Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Potential-induced nanoclustering of metallic catalysts during electrochemical CO2 reduction
Potential-induced nanoclustering of metallic catalysts during electrochemical CO2 reduction
While the degradation of materials during usage is crucial in understanding their performance, it is challenging to understand the corrosion processes. Here, authors find copper nanoparticles to undergo an unusual potential-driven nanoclustering degradation pathway during carbon dioxide reduction.
- Jianfeng Huang
- , Nicolas Hörmann
- & Raffaella Buonsanti
-
Article
| Open Access Low irradiance multiphoton imaging with alloyed lanthanide nanocrystals
Low irradiance multiphoton imaging with alloyed lanthanide nanocrystals
By using a near-IR optical excitation, upconverting nanoparticles may enable high-resolution imaging deep in tissue. Here, Tian et al. introduce alloyed upconverting nanoparticles with improved brightness due to newly described energy transfer pathways.
- Bining Tian
- , Angel Fernandez-Bravo
- & Bruce E. Cohen
-
Article
| Open Access Ba3Mg3(BO3)3F3 polymorphs with reversible phase transition and high performances as ultraviolet nonlinear optical materials
Ba3Mg3(BO3)3F3 polymorphs with reversible phase transition and high performances as ultraviolet nonlinear optical materials
Nonlinear optical crystals suitable for the UV spectral region could simplify short-wavelength generation and make it more efficient. Here, the authors design and demonstrate that one of two asymmetric borate polymorphs exhibits promising optical and mechanical properties for generating UV light.
- Miriding Mutailipu
- , Min Zhang
- & Shilie Pan
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic weakening during earthquakes controlled by fluid thermodynamics
Dynamic weakening during earthquakes controlled by fluid thermodynamics
Understanding the physics of fault lubrication during earthquake propagation can help assess seismic hazard. In this study, by replicating earthquakes in the laboratory at upper-crustal conditions, the authors show that fluid thermodynamics control fault lubrication, specifically at man-made earthquake depths.
- M. Acosta
- , F. X. Passelègue
- & M. Violay
-
Article
| Open Access Discovering privileged topologies of molecular knots with self-assembling models
Discovering privileged topologies of molecular knots with self-assembling models
Only a few different types of supramolecular knots have been synthesized so far. Here the authors use Monte Carlo sampling, molecular dynamics and combinatorics to discover new knot types made of identical templates.
- Mattia Marenda
- , Enzo Orlandini
- & Cristian Micheletti
-
Article
| Open Access Uniaxial stress flips the natural quantization axis of a quantum dot for integrated quantum photonics
Uniaxial stress flips the natural quantization axis of a quantum dot for integrated quantum photonics
The natural quantization axis in quantum dots, which is usually parallel to the growth direction, is not ideal for planar photonic circuits. Here Yuan et al. show that for gallium arsenide dots, the quantization axis can be flipped to lie in the growth plane via moderate in-plane uniaxial stress.
- Xueyong Yuan
- , Fritz Weyhausen-Brinkmann
- & Armando Rastelli
-
Article
| Open Access Direct imaging of structural changes induced by ionic liquid gating leading to engineered three-dimensional meso-structures
Direct imaging of structural changes induced by ionic liquid gating leading to engineered three-dimensional meso-structures
Local and reversible oxidation is used to exploit the very different properties of oxygen and vacancy ordered oxides. Here the authors directly image and make use of anisotropic migration velocities of oxygen in SrCoOx to create 3D meso-structures of those two phases by ionic liquid gating.
- Bin Cui
- , Peter Werner
- & Stuart S. P. Parkin
-
Article
| Open Access Spontaneous Hall effect in the Weyl semimetal candidate of all-in all-out pyrochlore iridate
Spontaneous Hall effect in the Weyl semimetal candidate of all-in all-out pyrochlore iridate
Material with both topological state and magnetic order remains rare. Here, Ueda et al. observe a sizable spontaneous Hall conductivity with minimal magnetization at a few Kelvin below the all-in-all-out magnetic ordering temperature in the predicted magnetic Weyl semimetal R2Ir2O7.
- Kentaro Ueda
- , Ryoma Kaneko
- & Yoshinori Tokura
-
Article
| Open Access Highly sensitive switching of solid-state luminescence by controlling intersystem crossing
Highly sensitive switching of solid-state luminescence by controlling intersystem crossing
The development of intelligent materials, in particular those showing the highly sensitive mechanoresponsive luminescence (MRL), remains challenging. Here the authors report a strategy for constructing high performance On-Off MRL materials by introducing nitrophenyl groups to molecules with aggregation-induced emission characteristic.
- Weijun Zhao
- , Zikai He
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access 2D perovskite stabilized phase-pure formamidinium perovskite solar cells
2D perovskite stabilized phase-pure formamidinium perovskite solar cells
Utilizing mixed-cation-halide can improve stability of the formamidinium perovskite films and devices but sacrifices the photocurrent due to an increase in bandgap. Here Lee et al. introduced small amounts of 2D perovskite to obtain high efficiency and stability based on phase-pure formamidinium based perovskite.
- Jin-Wook Lee
- , Zhenghong Dai
- & Yang Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Tailoring van der Waals dispersion interactions with external electric charges
Tailoring van der Waals dispersion interactions with external electric charges
The description of van der Waals interactions should often account for coupling with pervasive electric fields, but this effect has been omitted in atomistic simulations. Here, the authors develop a model to study the effects of external charge on long-range van der Waals interactions.
- Andrii Kleshchonok
- & Alexandre Tkatchenko
-
Article
| Open Access Distinct multiple fermionic states in a single topological metal
Distinct multiple fermionic states in a single topological metal
The existence of multiple topological phases in a single material, although theoretically possible, has not been verified. Here, the authors observe weak topological insulator surface states and a one-dimensional Dirac-node crossing surface state in a single metallic material Hf2Te2P.
- M. Mofazzel Hosen
- , Klauss Dimitri
- & Madhab Neupane
-
Article
| Open Access Block copolymer crystalsomes with an ultrathin shell to extend blood circulation time
Block copolymer crystalsomes with an ultrathin shell to extend blood circulation time
In block copolymer vesicles, crystallization often leads to defects and renders the structures leaky that undermines their potential biomedical application. Here the authors use an emulsion solution method to control the crystallization of an amphiphilic block copolymer at the curved liquid/liquid interface to improve the blood circulation time.
- Hao Qi
- , Hao Zhou
- & Christopher Y. Li
-
Article
| Open Access Facile transformation of imine covalent organic frameworks into ultrastable crystalline porous aromatic frameworks
Facile transformation of imine covalent organic frameworks into ultrastable crystalline porous aromatic frameworks
Despite recent success in developing new covalent organic frameworks (COFs) materials, synthesis of chemically stable COFs still remains challenging. Here the authors demonstrate a facile strategy that transforms imine-linked COFs into robust porous aromatic frameworks by kinetically fixing the reversible imine linkage via an aza-Diels-Alder cycloaddition reaction.
- Xinle Li
- , Changlin Zhang
- & Yi Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Spin-induced multiferroicity in the binary perovskite manganite Mn2O3
Spin-induced multiferroicity in the binary perovskite manganite Mn2O3
Multiferroic binary oxides with the perovskite structure have been very rare. Here, Cong et al. report magnetically-driven ferroelectricity and a large magnetoelectric effect in a binary perovskite compound Mn2O3 at low temperatures.
- Junzhuang Cong
- , Kun Zhai
- & Young Sun
-
Article
| Open Access New insights into the design of conjugated polymers for intramolecular singlet fission
New insights into the design of conjugated polymers for intramolecular singlet fission
Further mechanistic insight of intramolecular singlet fission (iSF) in conjugated polymers can enable novel material design for solar cells. Here, the authors use transient spectroscopy to show iSF in an isoindigo-based conjugated polymer and propose a design rule based on morphology-dependent iSF.
- Jiahua Hu
- , Ke Xu
- & Matthew Y. Sfeir
-
Comment
| Open Access The must-have and nice-to-have experimental and computational requirements for functional frequency doubling deep-UV crystals
The must-have and nice-to-have experimental and computational requirements for functional frequency doubling deep-UV crystals
- P. Shiv Halasyamani
- & James M. Rondinelli
-
Article
| Open Access Long range electronic phase separation in CaFe3O5
Long range electronic phase separation in CaFe3O5
Electronic phase separation is an important feature of many correlated perovskite compounds but hasn’t been seen in other complex oxides with similar physical behaviour such as magnetite. Hong et al. find phase separation between a magnetite-like charge ordered phase and a charge averaged phase in CaFe3O5.
- Ka. H. Hong
- , Angel M. Arevalo-Lopez
- & J. Paul Attfield
-
Article
| Open Access Transforming ground mica into high-performance biomimetic polymeric mica film
Transforming ground mica into high-performance biomimetic polymeric mica film
Biomimetic assembly of nanosheets into nacre-like structures and films is of interest for a range of applications; the abundance of mica makes it a good candidate. Here, the authors report on the large-scale exfoliation of ground mica into nanosheets and the assembly into polymeric mica films.
- Xiao-Feng Pan
- , Huai-Ling Gao
- & Shu-Hong Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Controllable protein phase separation and modular recruitment to form responsive membraneless organelles
Controllable protein phase separation and modular recruitment to form responsive membraneless organelles
Designer organelles with new biochemical functionalities are of great interest in synthetic biology and cellular engineering. Here the authors present a single-protein-based platform for generating synthetic membraneless compartments that is capable of enzymatically-triggered alterations to phase behavior and of recruiting and concentrating cargo proteins.
- Benjamin S. Schuster
- , Ellen H. Reed
- & Daniel A. Hammer
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced immunocompatibility of ligand-targeted liposomes by attenuating natural IgM absorption
Enhanced immunocompatibility of ligand-targeted liposomes by attenuating natural IgM absorption
Targeting ligands on drug carriers can trigger immune responses. Here, the authors modify liposomes with a peptidomimetic that preserves bioactivity of the nanocarrier in blood circulation and attenuates IgM absorption, thereby improving the immunocompatibility of brain-targeted liposomes.
- Juan Guan
- , Qing Shen
- & Changyou Zhan
-
Article
| Open Access Evolution of cooperativity in the spin transition of an iron(II) complex on a graphite surface
Evolution of cooperativity in the spin transition of an iron(II) complex on a graphite surface
Spin-crossover molecules offer a potential route towards molecular spintronics, but retaining the bistability of the spin state upon surface deposition is challenging. Here, the authors study the spin-crossover behaviours of an Fe(II) complex deposited on graphite, determining the scale limit at which cooperative spin switching becomes effective.
- Lalminthang Kipgen
- , Matthias Bernien
- & Wolfgang Kuch
-
Article
| Open Access Real-space imaging with pattern recognition of a ligand-protected Ag374 nanocluster at sub-molecular resolution
Real-space imaging with pattern recognition of a ligand-protected Ag374 nanocluster at sub-molecular resolution
Translating high-resolution imaging methods to the curved organic surface of a nanoparticle has been challenging. Here, the authors are able to spatially resolve the sub-molecular surface details of a silver nanocluster by comparing scanning tunneling microscopy images and simulated topography data through a pattern recognition algorithm.
- Qin Zhou
- , Sami Kaappa
- & Lansun Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanical dissipation from charge and spin transitions in oxygen-deficient SrTiO3 surfaces
Mechanical dissipation from charge and spin transitions in oxygen-deficient SrTiO3 surfaces
Non-contact atomic force microscope (AFM) dissipation contains rich information on the electron, phonon and spin states, but has been poorly understood. Here the authors demonstrated that tip-induced charge and spin state transitions in oxygen vacancies at SrTiO3 surface are revealed by AFM dissipation measurements.
- Marcin Kisiel
- , Oleg O. Brovko
- & Ernst Meyer
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional multibit optoelectronic memory with broadband spectrum distinction
Two-dimensional multibit optoelectronic memory with broadband spectrum distinction
Continued device miniaturization and feasibility of integrating two-dimensional materials into circuits have enabled flexible and transparent optoelectronic memories. Here, the authors show a WSe2–hBN-based heterostructure memory with switching ratio of ~1.1 × 106, ensuring over 128 distinct storage states and retention time of ~4.5 × 104 s.
- Du Xiang
- , Tao Liu
- & Wei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access A user-friendly herbicide derived from photo-responsive supramolecular vesicles
A user-friendly herbicide derived from photo-responsive supramolecular vesicles
Paraquat is a widely used herbicide that is highly toxic to humans upon acute ingestion or chronic exposure. Here, the authors generate a photosensitive formulation that releases paraquat upon exposure to UV light or sunlight, which shows an improved safety profile in zebrafish and mouse models, while maintaining substantial herbicidal activity.
- Cheng Gao
- , Qiaoxian Huang
- & Ruibing Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Strongly-coupled quantum critical point in an all-in-all-out antiferromagnet
Strongly-coupled quantum critical point in an all-in-all-out antiferromagnet
The critical behavior of a continuous phase transition is determined by both symmetry and dimensionality. Wang et al. present evidence that the cubic all-in-all-out spin order in Cd2Os2O7 leads to a realization of a non-mean-field strongly-coupled quantum phase transition in three dimensions.
- Yishu Wang
- , T. F. Rosenbaum
- & Yejun Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Chemically specific termination control of oxide interfaces via layer-by-layer mean inner potential engineering
Chemically specific termination control of oxide interfaces via layer-by-layer mean inner potential engineering
Precisely controlled growth of oxide interfaces at the atomic layer level is critical for device applications but quite challenging. Here Sun et al. show real time monitoring and control of the surface composition of epitaxial strontium titanate perovskite films by analysing the Kikuchi lines.
- H. Y. Sun
- , Z. W. Mao
- & X. Q. Pan
-
Article
| Open Access Non-hysteretic first-order phase transition with large latent heat and giant low-field magnetocaloric effect
Non-hysteretic first-order phase transition with large latent heat and giant low-field magnetocaloric effect
First order magnetic phase transitions have many practical applications but they often involve structural changes that make it difficult to control energy losses. Guillou et al. show that Eu2In has an isostructural transition with a mechanism distinct from other known magnetoelastic transitions.
- F. Guillou
- , A. K. Pathak
- & V. K. Pecharsky
-
Article
| Open Access Bottom-up growth of n-type monolayer molecular crystals on polymeric substrate for optoelectronic device applications
Bottom-up growth of n-type monolayer molecular crystals on polymeric substrate for optoelectronic device applications
New methods for obtaining large-area monolayer molecular crystals (MMCs) on hydrophobic surfaces are needed to realize the full potential of MMCs for organic electronics. Here, the authors demonstrate bottom-up growth of high-grade n-type MMCs, which show superior performance in device applications.
- Yanjun Shi
- , Lang Jiang
- & Henning Sirringhaus
-
Article
| Open Access High sensitivity organic inorganic hybrid X-ray detectors with direct transduction and broadband response
High sensitivity organic inorganic hybrid X-ray detectors with direct transduction and broadband response
X-ray detectors based on low-cost organic semiconductors have inherently low detector sensitivity due to poor X-ray to charge conversion and charge collection. Here, the authors demonstrate a flexible, high-sensitivity X-ray detector based on an organic bulk heterojunction-nanoparticle composite.
- H. M. Thirimanne
- , K. D. G. I. Jayawardena
- & S. R. P. Silva
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanical mismatch-driven rippling in carbon-coated silicon sheets for stress-resilient battery anodes
Mechanical mismatch-driven rippling in carbon-coated silicon sheets for stress-resilient battery anodes
Maintaining the structural stability during electrochemical cycling remains a big challenge facing the silicon anode material. Here, the authors have developed 2D silicon nanosheets coated with carbon layers, which show a unique mechanism in releasing internal stress by forming ripple structures.
- Jaegeon Ryu
- , Tianwu Chen
- & Soojin Park
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and topological nature of plasticity in sheared granular materials
Structural and topological nature of plasticity in sheared granular materials
It is a general consensus that the structural defects are the plasticity carriers in amorphous solids, but its microscopic view remains largely unknown. Cao et a. show that highly distorted coplanar tetrahedra act as defects in granular packings, which flip under shear to carry local plasticity.
- Yixin Cao
- , Jindong Li
- & Yujie Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Toroidal diamond anvil cell for detailed measurements under extreme static pressures
Toroidal diamond anvil cell for detailed measurements under extreme static pressures
Extreme static pressures exceeding a million atmospheres exist in a variety of natural environments, but obtaining such pressures in a laboratory is still a challenge. Here, the authors develop a toroidal diamond anvil design that allows for the generation of 600 GPa (6 million atmospheres) in routinely used diamond anvil cells.
- Agnès Dewaele
- , Paul Loubeyre
- & Mohamed Mezouar
-
Article
| Open Access Electrically driven three-dimensional solitary waves as director bullets in nematic liquid crystals
Electrically driven three-dimensional solitary waves as director bullets in nematic liquid crystals
Solitary waves which maintain their shape have many fascinating physical and mathematical properties. Here the authors observe waves trapped along three spatial dimensions in nematic liquid crystals due to an electric field and show that these director bullets can re-form after collisions.
- Bing-Xiang Li
- , Volodymyr Borshch
- & Oleg D. Lavrentovich
-
Article
| Open Access Suppression of atom motion and metal deposition in mixed ionic electronic conductors
Suppression of atom motion and metal deposition in mixed ionic electronic conductors
Mixed ionic–electronic conductors are limited by material decomposition. Here the authors reveal the mechanism for atom migration and deposition in Cu2–δ(S,Se) materials based on a critical chemical potential difference and propose electronically conducting, ion-blocking interfaces to enhance stability.
- Pengfei Qiu
- , Matthias T. Agne
- & G. Jeffrey Snyder
-
Article
| Open Access Bottle-grade polyethylene furanoate from ring-opening polymerisation of cyclic oligomers
Bottle-grade polyethylene furanoate from ring-opening polymerisation of cyclic oligomers
The synthesis of polyethylene furanoate, a promising renewable resource-based bioplastic, still has challenges. Here the authors show that bottle-grade polyethylene furanoate can be obtained within minutes from ring-opening polymerisation of its cyclic oligomers, thereby avoiding degradation and discolouration.
- Jan-Georg Rosenboom
- , Diana Kay Hohl
- & Massimo Morbidelli
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic-level insight into super-efficient electrocatalytic oxygen evolution on iron and vanadium co-doped nickel (oxy)hydroxide
Atomic-level insight into super-efficient electrocatalytic oxygen evolution on iron and vanadium co-doped nickel (oxy)hydroxide
While splitting water could provide a renewable way to produce fuel, highly active catalysts are needed to overcome water oxidation’s sluggish kinetics. Here, authors gain atomic-level insight on metal ion synergetic interactions that boost water oxidation performances in co-doped nickel hydroxide.
- Jian Jiang
- , Fanfei Sun
- & Mei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Room-temperature pyro-catalytic hydrogen generation of 2D few-layer black phosphorene under cold-hot alternation
Room-temperature pyro-catalytic hydrogen generation of 2D few-layer black phosphorene under cold-hot alternation
2D elemental materials, with their atomic-scale dimensions, present exciting opportunities for energy conversion applications. Here, the authors use few-layer black phosphorene to perform pyro-catalysis, in which thermal cycling the material induces hydrogen gas production and dye degradation.
- Huilin You
- , Yanmin Jia
- & Yu Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Lithography for robust and editable atomic-scale silicon devices and memories
Lithography for robust and editable atomic-scale silicon devices and memories
Manipulation at the atomic scale comes with a trade-off between simplicity and thermal stability. Here, Achal et al. demonstrate improved automated hydrogen lithography and repassivation, enabling error-corrected atomic writing of large-scale structures/memories that are stable at room temperature.
- Roshan Achal
- , Mohammad Rashidi
- & Robert A. Wolkow
-
Article
| Open Access Microscopic mechanism of biphasic interface relaxation in lithium iron phosphate after delithiation
Microscopic mechanism of biphasic interface relaxation in lithium iron phosphate after delithiation
Improving the performance of Li-ion batteries relies on understanding charging/discharging mechanisms. Here the authors visualize the interfacial structure and composition of a partially delithiated lithium iron phosphate single crystal as a function of time, revealing a mechanism of relaxation.
- Shunsuke Kobayashi
- , Akihide Kuwabara
- & Yuichi Ikuhara
-
Article
| Open Access Drug capture materials based on genomic DNA-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles
Drug capture materials based on genomic DNA-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles
Chemotherapy agents are prone to producing severe side-effects, and their sequestration prior to their entering of the circulatory system is thus highly desirable. Here, the authors functionalize iron oxide nanoparticles with genomic DNA and achieve sequestration of doxorubicin, cisplatin, and epirubicin from biological solutions.
- Carl M. Blumenfeld
- , Michael D. Schulz
- & Robert H. Grubbs
-
Article
| Open Access Gate-controlled quantum dots and superconductivity in planar germanium
Gate-controlled quantum dots and superconductivity in planar germanium
Superconductor–semiconductor hybrid systems can bring together physical properties that are promising for fast and coherent quantum technology. Here, Hendrickx et al. realize such a system in planar germanium heterostructures demonstrating excellent quantum dots and tunable Josephson supercurrents.
- N. W. Hendrickx
- , D. P. Franke
- & M. Veldhorst
-
Article
| Open Access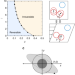 Hyperuniformity with no fine tuning in sheared sedimenting suspensions
Hyperuniformity with no fine tuning in sheared sedimenting suspensions
Suspensions appear in a wide range of industrial settings, and dispersing particles in a uniform manner throughout a fluid remains challenging for applications. Wang et al. obtain hyperuniform mixtures without fine tuning by harnessing self-organized criticality due to slow sedimentation and shear.
- Jikai Wang
- , J. M. Schwarz
- & Joseph D. Paulsen
-
Article
| Open Access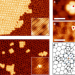 Non-covalent control of spin-state in metal-organic complex by positioning on N-doped graphene
Non-covalent control of spin-state in metal-organic complex by positioning on N-doped graphene
Molecules can change their electronic properties when they are adsorbed on substrates, which can be useful for sensing and catalysis. Here, the authors use atomic force microscopy to show that the spin state of an iron complex can be changed upon displacing the molecule to different sites of a nitrogen-doped graphene
- Bruno de la Torre
- , Martin Švec
- & Pavel Jelínek
-
Article
| Open Access Bistable and photoswitchable states of matter
Bistable and photoswitchable states of matter
Polymers cross-linked with dynamic bonds can switch the phase from solid to fluid upon stimulus but return quickly to the solid state once the stimulus is removed. Here the authors report a light triggered permanent solid to fluid transition at room temperature with inherent spatiotemporal control in either direction
- Brady T. Worrell
- , Matthew K. McBride
- & Christopher N. Bowman
-
Article
| Open Access Slow thermal equilibration in methylammonium lead iodide revealed by transient mid-infrared spectroscopy
Slow thermal equilibration in methylammonium lead iodide revealed by transient mid-infrared spectroscopy
Hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites are emerging materials for efficient photovoltaics; however understanding how charge/heat dissipates inside the material remains a challenge. Here, the authors use a spectroscopic approach to observe unusually slow thermal equilibration between the organic and inorganic components.
- Peijun Guo
- , Jue Gong
- & Richard D. Schaller
-
Article
| Open Access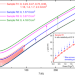 Using controlled disorder to probe the interplay between charge order and superconductivity in NbSe2
Using controlled disorder to probe the interplay between charge order and superconductivity in NbSe2
The interplay between superconductivity and charge density wave (CDW) in 2H-NbSe2 is still not fully understood. Here, Cho et al. use controlled disorder to probe the interplay between these two phases in 2H-NbSe2 and find that superconductivity initially competes with CDW but eventually long-range CDW order assists superconductivity.
- Kyuil Cho
- , M. Kończykowski
- & R. Prozorov
-
Article
| Open Access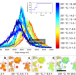 Propagation topography of redox phase transformations in heterogeneous layered oxide cathode materials
Propagation topography of redox phase transformations in heterogeneous layered oxide cathode materials
Here the authors demonstrate a spectroscopic and imaging approach to study redox solid-state phase transformation in lithium ion cathode materials under thermal abuse conditions. The valence curvature of the propagation front alternates as a result of local chemical and structural heterogeneities.
- Linqin Mu
- , Qingxi Yuan
- & Feng Lin

 Dipolar cations confer defect tolerance in wide-bandgap metal halide perovskites
Dipolar cations confer defect tolerance in wide-bandgap metal halide perovskites