Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Continuous artificial synthesis of glucose precursor using enzyme-immobilized microfluidic reactors
Continuous artificial synthesis of glucose precursor using enzyme-immobilized microfluidic reactors
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO) is a difficult enzyme to work with. Here, the authors covalently immobilized it in a microfluidic reactor to enhance its storage/thermal stabilities and reusability, which enabled the continuous artificial synthesis of glucose precursor.
- Yujiao Zhu
- , Ziyu Huang
- & Xuming Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access A glomerulus-on-a-chip to recapitulate the human glomerular filtration barrier
A glomerulus-on-a-chip to recapitulate the human glomerular filtration barrier
The glomerular filtration barrier is a complex structure in charge of renal ultrafiltration. Here the authors present a glomerulus-on-a-chip for disease modelling and high-throughput drug screening where human podocytes and human glomerular endothelial cells are separated by an extracellular matrix resembling the in vivo basement membrane.
- Astgik Petrosyan
- , Paolo Cravedi
- & Stefano Da Sacco
-
Article
| Open Access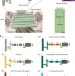 Ultra-sensitive digital quantification of proteins and mRNA in single cells
Ultra-sensitive digital quantification of proteins and mRNA in single cells
Digital proximity ligation assay (dPLA) can measure proteins and mRNAs in single cells, but is not compatible with cell imaging and cannot quantify rare proteins due to a high dilution factor. Here the authors present an automated microfluidic device that combines live-cell imaging, chemical stimulation, and dPLA in a smaller reaction volume.
- Jing Lin
- , Christian Jordi
- & Savaş Tay
-
Article
| Open Access Monitoring biomolecule concentrations in tissue using a wearable droplet microfluidic-based sensor
Monitoring biomolecule concentrations in tissue using a wearable droplet microfluidic-based sensor
Continuous real-time measurement of biomarker levels in body fluids offers many exciting possibilities. Here, the authors develop an integrated wearable droplet microfluidic sensor that combines continuous sampling of tissue fluid with in situ analysis using wet-chemical assays.
- Adrian M. Nightingale
- , Chi Leng Leong
- & Xize Niu
-
Article
| Open Access Hydro-Seq enables contamination-free high-throughput single-cell RNA-sequencing for circulating tumor cells
Hydro-Seq enables contamination-free high-throughput single-cell RNA-sequencing for circulating tumor cells
Transcriptome analysis of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) provides insights into monitoring target therapeutics and underlying tumor metastasis. Here the authors present Hydro-Seq, a contamination-free high-throughput hydrodynamic scRNA-seq barcoding technique for rare CTCs.
- Yu-Heng Cheng
- , Yu-Chih Chen
- & Euisik Yoon
-
Article
| Open Access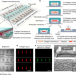 Microclot array elastometry for integrated measurement of thrombus formation and clot biomechanics under fluid shear
Microclot array elastometry for integrated measurement of thrombus formation and clot biomechanics under fluid shear
Blood clotting is a complex process involving platelet adhesion and clot stiffening. Here the authors present a microfluidic system to recapitulate the dynamic changes in clot mechanics under physiological shear.
- Zhaowei Chen
- , Jiankai Lu
- & Ruogang Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Spatiotemporal control of coacervate formation within liposomes
Spatiotemporal control of coacervate formation within liposomes
The understanding of liquid-liquid phase separation is crucial to cell biology and benefits from cell-mimicking in vitro assays. Here, the authors develop a microfluidic platform to study coacervate formation inside liposomes and show the potential of these hybrid systems to create synthetic cells.
- Siddharth Deshpande
- , Frank Brandenburg
- & Cees Dekker
-
Article
| Open Access Control of capillary behavior through target-responsive hydrogel permeability alteration for sensitive visual quantitative detection
Control of capillary behavior through target-responsive hydrogel permeability alteration for sensitive visual quantitative detection
DNA hydrogels have received considerable attention in analytical science but limitations still exist in the applications of intelligent hydrogels. Here, the authors describe a DNA hydrogel sensor for quantitative detection of cocaine based on the permeability change in a DNA hydrogel film.
- Yansheng Li
- , Yanli Ma
- & Yongqiang Wen
-
Article
| Open Access Long-term functional and structural preservation of precision-cut human myocardium under continuous electromechanical stimulation in vitro
Long-term functional and structural preservation of precision-cut human myocardium under continuous electromechanical stimulation in vitro
Myocardial tissue undergoes steady functional decline when cultured in vitro. Here, the authors report a protocol for culture of human cardiac slices that allows maintenance of contractility for up to four months, and show that the model is suitable for evaluation of drug safety, as exemplified for drugs interfering with cardiomyocyte repolarization.
- Carola Fischer
- , Hendrik Milting
- & Andreas Dendorfer
-
Article
| Open Access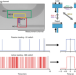 Microfluidic active loading of single cells enables analysis of complex clinical specimens
Microfluidic active loading of single cells enables analysis of complex clinical specimens
Single-cell detection methods are limited by the trade-off between flow rate and measurement precision. Here the authors introduce active loading, an optically triggered microfluidic system to concentrate diluted cell samples, which reduces clogging and decreases processing time in single-cell assays.
- Nicholas L. Calistri
- , Robert J. Kimmerling
- & Scott R. Manalis
-
Article
| Open Access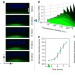 Self-induced mechanical stress can trigger biofilm formation in uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Self-induced mechanical stress can trigger biofilm formation in uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Bacterial biofilms are an increasingly important medical problem but the mechanisms by which they develop remain largely unknown. Here, using a high-throughput approach, the authors show that biofilm formation is linked to self-imposed mechanical stress.
- Eric K. Chu
- , Onur Kilic
- & Andre Levchenko
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell analysis reveals that stochasticity and paracrine signaling control interferon-alpha production by plasmacytoid dendritic cells
Single-cell analysis reveals that stochasticity and paracrine signaling control interferon-alpha production by plasmacytoid dendritic cells
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDC) are a pivotal component of the immune system. Here, the authors utilize single-cell microfluidics to interrogate the human pDC compartment and reveal a subset of type I IFN secreting pDCs that is regulated by stochastic gene expression and amplified by microenvironmental cues.
- Florian Wimmers
- , Nikita Subedi
- & Jurjen Tel
-
Article
| Open Access Digital acoustofluidics enables contactless and programmable liquid handling
Digital acoustofluidics enables contactless and programmable liquid handling
Contamination is an obstacle to the functioning of microfluidic devices. Here the authors exploit acoustic streaming to manipulate droplets which float on a layer of immiscible oil. This prevents contamination and enables rewritability by which different fluids can be used on the same substrate.
- Steven Peiran Zhang
- , James Lata
- & Tony Jun Huang
-
Article
| Open Access PreDicta chip-based high resolution diagnosis of rhinovirus-induced wheeze
PreDicta chip-based high resolution diagnosis of rhinovirus-induced wheeze
Rhinovirus (RV) infections can trigger acute exacerbations of respiratory diseases. Here, Niespodziana et al. develop a PreDicta chip that identifies the culprit RV strain from small blood samples and show that RV-A and RV-C strains are associated with most severe symptoms.
- Katarzyna Niespodziana
- , Katarina Stenberg-Hammar
- & Rudolf Valenta
-
Article
| Open Access Fibrotic microtissue array to predict anti-fibrosis drug efficacy
Fibrotic microtissue array to predict anti-fibrosis drug efficacy
A bottleneck in developing new anti-fibrosis therapies is the absence of suitable in vitro models that recapitulate key features of fibrogenesis. Here the authors develop a tissue-on-a-chip model of lung fibrosis and test the therapeutic efficacy of two recent FDA-approved drugs.
- Mohammadnabi Asmani
- , Sanjana Velumani
- & Ruogang Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access A microengineered vascularized bleeding model that integrates the principal components of hemostasis
A microengineered vascularized bleeding model that integrates the principal components of hemostasis
Hemostasis is a complex ensemble of events, but current bleeding assays only analyze single components like coagulation or platelet function. Here the authors present a comprehensive vascularized microfluidic mechanical injury bleeding model that addresses different aspects of the hemostatic process.
- Yumiko Sakurai
- , Elaissa T. Hardy
- & Wilbur A. Lam
-
Article
| Open Access Pixelated spatial gene expression analysis from tissue
Pixelated spatial gene expression analysis from tissue
Spatial localization of genetic information is important for tissue heterogeneity but difficult to capture with current analytical techniques. Here the authors present “Pixelated RT-LAMP”, an approach that uses parallel on-chip reactions to provide the distribution of target sequences directly from tissue.
- A. Ganguli
- , A. Ornob
- & R. Bashir
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered nanointerfaces for microfluidic isolation and molecular profiling of tumor-specific extracellular vesicles
Engineered nanointerfaces for microfluidic isolation and molecular profiling of tumor-specific extracellular vesicles
Extracellular vesicles can carry many different types of biological cargo and have been investigated as a biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Here the authors develop a microfluidic platform for rapid and sensitive isolation of tumor-specific extracellular vesicles.
- Eduardo Reátegui
- , Kristan E. van der Vos
- & Shannon L. Stott
-
Article
| Open Access Metas-Chip precisely identifies presence of micrometastasis in live biopsy samples by label free approach
Metas-Chip precisely identifies presence of micrometastasis in live biopsy samples by label free approach
Detecting metastatic cells in tumor/lymph node samples of breast cancer patients is extremely important for diagnosis. Here the authors develop a microelectronic biochip that detect the presence of invasive/metastatic cells in unprocessed biopsies and performs better than the current gold standards.
- Mohammad Saeid Nikshoar
- , Mohammad Ali Khayamian
- & Mohammad Abdolahad
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular rheotaxis directs DNA migration and concentration against a pressure-driven flow
Molecular rheotaxis directs DNA migration and concentration against a pressure-driven flow
Implementing a nucleic acid preconcentration method can improve the sensitivity of microfluidic analysis systems. Here Friedrich et al. concentrate DNA by many orders of magnitude using pressure-driven flow, which could lead to a simple and practical microanalysis platform.
- Sarah M. Friedrich
- , Jeffrey M. Burke
- & Tza-Huei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Microfluidics with fluid walls
Microfluidics with fluid walls
The complexity of fabricating and operating microfluidic devices limits their use. Walsh et al. describe a method in which circuits are printed as quickly and simply as writing with a pen, and liquids in them are confined by fluid instead of solid walls.
- Edmond J. Walsh
- , Alexander Feuerborn
- & Peter R. Cook
-
Article
| Open Access Matrix degradability controls multicellularity of 3D cell migration
Matrix degradability controls multicellularity of 3D cell migration
The fabrication of vascularized 3D tissues requires an understanding of how material properties govern endothelial cell invasion into the surrounding matrix. Here the authors integrate a non-swelling synthetic hydrogel with a microfluidic device to study chemokine gradient-driven angiogenic sprouting and find that matrix degradability modulates the collectivity of cell migration.
- Britta Trappmann
- , Brendon M. Baker
- & Christopher S. Chen
-
Article
| Open Access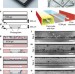 Membrane-free culture and real-time barrier integrity assessment of perfused intestinal epithelium tubes
Membrane-free culture and real-time barrier integrity assessment of perfused intestinal epithelium tubes
Efforts to determine the effects of drugs on epithelial barriers could benefit from better in vitro models. Here the authors develop a microfluidic device supporting the growth and function of extracellular matrix-supported intestinal tubules, and evaluate the effect of staurosporine and acetylsalicylic acid on barrier integrity.
- Sebastiaan J. Trietsch
- , Elena Naumovska
- & Paul Vulto
-
Article
| Open Access A microfluidic culture model of the human reproductive tract and 28-day menstrual cycle
A microfluidic culture model of the human reproductive tract and 28-day menstrual cycle
The female reproductive tract constitutes the ovary, fallopian tubes, uterus, and cervix, but it is challenging to engineer this systemin vitro. Here, the authors develop a microfluidic device (EVATAR) with reproductive tract and peripheral tissues to replicate hormone release of a 28-day menstrual cycle.
- Shuo Xiao
- , Jonathan R. Coppeta
- & Teresa K. Woodruff
-
Article
| Open Access Deep phenotyping unveils hidden traits and genetic relations in subtle mutants
Deep phenotyping unveils hidden traits and genetic relations in subtle mutants
Experimenter scoring of cellular imaging data can be biased. This study describes an automated and unbiased multidimensional phenotyping method that relies on machine learning and complex feature computation of imaging data, and identifies weak alleles affecting synapse morphology in live C. elegans.
- Adriana San-Miguel
- , Peri T. Kurshan
- & Hang Lu
-
Article
| Open Access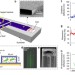 Microfluidic cantilever detects bacteria and measures their susceptibility to antibiotics in small confined volumes
Microfluidic cantilever detects bacteria and measures their susceptibility to antibiotics in small confined volumes
Analysis of bacteria and their response to antibiotics in real time is challenging. Here the authors report a microcantilever based system that can detect and discriminate between bacteria species and, due to the ability to discriminate between alive and dead samples, measure response to antibiotics.
- Hashem Etayash
- , M. F. Khan
- & Thomas Thundat
-
Article
| Open Access A coral-on-a-chip microfluidic platform enabling live-imaging microscopy of reef-building corals
A coral-on-a-chip microfluidic platform enabling live-imaging microscopy of reef-building corals
Studies of coral in laboratory settings are limited by a lack of reliable methods for manipulation of the coral microenvironment and monitoring of coral processes in vitro. Here the authors develop coral-on-a-chip, a microfluidic platform to enable study of coral processes at single-cell resolution.
- Orr H. Shapiro
- , Esti Kramarsky-Winter
- & Assaf Vardi
-
Article
| Open Access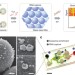 Chip-based analysis of exosomal mRNA mediating drug resistance in glioblastoma
Chip-based analysis of exosomal mRNA mediating drug resistance in glioblastoma
Predicting and monitoring chemotherapy response remains a challenge for glioma treatment. Here the authors show that a microfluidic device can isolate glioma-derived exosomes from patient blood and accurately determine the levels of mRNA of key enzymes important for chemoresponsiveness.
- Huilin Shao
- , Jaehoon Chung
- & Ralph Weissleder
-
Article |
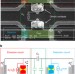 Detecting noise with shot noise using on-chip photon detector
Detecting noise with shot noise using on-chip photon detector
The detection of high-frequency radiation emitted by a quantum conductor is promising but current approaches exhibit limited sensitivity. Here, Jompol et al. propose on-chip radiation detection based on photo-assisted shot noise and show the response to be independent of the nature and geometry of the quantum conductor.
- Y. Jompol
- , P. Roulleau
- & D. C. Glattli
-
Article |
 Robust and versatile ionic liquid microarrays achieved by microcontact printing
Robust and versatile ionic liquid microarrays achieved by microcontact printing
Ionic liquids are widely used in diverse applications as solvents with high thermal and chemical stability. Gunawan et al.develop a protocol for fabrication of an ionic liquid microdroplet array using a soft lithography technique, and demonstrate its utility as a membrane-free high-performance gas sensor.
- Christian A. Gunawan
- , Mengchen Ge
- & Chuan Zhao
-
Article |
 Solution-based circuits enable rapid and multiplexed pathogen detection
Solution-based circuits enable rapid and multiplexed pathogen detection
Rapid, highly multiplexed molecular detection platforms may enable more specific and effective disease diagnosis. Here, a solution-based circuit is reported that enables the analysis of samples for panels of pathogens and antibiotic-resistance profiles at clinically relevant levels in less than 2 min.
- Brian Lam
- , Jagotamoy Das
- & Shana O. Kelley
-
Article
| Open Access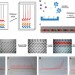 Multiplexed volumetric bar-chart chip for point-of-care diagnostics
Multiplexed volumetric bar-chart chip for point-of-care diagnostics
Diagnostic microfluidic devices often require complicated optical systems and computers to quantify results. Here, Qin and colleagues link enzymatic biomarker detection with the displacement of ink, resulting in a device that displays quantitative results as bar graphs directly on the device.
- Yujun Song
- , Yuanqing Zhang
- & Lidong Qin
-
Article |
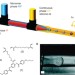 One-piece micropumps from liquid crystalline core-shell particles
One-piece micropumps from liquid crystalline core-shell particles
Liquid crystal elastomers can perform mechanical motion triggered by external stimuli, and are light weight, flexible materials that may be integrated into micromechanical systems. Here they are used to fabricate a one-piece temperature-responsive micropump viaa microfluidic double-emulsion process.
- Eva-Kristina Fleischmann
- , Hsin-Ling Liang
- & Rudolf Zentel

 A tunable dual-input system for on-demand dynamic gene expression regulation
A tunable dual-input system for on-demand dynamic gene expression regulation