Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid and high-resolution patterning of microstructure and composition in organic semiconductors using ‘molecular gates’
Rapid and high-resolution patterning of microstructure and composition in organic semiconductors using ‘molecular gates’
Although high‐resolution methods such as photolithography allow for organic semiconductor patterning, they are often limited by their high complexity. Here, the authors report a versatile “molecular gate”‐based method for micro‐patterning organic semiconductor films.
- Aleksandr Perevedentsev
- & Mariano Campoy-Quiles
-
Article
| Open Access Highly nonlinear trion-polaritons in a monolayer semiconductor
Highly nonlinear trion-polaritons in a monolayer semiconductor
Here, the authors report the creation of trion-polaritons in monolayer MoSe2 in an open microcavity exhibiting strong nonlinear interactions, one order of magnitude bigger than those observed for exciton polaritons in GaAs.
- R. P. A. Emmanuele
- , M. Sich
- & D. N. Krizhanovskii
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-single exciton optical gain threshold in colloidal semiconductor quantum wells with gradient alloy shelling
Sub-single exciton optical gain threshold in colloidal semiconductor quantum wells with gradient alloy shelling
Colloidal quantum wells are highly promising for applications of solution-processed lasers, but their performance is limited by multi-excitonic nature of the materials. Here, the authors demonstrate optical gain in graded alloy core/shell CdSe/CdS@CdZnS quantum wells at less than one exciton per particle resulting in ultralow thresholds.
- Nima Taghipour
- , Savas Delikanli
- & Hilmi Volkan Demir
-
Article
| Open Access Overcoming evanescent field decay using 3D-tapered nanocavities for on-chip targeted molecular analysis
Overcoming evanescent field decay using 3D-tapered nanocavities for on-chip targeted molecular analysis
Plasmon-enhanced fluorescence is strictly dependent on molecule size and surface position, restricting application of diversely sized molecules. Here, the authors overcome this by introducing a 3D tapered gap plasmon nanocavity with fluidic access and near homogeneous confinement of the electromagnetic fields.
- Shailabh Kumar
- , Haeri Park
- & Hyuck Choo
-
Article
| Open Access Tuning molecular emission of organic emitters from fluorescence to phosphorescence through push-pull electronic effects
Tuning molecular emission of organic emitters from fluorescence to phosphorescence through push-pull electronic effects
Though organic emitters with room temperature phosphorescence (RTP) are attractive for various applications, realizing highly efficient and long lifetime emission remains a challenge. Here, the authors report the role of push-pull electronic effects on emission for organic RTP emitters.
- Hai-Tao Feng
- , Jiajie Zeng
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Buoyant particulate strategy for few-to-single particle-based plasmonic enhanced nanosensors
Buoyant particulate strategy for few-to-single particle-based plasmonic enhanced nanosensors
Plasmonic-enhanced nanosensors are limited in practical applications, as it remains challenging to detect molecules at low concentrations. Here, the authors introduce a buoyant particulate strategy in order to enrich analytes in the plasmonic hot spots.
- Dongjie Zhang
- , Leqin Peng
- & Jixiang Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Extrinsic nature of the broad photoluminescence in lead iodide-based Ruddlesden–Popper perovskites
Extrinsic nature of the broad photoluminescence in lead iodide-based Ruddlesden–Popper perovskites
The Ruddlesden–Popper type of halide perovskites are gaining interest but the origin of their broad band emission remains elusive. Here Kahmann et al. suggest that in-gap states, instead of the commonly believed self-trapped excitons, are responsible for the broad band emission in crystalline samples.
- Simon Kahmann
- , Eelco K. Tekelenburg
- & Maria A. Loi
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrathin 2 nm gold as impedance-matched absorber for infrared light
Ultrathin 2 nm gold as impedance-matched absorber for infrared light
Long-term stability and broad spectral response are highly desired features of absorbers. Here, the authors report impedance matched absorbers based on 2 nm thick gold layer operating within the mid-infrared range from 2 to 20 μm, enabling stable long term absorptivity of 47(3) % which is mostly wavelength independent.
- Niklas Luhmann
- , Dennis Høj
- & Silvan Schmid
-
Article
| Open Access Solar-blind ultraviolet-C persistent luminescence phosphors
Solar-blind ultraviolet-C persistent luminescence phosphors
Ultraviolet-C radiation sources are important for disinfection and photochemical water purification, but development of persistent phosphors is needed for other applications. Here the authors report praseodymium-doped silicate ultraviolet-C persistent phosphors for self-sustained glowing tags in bright light.
- Xianli Wang
- , Yafei Chen
- & Zhengwei Pan
-
Article
| Open Access Exciton diffusion in two-dimensional metal-halide perovskites
Exciton diffusion in two-dimensional metal-halide perovskites
The so-called two-dimensional (2D) layered perovskites possess distinct optoelectronic properties from their 3D counterparts due to their reduced dimensionality. Here Seitz et al. investigate the exciton transport dynamics in 2D perovskites and highlight the impact of the stiffness of the lattice.
- Michael Seitz
- , Alvaro J. Magdaleno
- & Ferry Prins
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of quadratic Weyl points and double-helicoid arcs
Observation of quadratic Weyl points and double-helicoid arcs
Novel topological quasiparticles have attracted many interests recently. Here, He et al. observe quadratic Weyl points and identify double-helicoid surface arcs in sound waves traveling in a three-dimensional chiral metacrystal.
- Hailong He
- , Chunyin Qiu
- & Zhengyou Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Nanosecond-time-scale delayed fluorescence molecule for deep-blue OLEDs with small efficiency rolloff
Nanosecond-time-scale delayed fluorescence molecule for deep-blue OLEDs with small efficiency rolloff
Deep-blue emitting organic materials with low exciton lifetime are required to realize efficient organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) at high brightness. Here, the authors report deep-blue OLEDs featuring thermally activated delayed fluorescence molecules with subnano-second exciton lifetime.
- Jong Uk Kim
- , In Seob Park
- & Chihaya Adachi
-
Article
| Open Access Infrared dielectric metamaterials from high refractive index chalcogenides
Infrared dielectric metamaterials from high refractive index chalcogenides
High-index dielectric materials are in great demand for nanophotonic applications. Here, the authors show that chalcogenide topological insulators are suitable candidates for dielectric nanophotonics in the infrared spectral range by reporting resonances in Bi2Te3 crystals sustained in the mid-infrared.
- H. N. S. Krishnamoorthy
- , G. Adamo
- & C. Soci
-
Article
| Open Access Exfoliated near infrared fluorescent silicate nanosheets for (bio)photonics
Exfoliated near infrared fluorescent silicate nanosheets for (bio)photonics
Near-infrared (NIR) fluorophores have attracted interest for bioimaging; yet availability, biocompatibility and application can be an issue. Here, the authors report on the development of Egyptian Blue nanosheets with high NIR fluorescence and photostability demonstrating bioimaging applications in vivo.
- Gabriele Selvaggio
- , Alexey Chizhik
- & Sebastian Kruss
-
Article
| Open Access Conversionless efficient and broadband laser light diffusers for high brightness illumination applications
Conversionless efficient and broadband laser light diffusers for high brightness illumination applications
Laser-based lighting typically relies on wavelength conversion materials that reduce efficiency. The authors present a 3D boron nitride hollow-tube based foam structure that acts as a broadband diffuser with engineered disorder for conversionless white light generation from laser-diode light sources
- Fabian Schütt
- , Maximilian Zapf
- & Rainer Adelung
-
Article
| Open Access Structured graphene metamaterial selective absorbers for high efficiency and omnidirectional solar thermal energy conversion
Structured graphene metamaterial selective absorbers for high efficiency and omnidirectional solar thermal energy conversion
Here, the authors demonstrate a selective solar thermal absorber with wavelength selectivity, arising from metallic trench-like structures, using broadband dispersionless ultrathin graphene metamaterial film, with excellent thermal conductivity.
- Keng-Te Lin
- , Han Lin
- & Baohua Jia
-
Article
| Open Access Water-resistant perovskite nanodots enable robust two-photon lasing in aqueous environment
Water-resistant perovskite nanodots enable robust two-photon lasing in aqueous environment
Lead halide perovskite quantum dots (PQDs) promise applications in optoelectronics but are limited by sensitivity to wet environments. Here the authors develop a Pb-S bonding approach to synthesize PQDs@silica nanodots that are capable of emitting and lasing in aqueous environments for long periods.
- Siqi Li
- , Dangyuan Lei
- & Alex K.-Y. Jen
-
Article
| Open Access Continuous-wave quantum dot photonic crystal lasers grown on on-axis Si (001)
Continuous-wave quantum dot photonic crystal lasers grown on on-axis Si (001)
Fabricating semiconductor photonic lasers based on III-V materials are challenging because of the material mismatch with silicon. Here the authors monolithically grow quantum-dot-based photonic crystal membrane lasers directly on an on-axis silicon substrate.
- Taojie Zhou
- , Mingchu Tang
- & Huiyun Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Robust temporal pumping in a magneto-mechanical topological insulator
Robust temporal pumping in a magneto-mechanical topological insulator
A robust time-controlled energy pumping in a classical metamaterial remains to be achieved. Here, Grinberg et al. demonstrate a temporal topological pump that produces on-demand, robust transport of mechanical energy using a one-dimensional magneto-mechanical metamaterial.
- Inbar Hotzen Grinberg
- , Mao Lin
- & Gaurav Bahl
-
Article
| Open Access Long-living and highly efficient bio-hybrid light-emitting diodes with zero-thermal-quenching biophosphors
Long-living and highly efficient bio-hybrid light-emitting diodes with zero-thermal-quenching biophosphors
Bio-hybrid LEDs (HLED) are an environmental friendly alternative to LEDs based on inorganic phosphors but achieving long term is challenging. Here, the authors present a long-living Bio-HLED based on a zero-thermal-quenching biophosphor design and investigate the photo-induced heat generation and dissipation processes.
- Anna Espasa
- , Martina Lang
- & Rubén D. Costa
-
Article
| Open Access Synchronously wired infrared antennas for resonant single-quantum-well photodetection up to room temperature
Synchronously wired infrared antennas for resonant single-quantum-well photodetection up to room temperature
Applications of metasurfaces for optoelectronic devices require wiring to each isolated antenna for biasing and current flow. Here, the authors report optimal wire interconnects design for controlling the optical properties and present antenna-enhanced mid-infrared photodetection incorporating a single quantum well.
- Hideki T. Miyazaki
- , Takaaki Mano
- & Hiroshi Miyazaki
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmon–emitter interactions at the nanoscale
Plasmon–emitter interactions at the nanoscale
Plasmonic enhancements of light–matter interactions are generally maximal at short emitter–surface separations. Here, the authors investigate the impact of nonlocality, spill-out, and surface-assisted Landau damping at nanoscale separations using a mesoscopic electrodynamic framework.
- P. A. D. Gonçalves
- , Thomas Christensen
- & Marin Soljačić
-
Article
| Open Access Symmetry-protected hierarchy of anomalous multipole topological band gaps in nonsymmorphic metacrystals
Symmetry-protected hierarchy of anomalous multipole topological band gaps in nonsymmorphic metacrystals
Higher-order topological phenomenologies are usually observed separately, with each system giving rise to a specific type of topological insulator. Here, the authors realise a nonsymmorphic acoustic metacrystal where the first and the second band gap host dipole and quadrupole topology respectively.
- Xiujuan Zhang
- , Zhi-Kang Lin
- & Jian-Hua Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Slow recombination of spontaneously dissociated organic fluorophore excitons
Slow recombination of spontaneously dissociated organic fluorophore excitons
Though highly emissive charge-transfer type molecules in a host matrix is an attractive material for organic opto-electronics, concentration quenching limits photoluminescence quantum yield. Here, the authors report concentration quenching in fluorophores based on spontaneous exciton dissociation.
- Takahiko Yamanaka
- , Hajime Nakanotani
- & Chihaya Adachi
-
Article
| Open Access Photoresponsive spiro-polymers generated in situ by C–H-activated polyspiroannulation
Photoresponsive spiro-polymers generated in situ by C–H-activated polyspiroannulation
Photoresponsive polymers are receiving great attention due to the increasing demands on smart optical and biological materials. Here, the authors report a C–H-activated polyspiroannulation route to in situ generate photoresponsive spiro-polymers with potential applications in photopatterning and silicon photonics techniques.
- Ting Han
- , Zhanshi Yao
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access A rotary plasmonic nanoclock
A rotary plasmonic nanoclock
Current DNA-assembled nanophotonic devices can only reconfigure among random or few defined states. Here, the authors demonstrate a DNA-assembled rotary plasmonic nanoclock in which a rotor gold nanorod carries out directional and reversible 360° rotation transitioning among 16 well-defined configurations.
- Ling Xin
- , Chao Zhou
- & Na Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Locally collective hydrogen bonding isolates lead octahedra for white emission improvement
Locally collective hydrogen bonding isolates lead octahedra for white emission improvement
Low dimensional lead halide perovskites possess intriguing optical properties that are still under debate. Here Cui et al. use hydrogen bonds containing spacers to synthesize highly luminescent perovskites with fully isolated lead-bromide octahedras and shed light on the origin of the emission.
- Bin-Bin Cui
- , Ying Han
- & Qi Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Voltage-gated optics and plasmonics enabled by solid-state proton pumping
Voltage-gated optics and plasmonics enabled by solid-state proton pumping
The optical properties of certain metals can be reversibly switched by hydrogen loading but challenges remain to achieve electrical and reversible control. Here, the authors report a nanoscale proton switch that allows for electrical control of optical properties through electrochemical hydrogen gating.
- Mantao Huang
- , Aik Jun Tan
- & Geoffrey S. D. Beach
-
Article
| Open Access Photonic crystal for graphene plasmons
Photonic crystal for graphene plasmons
Traditional photonic crystals consist of periodic media with a pre-defined optical response. Here, the authors combine nanostructured back-gate insulators with a continuous layer of graphene to demonstrate an electrically tunable two-dimensional photonic crystal suitable for controlling the propagation of surface plasmon polaritons.
- L. Xiong
- , C. Forsythe
- & D. N. Basov
-
Article
| Open Access Dielectric multi-momentum meta-transformer in the visible
Dielectric multi-momentum meta-transformer in the visible
Here, the authors demonstrate a multi-momentum transformation metasurface. The orbital angular momentum meta-transformer reconstructs different vortex beams into on-axis distinct patterns, and the linear momentum meta-transformer converts red, green and blue beams to vivid color images.
- Lei Jin
- , Yao-Wei Huang
- & Cheng-Wei Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access Broadband transparent optical phase change materials for high-performance nonvolatile photonics
Broadband transparent optical phase change materials for high-performance nonvolatile photonics
Here, the authors introduce optical phase change materials based on Ge-Sb-Se-Te which breaks the coupling between refractive index and optical loss allowing low-loss performance benefits. They demonstrate low losses in nonvolatile photonic circuits and electrical pixelated switching have been demonstrated.
- Yifei Zhang
- , Jeffrey B. Chou
- & Juejun Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Structural color three-dimensional printing by shrinking photonic crystals
Structural color three-dimensional printing by shrinking photonic crystals
The ability to print arbitrary colors and shapes in all three dimensions at microscopic length scales is still lacking. Here, the authors introduce a means to produce three-dimensionally-printed photonic crystals with a periodicity as small as 280 nm, achieving sub-100-nm features with a full range of colors.
- Yejing Liu
- , Hao Wang
- & Joel K. W. Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Uprooting defects to enable high-performance III–V optoelectronic devices on silicon
Uprooting defects to enable high-performance III–V optoelectronic devices on silicon
The use of promising group III-V materials for optoelectronic applications is hindered by the high density of threading dislocations when integrated with silicon technology. Here, the authors present an electrochemical deep etching strategy to drastically reduce the the defect density.
- Youcef A. Bioud
- , Abderraouf Boucherif
- & Richard Arès
-
Article
| Open Access Spectroscopic studies of atomic defects and bandgap renormalization in semiconducting monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides
Spectroscopic studies of atomic defects and bandgap renormalization in semiconducting monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides
Atomic defects impact the electronic properties of atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs). Here, the authors locate the mid-gap states originating from single chalcogen-atom vacancies in four representative semiconducting monolayer films, and analyse their implications for the semiconducting properties of atomically thin TMDs through electron tunneling and optical spectroscopy measurements.
- Tae Young Jeong
- , Hakseong Kim
- & Suyong Jung
-
Article
| Open Access Identifying substitutional oxygen as a prolific point defect in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides
Identifying substitutional oxygen as a prolific point defect in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides
The nature of defects in transition metal dichalcogenide semiconductors is still under debate. Here, the authors determine the atomic structure and electronic properties of chalcogen-site point defects common to monolayer MoSe2 and WS2, and find that these are substitutional defects, where a chalcogen atom is substituted by an oxygen atom, rather than vacancies.
- Sara Barja
- , Sivan Refaely-Abramson
- & Alexander Weber-Bargioni
-
Article
| Open Access Solution-processed nanographene distributed feedback lasers
Solution-processed nanographene distributed feedback lasers
Chemically synthesized graphene nanosheets offer device design flexibility and improved optoelectronic performance. Here, the authors report solution-processed distributed feedback lasers with graphene nanosheets as active media having linewidths < 0.13 nm, long operational lifetimes and low thresholds.
- Víctor Bonal
- , Rafael Muñoz-Mármol
- & María A. Díaz-García
-
Article
| Open Access 2D semiconductor nonlinear plasmonic modulators
2D semiconductor nonlinear plasmonic modulators
Plasmonic modulators have many possible applications in optical-frequency devices. Here the authors report a 2D semiconductor nonlinear plasmonic modulator enabled through strong interaction between the surface plasmon polaritons and excitons in a monolayer semiconductor integrated on top of a metallic waveguide.
- Matthew Klein
- , Bekele H. Badada
- & John R. Schaibley
-
Article
| Open Access Uniaxial transition dipole moments in semiconductor quantum rings caused by broken rotational symmetry
Uniaxial transition dipole moments in semiconductor quantum rings caused by broken rotational symmetry
Annular semiconductor structures, or “quantum rings”, are of interest for quantum information and photonics applications. Here, the authors show that breaking rotational symmetry through elongation generates an in-plane optical transition dipole moment in CdSe quantum rings.
- Nicolai F. Hartmann
- , Matthew Otten
- & Xuedan Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Nanometer-precision non-local deformation reconstruction using nanodiamond sensing
Nanometer-precision non-local deformation reconstruction using nanodiamond sensing
Spatially resolved information about material deformation upon loading is critical to evaluate mechanical properties. Here the authors demonstrate integration of nanodiamond orientation sensing and atomic force microscopy nanoindentation as an approach to evaluate non-local material deformation on the nanoscale.
- Kangwei Xia
- , Chu-Feng Liu
- & Quan Li
-
Article
| Open Access Launching of hyperbolic phonon-polaritons in h-BN slabs by resonant metal plasmonic antennas
Launching of hyperbolic phonon-polaritons in h-BN slabs by resonant metal plasmonic antennas
Momentum mismatch prevents efficient coupling between free space photons and hyperbolic phonon polaritons. The authors show, using far-field infrared spectroscopy, infrared nanoimaging and numerical simulations, that resonant metallic antennas can efficiently launch hyperbolic phonon polaritons in thin h-BN slabs.
- P. Pons-Valencia
- , F. J. Alfaro-Mozaz
- & A. Y. Nikitin
-
Article
| Open Access Emergence of multiple fluorophores in individual cesium lead bromide nanocrystals
Emergence of multiple fluorophores in individual cesium lead bromide nanocrystals
Inorganic perovskite nanocrystals attract lots of research attention but the origin of their photoluminescence remains debatable. Here Zhang et al. show that behavior of both CsPbBr3 and Cs4PbBr6 nanocrystals is like individual molecular fluorophores and independent of the structural dimensionalities.
- Yuhai Zhang
- , Tianle Guo
- & Anton V. Malko
-
Article
| Open Access Short contacts between chains enhancing luminescence quantum yields and carrier mobilities in conjugated copolymers
Short contacts between chains enhancing luminescence quantum yields and carrier mobilities in conjugated copolymers
Designing conjugated polymers with high charge carrier mobility and fluorescence quantum efficiency, though attractive for optoelectronics, remains challenging. Here, the authors report a strategy for designing donor-acceptor copolymers whose optoelectronic properties exceed the state-of-the-art.
- Tudor H. Thomas
- , David J. Harkin
- & Henning Sirringhaus
-
Article
| Open Access Physical origin of giant excitonic and magneto-optical responses in two-dimensional ferromagnetic insulators
Physical origin of giant excitonic and magneto-optical responses in two-dimensional ferromagnetic insulators
The magneto-optical (MO) effects probe the electronic and magnetic properties of a material, particularly useful for 2D magnets. Here, the authors show that the large optical and MO responses in ferromagnetic monolayer CrI3 arise from strongly bound excitons, extending over several atoms.
- Meng Wu
- , Zhenglu Li
- & Steven G. Louie
-
Article
| Open Access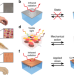 A dynamic thermoregulatory material inspired by squid skin
A dynamic thermoregulatory material inspired by squid skin
Thermoregulatory platforms that combine the advantages of passive and active thermal management systems have remained elusive. Here, the authors draw inspiration from the static infrared-reflecting space blanket and dynamic color-changing squid skin to develop a composite material that addresses this challenge.
- Erica M. Leung
- , Melvin Colorado Escobar
- & Alon A. Gorodetsky
-
Article
| Open Access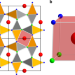 Sr[Li2Al2O2N2]:Eu2+—A high performance red phosphor to brighten the future
Sr[Li2Al2O2N2]:Eu2+—A high performance red phosphor to brighten the future
Developing innovative materials for reduced energy consumption in phosphor converted white light-emitting diodes remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a narrow band red-emitting oxonitride material with a highly symmetrical Sr2 + coordination for energy efficient white light-emitting diodes.
- Gregor J. Hoerder
- , Markus Seibald
- & Hubert Huppertz
-
Article
| Open Access Spectra stable blue perovskite light-emitting diodes
Spectra stable blue perovskite light-emitting diodes
Besides device operational stability, the color stability is also an important challenge for the perovskite light-emitting diodes, especially the blue ones. Here Jiang et al. report the most efficient and color stable pure-blue perovskite LEDs so far, with a half-lifetime of 14.5 minutes.
- Yuanzhi Jiang
- , Chaochao Qin
- & Jun Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Laser restructuring and photoluminescence of glass-clad GaSb/Si-core optical fibres
Laser restructuring and photoluminescence of glass-clad GaSb/Si-core optical fibres
Semiconductor-core optical fibres are of interest for their non-linear optical and electro-optical properties. Here, GaSb/Si composite-core optical fibres were fabricated and a CO2 laser was used to facilitate controlled GaSb segregation within the silicon. This has implications for embedding light sources in IR-transmitting fibers
- S. Song
- , K. Lønsethagen
- & U. J. Gibson
-
Article
| Open Access All-optical control of lead halide perovskite microlasers
All-optical control of lead halide perovskite microlasers
Lead halide perovskite lasers have great potential as microscale organic light sources, but dynamic tuning has yet to be achieved. Here, Zhang, Fan et al. investigate how nonlinear modal interactions enable ultrafast mode switching with crossgain saturation.
- Nan Zhang
- , Yubin Fan
- & Qinghai Song
-
Article
| Open Access Fabrication of arbitrary three-dimensional suspended hollow microstructures in transparent fused silica glass
Fabrication of arbitrary three-dimensional suspended hollow microstructures in transparent fused silica glass
Fused silica glass has excellent optical properties, chemical and thermal stability and hardness, but its microstructuring for miniaturized applications has proven difficult. Here the authors demonstrate obtainment of precise arbitrary three dimensional hollow microstructures in fused silica glass by sacrificial template replication.
- Frederik Kotz
- , Patrick Risch
- & Bastian E. Rapp

 Ultrashort laser pulse doubling by metal-halide perovskite multiple quantum wells
Ultrashort laser pulse doubling by metal-halide perovskite multiple quantum wells