Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Operando magnetic resonance imaging for mapping of temperature and redox species in thermo-electrochemical cells
Operando magnetic resonance imaging for mapping of temperature and redox species in thermo-electrochemical cells
Devices able to harvest heat to generate electricity are intensively studied for sustainable energy production. Here, the authors investigate the mechanism of thermo-electrochemical cells via operando magnetic resonance imaging.
- Isuru E. Gunathilaka
- , Jennifer M. Pringle
- & Luke A. O’Dell
-
Article
| Open Access Fast wide-field upconversion luminescence lifetime thermometry enabled by single-shot compressed ultrahigh-speed imaging
Fast wide-field upconversion luminescence lifetime thermometry enabled by single-shot compressed ultrahigh-speed imaging
Photoluminescence lifetime imaging of upconverting nanoparticles is useful for optical thermometry, but is limited for dynamic samples. Here, the authors present a wide-field and single shot approach based on compressive sensing, for video-rate upconversion temperature sensing of moving samples.
- Xianglei Liu
- , Artiom Skripka
- & Jinyang Liang
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast high-harmonic nanoscopy of magnetization dynamics
Ultrafast high-harmonic nanoscopy of magnetization dynamics
Light induced magnetization dynamics can be as fast as few tens of femtoseconds. Here, Zayko et al show ultrafast microscopy based on high-harmonic radiation for direct imaging of ultrafast phenomena and capture femtosecond spin dynamics at the nanoscale.
- Sergey Zayko
- , Ofer Kfir
- & Claus Ropers
-
Article
| Open Access Testing CPT symmetry in ortho-positronium decays with positronium annihilation tomography
Testing CPT symmetry in ortho-positronium decays with positronium annihilation tomography
CPT violation could manifest itself in annihilating positronium events, but searching for this effect would require to know the spin of the annihilating system. Here, the authors do this using a positron-emission tomography scanner, finding no violation with a statistical precision of 10−4.
- P. Moskal
- , A. Gajos
- & W. Wiślicki
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanical adaptation of brachiopod shells via hydration-induced structural changes
Mechanical adaptation of brachiopod shells via hydration-induced structural changes
Bioinspired materials require an understanding of how biomaterials achieve the materials properties. Here, the authors report on the load-bearing shell of Discinisca tenuis and explore how hydration changes the dry shell from hard and stiff to soft and flexible within minutes by reorganisation caused by organic matrix swelling.
- Johannes Ihli
- , Anna S. Schenk
- & Fabio Nudelman
-
Article
| Open Access Probing atom dynamics of excited Co-Mo-S nanocrystals in 3D
Probing atom dynamics of excited Co-Mo-S nanocrystals in 3D
The authors introduce an analytical approach for quantitative analysis of 3D atom dynamics during electron microscopy. They image a Co-Mo-S nanocrystal with 1.5 Å resolution, and observe chemical transformations caused by beam-stimulated vibrations.
- Fu-Rong Chen
- , Dirk Van Dyck
- & Stig Helveg
-
Article
| Open Access Superior photo-carrier diffusion dynamics in organic-inorganic hybrid perovskites revealed by spatiotemporal conductivity imaging
Superior photo-carrier diffusion dynamics in organic-inorganic hybrid perovskites revealed by spatiotemporal conductivity imaging
Spatiotemporal dynamic of charge carriers is commonly studied with optical or photoconductivity measurements, yet these techniques come with their own limitations. To circumvent these limits, the authors probe the free-carrier diffusion dynamics of microsecond lifetimes via laser-illuminated microwave impedance microscopy.
- Xuejian Ma
- , Fei Zhang
- & Keji Lai
-
Article
| Open Access Quasiadiabatic electron transport in room temperature nanoelectronic devices induced by hot-phonon bottleneck
Quasiadiabatic electron transport in room temperature nanoelectronic devices induced by hot-phonon bottleneck
Minimizing the energy dissipation is usually sought by eliminating phonon-emission process. Here, the authors find a different approach for facilitating energy transmission at room temperature that electrons exert diffusive but quasiadiabatic transport, free from substantial energy loss.
- Qianchun Weng
- , Le Yang
- & Susumu Komiyama
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying nanodiamonds biodistribution in whole cells with correlative iono-nanoscopy
Quantifying nanodiamonds biodistribution in whole cells with correlative iono-nanoscopy
The authors demonstrate efficient excitation of nanodiamonds by a focused beam of helium ions, resulting in ionoluminescence. They use this for quantification and correlative localization of single particles within a whole cell at sub-30 nm resolution, and investigate nanodiamond radiosensitisation effects.
- Zhaohong Mi
- , Ce-Belle Chen
- & Andrew A. Bettiol
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic-scale unveiling of multiphase evolution during hydrated Zn-ion insertion in vanadium oxide
Atomic-scale unveiling of multiphase evolution during hydrated Zn-ion insertion in vanadium oxide
The detailed understanding of the structural variations during cycling in cathodes for Zn-ion aqueous rechargeable batteries is still limited. Here, the authors utilize atomic-column-resolved scanning transmission electron microscopy to elucidate multiphase evolution during hydrated Zn-Ion insertion in vanadium oxide.
- Pilgyu Byeon
- , Youngjae Hong
- & Sung-Yoon Chung
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale cooperative adsorption for materials control
Nanoscale cooperative adsorption for materials control
Adsorption is a fundamentally important process but challenging to quantify, especially at the nanoscale. Here, the authors map the adsorption affinity and cooperativity of various ligands on single gold nanoparticles and discover adsorption crossover behaviors between different facets, leading to a strategy to control particle shape.
- Rong Ye
- , Ming Zhao
- & Peng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Continuous-capture microwave imaging
Continuous-capture microwave imaging
The authors present a microwave imaging system that can operate in continuous transmit-receive mode. Using an array of transmitters, a single receiver and a reconstruction matrix that correlate random time patterns with the captured signal, they demonstrate real-time imaging and tracking through a wall.
- Fabio C. S. da Silva
- , Anthony B. Kos
- & Archita Hati
-
Article
| Open Access Memory effect assisted imaging through multimode optical fibres
Memory effect assisted imaging through multimode optical fibres
Imaging through scattering media is possible using a transmission matrix or the memory effect. Here, the authors describe the nature of optical memory effects in structures of arbitrary geometry and use this framework to estimate the transmission matrix of an optical fibre from just one end.
- Shuhui Li
- , Simon A. R. Horsley
- & David B. Phillips
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time imaging of cellular forces using optical interference
Real-time imaging of cellular forces using optical interference
Studying dynamic processes in mechanobiology has been challenging due to lack of appropriate tools. Here, the authors present an interference-based method, illuminated via two rapidly alternating wavelengths, which enables real-time mapping of nanoscale forces with sub-second mechanical fluctuations.
- Andrew T. Meek
- , Nils M. Kronenberg
- & Malte C. Gather
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery and characterization of a new type of domain wall in a row-wise antiferromagnet
Discovery and characterization of a new type of domain wall in a row-wise antiferromagnet
Antiferromagnets (AFM) exhibit faster magnetization dynamics, and have immunity to stray fields, making AFMs attractive for spintronic devices. Here, the authors investigate the behaviour of domain walls in AFMs, and find a new type domain wall, a superposition of two adjacent rotational domains.
- Jonas Spethmann
- , Martin Grünebohm
- & André Kubetzka
-
Article
| Open Access Lead halide perovskite for efficient optoacoustic conversion and application toward high-resolution ultrasound imaging
Lead halide perovskite for efficient optoacoustic conversion and application toward high-resolution ultrasound imaging
Lead halide perovskites are widely used e.g. in solar cells and LEDs, but devices based on thermal properties have received little attention. Here, the authors take advantage of the thermal properties to fabricate an optoacoustic transducer with both broad bandwidth and high conversion efficiency.
- Xinyuan Du
- , Jiapu Li
- & Jiang Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetoelectric coupling of domains, domain walls and vortices in a multiferroic with independent magnetic and electric order
Magnetoelectric coupling of domains, domain walls and vortices in a multiferroic with independent magnetic and electric order
In h-RMnO3, the linear magnetoelectric effect is symmetry forbidden. Here, the authors show a pronounced magnetoelectric coupling driven by superexchange interaction giving rise to types of topological defects like magnetoelectric domain walls and vortex-like singularities.
- Marcela Giraldo
- , Quintin N. Meier
- & Thomas Lottermoser
-
Article
| Open Access Nanostructure-specific X-ray tomography reveals myelin levels, integrity and axon orientations in mouse and human nervous tissue
Nanostructure-specific X-ray tomography reveals myelin levels, integrity and axon orientations in mouse and human nervous tissue
Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) combines the high tissue penetration of X-rays with specificity to periodic nanostructures. The authors use SAXS tensor tomography (SAXS-TT) on intact mouse and human brain tissue samples, to quantify myelin levels and determine myelin integrity, myelinated axon orientation, and fibre tracts non-destructively.
- Marios Georgiadis
- , Aileen Schroeter
- & Markus Rudin
-
Article
| Open Access Early turbulence and pulsatile flows enhance diodicity of Tesla’s macrofluidic valve
Early turbulence and pulsatile flows enhance diodicity of Tesla’s macrofluidic valve
Nguyen et al. take a fresh look at Tesla’s concept of an asymmetric fluidic conduit. They show that for alternating flow at high frequencies the device can almost be operated as a diode, enabled by a transition to turbulent-like flow at rather low Reynolds numbers.
- Quynh M. Nguyen
- , Joanna Abouezzi
- & Leif Ristroph
-
Article
| Open Access Edge channels of broken-symmetry quantum Hall states in graphene visualized by atomic force microscopy
Edge channels of broken-symmetry quantum Hall states in graphene visualized by atomic force microscopy
The broken-symmetry edge states that are the hallmark of the quantum Hall effect in graphene have eluded spatial measurements. Here, the authors spatially map the quantum Hall broken-symmetry edge states using atomic force microscopy and show a gapped ground state proceeding from the bulk through to the quantum Hall edge boundary.
- Sungmin Kim
- , Johannes Schwenk
- & Joseph A. Stroscio
-
Article
| Open Access Photon quantum entanglement in the MeV regime and its application in PET imaging
Photon quantum entanglement in the MeV regime and its application in PET imaging
Gamma photons used in positron emission tomography are predicted to be produced in an entangled state. Here, the authors simulate the effects of entanglement and test them through comparison with experimental data from a PET demonstrator apparatus, showing the potential gains in background suppression.
- D. P. Watts
- , J. Bordes
- & N. A. Zachariou
-
Article
| Open Access Micron-scale phenomena observed in a turbulent laser-produced plasma
Micron-scale phenomena observed in a turbulent laser-produced plasma
Turbulence effects explored use macroscale systems in general. Here the authors generate a turbulent plasma using laser irradiation of a solid target and study the dynamics of the plasma flow at the micron-scale by using scattering of an XFEL beam.
- G. Rigon
- , B. Albertazzi
- & M. Koenig
-
Article
| Open Access Single-atom level determination of 3-dimensional surface atomic structure via neural network-assisted atomic electron tomography
Single-atom level determination of 3-dimensional surface atomic structure via neural network-assisted atomic electron tomography
Precise determination of surface atomic structure of metallic nanoparticles is key to unlock their surface/interface properties. Here the authors introduce a neural network-assisted atomic electron tomography approach that provides a three-dimensional reconstruction of metallic nanoparticles at individual atom level.
- Juhyeok Lee
- , Chaehwa Jeong
- & Yongsoo Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Measuring 3D orientation of nanocrystals via polarized luminescence of rare-earth dopants
Measuring 3D orientation of nanocrystals via polarized luminescence of rare-earth dopants
Determining the orientation of nanoscale objects in three-dimensional space has typically required complicated optical setups. Here, the authors develop a simple method to retrieve the 3D orientation of luminescent, lanthanide-doped nanorods from a single-shot emission spectrum.
- Jeongmo Kim
- , Reinaldo Chacón
- & Thierry Gacoin
-
Article
| Open Access Metamaterial assisted illumination nanoscopy via random super-resolution speckles
Metamaterial assisted illumination nanoscopy via random super-resolution speckles
Structured illumination microscopy is usually limited to 2 times spatial resolution improvement over the diffraction limit. Here, the authors introduce a metamaterial structure to generate speckle-like sub-diffraction limit illumination patterns in the near field, and achieve a 7-fold resolution improvement down to 40 nm.
- Yeon Ui Lee
- , Junxiang Zhao
- & Zhaowei Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Monitoring metallic sub-micrometric lithium structures in Li-ion batteries by in situ electron paramagnetic resonance correlated spectroscopy and imaging
Monitoring metallic sub-micrometric lithium structures in Li-ion batteries by in situ electron paramagnetic resonance correlated spectroscopy and imaging
Monitoring the nucleation of dendrites in Li-ion batteries during cell cycling is important for the development of new electrochemical materials. Here, the authors use the spectral-spatial mode in electron paramagnetic resonance imaging to visualize the spatial distribution of metallic sub-micrometric lithium structures.
- Charles-Emmanuel Dutoit
- , Mingxue Tang
- & Elodie Salager
-
Article
| Open Access Unlocking history through automated virtual unfolding of sealed documents imaged by X-ray microtomography
Unlocking history through automated virtual unfolding of sealed documents imaged by X-ray microtomography
Here, the authors present a fully automatic computational approach for reconstructing and virtually unfolding volumetric scans of locked letters with complex internal folding, producing legible images of the letter’s contents and crease pattern while preserving letterlocking evidence.
- Jana Dambrogio
- , Amanda Ghassaei
- & Erik D. Demaine
-
Article
| Open Access Direct imaging and electronic structure modulation of moiré superlattices at the 2D/3D interface
Direct imaging and electronic structure modulation of moiré superlattices at the 2D/3D interface
Here, advanced scanning transmission electron microscopy techniques are used to image the atomic structure at the interface between 2D MoS2 and 3D Au nanoislands, revealing a moiré superlattice and illustrating the potential for (opto-)electronic moiré engineering at the 2D/3D interface.
- Kate Reidy
- , Georgios Varnavides
- & Frances M. Ross
-
Article
| Open Access Bedside functional monitoring of the dynamic brain connectivity in human neonates
Bedside functional monitoring of the dynamic brain connectivity in human neonates
Monitoring of cerebral function in human neonates remains challenging. Here, the authors propose a bedside monitoring technique using functional ultrasound to identify markers of cerebral activity based on intrinsic functional connectivity for early brain function monitoring.
- Jerome Baranger
- , Charlie Demene
- & Mickael Tanter
-
Article
| Open Access Probing electronic structure in berkelium and californium via an electron microscopy nanosampling approach
Probing electronic structure in berkelium and californium via an electron microscopy nanosampling approach
The obtention and study of actinide elements is challenging due to various factors including their radioactivity and scarcity. Herein, the authors characterize the atomic and electronic structure of Am, Cm, Bk, and Cf compounds using a transmission electron microscopy-based workflow that only requires nanogram amounts of the actinide element.
- Alexander Müller
- , Gauthier J.-P. Deblonde
- & Andrew M. Minor
-
Article
| Open Access Addressable nanoantennas with cleared hotspots for single-molecule detection on a portable smartphone microscope
Addressable nanoantennas with cleared hotspots for single-molecule detection on a portable smartphone microscope
Single-molecule fluorescence currently requires specialized imaging equipment due to the low signal of a single emitter. Here the authors introduce NanoAntennas with Cleared HOtSpots (NACHOS) to boost the signal sufficient for detection of a single emitter by a smartphone, opening the door to point-of-care applications.
- Kateryna Trofymchuk
- , Viktorija Glembockyte
- & Philip Tinnefeld
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging non-collinear antiferromagnetic textures via single spin relaxometry
Imaging non-collinear antiferromagnetic textures via single spin relaxometry
In this manuscript, Finco et al demonstrate the use of a quantum magnetometer based on a single NV centre for all-optical imaging of antiferromagnetic (AFM) spin textures. By exploiting variations of the NV spin relaxation rate, they succeed in imaging AFM domain walls and skyrmions.
- Aurore Finco
- , Angela Haykal
- & Vincent Jacques
-
Article
| Open Access Topological optical differentiator
Topological optical differentiator
Spatial differentiation is a form of optical computation which has applications in image processing. Here, the authors exploit nontrivial topological charges in the transfer function to realise broadband isotropic two-dimensional differentiation.
- Tengfeng Zhu
- , Cheng Guo
- & Shanhui Fan
-
Article
| Open Access A data reduction and compression description for high throughput time-resolved electron microscopy
A data reduction and compression description for high throughput time-resolved electron microscopy
The use of electron detectors with high spatio-temporal resolution is limited by the large amounts of data generated. Here, the authors describe ReCoDe, a data reduction and compression scheme, that preserves individual electron events, and enable on-the-fly reduction and compression of raw data.
- Abhik Datta
- , Kian Fong Ng
- & N. Duane Loh
-
Article
| Open Access A self-matched leaky-wave antenna for ultrahigh-field magnetic resonance imaging with low specific absorption rate
A self-matched leaky-wave antenna for ultrahigh-field magnetic resonance imaging with low specific absorption rate
Magnetic resonance imaging of the prostate is challenging due to the trade-off between a high magnetic field and safety concern of local specific absorption rate. Here, the authors demonstrate that a leaky-wave antenna design can reduce local heating due to non-resonant radiation.
- G. Solomakha
- , J. T. Svejda
- & D. Erni
-
Article
| Open Access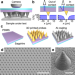 Massively parallel cantilever-free atomic force microscopy
Massively parallel cantilever-free atomic force microscopy
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) provides high resolution, but is limited to small areas. Here, the authors introduce a massively parallel AFM approach with >1000 probes in a cantilever-free probe architecture, and present an optical method for detecting probe–sample contact with sub-10 nm vertical precision.
- Wenhan Cao
- , Nourin Alsharif
- & Keith A. Brown
-
Article
| Open Access Selective filling of n-hexane in a tight nanopore
Selective filling of n-hexane in a tight nanopore
Molecular sieving typically occurs when molecules with smaller kinetic diameter than a nanopore selectively enter the pore. Here the authors show, using photoluminescence imaging and ab initio molecular dynamics simulations, that single-walled carbon nanotubes can separate n-hexane from cyclohexane, despite both having larger kinetic diameter than the nanopore.
- Haoran Qu
- , Archith Rayabharam
- & YuHuang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Pushing the limits of high-resolution polymer microscopy using antioxidants
Pushing the limits of high-resolution polymer microscopy using antioxidants
High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) has been transformative to the field of polymer science but most HRTEM studies are limited by beam damage on the material. Here, the authors examine the effect of the addition of antioxidants to a series of conjugated polymers and demonstrate minimized beam damage at increased resolution.
- Brooke Kuei
- & Enrique D. Gomez
-
Article
| Open Access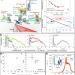 Laser-driven x-ray and proton micro-source and application to simultaneous single-shot bi-modal radiographic imaging
Laser-driven x-ray and proton micro-source and application to simultaneous single-shot bi-modal radiographic imaging
Here the authors show a synchronized single-shot bi-modal x-ray and proton source based on laser-generated plasma. This source can be useful for radiographic and tomographic imaging.
- T. M. Ostermayr
- , C. Kreuzer
- & J. Schreiber
-
Article
| Open Access Extreme anti-reflection enhanced magneto-optic Kerr effect microscopy
Extreme anti-reflection enhanced magneto-optic Kerr effect microscopy
Magneto-optic Kerr effect microscopy is useful for dynamic magnetic studies, but is limited by the weak magneto-optical activity. Here, the authors show that extreme anti-reflection result in a Kerr amplitude as large as 20° and enables real-time detection of sub-wavelength magnetic domain reversals.
- Dongha Kim
- , Young-Wan Oh
- & Min-Kyo Seo
-
Article
| Open Access Seeing around corners with edge-resolved transient imaging
Seeing around corners with edge-resolved transient imaging
Non-line-of-sight imaging is typically limited by loss of directional information due to diffuse reflections scattering light in all directions. Here, the authors see around corners by using vertical edges and temporal response to pulsed light to obtain angular and longitudinal resolution, respectively.
- Joshua Rapp
- , Charles Saunders
- & Vivek K. Goyal
-
Article
| Open Access Time-resolved in situ visualization of the structural response of zeolites during catalysis
Time-resolved in situ visualization of the structural response of zeolites during catalysis
Study of structural inhomogeneities in zeolites is important but limited by conventional techniques. Here the authors employ in situ free-electron-laser-based time-resolved coherent X-ray diffraction imaging to visualize the effect of these inhomogeneities during catalytic deoxygenation of NOx.
- Jinback Kang
- , Jerome Carnis
- & Hyunjung Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmonic nano-aperture label-free imaging (PANORAMA)
Plasmonic nano-aperture label-free imaging (PANORAMA)
Here, the authors report on an imaging method based on localized surface plasmon resonance excitation, employing gold nanodisk arrays as substrates that enable imaging of transparent dielectric particles of several sizes. They demonstrate the ability to detect and image particles smaller than the diffraction limit at 25 nm with standard bright-field imaging.
- Nareg Ohannesian
- , Ibrahim Misbah
- & Wei-Chuan Shih
-
Article
| Open Access Shortwave-infrared meso-patterned imaging enables label-free mapping of tissue water and lipid content
Shortwave-infrared meso-patterned imaging enables label-free mapping of tissue water and lipid content
Quantifying lipid and water content in tissues non-invasively is difficult, and no method exists to quantify lipids in blood non-invasively. Here the authors develop an imaging approach called shortwave infrared meso-patterned imaging (SWIR-MPI) to detect and spatially map tissue water and lipids in preclinical models.
- Yanyu Zhao
- , Anahita Pilvar
- & Darren Roblyer
-
Article
| Open Access Single-shot stereo-polarimetric compressed ultrafast photography for light-speed observation of high-dimensional optical transients with picosecond resolution
Single-shot stereo-polarimetric compressed ultrafast photography for light-speed observation of high-dimensional optical transients with picosecond resolution
Existing high-dimensional optical imaging techniques that record space and polarization cannot detect the photon’s time of arrival due to the limited speeds of electronic sensors. Here, the authors develop a single-shot ultrafast imaging modality to record light-speed high-dimensional events with picosecond resolution.
- Jinyang Liang
- , Peng Wang
- & Lihong V. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Computational optical imaging with a photonic lantern
Computational optical imaging with a photonic lantern
Here, the authors demonstrate a route to high resolution microendoscopy using a multicore fibre with a photonic lantern. They show that distinct multimode patterns of light can be projected from the output of the lantern by individually exciting the single-mode MCF cores, whose patterns are highly stable to fibre movement.
- Debaditya Choudhury
- , Duncan K. McNicholl
- & Robert R. Thomson
-
Article
| Open Access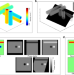 Fetal whole heart blood flow imaging using 4D cine MRI
Fetal whole heart blood flow imaging using 4D cine MRI
Three-dimensional imaging of the fetal heart and quantification of blood flow in the surrounding vessels is very challenging because the heart is small and the fetus is free to move in the womb. Here, the authors demonstrate motion-corrected 4D flow MRI of the whole fetal heart and major vessels.
- Thomas A. Roberts
- , Joshua F. P. van Amerom
- & Joseph V. Hajnal
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging how thermal capillary waves and anisotropic interfacial stiffness shape nanoparticle supracrystals
Imaging how thermal capillary waves and anisotropic interfacial stiffness shape nanoparticle supracrystals
Interfacial fluctuations at the nanoscale, such as shape evolution of a growing crystal, are prohibitively difficult to study experimentally. Here, the authors are able to map the kinetic and thermodynamic parameters involved in shaping of nanoparticle supracrystals by directly imaging the fluctuating crystal surface by liquid-phase TEM, and analyzing it in the context of capillary wave theory.
- Zihao Ou
- , Lehan Yao
- & Qian Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Spontaneous creation and annihilation dynamics and strain-limited stability of magnetic skyrmions
Spontaneous creation and annihilation dynamics and strain-limited stability of magnetic skyrmions
Skyrmions are spin textures which have integer topological charge. Typically they are very stable. Here, the authors observe the spontaneous creation and annihilation of skyrmions in regions of high exchange energy density, suggesting a limit to skyrmion stability.
- Frederic Rendell-Bhatti
- , Raymond J. Lamb
- & Damien McGrouther

 Low-latency time-of-flight non-line-of-sight imaging at 5 frames per second
Low-latency time-of-flight non-line-of-sight imaging at 5 frames per second