Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Lewis basicity generated by localised charge imbalance in noble metal nanoparticle-embedded defective metal–organic frameworks
Lewis basicity generated by localised charge imbalance in noble metal nanoparticle-embedded defective metal–organic frameworks
Interactions between metal nanoparticles (NPs) and metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) in their composite forms have proven to exhibit beneficial properties. Here the authors present a unique approach to immobilise Pd NPs and, more importantly, to generate tunable basic sites within an anionic defective MOF.
- Ying Chuan Tan
- & Hua Chun Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Anisotropic energy transfer in crystalline chromophore assemblies
Anisotropic energy transfer in crystalline chromophore assemblies
Exciton diffusion length and directionality are important parameters in artificial photosynthetic devices. Here, the authors present a way to make crystalline chromophore assemblies with bespoke architecture, fabricating one exhibiting anisotropic exciton transport properties.
- Ritesh Haldar
- , Marius Jakoby
- & Christof Wöll
-
Article
| Open Access Limitation of Fermi level shifts by polaron defect states in hematite photoelectrodes
Limitation of Fermi level shifts by polaron defect states in hematite photoelectrodes
Hematite has been proposed as a suitable photocatalyst for water splitting based on its stability and appealing optical band gap, but its performance has not reached theoretical expectations. Here the authors show that this is due to intra-gap polaronic states that reduce the effective electronic band gap.
- Christian Lohaus
- , Andreas Klein
- & Wolfram Jaegermann
-
Article
| Open Access Photo-induced semimetallic states realised in electron–hole coupled insulators
Photo-induced semimetallic states realised in electron–hole coupled insulators
Ultrafast light pulses can manipulate and probe materials faster than relaxation timescales, leading to new electronic states and insights into equilibrium properties. Okazaki et al. use the properties of photo-induced metallic states to investigate unconventional correlated behaviour in Ta2NiSe5 and Ta2NiS5.
- Kozo Okazaki
- , Yu Ogawa
- & Shik Shin
-
Article
| Open Access A hardware Markov chain algorithm realized in a single device for machine learning
A hardware Markov chain algorithm realized in a single device for machine learning
Despite the need to develop resistive random access memory (RRAM) devices for machine learning, RRAM array-based hardware methods for algorithm require external electronics. Here, the authors realize a Markov chain algorithm in a single 2D multilayer SnSe device without external electronics.
- He Tian
- , Xue-Feng Wang
- & Tian-Ling Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Narrow bandgap oxide nanoparticles coupled with graphene for high performance mid-infrared photodetection
Narrow bandgap oxide nanoparticles coupled with graphene for high performance mid-infrared photodetection
Coupling graphene with narrow band-gap Ti2O3 nanoparticles can enable efficient mid-infrared photodetection. Here, the authors report a graphene-Ti2O3 based hybrid photodetector with high responsivity of ~300 A W-1 up to 10 μm by varying the number of graphene layers and size of Ti2O3 nanoparticles.
- Xuechao Yu
- , Yangyang Li
- & Qi Jie Wang
-
Article
| Open Access DNA engineered micromotors powered by metal nanoparticles for motion based cellphone diagnostics
DNA engineered micromotors powered by metal nanoparticles for motion based cellphone diagnostics
Micromotors have a range of potential healthcare applications. Here, the authors describe the development of a metal nanoparticle DNA micromotor which can be used to detect human HIV-1 by a change in the motion of the micromotors, monitored by cell phone camera, triggered by binding of HIV-1 RNA.
- Mohamed Shehata Draz
- , Kamyar Mehrabi Kochehbyoki
- & Hadi Shafiee
-
Article
| Open Access Shaping the topology of folding pathways in mechanical systems
Shaping the topology of folding pathways in mechanical systems
Self-folding origami have applications for mechanical metamaterials but one of their pitfalls is that many undesirable folding modes exist. Here the authors propose an algorithm to determine which folding joints to make stiffer in order to ensure that the sheet is folded into the chosen state.
- Menachem Stern
- , Viraaj Jayaram
- & Arvind Murugan
-
Article
| Open Access Lipopolysaccharide-affinity copolymer senses the rapid motility of swarmer bacteria to trigger antimicrobial drug release
Lipopolysaccharide-affinity copolymer senses the rapid motility of swarmer bacteria to trigger antimicrobial drug release
Urinary tract infections are a common side effect of urethral catheters. Here, the authors report on the development of antibiotic loaded NPs with functional polymer coatings which attach too and are removed by motile bacteria to trigger the release of antibiotic.
- Shengtao Lu
- , Wuguo Bi
- & Edwin K. L. Yeow
-
Article
| Open Access Single Particle Automated Raman Trapping Analysis
Single Particle Automated Raman Trapping Analysis
Enabling concurrent, high throughput analysis of single nano particles would greatly increase the capacity to study size, composition and inter and intra particle population variance. Here, the authors present a comprehensive platform for single particle automated Raman trapping analysis without any target modification.
- Jelle Penders
- , Isaac J. Pence
- & Molly M. Stevens
-
Article
| Open Access Skin-touch-actuated textile-based triboelectric nanogenerator with black phosphorus for durable biomechanical energy harvesting
Skin-touch-actuated textile-based triboelectric nanogenerator with black phosphorus for durable biomechanical energy harvesting
Incorporation of triboelectric nanogenerators into textiles is attractive for self-powered wearable electronics. Here the authors employ black phosphorus with a hydrophobic coating in a durable, washable, and air permeable textile-based device that converts biomechanical motion into electricity.
- Jiaqing Xiong
- , Peng Cui
- & Pooi See Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Energy level tuned indium arsenide colloidal quantum dot films for efficient photovoltaics
Energy level tuned indium arsenide colloidal quantum dot films for efficient photovoltaics
Existing n-type colloidal quantum dot materials easily lose their doping polarity in air. Here Song et al. passivate the reactive covalent surface of indium arsenide quantum dots to gain the energy-level tunability and show p–n junction type solar cells with 7.92% certified efficiency.
- Jung Hoon Song
- , Hyekyoung Choi
- & Sohee Jeong
-
Article
| Open Access Harnessing copper-palladium alloy tetrapod nanoparticle-induced pro-survival autophagy for optimized photothermal therapy of drug-resistant cancer
Harnessing copper-palladium alloy tetrapod nanoparticle-induced pro-survival autophagy for optimized photothermal therapy of drug-resistant cancer
“Conventional chemotherapy-photothermal therapy combination has limited efficacy in drug resistant cancers. Here they develop Copper-palladium tetrapod nanoparticles to overcome these challenges and show them to work in synergy with autophagy inhibitors to treat drug resistant cancers”
- Yunjiao Zhang
- , Rui Sha
- & Long-ping Wen
-
Article
| Open Access Charging dynamics of an individual nanopore
Charging dynamics of an individual nanopore
Modern energy-storage technologies are based on porous electrodes that store charge within nanometrically-narrow pores or slits. Here the authors show an approach to probe and measure, for the first time, the charging dynamics within an individual nano-slit – the basic element of a porous electrode.
- Ran Tivony
- , Sam Safran
- & Jacob Klein
-
Article
| Open Access Spatially-resolved fluorescence-detected two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy probes varying excitonic structure in photosynthetic bacteria
Spatially-resolved fluorescence-detected two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy probes varying excitonic structure in photosynthetic bacteria
2D electronic spectroscopy enables a spatially-averaged view of the electronic structure of a heterogeneous system. Here, the authors extend it to sub-micron resolution and ~106 times better sensitivity, to resolve spatially varying excitonic structure in a heterogeneous mixture of photosynthetic cells.
- Vivek Tiwari
- , Yassel Acosta Matutes
- & Jennifer P. Ogilvie
-
Article
| Open Access Space- and time-resolved small angle X-ray scattering to probe assembly of silver nanocrystal superlattices
Space- and time-resolved small angle X-ray scattering to probe assembly of silver nanocrystal superlattices
How nanocrystals assemble into superlattices is poorly understood, given the difficulty of probing these processes in real time, in a controlled environment. Here, the authors use space- and time-resolved in situ small angle X-ray scattering to monitor the ordering of nanocrystal superlattices by electric field, which allows them to extract quantitative information about the assembly process.
- Yixuan Yu
- , Dian Yu
- & Christine A. Orme
-
Article
| Open Access Spectral field mapping in plasmonic nanostructures with nanometer resolution
Spectral field mapping in plasmonic nanostructures with nanometer resolution
Characterizing plasmonic coupling has proven elusive. Here, the authors obtain a spectrally resolved deflection map related to a focused electron beam, which has excited a surface plasmon resonance, and relate this deflection to the spectral component of the induced electric and magnetic fields pertaining to the mode.
- J. Krehl
- , G. Guzzinati
- & A. Lubk
-
Article
| Open Access Identifying triplet pathways in dilute pentacene films
Identifying triplet pathways in dilute pentacene films
Singlet fission results in the formation of a pair of triplets, known as a quintet. Here, the authors identify long-lived quintets in dilute pentacene films at room temperature, with lifetimes influenced by intermolecular geometry having implications for the design of triplet-harvesting films.
- Daphné Lubert-Perquel
- , Enrico Salvadori
- & Christopher W. M. Kay
-
Article
| Open Access Contact angle measurement of free-standing square-millimeter single-layer graphene
Contact angle measurement of free-standing square-millimeter single-layer graphene
Experimental determination of the contact angle of a two-dimensional film is crucial to understand its wettability characteristics. Here, the authors use the captive bubble method to estimate a contact angle value of 42° ± 3° for a monolayer graphene film.
- Anna V. Prydatko
- , Liubov A. Belyaeva
- & Grégory F. Schneider
-
Article
| Open Access Low threshold and efficient multiple exciton generation in halide perovskite nanocrystals
Low threshold and efficient multiple exciton generation in halide perovskite nanocrystals
The hot carriers in halide perovskite nanocrystals cool much slower than those in conventional semiconductor nanocrystals due to the phonon bottleneck. Here, Li et al. demonstrate enhanced multiple exciton generation with lower threshold in intermediate-confined perovskite nanocrystals based on this effect.
- Mingjie Li
- , Raihana Begum
- & Tze Chien Sum
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoporous aramid nanofibre separators for nonaqueous redox flow batteries
Nanoporous aramid nanofibre separators for nonaqueous redox flow batteries
Nonaqueous redox flow batteries may offer high energy and power densities, but development of separators is key for optimization. Here the authors achieve high coulombic efficiency with a nanoporous aramid nanofibres-based separator with low permeability, high ion conductivity, and exceptional stability.
- Siu on Tung
- , Sydney L. Fisher
- & Levi T. Thompson
-
Article
| Open Access A growing bacterial colony in two dimensions as an active nematic
A growing bacterial colony in two dimensions as an active nematic
Rod-shaped bacteria are an example of active matter. Here the authors find that a growing bacterial colony harbours internal cellular flows affecting orientational ordering in its interior and at the boundary. Results suggest this system may belong to a new active matter universality class.
- D. Dell’Arciprete
- , M. L. Blow
- & W. C. K. Poon
-
Article
| Open Access Interface-mediated hygroelectric generator with an output voltage approaching 1.5 volts
Interface-mediated hygroelectric generator with an output voltage approaching 1.5 volts
Hygroelectric generators comprised of electrodes and a hygroscopic material with a chemical-gradient structure can produce electricity by absorbing water vapor. Here, the authors achieve a high output voltage by employing hygroscopic heterogeneous graphene oxide and materials with Schottky junctions.
- Yaxin Huang
- , Huhu Cheng
- & Liangti Qu
-
Article
| Open Access Transformation of amorphous calcium phosphate to bone-like apatite
Transformation of amorphous calcium phosphate to bone-like apatite
The growth of apatite crystals from amorphous calcium phosphate is an area of intense study. Here, the authors report on the use of high resolution TEM imaging to provide evidence of nucleation clusters in the transformation process
- Antiope Lotsari
- , Anand K. Rajasekharan
- & Martin Andersson
-
Article
| Open Access Stabilizing black phosphorus nanosheets via edge-selective bonding of sacrificial C60 molecules
Stabilizing black phosphorus nanosheets via edge-selective bonding of sacrificial C60 molecules
Few-layered black phosphorus has unique and appealing electronic properties but is easily oxidized in air. Here, the authors covalently functionalize black phosphorus nanosheets with C60 at their edges, providing improved stability and enhanced photoelectrochemical and photocatalytic activities.
- Xianjun Zhu
- , Taiming Zhang
- & Shangfeng Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Physical descriptor for the Gibbs energy of inorganic crystalline solids and temperature-dependent materials chemistry
Physical descriptor for the Gibbs energy of inorganic crystalline solids and temperature-dependent materials chemistry
Materials databases currently neglect the temperature effect on compound thermodynamics. Here the authors introduce a Gibbs energy descriptor enabling the high-throughput prediction of temperature-dependent thermodynamics across a wide range of compositions and temperatures for inorganic solids.
- Christopher J. Bartel
- , Samantha L. Millican
- & Aaron M. Holder
-
Article
| Open Access Two-site H2O2 photo-oxidation on haematite photoanodes
Two-site H2O2 photo-oxidation on haematite photoanodes
Understanding fundamental processes that occur using solar-to-fuel conversion materials is crucial for constructing effective renewable energy collection. Here, authors find the hydrogen peroxide light-driven hole-scavenging mechanism over haematite to proceed with two active sites rather than one
- Yotam Y. Avital
- , Hen Dotan
- & Arik Yochelis
-
Article
| Open Access Reconfigurable photoactuator through synergistic use of photochemical and photothermal effects
Reconfigurable photoactuator through synergistic use of photochemical and photothermal effects
Despite recent advances in light-active soft actuators, demonstrating reconfigurable actuation under the same stimuli remains a challenge. Here, the authors realize reconfigurable photoactuation in liquid crystal polymer networks based on a synergistic use of photochemical and photothermal effects.
- Markus Lahikainen
- , Hao Zeng
- & Arri Priimagi
-
Article
| Open Access Ice rule fragility via topological charge transfer in artificial colloidal ice
Ice rule fragility via topological charge transfer in artificial colloidal ice
Spin ice materials are defined by ice rules, local constraints that lead to frustrated interactions and macroscopic numbers of degenerate configurations. Here the authors show that the ice rule in colloidal ice is emergent, limited to certain geometries, and demonstrate how it can break down under changes of the lattice structure.
- András Libál
- , Dong Yun Lee
- & Cristiano Nisoli
-
Article
| Open Access Fractionalized excitations in the partially magnetized spin liquid candidate YbMgGaO4
Fractionalized excitations in the partially magnetized spin liquid candidate YbMgGaO4
Recent experiments have indicated that YbMgGaO4 may be a quantum spin liquid with spinon Fermi surfaces but additional evidence is needed to support this interpretation. Shen et al. show weak magnetic fields cause changes in the excitation continuum that are consistent with spin liquid predictions.
- Yao Shen
- , Yao-Dong Li
- & Jun Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Salt concentration and charging velocity determine ion charge storage mechanism in nanoporous supercapacitors
Salt concentration and charging velocity determine ion charge storage mechanism in nanoporous supercapacitors
To improve supercapacitor performance, mechanisms of operation should be understood. Here the authors identify parameters controlling ion charge storage mechanisms and show that charging initially implies a non-equilibrium ion configuration followed by charge-neutral equilibration.
- C. Prehal
- , C. Koczwara
- & O. Paris
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasmall targeted nanoparticles with engineered antibody fragments for imaging detection of HER2-overexpressing breast cancer
Ultrasmall targeted nanoparticles with engineered antibody fragments for imaging detection of HER2-overexpressing breast cancer
One of the major obstacles in nanoparticle-based therapy is to achieve tumour targeting, limiting non-specific accumulation of the nanoparticles. Here the authors propose the conjugation of anti-HER2 scFv fragments to the silica nanoparticles, increasing specificity and limiting the final size of the immunoconjugates below the renal clearance threshold.
- Feng Chen
- , Kai Ma
- & Michelle S. Bradbury
-
Article
| Open Access Designed synthesis of stable light-emitting two-dimensional sp2 carbon-conjugated covalent organic frameworks
Designed synthesis of stable light-emitting two-dimensional sp2 carbon-conjugated covalent organic frameworks
Topological connection of organic chromophores is an attractive way to design light-emitting covalent organic frameworks but the synthesis of stable light-emitting frameworks remains challenging. Here the authors report the designed synthesis of sp2 carbon conjugated frameworks that combine stability with light-emitting activity
- Enquan Jin
- , Juan Li
- & Donglin Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Matrix mechanical plasticity regulates cancer cell migration through confining microenvironments
Matrix mechanical plasticity regulates cancer cell migration through confining microenvironments
In order to metastasize, cancer cells must migrate through basement membranes and dense stroma, and proteases are thought to be required due to the confining nature of these matrices. Here the authors use synthetic matrices to show that cells can migrate through confining matrices using force generation alone, rather than protease degradation, if the matrices exhibit mechanical plasticity.
- Katrina M. Wisdom
- , Kolade Adebowale
- & Ovijit Chaudhuri
-
Article
| Open Access Nickel nanoparticles set a new record of strength
Nickel nanoparticles set a new record of strength
While metallic nanosized objects are stronger than their macroscopic counterparts, they rarely reach the metal’s maximum theoretical strength. Here, the authors produce faceted nickel nanoparticles and show that their strength under compression matches the theoretically predicted strength in the literature.
- A. Sharma
- , J. Hickman
- & Y. Mishin
-
Article
| Open Access Orthogonal programming of heterogeneous micro-mechano-environments and geometries in three-dimensional bio-stereolithography
Orthogonal programming of heterogeneous micro-mechano-environments and geometries in three-dimensional bio-stereolithography
Tuning the mechanical properties of extracellular matrix is of great interest in tissue engineering but spatial control over stiffness in hydrogels has been demonstrated in two dimensions only. Here the authors developed a layer-by-layer printing technique which uses oxygen inhibition to control the heterogeneous stiffness in 3D printed structures.
- Hang Yin
- , Yonghui Ding
- & Xiaobo Yin
-
Article
| Open Access Thermal and electrical signatures of a hydrodynamic electron fluid in tungsten diphosphide
Thermal and electrical signatures of a hydrodynamic electron fluid in tungsten diphosphide
Advances in the fabrication of low-disorder metallic materials have made it possible to reach the hydrodynamic regime of electronic transport. Here the authors investigate a hydrodynamic electron fluid in tungsten diphosphide and find that both electrical and thermal transport are limited by the quantum indeterminacy.
- J. Gooth
- , F. Menges
- & B. Gotsmann
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-low-field magneto-elastocaloric cooling in a multiferroic composite device
Ultra-low-field magneto-elastocaloric cooling in a multiferroic composite device
The broad use of elastocaloric materials in cooling applications is hindered by the need to exert large forces onto the material. Compressing a magnetostrictive-elastocaloric composite using a low magnetic field of 0.16 T, temperature changes up to 4 K are achieved without applying external forces.
- Huilong Hou
- , Peter Finkel
- & Ichiro Takeuchi
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of Coulomb gap in the quantum spin Hall candidate single-layer 1T’-WTe2
Observation of Coulomb gap in the quantum spin Hall candidate single-layer 1T’-WTe2
The conductance from bulk bands in a topological insulator usually blurs effects arising from edge states. Here, Song et al. report a Coulomb gap opened by electron–electron interactions, which effectively suppress the bulk conductance and promote observation of topological edge states in the single-layer 1T’-WTe2.
- Ye-Heng Song
- , Zhen-Yu Jia
- & Shao-Chun Li
-
Article
| Open Access Twist angle-dependent conductivities across MoS2/graphene heterojunctions
Twist angle-dependent conductivities across MoS2/graphene heterojunctions
Twisting vertically stacked individual layers of two-dimensional materials can trigger exciting fundamental physics and advanced electronic device applications. Here, the authors report five times enhancement in vertical heterojunction conductivity on rotating MoS2 over graphene.
- Mengzhou Liao
- , Ze-Wen Wu
- & Guangyu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Sustainable scalable synthesis of sulfide nanocrystals at low cost with an ionic liquid sulfur precursor
Sustainable scalable synthesis of sulfide nanocrystals at low cost with an ionic liquid sulfur precursor
Developing sustainable and scalable nanocrystal syntheses is challenging but necessary for future technologies and the environment. Here, the authors show that using an ionic liquid to stabilize a highly reactive precursor can fulfill the major aims of sustainable nanocrystal synthesis, including high yields, energy efficiency, atom economy, and recyclability.
- Bin Yuan
- , Timothy Karl Egner
- & Ludovico Cademartiri
-
Article
| Open Access Quasicrystal nucleation and ℤ module twin growth in an intermetallic glass-forming system
Quasicrystal nucleation and ℤ module twin growth in an intermetallic glass-forming system
Elucidating the formation of quasicrystals, which have long-range orientational order but no translation periodicity, remains a challenge. Here, the authors track and geometrically describe how a decagonal nickel–zirconium seed grows into a tenfold twinned dendritic structure.
- Wolfgang Hornfeck
- , Raphael Kobold
- & Dieter Herlach
-
Article
| Open Access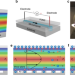 Enhanced voltage generation through electrolyte flow on liquid-filled surfaces
Enhanced voltage generation through electrolyte flow on liquid-filled surfaces
Superhydrophobic surfaces are expected to increase streaming potential, but are hindered by the presence of air. Here the authors enhance streaming potential by flowing high-dielectric salt water over liquid-filled surfaces infiltrated with low-dielectric liquid, harnessing electric slip and surface charge.
- B. Fan
- , A. Bhattacharya
- & P. R. Bandaru
-
Article
| Open Access Turning a native or corroded Mg alloy surface into an anti-corrosion coating in excited CO2
Turning a native or corroded Mg alloy surface into an anti-corrosion coating in excited CO2
Magnesium alloys usually have poor corrosion resistance, which inhibits their use in the automotive and biomedical industries. Here, the authors use an environmental TEM to carbonate the natural corrosion products at the surface of magnesium alloys and form a compact and protective surface layer.
- Yuecun Wang
- , Boyu Liu
- & Zhiwei Shan
-
Article
| Open Access High-content ductile coherent nanoprecipitates achieve ultrastrong high-entropy alloys
High-content ductile coherent nanoprecipitates achieve ultrastrong high-entropy alloys
High entropy alloys usually emphasize equiatomic compositions, which restrict the compositions available to induce strengthening via precipitation. Here the authors use spinodal decomposition in a five-element alloy to obtain high content nanophases and the highest tensile strength reported to date.
- Yao-Jian Liang
- , Linjing Wang
- & Hongnian Cai
-
Article
| Open Access Bi-directional cell-pericellular matrix interactions direct stem cell fate
Bi-directional cell-pericellular matrix interactions direct stem cell fate
3D hydrogels have provided information on the physical requirements of stem cell fate, but the contribution of interactions with the pericellular environment are under-explored. Here the authors show that pericellular matrix secreted by human bone marrow stromal cells (hMSC) embedded in a HA-based hydrogel contribute to hMSC fate.
- Silvia A. Ferreira
- , Meghna S. Motwani
- & Eileen Gentleman
-
Article
| Open Access Polymerization driven monomer passage through monolayer chemical vapour deposition graphene
Polymerization driven monomer passage through monolayer chemical vapour deposition graphene
Translocation of larger molecules through graphene holds potential for molecular sieving, however it is rarely observed. Here, the authors show the radical polymerization of vinyl monomers via their translocation through a single layer graphene to a monolayer initiator and additionally study the monomer-graphene interactions.
- Tao Zhang
- , Zhongquan Liao
- & Rainer Jordan
-
Article
| Open Access Tailoring manganese oxide with atomic precision to increase surface site availability for oxygen reduction catalysis
Tailoring manganese oxide with atomic precision to increase surface site availability for oxygen reduction catalysis
Controlling structures at the atomic level provides an opportunity to design and understand catalysts. Here the authors use thin-film deposition to fabricate perovskite heterostructures in a non-equilibrium manner to assess the effects on electrocatalytic activity for oxygen reduction.
- C. John Eom
- , Ding-Yuan Kuo
- & Jin Suntivich
-
Article
| Open Access Tensorial neutron tomography of three-dimensional magnetic vector fields in bulk materials
Tensorial neutron tomography of three-dimensional magnetic vector fields in bulk materials
Mapping the distribution of magnetic fields inside bulk materials is challenging but crucial to understand and develop functional magnetic materials. Here the authors demonstrate the capability to visualize 3D vector magnetic fields inside materials using spin-polarized neutron tomography and tensorial reconstruction techniques.
- A. Hilger
- , I. Manke
- & J. Banhart

 A discrete organoplatinum(II) metallacage as a multimodality theranostic platform for cancer photochemotherapy
A discrete organoplatinum(II) metallacage as a multimodality theranostic platform for cancer photochemotherapy