Featured
-
-
Article |
 Berberine activates thermogenesis in white and brown adipose tissue
Berberine activates thermogenesis in white and brown adipose tissue
Berberine is contained in some plant-derived medicines and is known to have anti-diabetic effects. Here the authors show that berberine activates thermogenesis in white and brown adipose tissues, thereby increasing organismal energy expenditure and limiting weight gain in genetically obese mice.
- Zhiguo Zhang
- , Huizhi Zhang
- & Guang Ning
-
Article
| Open Access Pathological roles of the VEGF/SphK pathway in Niemann–Pick type C neurons
Pathological roles of the VEGF/SphK pathway in Niemann–Pick type C neurons
Sphingosine is abnormally accumulated in Niemann–Pick type C disease (NP–C), but the causes of this accumulation have not been fully characterized. Here the authors show that sphingosine kinase activity is reduced in NP–C patient fibroblasts and NP–C mouse neurons due to defective vascular endothelial growth factor levels, suggesting therapeutic avenues.
- Hyun Lee
- , Jong Kil Lee
- & Hee Kyung Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Positron emission tomography and functional characterization of a complete PBR/TSPO knockout
Positron emission tomography and functional characterization of a complete PBR/TSPO knockout
The 18-kDa translocator protein (TSPO) has been implicated in steroid biogenesis and neuroinflammation. Here, the authors create viable and fertile global TSPO knockout mice, challenging the assumption that TSPO is essential for mouse development but suggesting that it may have a role under certain disease conditions.
- Richard B. Banati
- , Ryan J. Middleton
- & Guo-Jun Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence for henipavirus spillover into human populations in Africa
Evidence for henipavirus spillover into human populations in Africa
Henipaviruses (HNVs) infect bats in Asia and Africa, but transmission to humans (often with lethal consequences) is known only in Asia. Here the authors show that 3% of human serum samples from certain areas in Cameroon contain antibodies against HNV, indicating spillover into the human population.
- Olivier Pernet
- , Bradley S. Schneider
- & Benhur Lee
-
Article |
 A viral peptide that targets mitochondria protects against neuronal degeneration in models of Parkinson’s disease
A viral peptide that targets mitochondria protects against neuronal degeneration in models of Parkinson’s disease
Mitochondrial dysfunction is associated with a number of neurodegenerative diseases. Szelechowski et al.take advantage of a viral protein that suppresses apoptosis in neurons to isolate a peptide that protects mitochondria and reduces neuronal cell death in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease.
- Marion Szelechowski
- , Alexandre Bétourné
- & Daniel Gonzalez-Dunia
-
Article |
 Multiscale cardiac modelling reveals the origins of notched T waves in long QT syndrome type 2
Multiscale cardiac modelling reveals the origins of notched T waves in long QT syndrome type 2
Patients with the Long QT Syndrome type 2 have abnormal cardiac electrical activity, which is diagnosed by an electrocardiogram (ECG) that shows a prolonged QT interval and a notched T wave. Here the authors uncover the origins of this signature ECG phenotype by using a multi-scale cardiac modelling.
- Arash Sadrieh
- , Luke Domanski
- & Adam P Hill
-
Article |
 Scalable high-density peptide arrays for comprehensive health monitoring
Scalable high-density peptide arrays for comprehensive health monitoring
Health monitoring based on measuring circulating antibodies may enable the presymptomatic detection of diseases. Here, the authors report a large-scale peptide array platform that allows for a detection of the profile of circulating antibodies associated with cancers and infectious diseases.
- Joseph Barten Legutki
- , Zhan-Gong Zhao
- & Phillip Stafford
-
Article |
 A metabolic view on menopause and ageing
A metabolic view on menopause and ageing
Changes in serum metabolites can indicate the development of disease. Here, the authors measure serum metabolite and lipoprotein levels in a large cohort of Northern Europeans, creating metabolic fingerprints for various age groups and, specifically, for women at the onset of menopause.
- Kirsi Auro
- , Anni Joensuu
- & Markus Perola
-
Article
| Open Access Development of pro-apoptotic peptides as potential therapy for peritoneal endometriosis
Development of pro-apoptotic peptides as potential therapy for peritoneal endometriosis
Endometriosis is a painful condition in which endometrial cells are found outside the womb. Here, the authors identify a peptide that specifically binds to a receptor expressed on endometrial epithelial cells and use it to induce apoptosis in both cultured cells and baboons with endometriosis.
- K. Sugihara
- , Y. Kobayashi
- & M.N. Fukuda
-
Article
| Open Access H2S and NO cooperatively regulate vascular tone by activating a neuroendocrine HNO–TRPA1–CGRP signalling pathway
H2S and NO cooperatively regulate vascular tone by activating a neuroendocrine HNO–TRPA1–CGRP signalling pathway
Nitric oxide (NO) and hydrogen sulphide (H2S) are two gaseous signalling molecules produced in tissues. Here the authors propose that NO and H2S react with each other to form nitroxyl (HNO), which activates the TRPA1 channel in nerve cells and triggers the release of the vasoactive peptide CGRP.
- Mirjam Eberhardt
- , Maria Dux
- & Milos R. Filipovic
-
Article |
 Modelling Fanconi anemia pathogenesis and therapeutics using integration-free patient-derived iPSCs
Modelling Fanconi anemia pathogenesis and therapeutics using integration-free patient-derived iPSCs
Fanconi anaemia (FA) is a genetic disease associated with low levels of blood stem cells. Here Liu et al.report an improved method to generate genetically corrected induced pluripotent stem cells from an FA patient, and perform a screening to identify drugs that improve their differentiation into blood stem cells.
- Guang-Hui Liu
- , Keiichiro Suzuki
- & Juan Carlos Izpisua Belmonte
-
Article |
 FOXO1 inhibition yields functional insulin-producing cells in human gut organoid cultures
FOXO1 inhibition yields functional insulin-producing cells in human gut organoid cultures
The transcription factor FOXO1 has been shown to control the differentiation of enteroendocrine cells in mice. Here the authors extend these findings to humans by showing that FOXO1-expressing cells also exist in the human gut, and that inhibition of FOXO1 generates insulin-secreting cells in human gut organoid cultures.
- Ryotaro Bouchi
- , Kylie S. Foo
- & Domenico Accili
-
Review Article |
 Systemic regulation of mammalian ageing and longevity by brain sirtuins
Systemic regulation of mammalian ageing and longevity by brain sirtuins
Sirtuins have been implicated in the ageing process in a variety of organisms, but their role in mammalian ageing remains somewhat controversial. Here the authors discuss sirtuin proteins in the brain, providing an overview of their physiological functions as well as their implication in mammalian ageing.
- Akiko Satoh
- & Shin-ichiro Imai
-
Article |
 Human symptoms–disease network
Human symptoms–disease network
Unravelling the relationships between disease symptoms and underlying molecular origins is an important task in biomedical research. Here, Zhou et al.link diseases via their symptom overlap, and show that similar phenotypes are mirrored in networks that connect diseases with common genes or protein interactions.
- XueZhong Zhou
- , Jörg Menche
- & Amitabh Sharma
-
Article |
 Injectable bioadhesive hydrogels with innate antibacterial properties
Injectable bioadhesive hydrogels with innate antibacterial properties
Bioadhesives are materials frequently used as surgical sealants, though to date, these typically possess limited antibacterial properties. Here, the authors present a novel injectable and antibacterial bioadhesive hydrogel and demonstrate its performance in vivo.
- Michael C. Giano
- , Zuhaib Ibrahim
- & Joel P. Schneider
-
Article
| Open Access Temporal disease trajectories condensed from population-wide registry data covering 6.2 million patients
Temporal disease trajectories condensed from population-wide registry data covering 6.2 million patients
Population-wide analyses of healthcare data are challenging and thus often involve only few diseases or comparatively short time scales. Here the authors use healthcare records of all hospital encounters in Denmark over 15 years to describe how disease diagnoses progress over time.
- Anders Boeck Jensen
- , Pope L. Moseley
- & Søren Brunak
-
Article |
 Ultrafast fluorescence imaging in vivo with conjugated polymer fluorophores in the second near-infrared window
Ultrafast fluorescence imaging in vivo with conjugated polymer fluorophores in the second near-infrared window
In vivofluorescence imaging in the second near-infrared window allows high resolution and tissue penetration. Here, using conjugated polymers, the authors achieve imaging with high spatial and time resolutions capable of resolving mouse femoral artery blood-flow variations within a single cardiac cycle.
- Guosong Hong
- , Yingping Zou
- & Hongjie Dai
-
Article |
 LSD1 promotes oxidative metabolism of white adipose tissue
LSD1 promotes oxidative metabolism of white adipose tissue
Brown adipocytes are rich in mitochondria and influence whole-body energy balance. Here, Duteil et al. show that the lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) controls mitochondrial biogenesis and the formation of brown-like adipocytes, and that LSD1 overexpression in white fat reduces weight gain of mice on a high-fat diet.
- Delphine Duteil
- , Eric Metzger
- & Roland Schüle
-
Article |
 MRTF-A controls vessel growth and maturation by increasing the expression of CCN1 and CCN2
MRTF-A controls vessel growth and maturation by increasing the expression of CCN1 and CCN2
Myocardin-related transcription factors (MRTFs) increase muscle growth and regeneration. Here, Hinkel et al. show that MRTFs also promote microvessel growth and maturation in chronic ischaemic disease of the heart or peripheral muscle by increasing the expression of the pro-angiongenic factors, CCN1 and CCN2.
- Rabea Hinkel
- , Teresa Trenkwalder
- & Christian Kupatt
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic haematopoietic cell contribution to the developing and adult epicardium
Dynamic haematopoietic cell contribution to the developing and adult epicardium
The murine epicardium forms an envelope around the heart and contains cells that can participate in cardiac repair. Here the authors discover a population of epicardial cells derived from blood cells, which proliferate and change their surrounding extracellular matrix in response to cardiac injury.
- Gemma M. Balmer
- , Sveva Bollini
- & Paul R. Riley
-
Article |
 Cathepsin K-mediated notch1 activation contributes to neovascularization in response to hypoxia
Cathepsin K-mediated notch1 activation contributes to neovascularization in response to hypoxia
The cathepsin family of proteases cleaves intracellular as well as extracellular proteins. Here the authors implicate cathepsin K in ischaemia-induced neovascularization by showing that cathepsin K increases the levels of cleaved Notch1 and downstream Notch signalling in endothelial cells.
- Haiying Jiang
- , Xian Wu Cheng
- & Masafumi Kuzuya
-
Article
| Open Access Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach
Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach
An individual tumour is often heterogeneous and its various features can be visualised noninvasively using medical imaging. Here, the authors analyse large computed tomography data sets using radiomic algorithms to identify heterogeneity, and find that some of these tumour features have prognostic value across cancer types.
- Hugo J. W. L. Aerts
- , Emmanuel Rios Velazquez
- & Philippe Lambin
-
Article
| Open Access TRPV2 is critical for the maintenance of cardiac structure and function in mice
TRPV2 is critical for the maintenance of cardiac structure and function in mice
The TRPV2 calcium channel can be activated by mechanical stretch and may act as a mechanoreceptor in tissues. Here the authors deplete the TRPV2 calcium channel from the hearts of adult mice, showing that TRPV2 is important for the maintenance of cardiac structure and function.
- Yuki Katanosaka
- , Keiichiro Iwasaki
- & Keiji Naruse
-
Article |
 MitoNEET-mediated effects on browning of white adipose tissue
MitoNEET-mediated effects on browning of white adipose tissue
Mice overexpressing the mitochondrial protein MitoNEET in white adipose tissue (WAT) are very fat but metabolically healthy. Here the authors study the physiological consequences of MitoNEET overexpression in WAT, showing that this triggers an initial browning and that the subsequently expanded WAT is less fibrotic.
- Christine M. Kusminski
- , Jiyoung Park
- & Philipp E. Scherer
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical–genetic attenuation of focal neocortical seizures
Chemical–genetic attenuation of focal neocortical seizures
Focal epilepsy is difficult to treat with currently available drugs or surgical approaches. Kätzel et al.express mutant inhibitory receptors in the brains of rats with focal epilepsy and selectively activate these receptors by an exogenous compound, which results in region- and time-specific suppression of focal seizures
- Dennis Kätzel
- , Elizabeth Nicholson
- & Dimitri M. Kullmann
-
Article
| Open Access Mixed lineage kinases activate MEK independently of RAF to mediate resistance to RAF inhibitors
Mixed lineage kinases activate MEK independently of RAF to mediate resistance to RAF inhibitors
B-Raf is mutated in many melanomas but treatment of the disease with small molecules targeting the mutant protein often results in tumour resistance. Here, the authors show that mixed lineage kinases (MLK1-4) can reactivate the B-Raf signalling pathway in the presence of inhibitors, resulting in drug resistance.
- Anna A. Marusiak
- , Zoe C. Edwards
- & John Brognard
-
Article |
 Knockdown and knockout of β1-integrin in hepatocytes impairs liver regeneration through inhibition of growth factor signalling
Knockdown and knockout of β1-integrin in hepatocytes impairs liver regeneration through inhibition of growth factor signalling
Integrin signalling has been implicated in liver regeneration but the molecular processes are not well understood. Here the authors show that β1-integrin is required for liver regeneration and that its absence impairs ligand-induced activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor in mice.
- Tobias Speicher
- , Beat Siegenthaler
- & Sabine Werner
-
Article |
 Nanoparticle-formulated siRNA targeting integrins inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression in mice
Nanoparticle-formulated siRNA targeting integrins inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression in mice
Integrin proteins regulate important cellular processes such as proliferation and differentiation. Here the authors show that siRNA-mediated knockdown of two integrin subunits slows down progression of hepatocellular carcinoma in mice by reducing activation of the METoncogene.
- Roman L. Bogorad
- , Hao Yin
- & Victor Koteliansky
-
Article |
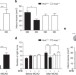 The β-hydroxybutyrate receptor HCA2 activates a neuroprotective subset of macrophages
The β-hydroxybutyrate receptor HCA2 activates a neuroprotective subset of macrophages
The ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate is produced in the liver in response to a ketogenic diet. Here, Rahman et al. show that β-hydroxybutyrate mediates the neuroprotective effect of a ketogenic diet by activating the HCA2receptor on a neuroprotective subset of macrophages.
- Mahbubur Rahman
- , Sajjad Muhammad
- & Markus Schwaninger
-
Article |
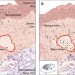 Nanoparticle exposure in animals can be visualized in the skin and analysed via skin biopsy
Nanoparticle exposure in animals can be visualized in the skin and analysed via skin biopsy
Nanoparticle exposure and accumulation can have detrimental health effects, but measuring these exposure levels in animals is difficult. Here, the authors show that exposure can be visualized on the skin, and can be used to quantify accumulation in the liver and spleen using elemental analysis.
- Edward A. Sykes
- , Qin Dai
- & Warren C. W. Chan
-
Article
| Open Access Exercise training reduces resting heart rate via downregulation of the funny channel HCN4
Exercise training reduces resting heart rate via downregulation of the funny channel HCN4
Endurance athletes are known to have a low resting heart rate. Here, D'Souza et al.propose that training-induced bradycardia is the result of electrophysiological changes in the sinus node, challenging the classical view that training-induced bradycardia is caused by increased activity of the autonomic nervous system.
- Alicia D’Souza
- , Annalisa Bucchi
- & Mark R. Boyett
-
Article
| Open Access Low abundance of the matrix arm of complex I in mitochondria predicts longevity in mice
Low abundance of the matrix arm of complex I in mitochondria predicts longevity in mice
Mitochondria are involved in ageing but exactly how they are involved is controversial. Here the authors show that optimal assembly of mitochondrial complex I predicts longevity in mice, whereas partial complex I assembly increases the production of reactive oxygen species.
- Satomi Miwa
- , Howsun Jow
- & Thomas von Zglinicki
-
Article |
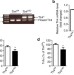 Hepatocyte Toll-like receptor 4 regulates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance
Hepatocyte Toll-like receptor 4 regulates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance
Mice lacking Toll-like receptor 4 (Tlr4) do not develop diet-induced insulin resistance. Here Jia et al.create two tissue-specific Tlr4 knockouts to demonstrate that hepatic Tlr4, but not Tlr4 expressed in myeloid cells, is driving obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance.
- Lin Jia
- , Claudia R. Vianna
- & Joel K. Elmquist
-
Article |
 Angiotensin II plasma levels are linked to disease severity and predict fatal outcomes in H7N9-infected patients
Angiotensin II plasma levels are linked to disease severity and predict fatal outcomes in H7N9-infected patients
An avian influenza H7N9 virus causes severe human disease, including acute and often lethal respiratory failure. Here, the authors report that plasma levels of angiotensin II, a regulatory peptide of the renin–angiotensin system, are associated with disease severity and fatal outcome in infected patients.
- Fengming Huang
- , Jing Guo
- & Lanjuan Li
-
Article |
 Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from lethal avian influenza A H5N1 infections
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from lethal avian influenza A H5N1 infections
H5N1 avian influenza viruses can be highly pathogenic. Here, the authors show that H5N1 infection leads to increased serum levels of angiotensin II in patients and mice, and that administration of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 ameliorates lung injury in infected mice.
- Zhen Zou
- , Yiwu Yan
- & Chengyu Jiang
-
Article |
 High-throughput and combinatorial gene expression on a chip for metabolism-induced toxicology screening
High-throughput and combinatorial gene expression on a chip for metabolism-induced toxicology screening
Current tools to test drug metabolism and toxicity in the liver are mainly based on time-consuming traditional cell culture methods. Here Kwon et al.report a high-throughput system employing cells cultured on micropillars that can be transfected with combinations of drug-metabolizing enzymes.
- Seok Joon Kwon
- , Dong Woo Lee
- & Moo-Yeal Lee
-
Article
| Open Access FoxO proteins restrain osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption by attenuating H2O2 accumulation
FoxO proteins restrain osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption by attenuating H2O2 accumulation
Osteoclasts are bone-resorbing cells responsible for the loss of bone mass in diseases such as osteoporosis. Here the authors show that osteoclast proliferation and survival is regulated by FoxO family transcription factors, which control levels of the signalling molecule hydrogen peroxide.
- Shoshana M. Bartell
- , Ha-Neui Kim
- & Maria Almeida
-
Article
| Open Access The short-chain fatty acid acetate reduces appetite via a central homeostatic mechanism
The short-chain fatty acid acetate reduces appetite via a central homeostatic mechanism
The consumption of fermentable carbohydrates, or fibre, is associated with weight loss. Here the authors show that the metabolite acetate, created by fermentation of fibre in the mouse colon, is taken up into the brain where it induces appetite-suppressing neuronal activity in the hypothalamus.
- Gary Frost
- , Michelle L. Sleeth
- & Jimmy D. Bell
-
Article
| Open Access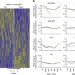 Maternal nutrition at conception modulates DNA methylation of human metastable epialleles
Maternal nutrition at conception modulates DNA methylation of human metastable epialleles
Maternal diet affects DNA methylation in the developing offspring, leading to phenotypic changes. Here, Dominguez-Salas et al. exploit seasonal variation in the diet of Gambian women to show that maternal methyl donor nutrient status around the time of conception predicts methylation levels at metastable epialleles in infants.
- Paula Dominguez-Salas
- , Sophie E. Moore
- & Branwen J. Hennig
-
Article |
 Alternative splicing regulates vesicular trafficking genes in cardiomyocytes during postnatal heart development
Alternative splicing regulates vesicular trafficking genes in cardiomyocytes during postnatal heart development
Alternative splicing is a process during gene expression that increases the diversity of proteins encoded by a single gene. Here, the authors perform RNA-sequencing on cardiac cells from mice and show that extensive changes in gene expression and alternative splicing occur during the first month after birth.
- Jimena Giudice
- , Zheng Xia
- & Thomas A. Cooper
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental orthotopic transplantation of a tissue-engineered oesophagus in rats
Experimental orthotopic transplantation of a tissue-engineered oesophagus in rats
Patients with oesophageal diseases may require surgical removal and replacement of the oesophagus. Here the authors seed mesenchymal stromal cells on a decellularized rat oesophagus and show that this bioengineered tissue construct restores swallowing function after transplantation into rats.
- Sebastian Sjöqvist
- , Philipp Jungebluth
- & Paolo Macchiarini
-
Article |
 Glycolytic genes are targets of the nuclear receptor Ad4BP/SF-1
Glycolytic genes are targets of the nuclear receptor Ad4BP/SF-1
The transcription factor NR5A1 has so far mainly been known for regulating the biosynthesis of steroids. Here the authors discover that NR5A1 also has a role in energy metabolism, demonstrating that NR5A1 regulates several key enzymes involved in the breakdown of glucose.
- Takashi Baba
- , Hiroyuki Otake
- & Ken-Ichirou Morohashi
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-sensitive liquid biopsy of circulating extracellular vesicles using ExoScreen
Ultra-sensitive liquid biopsy of circulating extracellular vesicles using ExoScreen
The potential of extracellular vesicles (EVs) as cancer biomarkers is substantial. Here, Yoshioka et al. describe a sensitive technique to analyse EVs directly from blood samples of patients with colorectal cancer, highlighting a liquid biopsy technique with cancer-detection possibilities.
- Yusuke Yoshioka
- , Nobuyoshi Kosaka
- & Takahiro Ochiya
-
Article |
 Methionine restriction extends lifespan of Drosophila melanogaster under conditions of low amino-acid status
Methionine restriction extends lifespan of Drosophila melanogaster under conditions of low amino-acid status
Dietary restriction of the amino acid methionine extends the lifespan of rodents. Here the authors systematically test diets with varying amino-acid content and show that methionine restriction extends the lifespan of yeast and flies only when the content of other amino acids in the diet is also low.
- Byung Cheon Lee
- , Alaattin Kaya
- & Vadim N. Gladyshev
-
Article |
 CARL lncRNA inhibits anoxia-induced mitochondrial fission and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes by impairing miR-539-dependent PHB2 downregulation
CARL lncRNA inhibits anoxia-induced mitochondrial fission and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes by impairing miR-539-dependent PHB2 downregulation
The prohibitin complex promotes cell survival by regulating mitochondrial morphogenesis. Wang et al.identify a long non-coding RNA that regulates this complex in cardiomyocytes by acting as a sponge to downregulate a prohibitin-targetting miRNA, protecting cells from apoptosis in anoxic conditions.
- Kun Wang
- , Bo Long
- & Pei-Feng Li
-
Article
| Open Access Caloric restriction reduces age-related and all-cause mortality in rhesus monkeys
Caloric restriction reduces age-related and all-cause mortality in rhesus monkeys
Caloric restriction extends the lifespan of various organisms but whether it works in monkeys is controversial. Here, Colman et al.report that caloric restriction reduces all-cause mortality of rhesus macaques, and perform a weight comparison that aims to reconcile their findings with contradictory results from a similar study.
- Ricki J. Colman
- , T. Mark Beasley
- & Rozalyn M. Anderson
-
Article |
 Direct visualization of HIV-enhancing endogenous amyloid fibrils in human semen
Direct visualization of HIV-enhancing endogenous amyloid fibrils in human semen
Semen-derived peptides can form amyloid fibrils that boost HIV infection in vitro, but the existence of such fibrils in semen remained to be demonstrated. Here, the authors show that human semen contains amyloid fibrils, which can bind HIV particles and increase their infectiveness.
- Shariq M. Usmani
- , Onofrio Zirafi
- & Jan Münch
-
Article |
 Hepatic IRE1α regulates fasting-induced metabolic adaptive programs through the XBP1s–PPARα axis signalling
Hepatic IRE1α regulates fasting-induced metabolic adaptive programs through the XBP1s–PPARα axis signalling
The IRE1α-XBP1 signalling pathway is part of the ER stress response but has also been linked to glucose and lipid metabolism. Here the authors show that IRE1α in the liver acts as a nutrient-sensor, regulating the metabolic adaptation to fasting and a ketogenic diet by inducing PPARα expression.
- Mengle Shao
- , Bo Shan
- & Yong Liu
-
Article |
 Selective inhibition of BET bromodomain epigenetic signalling interferes with the bone-associated tumour vicious cycle
Selective inhibition of BET bromodomain epigenetic signalling interferes with the bone-associated tumour vicious cycle
A major problem in the treatment of bone tumours and metastases is the vicious cycle between bone tumours and resorption. Here, the authors show that treatment with the BET bromodomain inhibitor JQ1 inhibits osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation, and bone tumour development.
- François Lamoureux
- , Marc Baud’huin
- & Benjamin Ory

 A genetic variant of p53 restricts the mucous secretory phenotype by regulating SPDEF and Bcl-2 expression
A genetic variant of p53 restricts the mucous secretory phenotype by regulating SPDEF and Bcl-2 expression