function of the malaria parasite’s chloroquine resistance transporter
Plasmodium falciparum chloroquine resistance transporter (PfCRT) mediates multidrug resistance, but its natural function remains unclear. Here, Shafik et al. show that PfCRT transports host-derived peptides of 4-11 residues but not other ions or metabolites, and that drug-resistance-conferring PfCRT mutants have reduced peptide transport.
- Sarah H. Shafik
- , Simon A. Cobbold
- & Rowena E. Martin
-
Article
| Open Access Multiplexed Optical Sensors in Arrayed Islands of Cells for multimodal recordings of cellular physiology
Multiplexed Optical Sensors in Arrayed Islands of Cells for multimodal recordings of cellular physiology
Existing fluorescent protein-based sensor measurements are limited to 4 or fewer simultaneously recorded modalities due to spectral overlap. Here the authors introduce Multiplexed Optical Sensors in Arrayed Islands of Cells (MOSAIC), which enables parallel recording of tens of physiological parameters using dense arrays of cell islands, each expressing a different fluorescent sensor.
- Christopher A. Werley
- , Stefano Boccardo
- & Adam E. Cohen
-
Article
| Open Access A global lipid map defines a network essential for Zika virus replication
A global lipid map defines a network essential for Zika virus replication
Zika virus (ZIKV) remodels intracellular membranes for replication, but the role of different lipid types for infection and disease is unclear. Here, the authors perform lipidomics, show perturbation of the lipid network during ZIKV infection and show that ceramides are important for ZIKV infection.
- Hans C. Leier
- , Jules B. Weinstein
- & Fikadu G. Tafesse
-
Article
| Open Access Fast and sensitive flow-injection mass spectrometry metabolomics by analyzing sample-specific ion distributions
Fast and sensitive flow-injection mass spectrometry metabolomics by analyzing sample-specific ion distributions
Flow-injection mass spectrometry (FI-MS) enables high-throughput metabolomic profiling, but ion overload typically limits its sensitivity. Here, the authors show rapid and highly sensitive FI-MS overcoming an overload of the Orbitrap by analyzing sample-specific ion distributions.
- Boris Sarvin
- , Shoval Lagziel
- & Tomer Shlomi
-
Article
| Open Access Using arterial–venous analysis to characterize cancer metabolic consumption in patients
Using arterial–venous analysis to characterize cancer metabolic consumption in patients
Cellular metabolism is altered in many cancer types and the advent of metabolomics has allowed us to understand more about how this is dysregulated. Here, the authors report a method named CARVE to analyse the arterial supply and venous drainage of glioma patients during surgery and identify the metabolites that may be consumed and produced by the cancer.
- Nanxiang Xiong
- , Xiaofei Gao
- & Woo-ping Ge
-
Article
| Open Access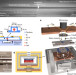 Sub-nanowatt microfluidic single-cell calorimetry
Sub-nanowatt microfluidic single-cell calorimetry
Calorimetrically measuring the heat of single cells is currently not possible due to the sensitivity of existing calorimeters. Here the authors present on-chip single cell calorimetry, with a sensitivity over ten-fold greater than the current gold-standard.
- Sahngki Hong
- , Edward Dechaumphai
- & Renkun Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Independent regulation of age associated fat accumulation and longevity
Independent regulation of age associated fat accumulation and longevity
Age-associated metabolic changes include lipid accumulation. Here, the authors show that with replicative aging yeast accumulate lipid droplets which protect cells from cold stress and can be modulated through Biosynthesis of NAD+ 2 (BNA2).
- Anthony O. Beas
- , Patricia B. Gordon
- & Daniel E. Gottschling
-
Article
| Open Access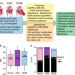 Core functional nodes and sex-specific pathways in human ischaemic and dilated cardiomyopathy
Core functional nodes and sex-specific pathways in human ischaemic and dilated cardiomyopathy
Study of human heart failure is limited by access to human tissue. Here, the authors apply multi-omic screening in human ischaemic and dilated myocardial tissue and matched controls to determine molecular changes common and unique to each aetiology and to reveal differences between male and female hearts.
- Mengbo Li
- , Benjamin L. Parker
- & John F. O’Sullivan
-
Article
| Open Access 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase regulates lipid homeostasis in treatment-resistant prostate cancer
2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase regulates lipid homeostasis in treatment-resistant prostate cancer
Androgen receptor (AR) signalling regulates cellular metabolism in prostate cancer. Here, the authors perform a proteomics and metabolomics characterisation of prostate cancer cells adapted to long-term resistance to AR inhibition and show rewiring of glucose and lipid metabolism, and further identify a signature associated with resistance to AR inhibition.
- Arnaud Blomme
- , Catriona A. Ford
- & Hing Y. Leung
-
Article
| Open Access Phagosomal removal of fungal melanin reprograms macrophage metabolism to promote antifungal immunity
Phagosomal removal of fungal melanin reprograms macrophage metabolism to promote antifungal immunity
Macrophages undergo a Warburg-like switch from oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis in response to inflammatory stimulus. Here the authors show that fungal melanin can trigger this switch in human macrophages by sequestering calcium in the phagosome and enabling protection against Aspergillus fumigatus infection.
- Samuel M. Gonçalves
- , Cláudio Duarte-Oliveira
- & Agostinho Carvalho
-
Article
| Open Access Aspartate aminotransferase Rv3722c governs aspartate-dependent nitrogen metabolism in Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Aspartate aminotransferase Rv3722c governs aspartate-dependent nitrogen metabolism in Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Gene rv3722c is essential for in vitro growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, but its function is unclear. Here, Jansen et al. show that Rv3722c is the primary aspartate aminotransferase of this pathogen, mediates nitrogen distribution, and is important for virulence during infection of macrophages and mice.
- Robert S. Jansen
- , Lungelo Mandyoli
- & Kyu Y. Rhee
-
Article
| Open Access OXPHOS remodeling in high-grade prostate cancer involves mtDNA mutations and increased succinate oxidation
OXPHOS remodeling in high-grade prostate cancer involves mtDNA mutations and increased succinate oxidation
The re-wiring of the metabolic machinery is a common feature in cancer. Here, the authors show, using paired normal and prostate cancer samples that the cancer samples exhibit a shift to succinate respiration, which is associated with elevated levels of mitochondrial DNA mutations.
- Bernd Schöpf
- , Hansi Weissensteiner
- & Helmut Klocker
-
Article
| Open Access Hyperoxia induces glutamine-fuelled anaplerosis in retinal Müller cells
Hyperoxia induces glutamine-fuelled anaplerosis in retinal Müller cells
Prematurely born babies need extra oxygen to survive, but this can cause damage to the eyes and lead to infant blindness. Here the authors show that this hyperoxia changes the metabolism of Müller cells in the retina such that they use up, rather than produce, glutamine and secrete excess ammonium.
- Charandeep Singh
- , Vincent Tran
- & Jonathan E. Sears
-
Article
| Open Access Sex and APOE ε4 genotype modify the Alzheimer’s disease serum metabolome
Sex and APOE ε4 genotype modify the Alzheimer’s disease serum metabolome
Sex and the APOE ε4 genotype are important risk factors for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. In the current study, the authors investigate how sex and APOE ε4 genotype modify the association between Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers and metabolites in serum.
- Matthias Arnold
- , Kwangsik Nho
- & Gabi Kastenmüller
-
Article
| Open Access Heritability estimates for 361 blood metabolites across 40 genome-wide association studies
Heritability estimates for 361 blood metabolites across 40 genome-wide association studies
Blood metabolite levels are under the influence of environmental and genetic factors. Here, Hagenbeek et al. perform heritability estimations for metabolite measures and determine the contribution of known metabolite loci to metabolite levels using data from 40 genome-wide association studies.
- Fiona A. Hagenbeek
- , René Pool
- & Dorret I. Boomsma
-
Article
| Open Access Relationship between gut microbiota and circulating metabolites in population-based cohorts
Relationship between gut microbiota and circulating metabolites in population-based cohorts
Here, the authors provide an in-depth study of the metabolome in two large population-based prospective cohorts and identify 32 microbial traits associated with various metabolic biomarkers and specific lipoprotein subfractions, providing insights into the role of microbiota in influencing host lipid levels.
- Dina Vojinovic
- , Djawad Radjabzadeh
- & Cornelia M. van Duijn
-
Article
| Open Access Metabolomics analysis of human acute graft-versus-host disease reveals changes in host and microbiota-derived metabolites
Metabolomics analysis of human acute graft-versus-host disease reveals changes in host and microbiota-derived metabolites
Graft versus host disease (GvHD) still hinders allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Here, the authors use metabolomics to analyze two cohorts of paired transplant recipients and donors, identifying significant differences in both host- and microbiota-derived metabolites.
- David Michonneau
- , Eleonora Latis
- & Gérard Socié
-
Article
| Open Access Metabolic balancing by miR-276 shapes the mosquito reproductive cycle and Plasmodium falciparum development
Metabolic balancing by miR-276 shapes the mosquito reproductive cycle and Plasmodium falciparum development
Plasmodium growth is adapted to the reproductive cycle of mosquitoes, but underlying mechanisms are unclear. Here, Lampe et al. show that the blood-meal induced miR-276 balances the termination of the mosquito amino acid catabolism and egg development, providing nutrients for Plasmodium sporozoite development.
- Lena Lampe
- , Marius Jentzsch
- & Elena A. Levashina
-
Article
| Open Access Reactive metabolite production is a targetable liability of glycolytic metabolism in lung cancer
Reactive metabolite production is a targetable liability of glycolytic metabolism in lung cancer
Glycolysis is elevated in many cancers. In this study, the authors show that lactoylglutathione, a by-product of methylglyoxal produced from increased glycolysis, is elevated in lung cancer in mouse models and humans, arguing reactive metabolite production can be a liability for cancers.
- Alba Luengo
- , Keene L. Abbott
- & Matthew G. Vander Heiden
-
Article
| Open Access 4-Octyl itaconate inhibits aerobic glycolysis by targeting GAPDH to exert anti-inflammatory effects
4-Octyl itaconate inhibits aerobic glycolysis by targeting GAPDH to exert anti-inflammatory effects
Redirection of the TCA cycle intermediate aconitate to itaconate production has anti-inflammatory effects. Here the authors show that the itaconate derivative 4-octyl-itaconate is anti-inflammatory partly as a result of inhibiting GAPDH enzymatic activity and thereby glycolysis in macrophages.
- Shan-Ting Liao
- , Chao Han
- & Ling-Yi Kong
-
Article
| Open Access Metabolic dysregulation in vitamin E and carnitine shuttle energy mechanisms associate with human frailty
Metabolic dysregulation in vitamin E and carnitine shuttle energy mechanisms associate with human frailty
Risk of age-related chronic disorders and decrease in resilience is associated with ageing. Here the authors analyse the human blood metabolome and identify metabolites associated with frailty.
- Nicholas J. W. Rattray
- , Drupad K. Trivedi
- & Royston Goodacre
-
Article
| Open Access DNA damage and transcription stress cause ATP-mediated redesign of metabolism and potentiation of anti-oxidant buffering
DNA damage and transcription stress cause ATP-mediated redesign of metabolism and potentiation of anti-oxidant buffering
ERCC1 is involved in a number of DNA repair pathways including nucleotide excision repair. Here the authors showed that reduced transcription in Ercc1-deficient mouse livers and cells increases ATP levels, suppressing glycolysis and rerouting glucose into the pentose phosphate shunt that generates reductive stress.
- Chiara Milanese
- , Cíntia R. Bombardieri
- & Pier G. Mastroberardino
-
Article
| Open Access A comprehensive study of metabolite genetics reveals strong pleiotropy and heterogeneity across time and context
A comprehensive study of metabolite genetics reveals strong pleiotropy and heterogeneity across time and context
Genome-wide association studies of metabolites have revealed hundreds of genetic associations using univariate analyses. Here, the authors use a multivariate approach to perform association analyses for 158 serum metabolites, followed by fine mapping and GxE interaction tests with statin use and age.
- Apolline Gallois
- , Joel Mefford
- & Hugues Aschard
-
Article
| Open Access Trisomy 21 activates the kynurenine pathway via increased dosage of interferon receptors
Trisomy 21 activates the kynurenine pathway via increased dosage of interferon receptors
Down syndrome (DS) is caused by trisomy 21 (T21), but the underlying etiology of the related immune and neurological dysfunction is unclear. Here, the authors show that T21 activates the kynurenine pathway via increased interferon receptor copy number, which could contribute to DS pathophysiology.
- Rani K. Powers
- , Rachel Culp-Hill
- & Joaquin M. Espinosa
-
Article
| Open Access RORγ is a targetable master regulator of cholesterol biosynthesis in a cancer subtype
RORγ is a targetable master regulator of cholesterol biosynthesis in a cancer subtype
Enhanced cholesterol biosynthesis is associated with cancer progression. Here the authors identify the nuclear receptor RORγ as a novel master regulator of cholesterol metabolism in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) and find that RORγ small-molecule antagonists induce tumor regression in patient-derived xenografts and immunocompetent mouse models.
- Demin Cai
- , Junjian Wang
- & Hong-Wu Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Mitochondrial calcium exchange links metabolism with the epigenome to control cellular differentiation
Mitochondrial calcium exchange links metabolism with the epigenome to control cellular differentiation
Myofibroblast differentiation contributes to extracellular matrix remodeling and fibrosis. Here, the authors report that alterations in mitochondrial calcium uptake is essential for metabolic reprogramming and epigenetic signaling for activation of the myofibroblast gene program.
- Alyssa A. Lombardi
- , Andrew A. Gibb
- & John W. Elrod
-
Article
| Open Access Interplay between the human gut microbiome and host metabolism
Interplay between the human gut microbiome and host metabolism
Here, the authors study the interplay between the microbiome and faecal and blood metabolome, and how the microbiome interacts in the dialogue between these metabolic compartments, identifying a key role for microbial functions and underscoring their relevance for microbiome therapeutic strategies.
- Alessia Visconti
- , Caroline I. Le Roy
- & Mario Falchi
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic identification of metabolites controlling gene expression in E. coli
Systematic identification of metabolites controlling gene expression in E. coli
Interactions between metabolites and transcription factors are known to control gene expression but analyzing these events at genome-scale is challenging. Here, the authors integrate dynamic metabolome and transcriptome data from E.coli to predict regulatory metabolite-transcription factor interactions.
- Martin Lempp
- , Niklas Farke
- & Hannes Link
-
Article
| Open Access Mitochondrial supercomplex assembly promotes breast and endometrial tumorigenesis by metabolic alterations and enhanced hypoxia tolerance
Mitochondrial supercomplex assembly promotes breast and endometrial tumorigenesis by metabolic alterations and enhanced hypoxia tolerance
Cancer cells rely on mitochondrial respiration to satisfy their metabolic demands. Here the authors show that the mitochondrial supercomplex assembly factor COX7RP is abundantly expressed in breast and endometrial cancer cells and promotes tumor growth and hypoxia tolerance partially by altering levels of the tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediates.
- Kazuhiro Ikeda
- , Kuniko Horie-Inoue
- & Satoshi Inoue
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid metabolic shifts occur during the transition between hunger and satiety in Drosophila melanogaster
Rapid metabolic shifts occur during the transition between hunger and satiety in Drosophila melanogaster
The relationship between metabolomic and behavioral changes is not well understood. Here, the authors analyze metabolome changes in D. melanogaster heads and bodies during hunger and satiety, and develop the Flyscape tool to visualize the resulting metabolic networks and integrate them with other omics data.
- Daniel Wilinski
- , Jasmine Winzeler
- & Monica Dus
-
Article
| Open Access Acetyl-CoA flux regulates the proteome and acetyl-proteome to maintain intracellular metabolic crosstalk
Acetyl-CoA flux regulates the proteome and acetyl-proteome to maintain intracellular metabolic crosstalk
The Endoplasmic Reticulum acetylation machinery ensures proper quality control and disposal of newly folded proteins transiting the secretory pathway. Here, the authors show that this machinery acts as a metabolic regulator of acetyl-CoA homeostasis, impacting intracellular crosstalk.
- Inca A. Dieterich
- , Alexis J. Lawton
- & Luigi Puglielli
-
Article
| Open Access A metabolic profile of all-cause mortality risk identified in an observational study of 44,168 individuals
A metabolic profile of all-cause mortality risk identified in an observational study of 44,168 individuals
Biomarkers that predict mortality are of interest for clinical as well as research applications. Here, the authors analyze metabolomics data from 44,168 individuals and identify key metabolites independently associated with all-cause mortality risk.
- Joris Deelen
- , Johannes Kettunen
- & P. Eline Slagboom
-
Article
| Open Access Regulatory mechanisms underlying coordination of amino acid and glucose catabolism in Escherichia coli
Regulatory mechanisms underlying coordination of amino acid and glucose catabolism in Escherichia coli
Bacteria must adapt their metabolism in the face of dynamically changing nutrient availability. Here, using their constraint-based modeling approach the authors analyze E. coli exometabolome data during growth in complex medium, revealing temporal coordination of glucose and amino acid catabolism.
- Mattia Zampieri
- , Manuel Hörl
- & Uwe Sauer
-
Article
| Open Access Pptc7 is an essential phosphatase for promoting mammalian mitochondrial metabolism and biogenesis
Pptc7 is an essential phosphatase for promoting mammalian mitochondrial metabolism and biogenesis
The mitochondria houses several phosphatases, but their function is not well characterized. Here, the authors show that mitochondrial phosphatase Pptc7 is important during development for proper mitochondrial function and has a role regulating protein import with the translocase subunit Timm50.
- Natalie M. Niemi
- , Gary M. Wilson
- & David J. Pagliarini
-
Article
| Open Access Predictive metabolomic profiling of microbial communities using amplicon or metagenomic sequences
Predictive metabolomic profiling of microbial communities using amplicon or metagenomic sequences
Obtaining metabolomic data from microbial communities can be costly and difficult, whereas many microbial community sequence datasets are already available. Here Mallick et al. describe a computational approach to predict metabolic features from microbial DNA sequencing information.
- Himel Mallick
- , Eric A. Franzosa
- & Curtis Huttenhower
-
Perspective
| Open Access Use cases, best practice and reporting standards for metabolomics in regulatory toxicology
Use cases, best practice and reporting standards for metabolomics in regulatory toxicology
Lack of best practice guidelines currently limits the application of metabolomics in the regulatory sciences. Here, the MEtabolomics standaRds Initiative in Toxicology (MERIT) proposes methods and reporting standards for several important applications of metabolomics in regulatory toxicology.
- Mark R. Viant
- , Timothy M. D. Ebbels
- & Ralf J. M. Weber
-
Article
| Open Access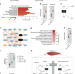 Skeletal muscle PGC-1α1 reroutes kynurenine metabolism to increase energy efficiency and fatigue-resistance
Skeletal muscle PGC-1α1 reroutes kynurenine metabolism to increase energy efficiency and fatigue-resistance
PGC-1α is activated by exercise and promotes resistance to fatigue in muscles. Here, the authors show that PGC-1α activates the malate-aspartate shuttle, and allows muscle to utilise kynurenine, leading to more efficient glucose oxidation and mitochondrial respiration.
- Leandro Z. Agudelo
- , Duarte M. S. Ferreira
- & Jorge L. Ruas
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of metabolic vulnerabilities of receptor tyrosine kinases-driven cancer
Identification of metabolic vulnerabilities of receptor tyrosine kinases-driven cancer
Cancer subtypes may have distinct metabolic vulnerabilities that can be exploited for therapeutic interventions. Here, the authors show that in lung cancer, genetic activation of distinct oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinases results in unique metabolic liabilities and, in particular, EGFR aberrant cancers rely on the serine biosynthetic pathway while FGFR aberrant cancers rely on glycolysis.
- Nan Jin
- , Aiwei Bi
- & Min Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Gut microbiome-derived phenyl sulfate contributes to albuminuria in diabetic kidney disease
Gut microbiome-derived phenyl sulfate contributes to albuminuria in diabetic kidney disease
Diabetes is a major cause of kidney disease. Here Kikuchi et al. show that phenol sulfate, a gut microbiota-derived metabolite, is increased in diabetic kidney disease and contributes to the pathology by promoting kidney injury, suggesting phenyl sulfate could be used a marker and therapeutic target for the treatment of diabetic kidney disease.
- Koichi Kikuchi
- , Daisuke Saigusa
- & Takaaki Abe
-
Article
| Open Access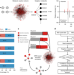 Metabolic reaction network-based recursive metabolite annotation for untargeted metabolomics
Metabolic reaction network-based recursive metabolite annotation for untargeted metabolomics
Untargeted metabolomics detects large numbers of metabolites but their annotation remains challenging. Here, the authors develop a metabolic reaction network-based recursive algorithm that expands metabolite annotation by taking advantage of the mass spectral similarity of reaction-paired neighbor metabolites.
- Xiaotao Shen
- , Ruohong Wang
- & Zheng-Jiang Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of human D lactate dehydrogenase deficiency
Identification of human D lactate dehydrogenase deficiency
D-lactic acidosis typically occurs in the context of short bowel syndrome; excess D-lactate is produced by intestinal bacteria. Here, the authors identify two point mutations in the human lactate dehydrogenase D (LDHD) gene that cause enzymatic loss of function and are associated with elevated plasma D-lactate.
- Glen R. Monroe
- , Albertien M. van Eerde
- & Judith J. Jans
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of serum metabolites associating with chronic kidney disease progression and anti-fibrotic effect of 5-methoxytryptophan
Identification of serum metabolites associating with chronic kidney disease progression and anti-fibrotic effect of 5-methoxytryptophan
Accurate monitoring of chronic kidney disease (CKD) progression is essential for efficient disease management. Here Chen et al. identify five serum metabolites in patients with stage 1–5 CKD whose levels associate with disease progression, and find that 5-methoxytryptophan and its regulatory enzyme TPH-1 exert anti-fibrotic effects in mouse models of kidney injury.
- Dan-Qian Chen
- , Gang Cao
- & Ying-Yong Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access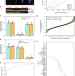 Spatial-fluxomics provides a subcellular-compartmentalized view of reductive glutamine metabolism in cancer cells
Spatial-fluxomics provides a subcellular-compartmentalized view of reductive glutamine metabolism in cancer cells
Measuring metabolic fluxes in cellular compartments is a challenge. Here, the authors introduce an approach to infer fluxes in mitochondria and cytosol, and find that IDH1 is the major producer of cytosolic citrate in HeLa cells and that in SDH- deficient cells citrate synthase functions in reverse.
- Won Dong Lee
- , Dzmitry Mukha
- & Tomer Shlomi
-
Article
| Open Access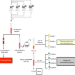 Dynamic molecular changes during the first week of human life follow a robust developmental trajectory
Dynamic molecular changes during the first week of human life follow a robust developmental trajectory
The first week of life impacts health for all of life, but the mechanisms are little-understood. Here the authors extract multi-omic data from small volumes of blood to study the dynamic molecular changes during the first week of life, revealing a robust developmental trajectory common to different populations.
- Amy H. Lee
- , Casey P. Shannon
- & Tobias R. Kollmann
-
Article
| Open Access Malonylation of GAPDH is an inflammatory signal in macrophages
Malonylation of GAPDH is an inflammatory signal in macrophages
Host metabolic reprogramming plays a role in functional responses against pathogens. Here, the authors characterise malonylated proteins in macrophages and show that malonylation of the glycolytic enzyme GAPDH impacts cytokine production by modulating both its enzymatic activity and RNA-binding capacity.
- Silvia Galván-Peña
- , Richard G. Carroll
- & Luke A. O’Neill
-
Article
| Open Access Coordinative metabolism of glutamine carbon and nitrogen in proliferating cancer cells under hypoxia
Coordinative metabolism of glutamine carbon and nitrogen in proliferating cancer cells under hypoxia
Glutamine metabolism is increased in proliferating cells under hypoxia potentially generating exceeding nitrogen. Here the authors show that under hypoxia a specific metabolic pathway is activated to push glutamine carbons and excess nitrogen via the reductive pathway to dihyroorotate which is then secreted by the cells and that such pathway is necessary for tumor growth.
- Yuanyuan Wang
- , Changsen Bai
- & Binghui Li

 Ion mobility collision cross-section atlas for known and unknown metabolite annotation in untargeted metabolomics
Ion mobility collision cross-section atlas for known and unknown metabolite annotation in untargeted metabolomics