Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmonic piezoelectric nanomechanical resonator for spectrally selective infrared sensing
Plasmonic piezoelectric nanomechanical resonator for spectrally selective infrared sensing
Plasmonic metasurfaces can provide exciting optical functionalities. Here, Hui et al. demonstrate an infrared sensor by combining plasmonic and piezoelectric electromechanical resonances, demonstrating efficient transduction of vibration with a strong and polarization-independent absorption over an ultrathin thickness.
- Yu Hui
- , Juan Sebastian Gomez-Diaz
- & Matteo Rinaldi
-
Article
| Open Access Free-carrier-induced soliton fission unveiled by in situ measurements in nanophotonic waveguides
Free-carrier-induced soliton fission unveiled by in situ measurements in nanophotonic waveguides
Solitons are nonlinear waves that exist in diverse forms of matter. Here, Husko et al. use near-field measurements to observe the spatio-temporal evolution of optical pulses in a nanophotonic semiconductor waveguide, demonstrating that nonlinear photo-carrier generation can induce fission of solitons.
- Chad Husko
- , Matthias Wulf
- & L. Kuipers
-
Article
| Open Access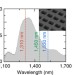 Magnetic hyperbolic optical metamaterials
Magnetic hyperbolic optical metamaterials
The ability to control both electric and magnetic dispersion of light allows a novel type of hyperbolic material with impedance matched to air. Here, the authors show experimentally a topological transition between elliptic and magnetic hyperbolic dispersions in a metamaterial for control of thermal radiation.
- Sergey S. Kruk
- , Zi Jing Wong
- & Xiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Giant photostriction in organic–inorganic lead halide perovskites
Giant photostriction in organic–inorganic lead halide perovskites
The photophysics of lead halide perovskites is under intense investigation. Here, the authors use force microscopy on single crystals to show that light induces drastic lattice changes, and propose that the weakening of the hydrogen coupling under illumination is responsible for the lattice dilatation.
- Yang Zhou
- , Lu You
- & Junling Wang
-
Article
| Open Access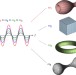 Geometry-invariant resonant cavities
Geometry-invariant resonant cavities
Resonant cavities are a ubiquitous building block in science and technology. Here, Liberal et al. demonstrate theoretically the existence of resonators whose eigenfrequencies are invariant with respect to geometrical deformations of their external boundaries, by exploiting the unusual properties of zero-index metamaterials.
- I. Liberal
- , A. M. Mahmoud
- & N. Engheta
-
Article
| Open Access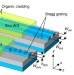 Lasing in silicon–organic hybrid waveguides
Lasing in silicon–organic hybrid waveguides
On-chip light sources for silicon photonic circuits remain a challenge since the indirect bandgap of silicon prevents efficient light emission. The authors demonstrate that lasing can be achieved by combining standard silicon-on-insulator waveguides with dye-doped organic cladding materials to provide optical gain.
- Dietmar Korn
- , Matthias Lauermann
- & Christian Koos
-
Article
| Open Access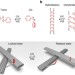 A light-driven three-dimensional plasmonic nanosystem that translates molecular motion into reversible chiroptical function
A light-driven three-dimensional plasmonic nanosystem that translates molecular motion into reversible chiroptical function
Controlled operation of individual molecular machines on a larger scale, 10-100 nm, remains challenging. Here, Kuzyk et al.demonstrate a light-driven plasmonic nanosystem that can amplify the molecular motion of azobenzene through a host nanostructure and translates it into reversible chiroptical response.
- Anton Kuzyk
- , Yangyang Yang
- & Na Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Amplification and generation of ultra-intense twisted laser pulses via stimulated Raman scattering
Amplification and generation of ultra-intense twisted laser pulses via stimulated Raman scattering
High intensity light with a non-zero orbital angular momentum could aid the development of laser-wakefield particle accelerators. Here, the authors theoretically show that stimulated Raman backscattering in plasmas can generate and amplify orbital angular momentum lasers to petawatt intensities.
- J. Vieira
- , R. M. G. M. Trines
- & L. O. Silva
-
Article
| Open Access Towards do-it-yourself planar optical components using plasmon-assisted etching
Towards do-it-yourself planar optical components using plasmon-assisted etching
Recently, there has been a growing interest in do-it-yourself components to accelerate development of inexpensive fabrication approaches. Here, Chen et al.present a plasmon-assisted etching technique to fabricate planar optical components using arrays of gold pillar-supported bowtie nanoantennas as a template.
- Hao Chen
- , Abdul M. Bhuiya
- & Kimani C. Toussaint Jr
-
Article
| Open Access Subwavelength nonlinear phase control and anomalous phase matching in plasmonic metasurfaces
Subwavelength nonlinear phase control and anomalous phase matching in plasmonic metasurfaces
The fundamental issue of phase-matching across metasurfaces has not been thoroughly addressed. Here, Almeida et al. show full phase control by introducing a spatially varying phase response of a metallic metasurface consisting of subwavelength nanoantennas and demonstrate metasurface-phase-matching.
- Euclides Almeida
- , Guy Shalem
- & Yehiam Prior
-
Article
| Open Access Host–guest chemistry for tuning colloidal solubility, self-organization and photoconductivity of inorganic-capped nanocrystals
Host–guest chemistry for tuning colloidal solubility, self-organization and photoconductivity of inorganic-capped nanocrystals
The high polarity of colloidal inorganic-ligand-functionalized nanocrystals can be problematic for their processing, limiting their optoelectronic applications. Here, by complexation with macrocycles, the authors enabled broad amphiphilicity of such nanocrystals and processing from a variety of solvents.
- Maryna I. Bodnarchuk
- , Sergii Yakunin
- & Maksym V. Kovalenko
-
Article
| Open Access Phase diagram for the transition from photonic crystals to dielectric metamaterials
Phase diagram for the transition from photonic crystals to dielectric metamaterials
Distinguishing between photonic crystals and metamaterials can provide a path for designing low-loss artificial materials with a range of novel applications. Here, Rybin et al. introduce a concept of phase transitions between all-dielectric metamaterials and photonic crystals based on the physics of Mie and Bragg resonances.
- Mikhail V. Rybin
- , Dmitry S. Filonov
- & Mikhail F. Limonov
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional magnetic cloak working from d.c. to 250 kHz
Three-dimensional magnetic cloak working from d.c. to 250 kHz
The development of invisibility cloaks which function at low frequencies are of practical importance, especially for magnetic fields involved in modern technologies. Here, Zhu et al. develop the bilayer approach to create a three-dimensional magnetic cloak able to work in both static and dynamic fields.
- Jianfei Zhu
- , Wei Jiang
- & Yungui Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast collisional ion heating by electrostatic shocks
Ultrafast collisional ion heating by electrostatic shocks
Short pulses of high intensity laser light usually heat the ions in dense plasmas indirectly via collisions with the electrons. Here, the authors identify an extremely rapid alternative heating mechanism based on ion-ion collisions.
- A. E. Turrell
- , M. Sherlock
- & S. J. Rose
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid graphene plasmonic waveguide modulators
Hybrid graphene plasmonic waveguide modulators
The combination of graphene with plasmonic waveguides remains largely unexplored. Here, Ansell et al. report the fabrication of hybrid graphene plasmonic waveguide modulators working in the telecom range, with a modulation depth greater than 0.03 dB μm−1and with comparable characteristics to silicon-based devices.
- D. Ansell
- , I. P. Radko
- & A. N. Grigorenko
-
Article
| Open Access Reversible gating of smart plasmonic molecular traps using thermoresponsive polymers for single-molecule detection
Reversible gating of smart plasmonic molecular traps using thermoresponsive polymers for single-molecule detection
Conventional substrates used for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) are slow in response and lack reproducibility. Here, Zheng et al.describe a plasmonic sensor that can trap a single molecule at hot spots for rapid single-molecule detection with repeated trap and release capability and good SERS reproducibility.
- Yuanhui Zheng
- , Alexander H. Soeriyadi
- & J. Justin Gooding
-
Article
| Open Access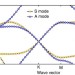 Topologically protected elastic waves in phononic metamaterials
Topologically protected elastic waves in phononic metamaterials
Metamaterials are engineered media with properties that mimic those of natural materials, but offer a much wider range of possibilities. Here, the authors numerically demonstrate an elastic-wave analogue of the quantum spin Hall effect in a phononic topological metamaterial.
- S. Hossein Mousavi
- , Alexander B. Khanikaev
- & Zheng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Optical meta-atom for localization of light with quantized energy
Optical meta-atom for localization of light with quantized energy
Plasmonics enables the medication of light on length-scales smaller than the wavelength of the light. Here, the authors present a theoretical investigation of optical meta-atoms based on core-shell plasmonic nanostructures, where light is confined into a small region of space.
- Sylvain Lannebère
- & Mário G. Silveirinha
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic control of light emission faster than the lifetime limit using VO2 phase-change
Dynamic control of light emission faster than the lifetime limit using VO2 phase-change
Erbium ions offer a way to integrate light emitters into silicon electronics, but their radiative decay time is too slow for effective light modulation. Here, the authors use phase changes in vanadium dioxide to enable all-optical modulation more than a thousand times faster than the erbium excited-state lifetime.
- Sébastien Cueff
- , Dongfang Li
- & Rashid Zia
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast electronic state conversion at room temperature utilizing hidden state in cuprate ladder system
Ultrafast electronic state conversion at room temperature utilizing hidden state in cuprate ladder system
Controlling material properties on sub-picosecond scales using photons could allow for ultrafast optoelectronic devices. Here, the authors propose an ultrafast photoinduced metal-to-insulator transition in a two-leg ladder cuprate superconductor based on time-resolved reflection spectroscopy.
- R. Fukaya
- , Y. Okimoto
- & T. Sasagawa
-
Article
| Open Access Purely organic electroluminescent material realizing 100% conversion from electricity to light
Purely organic electroluminescent material realizing 100% conversion from electricity to light
Organic light-emitting diodes promise a more environment-friendly future for light sources, but many use rare metals. Here, the authors present an approach that achieves external quantum efficiency over 40% by realising 100% up-conversion from triplet to singlet excitons and thus 100% radiative emission.
- Hironori Kaji
- , Hajime Suzuki
- & Chihaya Adachi
-
Article
| Open Access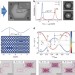 Dynamic acousto-optic control of a strongly coupled photonic molecule
Dynamic acousto-optic control of a strongly coupled photonic molecule
Dynamic control of components is required for large-scale quantum photonic networks. Here, Kapfingeret al. show dynamic control of the interaction between two coupled photonic crystal nanocavities forming a photonic molecule. Tuning is achieved by using an electrically generated radio frequency surface acoustic wave.
- Stephan Kapfinger
- , Thorsten Reichert
- & Hubert J. Krenner
-
Article
| Open Access Enantiomeric switching of chiral metamaterial for terahertz polarization modulation employing vertically deformable MEMS spirals
Enantiomeric switching of chiral metamaterial for terahertz polarization modulation employing vertically deformable MEMS spirals
Spectroscopy in the terahertz range requires polarization modulation. Here, Kan et al.demonstrate a chirality switchable metamaterial for polarization modulation employing deformable spirals. A polarization rotation as high as 28° is achieved, providing a practical and compact polarization modulator for the terahertz range.
- Tetsuo Kan
- , Akihiro Isozaki
- & Isao Shimoyama
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-low-power hybrid light–matter solitons
Ultra-low-power hybrid light–matter solitons
Harnessing nonlinear optics in optoelectronic devices requires a platform that exhibits both giant optical nonlinearity and is compatible with photonic-circuit fabrication. Here, the authors demonstrate such a system that uses strong light–matter coupling between waveguide photons and quantum-well excitons.
- P. M. Walker
- , L. Tinkler
- & D. N. Krizhanovskii
-
Article
| Open Access Highly efficient and ultra-broadband graphene oxide ultrathin lenses with three-dimensional subwavelength focusing
Highly efficient and ultra-broadband graphene oxide ultrathin lenses with three-dimensional subwavelength focusing
Lenses made from metamaterials often suffer from narrow operational bandwidth and complex design. Here, Zheng et al.demonstrate an ultrathin graphene oxide lens with farfield three-dimensional subwavelength focusing from the visible to near infrared and an absolute focusing efficiency greater than 32%.
- Xiaorui Zheng
- , Baohua Jia
- & Min Gu
-
Article
| Open Access A new class of tunable hypersonic phononic crystals based on polymer-tethered colloids
A new class of tunable hypersonic phononic crystals based on polymer-tethered colloids
Hybridization-type band gaps are known to persist in phononic crystals, but their fabrication remains challenging for all-solid hypersonic composites. Here, the authors utilize the elastic anisotropy at the interface of polymer-tethered colloidal particles to control phonon propagation in GHz regime.
- E. Alonso-Redondo
- , M. Schmitt
- & G. Fytas
-
Article
| Open Access Absorption-induced scattering and surface plasmon out-coupling from absorber-coated plasmonic metasurfaces
Absorption-induced scattering and surface plasmon out-coupling from absorber-coated plasmonic metasurfaces
Plasmonic surfaces are used as two-dimensional metamaterials for light manipulation on nanoscale, and their optical properties can be further tuned by coating. Here the authors report a new absorption-induced scattering mode in a silver nanoparticle array coated with semiconducting organic absorbers.
- Christopher E. Petoukhoff
- & Deirdre M. O’Carroll
-
Article
| Open Access Eliminating material constraints for nonlinearity with plasmonic metamaterials
Eliminating material constraints for nonlinearity with plasmonic metamaterials
Nonlinear optical properties of conventional materials have limited spectral tuneability as they are defined by the material properties themselves. Here, the authors demonstrate that strong nonlinearity can be achieved in metamaterials where negligible nonlinearity of the constituent materials exists.
- Andres D. Neira
- , Nicolas Olivier
- & Anatoly V. Zayats
-
Article
| Open Access Spin–cavity interactions between a quantum dot molecule and a photonic crystal cavity
Spin–cavity interactions between a quantum dot molecule and a photonic crystal cavity
Optical cavities enhance light–matter interactions, and have been used to strongly couple a photon to a single spin. Here, the authors take this a step further by coupling a photon to a two-spin system by embedding an indium arsenide quantum-dot molecule in a photonic crystal cavity.
- Patrick M. Vora
- , Allan S. Bracker
- & Daniel Gammon
-
Article
| Open Access A spectrally tunable all-graphene-based flexible field-effect light-emitting device
A spectrally tunable all-graphene-based flexible field-effect light-emitting device
Wavelength tuning of a light emitting diode (LED) by an external electrical bias would benefit display technologies. Here, Wang et al. demonstrate wavelength-tuning from blue to the near-infrared in an all-graphene-based field effect LED by gate modulation
- Xiaomu Wang
- , He Tian
- & Tian-Ling Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Single-step fabrication of quantum funnels via centrifugal colloidal casting of nanoparticle films
Single-step fabrication of quantum funnels via centrifugal colloidal casting of nanoparticle films
Centrifugal casting is widely used to fabricate functional materials that exhibit built-in spatial gradients due to the variation in material density. Kim et al.use this method to prepare colloidal quantum dot films for the first time, based on which photodetectors with gradient bandgap are built.
- Jin Young Kim
- , Valerio Adinolfi
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Article
| Open Access Hot electron-induced reduction of small molecules on photorecycling metal surfaces
Hot electron-induced reduction of small molecules on photorecycling metal surfaces
Hot electrons are generated when energy is transferred from an incoming photon, enabling an electron from a metal surface to become mobile. Here, the authors irradiate plasmonically active silver core-satellite superstructures and use the hot electrons to effect chemical reactions via photorecycling.
- Wei Xie
- & Sebastian Schlücker
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental evidence of new tetragonal polymorphs of silicon formed through ultrafast laser-induced confined microexplosion
Experimental evidence of new tetragonal polymorphs of silicon formed through ultrafast laser-induced confined microexplosion
Ordinary materials can transform into exotic phases with new crystal structures at high pressure and temperature. Here, the authors demonstrate metastable phases of silicon, created by confined microexplosions initiated by ultrafast laser pulses, that are preserved for further utilisation.
- L. Rapp
- , B. Haberl
- & A.V. Rode
-
Article
| Open Access Colloidal metasurfaces displaying near-ideal and tunable light absorbance in the infrared
Colloidal metasurfaces displaying near-ideal and tunable light absorbance in the infrared
Metasurfaces are arrays of subwavelength structures that are tailored to produce specific optical responses. Rozin et al.show that large-area metasurfaces can be readily fabricated by self-assembly of colloidal nanocrystals of different geometries, producing tunable reflectance and absorbance properties.
- Matthew J. Rozin
- , David A. Rosen
- & Andrea R. Tao
-
Article
| Open Access Photonic sensing of organic solvents through geometric study of dynamic reflection spectrum
Photonic sensing of organic solvents through geometric study of dynamic reflection spectrum
Photonic sensing is a method for detecting individual chemical species, but can fail when they are sufficiently similar in physical properties. Here, the authors report a method that can distinguish even very closely related species, such as homologues and chemical isomers.
- Yuqi Zhang
- , Qianqian Fu
- & Jianping Ge
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental demonstration of a non-resonant hyperlens in the visible spectral range
Experimental demonstration of a non-resonant hyperlens in the visible spectral range
Metamaterial hyperlenses convert evanescent waves into propagating ones, thereby beating the diffraction limit. Sun et al. present a non-resonant waveguide-integrated hyperlens designed around a radial fan structure that provides imaging at visible wavelengths with low losses.
- Jingbo Sun
- , Mikhail I. Shalaev
- & Natalia M. Litchinitser
-
Article
| Open Access Wearable red–green–blue quantum dot light-emitting diode array using high-resolution intaglio transfer printing
Wearable red–green–blue quantum dot light-emitting diode array using high-resolution intaglio transfer printing
Deformable and high-resolution LEDs have attracted great interest for wearable electronics, but full-colour display is still challenging. Using a stamp printing technology, Choi et al. build ultra-thin RGB quantum dot pixel arrays with luminous efficiency of 14,000 cd m−2operated at low voltage of 7 V.
- Moon Kee Choi
- , Jiwoong Yang
- & Dae-Hyeong Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Active graphene–silicon hybrid diode for terahertz waves
Active graphene–silicon hybrid diode for terahertz waves
Graphene has demonstrated the ability to modulate terahertz (THz) waves by optical or electrical excitation, but modulation depths have been low. Here, Li et al. demonstrate enhanced modulation and polarity-dependent THz attenuation using external voltage bias and photoexcitation on a graphene–silicon film.
- Quan Li
- , Zhen Tian
- & Weili Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Stochasticity, periodicity and localized light structures in partially mode-locked fibre lasers
Stochasticity, periodicity and localized light structures in partially mode-locked fibre lasers
The interplay of processes with different spatio-temporal scales is present in many physical systems but its study is challenging. Here, Churkin et al. study the dynamics of a partially mode-locked laser where stochastic and periodic processes interplay by mapping the evolution of the intensity autocorrelation function.
- D. V. Churkin
- , S. Sugavanam
- & S. K. Turitsyn
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetically induced forward scattering at visible wavelengths in silicon nanosphere oligomers
Magnetically induced forward scattering at visible wavelengths in silicon nanosphere oligomers
A weak and narrow electric dipole has limited the use of silicon nanospheres in nanophotonic applications requiring strong interaction between electric and magnetic modes. Here, Yan et al.demonstrate effective coupling between the magnetic resonance and the electric gap mode in nearly touching silicon nanospheres.
- J. H. Yan
- , P. Liu
- & G. W. Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Subdiffractional focusing and guiding of polaritonic rays in a natural hyperbolic material
Subdiffractional focusing and guiding of polaritonic rays in a natural hyperbolic material
Hexagonal boron nitride has many interesting properties, including a natural hyperbolic dispersion, making it attractive for nanophotonic applications. Here, Dai et al. show that metallic disks under the material launch phonon–polaritons, turning it into a hyper-focusing lens.
- S. Dai
- , Q. Ma
- & D. N. Basov
-
Article |
 Optically switchable transistors by simple incorporation of photochromic systems into small-molecule semiconducting matrices
Optically switchable transistors by simple incorporation of photochromic systems into small-molecule semiconducting matrices
Organic thin-film transistors can be photomodulated by incorporating photochromic molecules, but the state-of-the-art suffers from poor charge transport. Here, the authors improve charge mobility by three orders of magnitude by blending small conjugated molecules into diarylethene.
- Mirella El Gemayel
- , Karl Börjesson
- & Paolo Samorì
-
Article |
 Interference and holography with femtosecond laser pulses of different colours
Interference and holography with femtosecond laser pulses of different colours
High-contrast fringes and holographic grating imprinting rely on the coherence of the superimposing beams, and thus, it typically requires the interference of beams originating from a single laser. Here, Odoulov et al. demonstrate that holographic grating recording is possible using pulses of different colour.
- Serguey Odoulov
- , Alexandr Shumelyuk
- & Mirco Imlau
-
Article
| Open Access Femtosecond all-optical synchronization of an X-ray free-electron laser
Femtosecond all-optical synchronization of an X-ray free-electron laser
Few-femtosecond synchronization at free-electron lasers is key for nearly all experimental applications, stable operation and future light source development. Here, Schulz et al. demonstrate all-optical synchronization of the soft X-ray FEL FLASH to better than 30 fs and illustrate a pathway to sub-10 fs.
- S. Schulz
- , I. Grguraš
- & A. L. Cavalieri
-
Article
| Open Access Dip-pen patterning of poly(9,9-dioctylfluorene) chain-conformation-based nano-photonic elements
Dip-pen patterning of poly(9,9-dioctylfluorene) chain-conformation-based nano-photonic elements
The optoelectronic properties of semiconducting polymers are controlled by altering chemical structure and/or inter-chain order. Perevedentsev et al. propose a nanopatterning approach whereby the geometry of polymer chain segments is modified to engineer metamaterial structures for visible light.
- Aleksandr Perevedentsev
- , Yannick Sonnefraud
- & Donal D. C. Bradley
-
Article |
 An invisible acoustic sensor based on parity-time symmetry
An invisible acoustic sensor based on parity-time symmetry
Any typical sensing device must absorb energy, thereby altering the measured signal as it propagates on. By exploiting parity-time symmetry via non-Foster circuits, Fleury et al. show that a sensor can be built that absorbs incoming signals without perturbing them or creating a shadow, rendering it invisible.
- Romain Fleury
- , Dimitrios Sounas
- & Andrea Alù
-
Article
| Open Access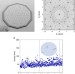 Photonic quasi-crystal terahertz lasers
Photonic quasi-crystal terahertz lasers
Various vertical surface emitting, terahertz quantum-cascade lasers have been proposed recently but these suffer from power cancellations in the far-field and limited extraction efficiencies. Here, Vitiello et al.circumvent these issues using two-dimensional photonic quasi-crystalline resonators.
- Miriam Serena Vitiello
- , Michele Nobile
- & A. Giles Davies
-
Article |
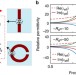 Microwave gain medium with negative refractive index
Microwave gain medium with negative refractive index
Negative index metamaterials have been proposed for super-lensing and electromagnetic invisibility but real applications have been hindered by their high losses. Here, Ye et al.demonstrate an effective gain medium that overcompensates the loss of a passive metamaterial while keeping its negative index.
- Dexin Ye
- , Kihun Chang
- & Hao Xin
-
Article |
 Solution-processed multilayer small-molecule light-emitting devices with high-efficiency white-light emission
Solution-processed multilayer small-molecule light-emitting devices with high-efficiency white-light emission
High-efficiency organic light-emitting devices usually require the growth of many layers of different materials by vapour deposition in vacuum. Naoya Aizawa et al. demonstrate the fabrication of high-efficiency multilayer organic LEDs from solution.
- Naoya Aizawa
- , Yong-Jin Pu
- & Junji Kido

 Giant photoluminescence enhancement in tungsten-diselenide–gold plasmonic hybrid structures
Giant photoluminescence enhancement in tungsten-diselenide–gold plasmonic hybrid structures