Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Design and application of volatilizable solid additives in non-fullerene organic solar cells
Design and application of volatilizable solid additives in non-fullerene organic solar cells
High-boiling-point solvent additives are commonly used to optimize the device performance of organic solar cells but they make problems for device stability and reproducibility. Here Yu et al. design volatilizable solid additives that can improve the device performance without causing above issues.
- Runnan Yu
- , Huifeng Yao
- & Jianhui Hou
-
Article
| Open Access Chiral domain wall motion in unit-cell thick perpendicularly magnetized Heusler films prepared by chemical templating
Chiral domain wall motion in unit-cell thick perpendicularly magnetized Heusler films prepared by chemical templating
Heusler compounds are of great interest for spintronic applications. Here the authors report current driven domain wall motion in unit cell thick perpendicularly magnetized Heusler films with low current densities and show the velocity is dominated by the bulk chiral Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya exchange interaction.
- Panagiotis Ch. Filippou
- , Jaewoo Jeong
- & Stuart S. P. Parkin
-
Article
| Open Access Roll-to-roll fabrication of touch-responsive cellulose photonic laminates
Roll-to-roll fabrication of touch-responsive cellulose photonic laminates
Self-assembled structures are typically demonstrated on small scales under well-controlled lab environments. Here, the authors present a roll-to-roll process for the continuous manufacturing of square-meters of self-assembled cellulose-based mechano-chromic films and demonstrate the recording of pressure profiles generated by foot-imprints in real time.
- Hsin-Ling Liang
- , Mélanie M. Bay
- & Silvia Vignolini
-
Article
| Open Access Copper adparticle enabled selective electrosynthesis of n-propanol
Copper adparticle enabled selective electrosynthesis of n-propanol
Upgrading wasted carbon emissions to high-value, multi-carbon products provides an economic route to reduce carbon dioxide levels, but such conversions have proven challenging. Here, authors explore copper adparticles as highly active surfaces that convert CO to n-propanol with high selectivities.
- Jun Li
- , Fanglin Che
- & David Sinton
-
Article
| Open Access Compliant rolling-contact architected materials for shape reconfigurability
Compliant rolling-contact architected materials for shape reconfigurability
The authors introduce a compliant rolling-contact architected material as a class of shape reconfigurable mechanical metamaterial. They also devise an approach that combines two photon stereolithography and scanning holographic optical tweezers, which allows them to fabricate these architected materials on the microscale.
- Lucas A. Shaw
- , Samira Chizari
- & Jonathan B. Hopkins
-
Article
| Open Access Programming molecular topologies from single-stranded nucleic acids
Programming molecular topologies from single-stranded nucleic acids
Designing nucleic acid-based nanostructures with knots remains challenging. Here the authors present a general strategy to design and construct highly knotted 2D and 3D nanostructures from single-stranded DNA or RNA
- Xiaodong Qi
- , Fei Zhang
- & Hao Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Theory of photoinduced ultrafast switching to a spin-orbital ordered hidden phase
Theory of photoinduced ultrafast switching to a spin-orbital ordered hidden phase
Ultrafast excitation of materials can cause the formation of hidden phases that are not accessible in thermal equilibrium. Li et al. identify and investigate theoretically a hidden phase that can be accessed in systems with intertwined spin and orbital-ordering such as KCuF3.
- Jiajun Li
- , Hugo U. R. Strand
- & Martin Eckstein
-
Article
| Open Access Universal passivation strategy to slot-die printed SnO2 for hysteresis-free efficient flexible perovskite solar module
Universal passivation strategy to slot-die printed SnO2 for hysteresis-free efficient flexible perovskite solar module
Uniformity and hysteresis are long lasting problems for flexible perovskite solar modules. Here Bu et al. develop a universal potassium passivation strategy to improve the quality of slot-die printed tin oxide electron transport layers and demonstrate highly efficient and hysteresis-free flexible devices.
- Tongle Bu
- , Jing Li
- & Fuzhi Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Alleviating oxygen evolution from Li-excess oxide materials through theory-guided surface protection
Alleviating oxygen evolution from Li-excess oxide materials through theory-guided surface protection
Rechargeable Li-ion batteries can show extensive oxygen loss from the cathode material under operating conditions. Here, the authors use high-throughput computational screening to guide the synthesis of a Tantalum-doped Li-excess cathode that significantly reduces oxygen loss.
- Yongwoo Shin
- , Wang Hay Kan
- & Kristin A. Persson
-
Article
| Open Access Non-equilibrium anisotropic colloidal single crystal growth with DNA
Non-equilibrium anisotropic colloidal single crystal growth with DNA
Colloidal crystal engineering with DNA can be used to synthesize highly anisotropic hexagonal prismatic microcrystals. This manuscript introduces a plane multiplicity mechanism that can be used to deliberately design non-equilibrium Wulff shapes, a capability important in many areas, including optics and photocatalysis.
- Soyoung E. Seo
- , Martin Girard
- & Chad A. Mirkin
-
Article
| Open Access Stability and nature of the volume collapse of ε-Fe2O3 under extreme conditions
Stability and nature of the volume collapse of ε-Fe2O3 under extreme conditions
Iron oxides exist in a variety of polymorphs at different pressure and temperature conditions, displaying important magnetic properties, and are major constituents of the Earth’s interior. Here the authors investigate the structural and electronic changes in the uncommon epsilon phase under compression to deep Mantle pressures.
- J. A. Sans
- , V. Monteseguro
- & C. Popescu
-
Article
| Open Access Direct oxygen isotope effect identifies the rate-determining step of electrocatalytic OER at an oxidic surface
Direct oxygen isotope effect identifies the rate-determining step of electrocatalytic OER at an oxidic surface
Understanding reaction mechanisms is crucial for catalyst design. Here, natural-abundance isotope quantifications of O2 yield mechanistically significant reaction kinetic isotope effects for water oxidation over metal oxide electrodes, the bottleneck step of water electrolysis.
- Sandra Haschke
- , Michael Mader
- & Julien Bachmann
-
Article
| Open Access Non-resonant light scattering in dispersions of 2D nanosheets
Non-resonant light scattering in dispersions of 2D nanosheets
Quantitative analysis of the extinction spectra of dispersions of 2D materials is complicated by light scattering. Here, the authors investigate non-resonant scattering in suspensions of wide-bandgap nanosheets, and develop a general model which allows the scattering spectra to be used as metrics for particle size in nanosheet dispersions.
- Andrew Harvey
- , Claudia Backes
- & Jonathan N. Coleman
-
Article
| Open Access All-inorganic cesium lead iodide perovskite solar cells with stabilized efficiency beyond 15%
All-inorganic cesium lead iodide perovskite solar cells with stabilized efficiency beyond 15%
Black phase cesium lead iodide perovskite is regarded as a promising candidate for solar cells, but it easily transits to undesired yellow phase. Herein, Wang et al. stabilized the black phase using molecular additives to achieve device efficiency beyond 15% with high light soaking stability.
- Kang Wang
- , Zhiwen Jin
- & Shengzhong Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Management of transition dipoles in organic hole-transporting materials under solar irradiation for perovskite solar cells
Management of transition dipoles in organic hole-transporting materials under solar irradiation for perovskite solar cells
In perovskite solar cells, the excited state property of hole-transport layer is not usually considered for the devices. Here the authors design organic hole-transport materials with high transition dipoles having extended lifetime at the excited states to improve the charge extraction of the devices.
- Song Ah Ok
- , Bonghyun Jo
- & Hui Joon Park
-
Article
| Open Access Interfacing nickel nitride and nickel boosts both electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution and oxidation reactions
Interfacing nickel nitride and nickel boosts both electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution and oxidation reactions
Efficient hydrogen production and utilization materials will be crucial in order to compete with fossil fuel technologies. Here, authors report nickel and nickel nitride interfaces as effected catalysts for hydrogen evolution and oxidation in water.
- Fuzhan Song
- , Wei Li
- & Yujie Sun
-
Article
| Open Access In situ strain tuning of the metal-insulator-transition of Ca2RuO4 in angle-resolved photoemission experiments
In situ strain tuning of the metal-insulator-transition of Ca2RuO4 in angle-resolved photoemission experiments
The role of the lattice in the correlated metal-insulator transition of Ca2RuO4 has led to significant interest but experiments that are at the same time sensitive to crystal and electronic structure are difficult. Riccò et al. successfully combine ARPES measurements with in situ strain tuning across the Mott transition.
- S. Riccò
- , M. Kim
- & F. Baumberger
-
Article
| Open Access Establishing the effects of mesoporous silica nanoparticle properties on in vivo disposition using imaging-based pharmacokinetics
Establishing the effects of mesoporous silica nanoparticle properties on in vivo disposition using imaging-based pharmacokinetics
Nanoparticle applications are limited by insufficient understanding of physiochemical properties on in vivo disposition. Here, the authors explore the influence of size, surface chemistry and administration on the biodisposition of mesoporous silica nanoparticles using image-based pharmacokinetics.
- Prashant Dogra
- , Natalie L. Adolphi
- & C. Jeffrey Brinker
-
Article
| Open Access Interactions between callose and cellulose revealed through the analysis of biopolymer mixtures
Interactions between callose and cellulose revealed through the analysis of biopolymer mixtures
Despite their importance in plant development and defence the properties of (1,3)-β-glucan remain largely unknown. Here, the authors find that addition of (1,3)-β-glucans increases the flexibility of cellulose and its resilience to high strain, an effect originating in molecular level interactions.
- Radwa H. Abou-Saleh
- , Mercedes C. Hernandez-Gomez
- & Yoselin Benitez-Alfonso
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis and assembly of colloidal cuboids with tunable shape biaxiality
Synthesis and assembly of colloidal cuboids with tunable shape biaxiality
Monodisperse biaxial colloidal particles are used as model systems to understand the phase behavior of biaxial molecules but high-quality biaxial colloids are limited. Here the authors describe gram-scale synthesis of uniform biaxial colloidal cuboids and their assembly into mesophasic structures.
- Yang Yang
- , Guangdong Chen
- & Zhihong Nie
-
Article
| Open Access Predictive multiphase evolution in Al-containing high-entropy alloys
Predictive multiphase evolution in Al-containing high-entropy alloys
Exploration of high entropy alloy phases where little experimental data exists is still challenging. Here, the authors develop an approach where parameters from first principle simulations are incorporated into Monte Carlo simulations to reproduce phase evolution of aluminium-containing high entropy alloys.
- L. J. Santodonato
- , P. K. Liaw
- & J. R. Morris
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated silicon qubit platform with single-spin addressability, exchange control and single-shot singlet-triplet readout
Integrated silicon qubit platform with single-spin addressability, exchange control and single-shot singlet-triplet readout
Significant progress has been made developing the different methods needed for a spin-based quantum computer but the challenge of integrating them remains. Fogarty et al. present a system with single-spin addressability, spin-spin interactions and high-fidelity readout that provides a scalable foundation for error-corrected devices.
- M. A. Fogarty
- , K. W. Chan
- & A. S. Dzurak
-
Article
| Open Access An electrochemical thermal transistor
An electrochemical thermal transistor
Thermal transistors can enable game changing applications in energy harvesting and heat routing. Here, the authors demonstrate reversible thermal modulation of nearly 10 times by ion intercalation in MoS2 nanofilms. A new thermal microscopy technique allows operando imaging of Li ion segregation.
- Aditya Sood
- , Feng Xiong
- & Kenneth E. Goodson
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of selective autophagy induction in cells and tissues by self-assembled chiral nanodevice
Direct observation of selective autophagy induction in cells and tissues by self-assembled chiral nanodevice
Chiral assemblies have gained great interest for probing intracellular effects. Here, the authors report on the development of an upconversion nanoparticle-centred yolk-shell nanoparticle tetrahedron for the induction of autophagy and the monitoring of ATP levels both in living cells and in vivo.
- Maozhong Sun
- , Tiantian Hao
- & Hua Kuang
-
Article
| Open Access Pressure-induced emission of cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals
Pressure-induced emission of cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals
The potential optoelectronic applications of metal halide perovskites make exploration and tuning of their optical properties of great interest. Here the authors show that non-emitting zero-dimensional cesium lead halide perovskites become strongly fluorescent under high pressure, due to distortion-induced effects.
- Zhiwei Ma
- , Zhun Liu
- & Bo Zou
-
Article
| Open Access Designing soft materials with interfacial instabilities in liquid films
Designing soft materials with interfacial instabilities in liquid films
Interfacial instabilities can be damaging as they may lead to fabrication defects. Here the authors harness a fluid instability to their advantage to produce thin polymeric films with drop-shaped structures which have tailored geometrical properties.
- J. Marthelot
- , E. F. Strong
- & P.-T. Brun
-
Article
| Open Access An optical reaction micro-turbine
An optical reaction micro-turbine
Light can be used to rotate micrometric turbines that usually rely on scattering to redistribute optical momentum and generate a mechanical torque. Here, 3D microfabricated light guiding structures can reroute an incoming flow of optical energy to generate a strong, uniform and controllable torque.
- Silvio Bianchi
- , Gaszton Vizsnyiczai
- & Roberto Di Leonardo
-
Article
| Open Access High-power hybrid biofuel cells using layer-by-layer assembled glucose oxidase-coated metallic cotton fibers
High-power hybrid biofuel cells using layer-by-layer assembled glucose oxidase-coated metallic cotton fibers
Biofuel cells offer biocompatibility and operation at mild conditions, but application is limited by relatively low output power. Here the authors use layer-by-layer assembly for glucose oxidase-coated metallic cotton fibers for use as electrodes in a hybrid biofuel cell to achieve high output power.
- Cheong Hoon Kwon
- , Yongmin Ko
- & Jinhan Cho
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering bacterial vortex lattice via direct laser lithography
Engineering bacterial vortex lattice via direct laser lithography
Geometrically confined suspensions of swimming bacteria can self-organize into an ordered state. Here, the authors use tiny pillars to trigger organization of bacterial motion into a stable lattice of vortices with a long-range antiferromagnetic order and control vortex direction through pillar chirality.
- Daiki Nishiguchi
- , Igor S Aranson
- & Andrey Sokolov
-
Article
| Open Access Cooperative mechanisms of oxygen vacancy stabilization and migration in the isolated tetrahedral anion Scheelite structure
Cooperative mechanisms of oxygen vacancy stabilization and migration in the isolated tetrahedral anion Scheelite structure
Fast oxide ion conductors are the key materials for some technological devices. Here the authors report the creation and stabilization of oxygen vacancies in BiVO4 Scheelite with isolated tetrahedral anion structures for improved ionic conducting performance and understanding of the conduction mechanism.
- Xiaoyan Yang
- , Alberto J. Fernández-Carrión
- & Xiaojun Kuang
-
Article
| Open Access Breaking the scaling relationship via thermally stable Pt/Cu single atom alloys for catalytic dehydrogenation
Breaking the scaling relationship via thermally stable Pt/Cu single atom alloys for catalytic dehydrogenation
Enhancing the catalytic activity of noble-metal alloys is frequently accompanied by side reactions. Here, the authors describe an approach to break the scaling relationship for propane dehydrogenation, by assembling single atom alloys, to achieve simultaneous enhancement of propylene selectivity and propane conversion.
- Guodong Sun
- , Zhi-Jian Zhao
- & Jinlong Gong
-
Article
| Open Access Extremely rapid isotropic irradiation of nanoparticles with ions generated in situ by a nuclear reaction
Extremely rapid isotropic irradiation of nanoparticles with ions generated in situ by a nuclear reaction
Mass production of nanoparticles containing well-controlled structural defects is a challenge. Here the authors demonstrate the feasibility of homogeneous ion irradiation generated in a nuclear reactor, for the preparation of fluorescent nanodiamonds and silicon carbide nanoparticles.
- Jan Havlik
- , Vladimira Petrakova
- & Petr Cigler
-
Article
| Open Access High-energy-density dual-ion battery for stationary storage of electricity using concentrated potassium fluorosulfonylimide
High-energy-density dual-ion battery for stationary storage of electricity using concentrated potassium fluorosulfonylimide
Lithium-free graphite dual-ion battery offers a new means of energy storage. Here the authors show such device utilizing a highly concentrated electrolyte solution of KFSI in alkyl carbonates that exhibits a high energy density and high energy efficiency as well as an average discharge voltage of 4.7 V.
- Kostiantyn V. Kravchyk
- , Preeti Bhauriyal
- & Maksym V. Kovalenko
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible and stable high-energy lithium-sulfur full batteries with only 100% oversized lithium
Flexible and stable high-energy lithium-sulfur full batteries with only 100% oversized lithium
Lightweight and flexible energy storage devices are needed to persistently power wearable devices. Here the authors employ metallized carbon fabrics as hosts for sulfur and lithium to achieve flexibility, electrochemical stability and high energy density in a lithium-sulfur battery.
- Jian Chang
- , Jian Shang
- & Zijian Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Oriented electron transmission in polyoxometalate-metalloporphyrin organic framework for highly selective electroreduction of CO2
Oriented electron transmission in polyoxometalate-metalloporphyrin organic framework for highly selective electroreduction of CO2
While CO2 reduction provides a way to remove carbon from the atmosphere, it is challenging to design effective, selective materials for this process. Here, authors construct metal-organic frameworks from polyoxometalates and porphryins to direct electron flow and improve CO2 reduction efficiencies.
- Yi-Rong Wang
- , Qing Huang
- & Ya-Qian Lan
-
Article
| Open Access Enabling nanoscale flexoelectricity at extreme temperature by tuning cation diffusion
Enabling nanoscale flexoelectricity at extreme temperature by tuning cation diffusion
The limited number of materials with a switchable electrical polarization available for applications can be increased by exploiting the flexoelectric effect. Here, switchable polarization in nanoparticles induced by an elemental distribution dependent strain gradient up to 800 °C is demonstrated.
- Leopoldo Molina-Luna
- , Shuai Wang
- & Matias Acosta
-
Article
| Open Access Nanocardboard as a nanoscale analog of hollow sandwich plates
Nanocardboard as a nanoscale analog of hollow sandwich plates
Sandwich structures such as corrugated cardboard offer low weight and high bending stiffness, but they are difficult to produce at the nanoscale. Here, the authors combine webbing and perforation to produce alumina ‘nanocardboard’ with ultralow areal density that recovers without damage from extreme deformation.
- Chen Lin
- , Samuel M. Nicaise
- & Igor Bargatin
-
Article
| Open Access Rewriting the phase diagram of a diamagnetic liquid crystal by a magnetic field
Rewriting the phase diagram of a diamagnetic liquid crystal by a magnetic field
Magnetically induced phase behaviour in a soft matter system is of potential interest for magneto-responsive compounds. Here the authors fabricate a discotic ionic liquid crystalline hybrid material which can be switched from orthorhombic to cubic phase in the absence or presence of a strong magnetic field.
- Fatin Hajjaj
- , Takashi Kajitani
- & Takanori Fukushima
-
Article
| Open Access Shear-band affected zone revealed by magnetic domains in a ferromagnetic metallic glass
Shear-band affected zone revealed by magnetic domains in a ferromagnetic metallic glass
Metallic glasses deform along nanoscale shear bands, and while it is known that they affect the neighboring glass regions, exactly how is unclear. Here, the authors use magnetic force microscopy to atomically resolve the shear-band affected zone and show its effects extends much further than previously thought.
- L. Q. Shen
- , P. Luo
- & W. H. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Physical reality of the Preisach model for organic ferroelectrics
Physical reality of the Preisach model for organic ferroelectrics
Though the Preisach model successfully describes hysteretic switching in ferroelectrics, the physical reality of the model remains elusive. Here, the authors explained the origin of the experimental Preisach distribution and its effect on switching kinetics and materials’ potential applications
- Indrė Urbanavičiūtė
- , Tim D. Cornelissen
- & Martijn Kemerink
-
Article
| Open Access Spin transfer torque driven higher-order propagating spin waves in nano-contact magnetic tunnel junctions
Spin transfer torque driven higher-order propagating spin waves in nano-contact magnetic tunnel junctions
Nano-contact-based spin wave generation may enable high-frequency magnonic devices but has been limited to long wavelengths and weak signal strengths. Here the authors demonstrate high-order short-wavelength propagating spin waves with increased transmission rates and propagation lengths in magnetic tunnel junction stacks.
- A. Houshang
- , R. Khymyn
- & J. Åkerman
-
Article
| Open Access Universality of defect-skyrmion interaction profiles
Universality of defect-skyrmion interaction profiles
Clear understanding of the influence from material inhomogeneities and defects is one of the keys to achieve reliable Skyrmion based devices. Here the authors report their first principles studies on the interaction of single skyrmions with single-atom impurities and reveal its universal shape originated from the defect’s electron filling.
- Imara Lima Fernandes
- , Juba Bouaziz
- & Samir Lounis
-
Article
| Open Access Identifying an efficient, thermally robust inorganic phosphor host via machine learning
Identifying an efficient, thermally robust inorganic phosphor host via machine learning
Identifying phosphors with good thermal stability and quantum efficiency is a prerequisite to improve the performance of white LED light sources. Here, a combined machine learning and density functional theory method is introduced to identify next generation inorganic phosphors.
- Ya Zhuo
- , Aria Mansouri Tehrani
- & Jakoah Brgoch
-
Article
| Open Access Reconfigurable infrared hyperbolic metasurfaces using phase change materials
Reconfigurable infrared hyperbolic metasurfaces using phase change materials
Here, the authors demonstrate that the dispersion of hyperbolic phonon polaritons can be controlled using the permittivity changes inherent in the different phases of phase change materials. This enables direct launching, reflection, transmission and refraction at the phase change material domain boundaries.
- T. G. Folland
- , A. Fali
- & J. D. Caldwell
-
Article
| Open Access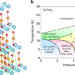 Spherical neutron polarimetry under high pressure for a multiferroic delafossite ferrite
Spherical neutron polarimetry under high pressure for a multiferroic delafossite ferrite
Spherical neutron polarimetry (SNP) experiment in conjunction with high pressure condition faces many experimental difficulties. Here the authors report development of SNP with nonmagnetic hybrid anvil high pressure cell and application to the magnetoelectric multiferroic delafossite CuFeO2 system.
- Noriki Terada
- , Navid Qureshi
- & Toyotaka Osakabe
-
Article
| Open Access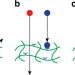 Enhanced diffusion by binding to the crosslinks of a polymer gel
Enhanced diffusion by binding to the crosslinks of a polymer gel
Gels filtering particles by interactions are a goal of nanotechnology; this is difficult when particles are larger than the mesh of the gel. Here, the authors present an equilibrium mechanism where binding dynamics of crosslinks are affected by interacting particles so that particles experience enhanced diffusion.
- Carl P. Goodrich
- , Michael P. Brenner
- & Katharina Ribbeck
-
Article
| Open Access Complex assembly from planar and twisted π-conjugated molecules towards alloy helices and core-shell structures
Complex assembly from planar and twisted π-conjugated molecules towards alloy helices and core-shell structures
Manipulating the assembly of π-conjugated organic molecules into alloys to control composition and shape remains a largely unsolved problem. Here the authors show the co-assembly of two structurally similar organic semiconductors into two-component helices by control of their growth kinetics as well as the molar ratio of the building blocks.
- Yilong Lei
- , Yanqiu Sun
- & Hongbing Fu
-
Article
| Open Access Self-powered H2 production with bifunctional hydrazine as sole consumable
Self-powered H2 production with bifunctional hydrazine as sole consumable
While water electrolysis provides an attractive means to produce high-energy hydrogen (H2), the process imposes significant material overpotential barriers. Here, authors employ the more-facile hydrazine splitting reaction, coupled to a hydrazine fuel cell, to perform self-powered H2 evolution.
- Xijun Liu
- , Jia He
- & Yi Ding
-
Article
| Open Access A RNA producing DNA hydrogel as a platform for a high performance RNA interference system
A RNA producing DNA hydrogel as a platform for a high performance RNA interference system
Interfering RNA have a range of therapeutic and research based applications, issues with delivery have made systems that make siRNA in situ of interest. Here, the author report on the creation of a DNA hydrogel with improved stability and transcription efficiency over plasmid DNA.
- Jaejung Song
- , Minhyuk Lee
- & Nokyoung Park

 Signature of quantum Griffiths singularity state in a layered quasi-one-dimensional superconductor
Signature of quantum Griffiths singularity state in a layered quasi-one-dimensional superconductor