Featured
-
-
Article |
 TRF1 is a stem cell marker and is essential for the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells
TRF1 is a stem cell marker and is essential for the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells
TRF-1 is a telomere-binding protein that protects chromosome ends from degradation. Schneider and colleagues show that TRF1 is a marker of adult stem cell compartments and of induced pluripotent stem cells, and that TRF1 is essential for the induction and maintenance of pluripotency.
- Ralph P. Schneider
- , Ianire Garrobo
- & Maria A. Blasco
-
Article |
 A mouse model of adult-onset anaemia due to erythropoietin deficiency
A mouse model of adult-onset anaemia due to erythropoietin deficiency
Kidney diseases often cause anaemia due to damage of renal erythropoietin-producing cells. Yamazaki et al. identify a new population of erythropoietin-producing cells in the renal cortex and outer medulla by establishing a mouse model for adult-onset erythropoietin-deficient anaemia.
- Shun Yamazaki
- , Tomokazu Souma
- & Masayuki Yamamoto
-
Article |
 The antiparasitic drug ivermectin is a novel FXR ligand that regulates metabolism
The antiparasitic drug ivermectin is a novel FXR ligand that regulates metabolism
The nuclear Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) regulates bile acid and cholesterol production. Here Jin et al. identify the clinically approved antiparasitic drug ivermectin as a novel FXR ligand and show that it has antidiabetic effects in mice.
- Lihua Jin
- , Xuhui Feng
- & Yong Li
-
Article
| Open Access Depleting the methyltransferase Suv39h1 improves DNA repair and extends lifespan in a progeria mouse model
Depleting the methyltransferase Suv39h1 improves DNA repair and extends lifespan in a progeria mouse model
Accelerated cellular ageing in patients with progeria can be caused by the accumulation of nuclear lamins, leading to DNA damage and histone methylation. Here Liu et al. show that the metyltransferase SUV39H1 regulates lamin A stability, and that SUV39H1 depletion extends lifespan in a progeria mouse model.
- Baohua Liu
- , Zimei Wang
- & Zhongjun Zhou
-
Article |
 Delivery of therapeutic agents by nanoparticles made of grapefruit-derived lipids
Delivery of therapeutic agents by nanoparticles made of grapefruit-derived lipids
Nanoparticles released from living cells can be used as drug delivery vehicles, but scaling up their production is challenging. Here, Wang and colleagues create nanoparticles from natural lipids contained in grapefruit juice that can encapsulate various types of therapeutics and deliver them to cells in vitro and in vivo.
- Qilong Wang
- , Xiaoying Zhuang
- & Huang-Ge Zhang
-
Article |
 Flexible polymer transistors with high pressure sensitivity for application in electronic skin and health monitoring
Flexible polymer transistors with high pressure sensitivity for application in electronic skin and health monitoring
Flexible pressure sensors may be key in realising biomedical prostheses and robots that can interact with their environment. Here, Schwartz et al.report an organic thin film pressure sensing device that combines fast response times with low power consumption and cyclic stability.
- Gregor Schwartz
- , Benjamin C.-K. Tee
- & Zhenan Bao
-
Article |
 SMRT compounds abrogate cellular phenotypes of ataxia telangiectasia in neural derivatives of patient-specific hiPSCs
SMRT compounds abrogate cellular phenotypes of ataxia telangiectasia in neural derivatives of patient-specific hiPSCs
Ataxia telangiectasia is a genetic disease that results in various pathological disorders. In this study, the authors develop an in vitromodel of Ataxia telangiectasia using human induced pluripotent stem cells, and find that physiological defects can be alleviated by small molecule read-through compounds.
- Peiyee Lee
- , Nathan T. Martin
- & William E. Lowry
-
Article |
 Recruitment of mesenchymal stem cells into prostate tumours promotes metastasis
Recruitment of mesenchymal stem cells into prostate tumours promotes metastasis
Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote tumour growth and metastasis by secreting signalling molecules. Jung and colleagues show that prostate cancer cells secrete CXC chemokine ligand 16, which recruits mesenchymal stem cells and converts them into cancer-associated fibroblasts.
- Younghun Jung
- , Jin Koo Kim
- & Russell S. Taichman
-
Article |
 Trapping red blood cells in living animals using optical tweezers
Trapping red blood cells in living animals using optical tweezers
Optical tweezers based on focused laser beams are widely used for biophysical measurements of single molecules in vitro. Here Zhong et al. use infrared optical tweezers to trap and manipulate red blood cells within subdermal capillaries in living mice.
- Min-Cheng Zhong
- , Xun-Bin Wei
- & Yin-Mei Li
-
Article |
 Control of lung vascular permeability and endotoxin-induced pulmonary oedema by changes in extracellular matrix mechanics
Control of lung vascular permeability and endotoxin-induced pulmonary oedema by changes in extracellular matrix mechanics
Vascular permeability is increased by inflammation and in disorders such as acute respiratory distress syndrome. Mammoto et al. show that lung vascular permeability is controlled by the stiffness of the extracellular matrix and identify lysyl oxidase as a regulator of vascular leakage in pulmonary oedema in mice.
- Akiko Mammoto
- , Tadanori Mammoto
- & Donald E. Ingber
-
Article |
 Magnetic barcode assay for genetic detection of pathogens
Magnetic barcode assay for genetic detection of pathogens
Detecting and phenotyping Mycobacterium tuberculosis, especially in resource-limited settings, is important for global tuberculosis control. Here Liong et al. report a point-of-care diagnostic platform based on magnetic barcoding and nuclear magnetic resonance for the detection of mycobacterial nucleic acids.
- Monty Liong
- , Anh N. Hoang
- & Ralph Weissleder
-
Article |
 Titanium dioxide nanomaterials cause endothelial cell leakiness by disrupting the homophilic interaction of VE–cadherin
Titanium dioxide nanomaterials cause endothelial cell leakiness by disrupting the homophilic interaction of VE–cadherin
Nanoparticles can accumulate in tissues but how they interact with cells is poorly understood. Here Setyawati and colleagues report that titanium dioxide nanoparticles disrupt protein complexes of the tight junction protein VE-cadherin on endothelial cells to increase blood vessel permeability.
- M.I. Setyawati
- , C.Y. Tay
- & D.T. Leong
-
Article |
 Normal muscle regeneration requires tight control of muscle cell fusion by tetraspanins CD9 and CD81
Normal muscle regeneration requires tight control of muscle cell fusion by tetraspanins CD9 and CD81
The skeletal muscle has a remarkable capacity to regenerate after injury. Here Charrin et al. reveal that restoration of muscle architecture after injury requires a tight control of muscle cell fusion by the tetraspanin proteins CD9 and CD81 through their interaction with the cell surface protein CD9P-1.
- Stéphanie Charrin
- , Mathilde Latil
- & Eric Rubinstein
-
Article
| Open Access A chronic model of arthritis supported by a strain-specific periarticular lymph node in BALB/c mice
A chronic model of arthritis supported by a strain-specific periarticular lymph node in BALB/c mice
Mouse models of arthritis generally do not result in both chronic disease and autoantibody production—two key features of the human disease. Here the authors obtain both features by combining two common protocols, and find that disease severity is associated with the presence of a previously unidentified lymph node.
- Uta Baddack
- , Sven Hartmann
- & Gerd Müller
-
Article |
 Microbiota-derived lactate accelerates colon epithelial cell turnover in starvation-refed mice
Microbiota-derived lactate accelerates colon epithelial cell turnover in starvation-refed mice
Epithelial cells in the colon mainly use microbial fermentation products as energy sources. Here Okada et al. find that lactate produced by commensal Lactobacillus murinusregulates colonic epithelial cell proliferation and show that mice are more susceptible to carcinogens when refed after a period of starvation.
- Toshihiko Okada
- , Shinji Fukuda
- & Taeko Dohi
-
Article |
 Sulfhydration mediates neuroprotective actions of parkin
Sulfhydration mediates neuroprotective actions of parkin
The gasotransmitter hydrogen sulfide signals by sulfide modification of target proteins. Vandiver and colleagues study the sulfhydration of parkin by hydrogen sulfide and find that sulfhydration stimulates its activity, and that this activity is reduced in patients with Parkinson’s disease.
- M. Scott Vandiver
- , Bindu D. Paul
- & Solomon H. Snyder
-
Article
| Open Access Telomeres shorten at equivalent rates in somatic tissues of adults
Telomeres shorten at equivalent rates in somatic tissues of adults
Telomere shortening as a result of cell proliferation has been implicated in human ageing. Here, Daniali and colleagues show that telomere length and the rate of age-dependent shortening vary between adults but are similar within tissues of the same individual.
- Lily Daniali
- , Athanase Benetos
- & Abraham Aviv
-
Article
| Open Access A model of parity-dependent immunity to placental malaria
A model of parity-dependent immunity to placental malaria
Exposure to malaria during pregnancy can result in its spread to the placenta; however, the risk of placental infection decreases with subsequent pregnancies. By constructing a mathematical model, the authors find that this is likely due to a reduction in the duration of infection rather than a reduced risk of transfer.
- Patrick G. T. Walker
- , Jamie T. Griffin
- & Azra C. Ghani
-
Article |
 Engineering the type III secretion system in non-replicating bacterial minicells for antigen delivery
Engineering the type III secretion system in non-replicating bacterial minicells for antigen delivery
Bacterial type III secretion systems (T3SS) improve the delivery of vaccine antigens and antigen-specific immune responses but require the use of live vaccines. Carleton et al. report the assembly of a functional T3SS in replication-incompetent bacterial minicells that can deliver vaccine antigens in vitro and in vivo.
- Heather A. Carleton
- , María Lara-Tejero
- & Jorge E. Galán
-
Article |
 Human hypocretin and melanin-concentrating hormone levels are linked to emotion and social interaction
Human hypocretin and melanin-concentrating hormone levels are linked to emotion and social interaction
The emotional state of humans depends on the temporal concentration of neurochemicals. Blouin et al. measure temporal changes in two neuropeptides, hypocretin and melanin-concentrating hormone, and find that hypocretin but not melanin-concentrating hormone is linked to positive emotions and social interaction.
- Ashley M. Blouin
- , Itzhak Fried
- & Jerome M. Siegel
-
Article
| Open Access Phantom pain is associated with preserved structure and function in the former hand area
Phantom pain is associated with preserved structure and function in the former hand area
Reorganization of the sensorimotor cortex due to loss of sensory input is implicated in phantom pain. Makin and colleagues use functional MRI to show that phantom pain experience is instead associated with maintained local functional and structural cortical representations but disrupted inter-regional connectivity.
- Tamar R. Makin
- , Jan Scholz
- & Heidi Johansen-Berg
-
Article |
 An ex vivo gene therapy approach to treat muscular dystrophy using inducible pluripotent stem cells
An ex vivo gene therapy approach to treat muscular dystrophy using inducible pluripotent stem cells
Patient-specific induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells hold great potential for regenerative cell therapies. Here Filareto et al. genetically correct iPS cells from mice with muscular dystrophy and use these cells to treat the same animals, providing a proof-of-principle for autologous iPS cell therapy.
- Antonio Filareto
- , Sarah Parker
- & Rita C. R. Perlingeiro
-
Article |
 Aldara activates TLR7-independent immune defence
Aldara activates TLR7-independent immune defence
The skin cancer treatment Aldara generates psoriasis-like symptoms in mice, which are thought to be due to stimulation of TLR7 by the active ingredient imiquimod. The authors show that some of these inflammatory effects are independent of both imiquimod and TLR7, implicating an unexpected role for the vehicle.
- Anne Walter
- , Matthias Schäfer
- & Maries van den Broek
-
Article |
 Loss of TRPM2 function protects against irradiation-induced salivary gland dysfunction
Loss of TRPM2 function protects against irradiation-induced salivary gland dysfunction
A debilitating side effect of radiotherapy in patients with head and neck cancers is xerostomia as a result of salivary gland dysfunction. Here Liu et al. show that activation of the calcium channel TRPM2 in salivary gland cells contributes to irradiation-induced loss of salivary fluid secretion.
- Xibao Liu
- , Ana Cotrim
- & Indu Ambudkar
-
Article |
 Holographic optogenetic stimulation of patterned neuronal activity for vision restoration
Holographic optogenetic stimulation of patterned neuronal activity for vision restoration
Photo-stimulation can be used to control neuronal circuits, but current strategies lack optimal precision and resolution. Reutsky-Gefen et al. demonstrate a potential approach for vision restoration via holographically patterned, optogenetic stimulation of retinal ganglion cells, with temporal precision.
- Inna Reutsky-Gefen
- , Lior Golan
- & Shy Shoham
-
Article |
 Parasympathetic stimulation improves epithelial organ regeneration
Parasympathetic stimulation improves epithelial organ regeneration
Irradiation treatment for cancer therapy often causes irreparable damage to adult organs. Knox and colleagues study irradiated mouse submandibular salivary glands and find that restoring parasympathetic nerve function with the neurotrophic factor neurturin improves regeneration.
- Sarah M. Knox
- , Isabelle M. A. Lombaert
- & Matthew P. Hoffman
-
Article |
 High-throughput hyperdimensional vertebrate phenotyping
High-throughput hyperdimensional vertebrate phenotyping
Large-scale screening of animal phenotypes requires automated detection and analysis of complex morphological information. Here, Yanik and colleagues present an imaging system based on optical projection tomography that generates micrometre-resolution 3D images of zebrafish larvae with within tens of seconds per animal.
- Carlos Pardo-Martin
- , Amin Allalou
- & Mehmet Fatih Yanik
-
Article
| Open Access Genome of the Chinese tree shrew
Genome of the Chinese tree shrew
The Chinese tree shrew, Tupaia belangeri chinensis, has been proposed as a potential animal model in biomedical research and drug safety testing. This study presents the full genome of the Chinese tree shrew, identifying common features between the tree shrew and primates.
- Yu Fan
- , Zhi-Yong Huang
- & Yong-Gang Yao
-
Article
| Open Access In vitro fabrication of functional three-dimensional tissues with perfusable blood vessels
In vitro fabrication of functional three-dimensional tissues with perfusable blood vessels
Artificially engineered tissues may have many therapeutic applications but complex tissues are hard to create in vitro. Here, Okano and colleagues report the production of functional cardiac tissue sheets with perfusable blood vessels, which increase the thickness and survival of transplanted tissue.
- Hidekazu Sekine
- , Tatsuya Shimizu
- & Teruo Okano
-
Article
| Open Access Computational identification of a transiently open L1/S3 pocket for reactivation of mutant p53
Computational identification of a transiently open L1/S3 pocket for reactivation of mutant p53
About 40% of human cancers carry missense mutations in the tumour suppressor protein p53. Here the authors identify a transiently open pocket in the protein, and by targeting a small molecule to it, partially restore mutant p53 tumour suppressor activity.
- Christopher D. Wassman
- , Roberta Baronio
- & Rommie E. Amaro
-
Article |
 A novel pathway for the production of hydrogen sulfide from D-cysteine in mammalian cells
A novel pathway for the production of hydrogen sulfide from D-cysteine in mammalian cells
Hydrogen sulphide is a signalling molecule with cytoprotective activity in mammals. Here, Kimura and colleagues identify a new biosynthetic pathway for the production of hydrogen sulphide from D-cysteine, which is shown to protect mouse kidneys from oxidative stress after ischaemia/reperfusion injury.
- Norihiro Shibuya
- , Shin Koike
- & Hideo Kimura
-
Article
| Open Access On-demand optogenetic control of spontaneous seizures in temporal lobe epilepsy
On-demand optogenetic control of spontaneous seizures in temporal lobe epilepsy
Temporal lobe epilepsy in adults does not always respond to treatment. Krook-Magnuson and colleagues use optogenetics to inhibit and activate excitatory and inhibitory neurons, respectively, in a mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy, and find that they can stop seizures on a moment-to-moment basis.
- Esther Krook-Magnuson
- , Caren Armstrong
- & Ivan Soltesz
-
Article
| Open Access The miRNA-212/132 family regulates both cardiac hypertrophy and cardiomyocyte autophagy
The miRNA-212/132 family regulates both cardiac hypertrophy and cardiomyocyte autophagy
Heart failure is often a consequence of pathological growth of cardiomyocytes or cardiac hypertrophy. Here Ucar and colleagues report that the microRNAs miR-132 and miR-212 promote cardiac hypertrophy and inhibit autophagy in cardiomyocytes by downregulating the transcription factor FoxO3.
- Ahmet Ucar
- , Shashi K. Gupta
- & Thomas Thum
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence of an inhibitory restraint of seizure activity in humans
Evidence of an inhibitory restraint of seizure activity in humans
Seizure activity in the brain is characterized by the recruitment of cortical neuronal activity. Schevon and colleagues study seizure activity in human subjects and find that the recruitment of neurons is hypersynchronous and that there is an intrinsic restraint on the propagation of this activity.
- Catherine A. Schevon
- , Shennan A. Weiss
- & Andrew J. Trevelyan
-
Article
| Open Access Extracellular ATP mediates mast cell-dependent intestinal inflammation through P2X7 purinoceptors
Extracellular ATP mediates mast cell-dependent intestinal inflammation through P2X7 purinoceptors
Mast cells are mediators of type I allergic disease and inflammation. Here, Kurashimaet al. show that mast cells are increased in the colons of mice with colitis, and that activation of the cells and subsequent inflammation can be blocked by inhibition of the purinoceptor, P2X7.
- Yosuke Kurashima
- , Takeaki Amiya
- & Hiroshi Kiyono
-
Article |
 Skeletal muscle stem cells adopt a dormant cell state post mortem and retain regenerative capacity
Skeletal muscle stem cells adopt a dormant cell state post mortem and retain regenerative capacity
Stem cells hold great potential for therapeutic use but their supply is limited. Latilet al.isolate muscle stem cells from human and mouse cadavers after 17 and 14 days, respectively, and show that when transplanted into mice the cells can regenerate tissues.
- Mathilde Latil
- , Pierre Rocheteau
- & Fabrice Chrétien
-
Article
| Open Access Cancer cells that survive radiation therapy acquire HIF-1 activity and translocate towards tumour blood vessels
Cancer cells that survive radiation therapy acquire HIF-1 activity and translocate towards tumour blood vessels
Radiotherapy is used to treat many cancers but radiation-resistant cells can result in recurrence of the tumour. Here, Harada and colleagues develop a method to track cells that persist after radiation treatment and show that the cells acquire transcriptional activity of HIF-1 and move towards blood vessels.
- Hiroshi Harada
- , Masahiro Inoue
- & Masahiro Hiraoka
-
Article |
 Host factors dictate control of viral replication in two HIV-1 controller/chronic progressor transmission pairs
Host factors dictate control of viral replication in two HIV-1 controller/chronic progressor transmission pairs
Human immunodeficiency virus patients who maintain low levels of virus or have undetectable levels of virus exist. In this study, the HIV found in two of these patients is shown to replicatein vitro, suggesting that host factors have a role in suppressing virus levels.
- Robert W. Buckheit III
- , Tracy G. Allen
- & Joel N. Blankson
-
Article
| Open Access Wind direction and proximity to larval sites determines malaria risk in Kilifi District in Kenya
Wind direction and proximity to larval sites determines malaria risk in Kilifi District in Kenya
Spatial epidemiology studies identify malaria hotspots, which sustain transmission and so could be targeted by control programmes. This study uses spatial data on larval sites and malaria episodes to show that transmission can be disrupted by targeting vector breeding sites close to and downwind of malaria hotspots.
- Janet T. Midega
- , Dave L. Smith
- & Philip Bejon
-
Article |
 Parkin controls dopamine utilization in human midbrain dopaminergic neurons derived from induced pluripotent stem cells
Parkin controls dopamine utilization in human midbrain dopaminergic neurons derived from induced pluripotent stem cells
Mutations in parkin, an ubiquitin ligase, cause an inherited form of Parkinson's disease. Here, Jianget al. generate induced pluripotent stem cells from two patients with parkin mutations and find that neurons derived from the stem cells have defects in dopamine release, dopamine uptake and oxidative metabolism.
- Houbo Jiang
- , Yong Ren
- & Jian Feng
-
Article |
 c-Src and IL-6 inhibit osteoblast differentiation and integrate IGFBP5 signalling
c-Src and IL-6 inhibit osteoblast differentiation and integrate IGFBP5 signalling
Osteoblast maturation is regulated by c-Src and IL-6, but how these signalling pathways are integrated is not known. Here c-Src is shown to induce 1GFBP5 in immature osteoblasts in a STAT3 and IL-6-dependent manner, in mature osteoblasts, which express lower levels of c-Src, this signalling is lost.
- Barbara Peruzzi
- , Alfredo Cappariello
- & Anna Teti
-
Article
| Open Access Promotion of plasma membrane repair by vitamin E
Promotion of plasma membrane repair by vitamin E
Membrane repair of myocytes is important to prevent such disease as muscular dystrophy but the properties of this repair are not well characterised. In this study, vitamin E is shown to be important in the repair of myocyte cell membranes in cultured cells and in intact muscle.
- Amber C. Howard
- , Anna K. McNeil
- & Paul L. McNeil
-
Article |
 A role for T-bet-mediated tumour immune surveillance in anti-IL-17A treatment of lung cancer
A role for T-bet-mediated tumour immune surveillance in anti-IL-17A treatment of lung cancer
The tumour microenvironment is often found to be immunosuppressive. Reppert and colleagues show that human and murine lung tumours harbour IL-17A-producing T cells, and that blocking IL-17A increases survival in mice, suggesting that anti-IL-17A therapy may be useful in treating lung cancer.
- S. Reppert
- , I. Boross
- & S. Finotto
-
Article
| Open Access Competition for FcRn-mediated transport gives rise to short half-life of human IgG3 and offers therapeutic potential
Competition for FcRn-mediated transport gives rise to short half-life of human IgG3 and offers therapeutic potential
The half-life of IgG is regulated by binding to the neonatal Fc receptor and, in the case of IgG3, is reduced compared to other IgG proteins. In this study, a mutation in IgG3 is shown to reduce binding to the neonatal Fc receptor, which can be competitively blocked by IgG1.
- Nigel M. Stapleton
- , Jan Terje Andersen
- & Gestur Vidarsson
-
Article
| Open Access Activin enhances skin tumourigenesis and malignant progression by inducing a pro-tumourigenic immune cell response
Activin enhances skin tumourigenesis and malignant progression by inducing a pro-tumourigenic immune cell response
Activin is known to have a role in wound healing, but its role in skin cancer is unknown. Antsiferovaet al. show that activin is elevated in human skin tumours, and by modulating epidermal immune cells, exacerbates tumour progression in a mouse model of skin cancer.
- Maria Antsiferova
- , Marcel Huber
- & Sabine Werner
-
Article
| Open Access Global kinomic and phospho-proteomic analyses of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum
Global kinomic and phospho-proteomic analyses of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum
New approaches are required to combatPlasmodium falciparuminfection. In this proteome-wide study, 1305 phosphorylation sites are identified and 36 kinases are shown to have crucial roles in parasite survival, providing new insights into parasite biology and potential new drug targets for anti-malarial chemotherapy.
- Lev Solyakov
- , Jean Halbert
- & Christian Doerig
-
Article
| Open Access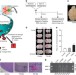 The collagen-binding protein of Streptococcus mutans is involved in haemorrhagic stroke
The collagen-binding protein of Streptococcus mutans is involved in haemorrhagic stroke
The risk factors associated with both ischemic and haemorrhagic stroke are not fully understood. Here a certain strain of the bacteria,Streptococcus mutans, which expresses a collagen-binding protein, is shown to be associated with haemorrhagic stroke in both animal models and human patients.
- Kazuhiko Nakano
- , Kazuya Hokamura
- & Takashi Ooshima
-
Article |
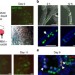 In vitro production of fertile sperm from murine spermatogonial stem cell lines
In vitro production of fertile sperm from murine spermatogonial stem cell lines
Recent technological advances have allowed the expansion of spermatogonial stem cellsin vitro; however, in vivo conditions are required for the full differentiation of the cells. In this study, an in vitroorgan culture system is developed that allows the differentiation of the germ cells in the laboratory.
- Takuya Sato
- , Kumiko Katagiri
- & Takehiko Ogawa
-
Article |
 In-vitro derived germinal centre B cells differentially generate memory B or plasma cells in vivo
In-vitro derived germinal centre B cells differentially generate memory B or plasma cells in vivo
In response to antigens, B cells proliferate and form germinal centres before differentiating into memory B cells or long-lived plasma cells. Here, a culture method is used to expand B cells in vitro, with the ability to shift the fate of the cells between memory B cells and long-lived plasma cells.
- Takuya Nojima
- , Kei Haniuda
- & Daisuke Kitamura

 A common functional promoter variant links CNR1 gene expression to HDL cholesterol level
A common functional promoter variant links CNR1 gene expression to HDL cholesterol level