Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Nanomaterials design for super-degenerate electronic state beyond the limit of geometrical symmetry
Nanomaterials design for super-degenerate electronic state beyond the limit of geometrical symmetry
No substances with greater degrees of degeneracy than spherical atoms are known, due to geometrical limitations. In this work the authors combine density functional theory and tight-binding models to predict metal clusters with higher-fold degeneracies than spherical atoms, which are ascribed to dynamical symmetry.
- Naoki Haruta
- , Takamasa Tsukamoto
- & Kimihisa Yamamoto
-
Article
| Open Access Modular DNA strand-displacement controllers for directing material expansion
Modular DNA strand-displacement controllers for directing material expansion
Materials which change shape in response to a trigger are of interest for soft robotics and targeted therapeutic delivery. Here, the authors report on the development of DNA-crosslinked hydrogels which can expand upon the detection of different biomolecular inputs mediated by DNA strand-displacement.
- Joshua Fern
- & Rebecca Schulman
-
Article
| Open Access All carbon materials pn diode
All carbon materials pn diode
Chemically functionalized graphene oxide-based pn junction diodes have potential for future electronic device applications. Here, the authors report an all carbon pn diode with graphene oxide and carbon nanotubes electrodes showing excellent current rectification and efficient logic gates.
- Xiaojing Feng
- , Xing Zhao
- & Yong Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient generation of neutral and charged biexcitons in encapsulated WSe2 monolayers
Efficient generation of neutral and charged biexcitons in encapsulated WSe2 monolayers
High-order correlated states in atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides may be facilitated by long-lived optically dark excitons. Here, the authors report experimentally the emergence of neutral and charged biexciton species at low light intensities in encapsulated WSe2 monolayers.
- Ziliang Ye
- , Lutz Waldecker
- & Tony F. Heinz
-
Article
| Open Access Charge-tuneable biexciton complexes in monolayer WSe2
Charge-tuneable biexciton complexes in monolayer WSe2
Multi-exciton states may emerge in atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides as a result of strong many-body interactions. Here, the authors report experimental evidence of four- and five-particle biexciton complexes in monolayer WSe2 and their electrical control.
- Matteo Barbone
- , Alejandro R.-P. Montblanch
- & Mete Atatüre
-
Article
| Open Access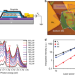 Revealing the biexciton and trion-exciton complexes in BN encapsulated WSe2
Revealing the biexciton and trion-exciton complexes in BN encapsulated WSe2
Owing to strong Coulomb interactions, atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides host strongly bound excitonic complexes. Here, the authors report charge-neutral biexciton and negatively charged trion-exciton complexes in hBN encapsulated monolayer WSe2 by employing low-temperature photoluminescence spectroscopy.
- Zhipeng Li
- , Tianmeng Wang
- & Su-Fei Shi
-
Article
| Open Access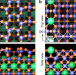 Influence of surface atomic structure demonstrated on oxygen incorporation mechanism at a model perovskite oxide
Influence of surface atomic structure demonstrated on oxygen incorporation mechanism at a model perovskite oxide
The availability of surface oxygen vacancies or electrons is often viewed as the defining factor for the reactivity of perovskite oxides. Two precisely controlled surfaces on SrTiO3(110) show strikingly different O exchange kinetics, which the authors ascribe to the flexibility of the surface polyhedra.
- Michele Riva
- , Markus Kubicek
- & Ulrike Diebold
-
Article
| Open Access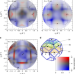 Nonlocal electron correlations in an itinerant ferromagnet
Nonlocal electron correlations in an itinerant ferromagnet
The consequences of electron-electron interactions are difficult to calculate reliably but this is needed to understand important physical properties such as ferromagnetism. Tusche et al. show that interaction effects in cobalt are nonlocal, presenting a challenge to future theoretical approaches.
- Christian Tusche
- , Martin Ellguth
- & Jürgen Kirschner
-
Article
| Open Access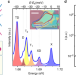 Coulomb-bound four- and five-particle intervalley states in an atomically-thin semiconductor
Coulomb-bound four- and five-particle intervalley states in an atomically-thin semiconductor
Valleytronic devices of atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides may benefit from high-order exciton complexes. Here, the authors present experimental evidence for four-particle biexcitons and five-particle exciton-trions in high-quality monolayer WSe2.
- Shao-Yu Chen
- , Thomas Goldstein
- & Jun Yan
-
Article
| Open Access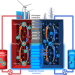 Negatively charged nanoporous membrane for a dendrite-free alkaline zinc-based flow battery with long cycle life
Negatively charged nanoporous membrane for a dendrite-free alkaline zinc-based flow battery with long cycle life
Dendrite accumulation is a hindrance for alkaline zinc-based flow batteries. Here the authors design a negatively charged nanoporous membrane that mitigates zinc dendrite growth by repulsion of zincate anions, leading to a zinc-based flow battery with high power density and cycling stability.
- Zhizhang Yuan
- , Xiaoqi Liu
- & Xianfeng Li
-
Article
| Open Access Seed-mediated atomic-scale reconstruction of silver manganate nanoplates for oxygen reduction towards high-energy aluminum-air flow batteries
Seed-mediated atomic-scale reconstruction of silver manganate nanoplates for oxygen reduction towards high-energy aluminum-air flow batteries
Aluminum-air batteries are lightweight and cost effective, but performance is limited by corrosion and solid by-products. Here the authors catalyze oxygen reduction with silver manganate nanoplates and develop an aluminum-air flow battery that delivers high energy density and alleviates side reactions.
- Jaechan Ryu
- , Haeseong Jang
- & Jaephil Cho
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired 3D structures with programmable morphologies and motions
Bioinspired 3D structures with programmable morphologies and motions
Spatially controlled expansion and contraction of soft tissues to achieve complex three dimensional morphologies remains challenging in man-made materials. Here the authors demonstrate encoding of 2D hydrogels with spatially and temporally controlled growth to create dynamic 3D structures.
- Amirali Nojoomi
- , Hakan Arslan
- & Kyungsuk Yum
-
Article
| Open Access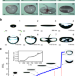 Inducing drop to bubble transformation via resonance in ultrasound
Inducing drop to bubble transformation via resonance in ultrasound
Bubbles tend to burst and retract into droplets. Here the authors show how a droplet can be turned into a bubble by levitating the droplets acoustically and exploiting their buckling to form gas bubbles.
- Duyang Zang
- , Lin Li
- & Xingguo Geng
-
Article
| Open Access Trojan Horse nanotheranostics with dual transformability and multifunctionality for highly effective cancer treatment
Trojan Horse nanotheranostics with dual transformability and multifunctionality for highly effective cancer treatment
Size and charge can significantly affect delivery of therapeutic agents to tumours. Here, the authors report on nanoparticles optimised for delivery to the tumour which release smaller particles and change charge in the tumour microenvironment to optimise tumour penetration and cellular uptake.
- Xiangdong Xue
- , Yee Huang
- & Yuanpei Li
-
Article
| Open Access Compartmentalised RNA catalysis in membrane-free coacervate protocells
Compartmentalised RNA catalysis in membrane-free coacervate protocells
Phase separation of mixtures of oppositely charged polymers provides a simple and direct route to compartmentalisation via coacervation. Here authors demonstrate that a coacervate microenvironment supports RNA catalysis whilst selectively sequestering RNA based on length.
- Björn Drobot
- , Juan M. Iglesias-Artola
- & T-Y Dora Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Solubility-mediated sustained release enabling nitrate additive in carbonate electrolytes for stable lithium metal anode
Solubility-mediated sustained release enabling nitrate additive in carbonate electrolytes for stable lithium metal anode
The solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) is one of the governing factors for the reversibility of Li metal anode. Here, the authors reveal the impact of nitrate additive on the SEI in carbonate electrolytes, and demonstrate a method to overcome the solubility limitation of nitrate.
- Yayuan Liu
- , Dingchang Lin
- & Yi Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Correct determination of charge transfer state energy from luminescence spectra in organic solar cells
Correct determination of charge transfer state energy from luminescence spectra in organic solar cells
The charge transfer state is the key to understand the open circuit voltage of organic solar cells and is commonly accessed by electroluminescence spectra. Here List et al. show that the reliable spectra can only be obtained by a correction of the device-specific out-coupling effect.
- Mathias List
- , Tanmoy Sarkar
- & Uli Würfel
-
Article
| Open Access Antagonistic chemical coupling in self-reconfigurable host–guest protocells
Antagonistic chemical coupling in self-reconfigurable host–guest protocells
Multi-compartmentalised soft micro-systems are used as models of synthetic protocells. Here, the authors developed nested host–guest protocell constructs capable of self-reconfiguration in response to changes in pH generated by antagonistic modes of enzyme-mediated coupling.
- Nicolas Martin
- , Jean-Paul Douliez
- & Stephen Mann
-
Article
| Open Access Selective sorting of polymers with different terminal groups using metal-organic frameworks
Selective sorting of polymers with different terminal groups using metal-organic frameworks
The separation of high molecular weight polymers composed of the same number of monomeric units remains highly challenging. Here, the authors show that efficient separation and purification of mixtures of polymers that differ only by their terminal groups can be achieved through polymer threading in metal-organic framework channels.
- Benjamin Le Ouay
- , Chikara Watanabe
- & Takashi Uemura
-
Article
| Open Access Unexpected stability of aqueous dispersions of raspberry-like colloids
Unexpected stability of aqueous dispersions of raspberry-like colloids
The ability to stabilise colloidal suspensions in solution against salt-induced aggregation is critical to many industrial applications, but it remains challenging at high salt concentration. To overcome this problem, Lan et al. introduce a raspberry-like colloidal particle with controllable morphology.
- Yang Lan
- , Alessio Caciagli
- & Erika Eiser
-
Article
| Open Access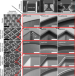 Biomimetic coating-free surfaces for long-term entrapment of air under wetting liquids
Biomimetic coating-free surfaces for long-term entrapment of air under wetting liquids
Trapping air at the solid-liquid interface is a promising strategy for reducing frictional drag but could not be realized without perfluorinated coatings so-far. Here the authors demonstrate a biomimetic coating-free approach for entrapping air for long periods upon immersion in liquids.
- Eddy M. Domingues
- , Sankara Arunachalam
- & Himanshu Mishra
-
Article
| Open Access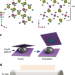 Printing two-dimensional gallium phosphate out of liquid metal
Printing two-dimensional gallium phosphate out of liquid metal
Two-dimensional piezoelectric materials hold promise for nano-electromechanical technologies, yet it is challenging to prepare them in large areas with high sample homogeneity. Syed et al. surface print GaPO4 sheets with unit cell thickness over centimetres using a liquid metal-based synthesis process.
- Nitu Syed
- , Ali Zavabeti
- & Kourosh Kalantar-Zadeh
-
Article
| Open Access Realization of vertical metal semiconductor heterostructures via solution phase epitaxy
Realization of vertical metal semiconductor heterostructures via solution phase epitaxy
Controlling the composition and crystal phase of layered heterostructures is important. Here, the authors report the liquid-phase epitaxial growth of Sn0.5W0.5S2 nanosheets with 83% metallic phase on SnS2 nanoplates, which are used as 100 ppb level chemiresistive gas sensors at room temperature.
- Xiaoshan Wang
- , Zhiwei Wang
- & Wei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access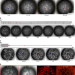 Dynamic capillary assembly of colloids at interfaces with 10,000g accelerations
Dynamic capillary assembly of colloids at interfaces with 10,000g accelerations
The deformation of soft materials under high rates remains challenging to be probed directly and thus understood. Huerre et al. examine the self-assembly of colloids confined at a fluid interface driven by ultrasound and show the formation of string-like microstructures caused by dynamic capillarity.
- Axel Huerre
- , Marco De Corato
- & Valeria Garbin
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous twin boundaries in two dimensional materials
Anomalous twin boundaries in two dimensional materials
All materials subjected to mechanical deformation form low energy interfaces known as twin boundaries. Here, the authors investigate a variety of structural features that form upon bending atomically thin 2D-crystals, and predict distinct classes of post deformation microstructure based on their atomic arrangement, bend angle and flake thickness.
- A. P. Rooney
- , Z. Li
- & S. J. Haigh
-
Article
| Open Access Exploring Peltier effect in organic thermoelectric films
Exploring Peltier effect in organic thermoelectric films
Observing the Peltier effect, e.g. cooling/heating at material junctions due to current flow, in organic thermoelectric films remains a challenge due the inherent properties of these materials. Here, the authors use IR imaging to experimentally observe the Peltier effect in poly(Ni-ett)-based films.
- Wenlong Jin
- , Liyao Liu
- & Daoben Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired ultra-stretchable and anti-freezing conductive hydrogel fibers with ordered and reversible polymer chain alignment
Bioinspired ultra-stretchable and anti-freezing conductive hydrogel fibers with ordered and reversible polymer chain alignment
High-performance stretchable conductive fibers are desired for the development of stretchable electronic devices but preparation of conductive hydrogel fibers is challenging. Inspired by spider silk the authors demonstrate here a spinning method to prepare stretchable conductive hydrogel fibers with ordered polymer chain alignment.
- Xue Zhao
- , Fang Chen
- & Mingming Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic force microscopy methodology and AFMech Suite software for nanomechanics on heterogeneous soft materials
Atomic force microscopy methodology and AFMech Suite software for nanomechanics on heterogeneous soft materials
Atomic force microscopy is an indispensable method in characterizing soft materials but the complexity of biological samples makes reproducible measurements difficult. Here the authors use a 3-step method to investigate biological specimens in which vertical and lateral heterogeneity hinders a precise quantitative characterization.
- Massimiliano Galluzzi
- , Guanlin Tang
- & Florian J. Stadler
-
Article
| Open Access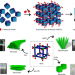 Binder driven self-assembly of metal-organic cubes towards functional hydrogels
Binder driven self-assembly of metal-organic cubes towards functional hydrogels
A possible route to producing processable soft materials is by assembling metal organic cubes into hydrogels. Here the authors show charge-assisted H-bond driven self-assembly of Ga3+-based anionic metal organic cubes and suitable molecular binders towards multi-functional hydrogels.
- Papri Sutar
- , Venkata M. Suresh
- & Tapas Kumar Maji
-
Article
| Open Access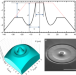 Single crystal toroidal diamond anvils for high pressure experiments beyond 5 megabar
Single crystal toroidal diamond anvils for high pressure experiments beyond 5 megabar
Static pressures exceeding 4 million atmospheres are extremely challenging to achieve, but are necessary for the study of matter that exists under these conditions in natural environments. Here, diamonds anvils with a toroidal design are demonstrated to sustain over 6 million atmospheres in a diamond anvil cell.
- Zs. Jenei
- , E. F. O’Bannon
- & W. J. Evans
-
Article
| Open Access Room-temperature polarized spin-photon interface based on a semiconductor nanodisk-in-nanopillar structure driven by few defects
Room-temperature polarized spin-photon interface based on a semiconductor nanodisk-in-nanopillar structure driven by few defects
Room-temperature spin-generation in 1D systems like semiconductor nanopillars is typically inefficient. Here, the authors demonstrate an approach to achieve efficient spin polarization, even in the absence of a magnetic field, by selectively enhancing the radiative efficiency of one spin direction.
- Shula Chen
- , Yuqing Huang
- & Weimin M. Chen
-
Article
| Open Access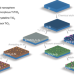 Crystalline TiO2 protective layer with graded oxygen defects for efficient and stable silicon-based photocathode
Crystalline TiO2 protective layer with graded oxygen defects for efficient and stable silicon-based photocathode
While silicon-based materials can convert sunlight directly to fuel and electricity, balancing their stability and efficiency constrains usage. Here, authors protect silicon photocathodes with crystalline titanium dioxide layers with graded oxygen defects to improve both durability and efficiency.
- Jianyun Zheng
- , Yanhong Lyu
- & Shuangyin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Long-lived polarization memory in the electronic states of lead-halide perovskites from local structural dynamics
Long-lived polarization memory in the electronic states of lead-halide perovskites from local structural dynamics
Anharmonic ultrafast structural dynamics are expected in lead halide perovskites due to their soft nature. Here Rivett et al. show that these dynamics lead to picosecond-long polarization anisotropy of photo-carriers in several halide perovskites, orders of magnitude slower than in conventional semiconductors.
- Jasmine P. H. Rivett
- , Liang Z. Tan
- & Felix Deschler
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative mappings between symmetry and topology in solids
Quantitative mappings between symmetry and topology in solids
The defining quantities of topological materials—the topological invariants—are often difficult to calculate. Here, Song et al. report a simplified method to calculate both the symmetry data and the topological invariants for arbitrary gapped band structure with time-reversal symmetry.
- Zhida Song
- , Tiantian Zhang
- & Chen Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Color-stable highly luminescent sky-blue perovskite light-emitting diodes
Color-stable highly luminescent sky-blue perovskite light-emitting diodes
Perovskite light-emitting diodes show promising color tunability and device performance but suffer from emission color shift at higher driving voltages. Here Xing et al. report color stable blue light-emitting diodes by drastically increasing the phase purity of the quasi-2D perovskite thin films.
- Jun Xing
- , Yongbiao Zhao
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Article
| Open Access The photoregulation of a mechanochemical polymer scission
The photoregulation of a mechanochemical polymer scission
Control over mechanochemical polymer scission by external stimuli may offer an avenue to further advance the fields of polymer chemistry, mechanochemistry, and materials science. Here the authors show light regulating the mechanochemical behavior of a diarylethene-conjugated Diels–Alder adduct.
- Jumpei Kida
- , Keiichi Imato
- & Hideyuki Otsuka
-
Article
| Open Access Role of hydrogen bonding in hysteresis observed in sorption-induced swelling of soft nanoporous polymers
Role of hydrogen bonding in hysteresis observed in sorption-induced swelling of soft nanoporous polymers
Water uptake of natural polymers is accompanied by swelling and changes in the internal structure of the polymeric system but the exact mechanism of water-uptake and swelling remained unknown. Here the authors use atom-scale simulations to identify a molecular mechanism which is responsible for hysteresis in sorption-induced swelling in natural polymers.
- Mingyang Chen
- , Benoit Coasne
- & Jan Carmeliet
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient and scalable synthesis of highly aligned and compact two-dimensional nanosheet films with record performances
Efficient and scalable synthesis of highly aligned and compact two-dimensional nanosheet films with record performances
Aligning 2D nanosheets to form a compact layered structure can maximize the in-plane properties. Here the authors report an efficient and scalable continuous centrifugal casting method to produce highly compact and well-aligned films of GO nanosheets that show record performances in some applications.
- Jing Zhong
- , Wei Sun
- & Wencai Ren
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance artificial nitrogen fixation at ambient conditions using a metal-free electrocatalyst
High-performance artificial nitrogen fixation at ambient conditions using a metal-free electrocatalyst
Electrochemical reduction of nitrogen is a promising route to industrial-scale nitrogen fixation at ambient conditions, but is challenged by activation of inert nitrogen. Here the authors report a metal-free catalyst that selectively reduces nitrogen to ammonia with high efficiency and stability.
- Weibin Qiu
- , Xiao-Ying Xie
- & Xuping Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Transformation from crystalline precursor to perovskite in PbCl2-derived MAPbI3
Transformation from crystalline precursor to perovskite in PbCl2-derived MAPbI3
The existence of a crystalline precursor is key to perovskite film formation, but the precise chemistry of the precursor and its transformation into perovskite are poorly understood. Here, the authors identify the crystal structure and conversion chemistry of the precursor for PbCl2-derived methylammonium lead iodide perovskites.
- Kevin H. Stone
- , Aryeh Gold-Parker
- & Christopher J. Tassone
-
Article
| Open Access A molecular overlayer with the Fibonacci square grid structure
A molecular overlayer with the Fibonacci square grid structure
Quasicrystals possess long range order but no translational symmetry, and rotational symmetries that are forbidden in periodic crystals. Here, a fullerene overlayer deposited on a surface of an icosahedral intermetallic quasicrystal achieves a Fibonacci square grid structure, by selective adsorption at specific sites.
- Sam Coates
- , Joseph A. Smerdon
- & Hem Raj Sharma
-
Article
| Open Access Active site localization of methane oxidation on Pt nanocrystals
Active site localization of methane oxidation on Pt nanocrystals
The structural changes at low-coordination sites of nanocatalysts such as edges, remain poorly understood. Here, the authors report observations of high-lattice distortion at edges of Pt nanocrystals during heterogeneous catalytic methane oxidation by using in situ 3D Bragg coherent X-ray diffraction imaging.
- Dongjin Kim
- , Myungwoo Chung
- & Hyunjung Kim
-
Article
| Open Access High entropy oxides for reversible energy storage
High entropy oxides for reversible energy storage
High entropy oxides provide a new strategy toward materials design by stabilizing single-phase crystal structures composed of multiple cations. Here, the authors apply this concept to the development of conversion-type electrode materials for lithium-ion storage and show the underlying mechanism.
- Abhishek Sarkar
- , Leonardo Velasco
- & Ben Breitung
-
Article
| Open Access Peritectic titanium alloys for 3D printing
Peritectic titanium alloys for 3D printing
3D printing of titanium alloys today is based on known alloy compositions that result in anisotropic structural properties. Here, the authors add lanthanum to commercially pure titanium and exploit a solidification path that reduces texture and anisotropy.
- Pere Barriobero-Vila
- , Joachim Gussone
- & Guillermo Requena
-
Article
| Open Access Accelerated discovery of stable lead-free hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites via machine learning
Accelerated discovery of stable lead-free hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites via machine learning
Conventional trial-error method is inefficient in discovering new functional materials in vast chemical and structural space. Here Lu et al. use machine learning techniques to screen out the most promising lead-free organic-inorganic perovskites with proper bandgap and stability from thousands of them in a flash.
- Shuaihua Lu
- , Qionghua Zhou
- & Jinlan Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Impact ionization by hot carriers in a black phosphorus field effect transistor
Impact ionization by hot carriers in a black phosphorus field effect transistor
Carrier multiplication processes based on new electron-hole pair generation is instrumental to realizing ultrafast and efficient optoelectronic devices. Here, the authors demonstrate multilayered black phosphorous-based transistors that show enhanced performance due to carrier multiplication.
- Faisal Ahmed
- , Young Duck Kim
- & Won Jong Yoo
-
Article
| Open Access Morphology and structure of ZIF-8 during crystallisation measured by dynamic angle-resolved second harmonic scattering
Morphology and structure of ZIF-8 during crystallisation measured by dynamic angle-resolved second harmonic scattering
Angle-resolved monitoring of structure parameters during crystal growth is often slow owing to mechanical movements. Here, the authors use second harmonic scattering and Fourier-plane imaging to dynamically monitor size, shape and concentration of ZIF-8 in situ during the growth process.
- Stijn Van Cleuvenbergen
- , Zachary J. Smith
- & Monique A. van der Veen
-
Article
| Open Access In-built thermo-mechanical cooperative feedback mechanism for self-propelled multimodal locomotion and electricity generation
In-built thermo-mechanical cooperative feedback mechanism for self-propelled multimodal locomotion and electricity generation
Existing thermal technologies are mainly designed to harvest heat at high temperature, whilst low-grade heat is hardly utilized to date. Here, Wang et al. show an interlocked thermo-mechano feedback mechanism that transfers ambient heat to multimodal locomotions, potentially for soft robotics applications.
- Xiao-Qiao Wang
- , Chuan Fu Tan
- & Ghim Wei Ho
-
Article
| Open Access Intertidal exposure favors the soft-studded armor of adaptive mussel coatings
Intertidal exposure favors the soft-studded armor of adaptive mussel coatings
There is interest in the development of mussel inspired materials; however, this requires an understanding of the materials. Here, the authors report on an investigation into the properties of mussel cuticle from different species that challenges conventional wisdom about particle filled composites.
- Christophe A. Monnier
- , Daniel G. DeMartini
- & J. Herbert Waite

 Hydrogen spillover through Matryoshka-type (ZIFs@)n−1ZIFs nanocubes
Hydrogen spillover through Matryoshka-type (ZIFs@)n−1ZIFs nanocubes