Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access A phenotypic Caenorhabditis elegans screen identifies a selective suppressor of antipsychotic-induced hyperphagia
A phenotypic Caenorhabditis elegans screen identifies a selective suppressor of antipsychotic-induced hyperphagia
The molecular pathway(s) driving antipsychotics (AP) induced hyperphagia remains unclear. A novel C. elegans system is used here to screen for FDA approved drugs that selectively suppresses this response, unraveling potential molecular mediators influencing AP induced hyperphagia in mouse models.
- Anabel Perez-Gomez
- , Maria Carretero
- & Michael Petrascheck
-
Article
| Open Access Adipocyte OGT governs diet-induced hyperphagia and obesity
Adipocyte OGT governs diet-induced hyperphagia and obesity
Endocannabinoid signaling regulates food intake and is a potential therapeutic target for obesity. Here the authors show that adipocyte O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) is required for high fat diet-induced hyperphagia via transcriptional activation of de novo lipid desaturation and accumulation of an endogenous appetite-inducing cannabinoid.
- Min-Dian Li
- , Nicholas B. Vera
- & Xiaoyong Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Subcellular connectomic analyses of energy networks in striated muscle
Subcellular connectomic analyses of energy networks in striated muscle
Assessing biological circuit connections in single cells has been intractable due to lack of appropriate tools. Here, Bleck et al. develop a method to assess mitochondrial network connectivity in muscle cells and observe clear differences consistent with differing energy requirements.
- Christopher K. E. Bleck
- , Yuho Kim
- & Brian Glancy
-
Article
| Open Access Adipocyte-secreted BMP8b mediates adrenergic-induced remodeling of the neuro-vascular network in adipose tissue
Adipocyte-secreted BMP8b mediates adrenergic-induced remodeling of the neuro-vascular network in adipose tissue
Enhancing thermogenesis is a promising therapeutic strategy for promoting metabolic health. Here the authors show that adipocyte-secreted BMP8b contributes to optimizing the thermogenic response by remodeling of the neuro-vascular networks in brown and white adipose tissue.
- Vanessa Pellegrinelli
- , Vivian J. Peirce
- & Antonio Vidal-Puig
-
Article
| Open Access Serotonin signals through a gut-liver axis to regulate hepatic steatosis
Serotonin signals through a gut-liver axis to regulate hepatic steatosis
No effective pharmacological treatments exist for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Here, the authors show that serotonin concentration in the portal blood is increased in nine human subjects and in mice fed a high-fat diet, and that local serotonin signaling ablation, either genetically or with an antagonist, prevents hepatic steatosis in mice.
- Wonsuk Choi
- , Jun Namkung
- & Hail Kim
-
Article
| Open Access A low-gluten diet induces changes in the intestinal microbiome of healthy Danish adults
A low-gluten diet induces changes in the intestinal microbiome of healthy Danish adults
Gluten-free diets are increasingly common in the general population. Here, the authors report the results of a randomised cross-over trial involving middle-aged, healthy Danish adults, showing evidence that a low-gluten diet leads to gut microbiome changes, possibly due to variations in dietary fibres.
- Lea B. S. Hansen
- , Henrik M. Roager
- & Oluf Pedersen
-
Article
| Open Access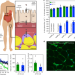 Human adipose glycerol flux is regulated by a pH gate in AQP10
Human adipose glycerol flux is regulated by a pH gate in AQP10
Uptake and release of glycerol from the small intestine and adipocytes is facilitated by a subclass of aquaporins (AQP), but how glycerol flow is regulated remains poorly understood. Here authors solve the crystal structure of AQP10 and show how lipolysis is coupled to AQP10 regulation in
- Kamil Gotfryd
- , Andreia Filipa Mósca
- & Pontus Gourdon
-
Article
| Open Access Diet-induced adaptive thermogenesis requires neuropeptide FF receptor-2 signalling
Diet-induced adaptive thermogenesis requires neuropeptide FF receptor-2 signalling
Excess caloric intake leads to increased thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue, to limit weight gain. Here, the authors show that neuropeptide FF receptor-2 signalling promotes thermogenesis via control of NPY expression in the arcuate nucleus, and that it absence in mice leads to a failure of activation of diet-induced thermogenesis and the development of exacerbated obesity.
- Lei Zhang
- , Chi Kin Ip
- & Herbert Herzog
-
Article
| Open Access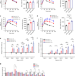 Long term but not short term exposure to obesity related microbiota promotes host insulin resistance
Long term but not short term exposure to obesity related microbiota promotes host insulin resistance
Gut microbiota impact host metabolism and gut microbiome composition reflects dietary habits. Here the authors show that, in animals fed obesogenic diets, changes in gut microbiota precede changes in glucose homeostasis. Importantly, long term exposure of the host to the changed microbiota is required to impair glucose homeostasis.
- Kevin P. Foley
- , Soumaya Zlitni
- & Jonathan D. Schertzer
-
Article
| Open Access Proteome evolution under non-substitutable resource limitation
Proteome evolution under non-substitutable resource limitation
Organisms could respond to essential resource limitation by increasing metabolic efficiency or resource acquisition ability. Here, the authors experimentally evolve green algae under different resource limitations and show convergent evolution of core metabolism rather than resource specialization.
- Manu Tamminen
- , Alexander Betz
- & Anita Narwani
-
Article
| Open Access PRKAA1/AMPKα1-driven glycolysis in endothelial cells exposed to disturbed flow protects against atherosclerosis
PRKAA1/AMPKα1-driven glycolysis in endothelial cells exposed to disturbed flow protects against atherosclerosis
Increased glycolysis and inflammatory responses have been observed in endothelial cells exposed to disturbed flow. However, the role of endothelial glycolysis in atherosclerosis is unclear. Here the authors unveil a protective role for glycolysis by showing that endothelial deletion of Prkaa1 accelerates atherosclerosis in hyperlipidemic mice through a reduction of glycolytic metabolism.
- Qiuhua Yang
- , Jiean Xu
- & Yuqing Huo
-
Article
| Open Access Neuronal SIRT1 regulates macronutrient-based diet selection through FGF21 and oxytocin signalling in mice
Neuronal SIRT1 regulates macronutrient-based diet selection through FGF21 and oxytocin signalling in mice
SIRT1 is a NAD+-dependent deacetylase whose functions have been linked to organismal longevity, aging and metabolism. Here, Matsui and colleagues show that neuronal SIRT1 can affect nutrient-related dietary choice in mice, and this effect is mediated by FGF21 signalling and oxytocin.
- Sho Matsui
- , Tsutomu Sasaki
- & Tadahiro Kitamura
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide analyses identify a role for SLC17A4 and AADAT in thyroid hormone regulation
Genome-wide analyses identify a role for SLC17A4 and AADAT in thyroid hormone regulation
Thyroid dysfunction is a common public health problem and associated with cardiovascular co-morbidities. Here, the authors carry out genome-wide meta-analysis for thyroid hormone (TH) levels, hyper- and hypothyroidism and identify SLC17A4 as a TH transporter and AADAT as a TH metabolizing enzyme.
- Alexander Teumer
- , Layal Chaker
- & Marco Medici
-
Article
| Open Access Coordinated targeting of cold and nicotinic receptors synergistically improves obesity and type 2 diabetes
Coordinated targeting of cold and nicotinic receptors synergistically improves obesity and type 2 diabetes
Tobacco smoking and cold exposure are environmental modulators of human energy metabolism suppressing appetite and increasing energy expenditure, respectively. Here, the authors develop a novel pharmacological strategy in which they simultaneously mimic the metabolic benefits of both phenomena through small-molecule combination therapy, and show that this treatment improves metabolic health of obese mice.
- Christoffer Clemmensen
- , Sigrid Jall
- & Matthias H. Tschöp
-
Article
| Open Access Precisely measured protein lifetimes in the mouse brain reveal differences across tissues and subcellular fractions
Precisely measured protein lifetimes in the mouse brain reveal differences across tissues and subcellular fractions
Measuring precise protein turnover rates in animals is technically challenging at the proteomic level. Here, Fornasiero and colleagues use isotopic labeling with mass spectrometry and mathematical modeling to accurately determine protein lifetimes in the mouse brain
- Eugenio F. Fornasiero
- , Sunit Mandad
- & Silvio O. Rizzoli
-
Article
| Open Access Alpha-enolase regulates the malignant phenotype of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells via the AMPK-Akt pathway
Alpha-enolase regulates the malignant phenotype of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells via the AMPK-Akt pathway
Metabolic reprogramming of smooth muscle cells (SMCs) plays an important role in the pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Here, Dai et al. show that the glycolytic enzyme alpha-enolase contributes to this reprogramming, and that its inhibition limits SMC proliferation and disease progression in animal models of PAH.
- Jingbo Dai
- , Qiyuan Zhou
- & Guofei Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access The gut microbiota promotes hepatic fatty acid desaturation and elongation in mice
The gut microbiota promotes hepatic fatty acid desaturation and elongation in mice
The role of the gut microbiota in hepatic lipid metabolism is controversial and incompletely understood. Here the authors perform multi-omics analyses of altered lipid metabolic processes in germ-free and specific pathogen-free mice, revealing how the gut microbiota affects hepatic fatty acid desaturation and elongation.
- Alida Kindt
- , Gerhard Liebisch
- & Josef Ecker
-
Article
| Open Access LincRNA H19 protects from dietary obesity by constraining expression of monoallelic genes in brown fat
LincRNA H19 protects from dietary obesity by constraining expression of monoallelic genes in brown fat
Brown adipose tissue (BAT) thermogenesis counteracts obesity and promotes metabolic health. The role of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in the regulation of this process is not well understood. Here the authors identify a maternally expressed lncRNA, H19, that increases BAT oxidative metabolism and energy expenditure.
- Elena Schmidt
- , Ines Dhaouadi
- & Jan-Wilhelm Kornfeld
-
Article
| Open Access Loss of the E3 ubiquitin ligase MKRN1 represses diet-induced metabolic syndrome through AMPK activation
Loss of the E3 ubiquitin ligase MKRN1 represses diet-induced metabolic syndrome through AMPK activation
AMPK activation has been suggested as treatment for obesity and its complications. Here the authors show that the ubiquitin ligase MKRN1 binds to AMPK and mediates its ubiquitination and degradation. Loss of MKRN1 leads to AMPK activation, increased glucose consumption and decreased lipid accumulation.
- Min-Sik Lee
- , Hyun-Ji Han
- & Jaewhan Song
-
Article
| Open Access Deep-coverage whole genome sequences and blood lipids among 16,324 individuals
Deep-coverage whole genome sequences and blood lipids among 16,324 individuals
Common genetic variants associated with plasma lipids have been extensively studied for a better understanding of common diseases. Here, the authors use whole-genome sequencing of 16,324 individuals to analyze rare variant associations and to determine their monogenic and polygenic contribution to lipid traits.
- Pradeep Natarajan
- , Gina M. Peloso
- & Sebastian Zoellner
-
Article
| Open Access A selective inhibitor of ceramide synthase 1 reveals a novel role in fat metabolism
A selective inhibitor of ceramide synthase 1 reveals a novel role in fat metabolism
Ceramides are signalling molecules that regulate several physiological functions including insulin sensitivity. Here the authors report a selective ceramide synthase 1 inhibitor that counteracts lipid accumulation within the muscle and adiposity by increasing fatty acid oxidation but without affecting insulin sensitivity in mice fed with an obesogenic diet.
- Nigel Turner
- , Xin Ying Lim
- & Anthony S. Don
-
Review Article
| Open Access Microbial tryptophan catabolites in health and disease
Microbial tryptophan catabolites in health and disease
Gut microbial metabolites are known to impact many physiological processes of the host and play a critical role in immune-homeostasis. Here the authors review our current understanding and appreciation of the importance of microbially derived tryptophan catabolites during both health and disease.
- Henrik M. Roager
- & Tine R. Licht
-
Article
| Open Access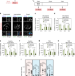 Dietary stearic acid regulates mitochondria in vivo in humans
Dietary stearic acid regulates mitochondria in vivo in humans
Dietary fatty acids have different effects on human health. Here, the authors show that ingestion of the fatty acid C18:0, but not of C16:0, rapidly leads to fusion of mitochondria and fatty acid oxidation in humans, possibly explaining the health benefits of C18:0.
- Deniz Senyilmaz-Tiebe
- , Daniel H. Pfaff
- & Aurelio A. Teleman
-
Article
| Open Access Statin as a novel pharmacotherapy of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
Statin as a novel pharmacotherapy of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) is associated with defective macrophage clearance of surfactant. Here, the authors show that patients with PAP have altered cholesterol-to-phospholipid ratio in their surfactant, and that more importantly, statin therapy and reduction of cholesterol accumulation in macrophages can ameliorate PAP in both humans and mice.
- Cormac McCarthy
- , Elinor Lee
- & Bruce C. Trapnell
-
Article
| Open Access Myeloid apolipoprotein E controls dendritic cell antigen presentation and T cell activation
Myeloid apolipoprotein E controls dendritic cell antigen presentation and T cell activation
Cholesterol homeostasis can modulate immunity via multiple pathways. Here the authors show that apolipoprotein E, an important regulator of cholesterol, produced by myeloid cells can regulate T cell activation by controlling the antigen presentation activity of dendritic cells in both humans and mice.
- Fabrizia Bonacina
- , David Coe
- & Giuseppe D. Norata
-
Article
| Open Access Glucose promotes cell growth by suppressing branched-chain amino acid degradation
Glucose promotes cell growth by suppressing branched-chain amino acid degradation
Hypertrophic cardiomyocytes switch their metabolism from fatty acid oxidation to glucose use, but the functional role of this change is unclear. Here the authors show that high intracellular glucose inhibits the degradation of branched-chain amino acids, which is required for the activation of pro-growth mTOR signaling.
- Dan Shao
- , Outi Villet
- & Rong Tian
-
Article
| Open Access Antibiotic-induced microbiome depletion alters metabolic homeostasis by affecting gut signaling and colonic metabolism
Antibiotic-induced microbiome depletion alters metabolic homeostasis by affecting gut signaling and colonic metabolism
Antibiotic-induced microbiome depletion is one of the most common approaches to modulate the gut microbiome. Here the authors demonstrate that it affects gut homeostasis and glucose metabolism by decreasing luminal short chain fatty acids and leading to a shift of energy utilization by colonocytes.
- Amir Zarrinpar
- , Amandine Chaix
- & Satchidananda Panda
-
Article
| Open Access Deep coverage whole genome sequences and plasma lipoprotein(a) in individuals of European and African ancestries
Deep coverage whole genome sequences and plasma lipoprotein(a) in individuals of European and African ancestries
Circulating lipoprotein(a) is an important risk factor for cardiovascular disease and shows variability between different ethnic groups. Here, Zekavat et al. perform whole-genome sequencing in individuals of European and African ancestries and find ancestry-specific genetic determinants for lipoprotein(a) levels.
- Seyedeh M. Zekavat
- , Sanni Ruotsalainen
- & Sebastian Zoellner
-
Article
| Open Access Postprandial FGF19-induced phosphorylation by Src is critical for FXR function in bile acid homeostasis
Postprandial FGF19-induced phosphorylation by Src is critical for FXR function in bile acid homeostasis
FXR plays an important role in bile acid homeostasis by transcriptionally modulating several enterohepatic genes, including intestinal FGF19, that repress hepatic bile acid synthesis. Here the authors show that postprandial FGF19 regulates FXR transcriptional activity via its action on the tyrosine kinase Src, which phosphorylates FXR.
- Sangwon Byun
- , Dong-Hyun Kim
- & Jongsook Kim Kemper
-
Article
| Open Access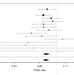 Genetic inactivation of ANGPTL4 improves glucose homeostasis and is associated with reduced risk of diabetes
Genetic inactivation of ANGPTL4 improves glucose homeostasis and is associated with reduced risk of diabetes
Genetic variation in ANGPTL4 is associated with lipid traits. Here, the authors find that predicted loss-of-function variants in ANGPTL4 are associated with glucose homeostasis and reduced risk of type 2 diabetes and that Angptl4−/− mice on a high-fat diet show improved insulin sensitivity.
- Viktoria Gusarova
- , Colm O’Dushlaine
- & Jesper Gromada
-
Article
| Open Access Alternative assembly of respiratory complex II connects energy stress to metabolic checkpoints
Alternative assembly of respiratory complex II connects energy stress to metabolic checkpoints
Mitochondrial complex II is normally composed of four subunits. Here the authors show that bioenergetic stress conditions give rise to a partially assembled variant of complex II, which shifts the anabolic pathways to less energy demanding processes.
- Ayenachew Bezawork-Geleta
- , He Wen
- & Jiri Neuzil
-
Article
| Open Access Deficiency of PRKD2 triggers hyperinsulinemia and metabolic disorders
Deficiency of PRKD2 triggers hyperinsulinemia and metabolic disorders
Hyperinsulinemia can precede the development of insulin resistance. Here the authors identify a PKD2 mutation that leads to hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance in Rhesus monkey and show that PKD2 deficiency promotes beta cell insulin secretion by activating L-type Ca2+ channels.
- Yao Xiao
- , Can Wang
- & Xiuqin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access LRRC8/VRAC anion channels enhance β-cell glucose sensing and insulin secretion
LRRC8/VRAC anion channels enhance β-cell glucose sensing and insulin secretion
Insulin secretion by β-cells is stimulated by glucose and is dependent on the induction of β-cell membrane depolarization, mainly driven by the closure of KATP channels, which in turn promotes voltage-gated Ca2+ channel opening. Here the authors show that LRRC8 volume-regulated anion channels (VRACs) modulate glucose-stimulated calcium increase and insulin secretion.
- Till Stuhlmann
- , Rosa Planells-Cases
- & Thomas J. Jentsch
-
Article
| Open Access A joint view on genetic variants for adiposity differentiates subtypes with distinct metabolic implications
A joint view on genetic variants for adiposity differentiates subtypes with distinct metabolic implications
In GWAS, waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) is often adjusted for body mass index (BMI) to account for their correlation (WHRadjBMI). Here, Winkler et al. classify 159 genetic variants for BMI, WHR, or WHRadjBMI based on their effect directions for BMI and WHR to differentiate subtypes of adiposity genetics.
- Thomas W Winkler
- , Felix Günther
- & Iris M Heid
-
Article
| Open Access Tip60-mediated lipin 1 acetylation and ER translocation determine triacylglycerol synthesis rate
Tip60-mediated lipin 1 acetylation and ER translocation determine triacylglycerol synthesis rate
The acetyltransferase Tip60 mediates signaling pathways by acetylating non-histone proteins. Here the authors show that fatty acids induce Tip60–dependent acetylation of phosphatidic acid phosphatase lipin1 which, then, translocates to the ER and generates diacylglycerols for triglyceride synthesis.
- Terytty Yang Li
- , Lintao Song
- & Sheng-Cai Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Depletion of Nsd2-mediated histone H3K36 methylation impairs adipose tissue development and function
Depletion of Nsd2-mediated histone H3K36 methylation impairs adipose tissue development and function
The epigenetic mechanisms regulating adipose tissue development are poorly understood. Here the authors show that reduction of H3K36 methylation in preadipocytes, both by H3.3K36M expression and depletion of H3K36 methyltransferase Nsd2, impairs adipogenesis by increasing H3K27me3.
- Lenan Zhuang
- , Younghoon Jang
- & Kai Ge
-
Article
| Open Access Contrast-enhanced ultrasound measurement of pancreatic blood flow dynamics predicts type 1 diabetes progression in preclinical models
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound measurement of pancreatic blood flow dynamics predicts type 1 diabetes progression in preclinical models
Non-invasive techniques to assess the progression of type 1 diabetes prior to clinical onset are needed. Here the authors apply a contrast-enhanced ultrasound measurement of mouse pancreatic blood flow to detect changes in the islet microvasculature that undergoes rearrangements during diabetes and predict disease progression.
- Joshua R. St Clair
- , David Ramirez
- & Richard K. P. Benninger
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for GPR40 allosteric agonism and incretin stimulation
Structural basis for GPR40 allosteric agonism and incretin stimulation
GPR40 is a G-protein coupled receptor that binds to free fatty acids, mediating insulin and incretin secretion. Here, the authors present the crystal structure of human GPR40 with an agonist bound to an allosteric site located near the lipid-rich region that suggests a mechanism for biased agonism.
- Joseph D. Ho
- , Betty Chau
- & Chafiq Hamdouchi
-
Article
| Open Access Histone demethylase JMJD1A coordinates acute and chronic adaptation to cold stress via thermogenic phospho-switch
Histone demethylase JMJD1A coordinates acute and chronic adaptation to cold stress via thermogenic phospho-switch
JMJD1A is essential for thermogenic gene induction in brown adipose tissue. Here the authors show that white adipose tissue beige-ing requires both β-adrenergic-dependent phosphorylation of S265 and demethylation activity of JMJD1A while brown adipose tissue-driven thermogenesis requires β-adrenergic dependent phosphorylation of S265 but is independent of H3K9me2 demethylation.
- Yohei Abe
- , Yosuke Fujiwara
- & Juro Sakai
-
Article
| Open Access TAp63 contributes to sexual dimorphism in POMC neuron functions and energy homeostasis
TAp63 contributes to sexual dimorphism in POMC neuron functions and energy homeostasis
Sexual dimorphism exists in a number of physiological processes, including energy homeostasis. Here, the authors show that pro-opiomelanocortin neurons in female mice fire more rapidly than males, and that deletion of the transcription TAp63 leads to a reduced neuronal firing rate and a male-like susceptibility to diet-induced obesity.
- Chunmei Wang
- , Yanlin He
- & Yong Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Matriptase-2 deficiency protects from obesity by modulating iron homeostasis
Matriptase-2 deficiency protects from obesity by modulating iron homeostasis
Iron homeostasis dysfunctions have been associated with several metabolic disorders including obesity, steatosis and diabetes. Here the authors demonstrate that the hepcidin repressor matriptase-2 regulates adiposity and its deficiency protects mice against obesity and promotes lipolysis.
- Alicia R. Folgueras
- , Sandra Freitas-Rodríguez
- & Carlos López-Otín
-
Article
| Open Access PHA-4/FoxA senses nucleolar stress to regulate lipid accumulation in Caenorhabditis elegans
PHA-4/FoxA senses nucleolar stress to regulate lipid accumulation in Caenorhabditis elegans
Nucleolar stress can disrupt ribosome biogenesis and in turn energy metabolism and lipid storage, but how this is regulated is unclear. Here, the authors show in C. elegans that the transcription factor PHA-4/FOXA acts as a sensor for nucleolar stress and can regulate expression of lipogenic genes
- Jieyu Wu
- , Xue Jiang
- & Bin Liang
-
Article
| Open Access Physiological and therapeutic regulation of glucose homeostasis by upper small intestinal PepT1-mediated protein sensing
Physiological and therapeutic regulation of glucose homeostasis by upper small intestinal PepT1-mediated protein sensing
High protein diets are known to improve metabolic parameters including adiposity and glucose homeostasis. Here the authors demonstrate that preabsorptive upper small intestinal protein-sensing mechanisms mediated by peptide transporter 1 improve glucose homeostasis by inhibiting hepatic glucose production.
- Helen J. Dranse
- , T. M. Zaved Waise
- & Tony K. T. Lam
-
Article
| Open Access Lkb1 deficiency confers glutamine dependency in polycystic kidney disease
Lkb1 deficiency confers glutamine dependency in polycystic kidney disease
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is characterized by the formation of large fluid-filled cysts. Here Flowers and colleagues show that loss of Lkb1, downregulated in PKD, renders kidney cells dependent on glutamine for growth, and suggest that inhibition of glutamine metabolism may prevent cyst development in PKD.
- Ebony M. Flowers
- , Jessica Sudderth
- & Thomas J. Carroll
-
Article
| Open Access Bone marrow lympho-myeloid malfunction in obesity requires precursor cell-autonomous TLR4
Bone marrow lympho-myeloid malfunction in obesity requires precursor cell-autonomous TLR4
Obesity can affect bone marrow cell differentiation and the generation of myeloid and lymphoid cells. Here, the authors show that diet and obesity, as well as low-dose lipopolysaccharide, can alter Toll-like receptor 4 signaling bone marrow cells to skew the myeloid-lymphoid homeostasis in mice.
- Ailing Liu
- , Minhui Chen
- & Lisa Borghesi
-
Article
| Open Access α-cell glucokinase suppresses glucose-regulated glucagon secretion
α-cell glucokinase suppresses glucose-regulated glucagon secretion
Glucagon secretion is promoted during hypoglycemia and inhibited by increased glucose levels. Here, Basco et al. show that glucokinase suppresses glucose-regulated glucagon secretion by modulating the intracellular ATP/ADP ratio and the closure of KATP channels in α-cells.
- Davide Basco
- , Quan Zhang
- & Bernard Thorens
-
Article
| Open Access AhR and SHP regulate phosphatidylcholine and S-adenosylmethionine levels in the one-carbon cycle
AhR and SHP regulate phosphatidylcholine and S-adenosylmethionine levels in the one-carbon cycle
Methyl metabolites in the one-carbon cycle, such as phosphatidylcholines and S-adenosylmethionine, play a role in hepatic triglyceride regulation. Here Kim et al. show that AhR and SHP are both involved in the expression of several key enzymes of one-carbon metabolism, with the former regulating them early after feeding and the latter inhibiting AhR at later stages.
- Young-Chae Kim
- , Sunmi Seok
- & Jongsook Kim Kemper
-
Article
| Open Access Fibroblast growth factor 21 increases insulin sensitivity through specific expansion of subcutaneous fat
Fibroblast growth factor 21 increases insulin sensitivity through specific expansion of subcutaneous fat
FGF21 has a number of beneficial metabolic effects. Here, Li et al. show that FGF21 promotes the healthy expansion of subcutaneous white adipose tissue, promoting the healthy expansion of fat tissue as a regulatory mechanism to maintain systemic insulin sensitivity during nutrient excess.
- Huating Li
- , Guangyu Wu
- & Weiping Jia
-
Article
| Open Access TGR5 signalling promotes mitochondrial fission and beige remodelling of white adipose tissue
TGR5 signalling promotes mitochondrial fission and beige remodelling of white adipose tissue
White adipose tissue can undergo a process of beiging and acquire functional characteristics similar to brown adipose tissue, including the ability to dissipate energy via uncoupled respiration. Here, Velazquez-Villegas et al. show that activation of the bile acid membrane receptor, TGR5, leads to white adipocyte beiging by promoting mitochondrial fission.
- Laura A. Velazquez-Villegas
- , Alessia Perino
- & Kristina Schoonjans

 Bioconjugation strategy for cell surface labelling with gold nanostructures designed for highly localized pH measurement
Bioconjugation strategy for cell surface labelling with gold nanostructures designed for highly localized pH measurement