Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling the orbital angular momentum of high harmonic vortices
Controlling the orbital angular momentum of high harmonic vortices
Few methods can produce orbital angular momentum beams in the extreme ultraviolet or X-ray, and controlling orbital angular momentum on these beams remains challenging. Here the authors apply wave mixing to a tabletop high-harmonic source and control the topological charge of extreme ultraviolet beams.
- Fanqi Kong
- , Chunmei Zhang
- & P. B. Corkum
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmon-assisted high-harmonic generation in graphene
Plasmon-assisted high-harmonic generation in graphene
High-harmonic generation is a nonlinear optical phenomenon that may be harnessed towards realisation of ultrafast light sources. Here, the authors theoretically show that localized plasmons in graphene nanodisks result in broadband and electrically tunable high-harmonic generation.
- Joel D. Cox
- , Andrea Marini
- & F. Javier García de Abajo
-
Article
| Open Access High-harmonic generation by field enhanced femtosecond pulses in metal-sapphire nanostructure
High-harmonic generation by field enhanced femtosecond pulses in metal-sapphire nanostructure
It has been suggested that strong field enhancement for high harmonic generation may be achievable with nano-antennas. Here, the authors show relevant field enhancement using a metal-sapphire nanostructure that provides a solid tip as the high harmonic emitter, replacing commonly used gaseous atoms.
- Seunghwoi Han
- , Hyunwoong Kim
- & Seung-Woo Kim
-
Article
| Open Access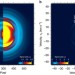 Sub-10-fs control of dissociation pathways in the hydrogen molecular ion with a few-pulse attosecond pulse train
Sub-10-fs control of dissociation pathways in the hydrogen molecular ion with a few-pulse attosecond pulse train
Attosecond laser pulses allow to explore the ultrafast atomic or molecular processes occurring in chemical reactions. Here the authors utilize a sequence of two XUV pump-probe pulses to control the dissociation dynamics of the hydrogen molecular ion.
- Yasuo Nabekawa
- , Yusuke Furukawa
- & Katsumi Midorikawa
-
Article
| Open Access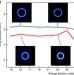 Synthesis and characterization of attosecond light vortices in the extreme ultraviolet
Synthesis and characterization of attosecond light vortices in the extreme ultraviolet
Twisted light beams have found several applications in the infrared and visible regime, but reaching the extreme ultraviolet has been difficult due to lack of sources. Here the authors report generation of helically shaped extreme ultraviolet trains of attosecond pulses via high harmonic generation.
- R. Géneaux
- , A. Camper
- & T. Ruchon
-
Article
| Open Access Volume-wise destruction of the antiferromagnetic Mott insulating state through quantum tuning
Volume-wise destruction of the antiferromagnetic Mott insulating state through quantum tuning
Knowing whether a quantum phase transition is first- or second-order is crucial for understanding any associated exotic phenomena, but direct experimental evidence has been scarce. Here, Frandsen et al. report first-order magnetic quantum phase transitions in archetypal Mott systems, providing insight into the underlying quantum fluctuations.
- Benjamin A. Frandsen
- , Lian Liu
- & Yasutomo J. Uemura
-
Article
| Open Access Guided post-acceleration of laser-driven ions by a miniature modular structure
Guided post-acceleration of laser-driven ions by a miniature modular structure
Intense laser-driven acceleration mechanisms are promising for the realization of compact particle accelerators. Here, the authors present a miniature linear accelerating module for laser-driven protons from a foil that addresses limitation in terms of peak energy, bandwidth and beam divergence.
- Satyabrata Kar
- , Hamad Ahmed
- & Marco Borghesi
-
Article |
 Perturbative optical parametric amplification in the extreme ultraviolet
Perturbative optical parametric amplification in the extreme ultraviolet
The generation of coherent X-ray radiation using a perturbative approach holds benefits over non-perturbative methods. Here, Dao et al. use high-intensity pulses at 800 and 1,400 nm to demonstrate an order-of-magnitude flux enhancement of extreme ultraviolet radiation by perturbative parametric amplification.
- L V. Dao
- , K B. Dinh
- & P Hannaford
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamical origin of near- and below-threshold harmonic generation of Cs in an intense mid-infrared laser field
Dynamical origin of near- and below-threshold harmonic generation of Cs in an intense mid-infrared laser field
High harmonic generation (HHG) above the HHG threshold is understood using the three-step model, but the near- and below-threshold regimes are largely unexplored. Here, Li et al. shed light on the dynamic origin of the near- and below-threshold harmonic generation of caesium atoms in an intense mid-infrared laser field.
- Peng-Cheng Li
- , Yae-Lin Sheu
- & Shih-I Chu
-
Article
| Open Access Spatiotemporal isolation of attosecond soft X-ray pulses in the water window
Spatiotemporal isolation of attosecond soft X-ray pulses in the water window
Time-resolved probing of electronic dynamics such as exciton formation and annihilation requires attosecond pulses at photon energies covering the absorption edges of materials. Here, Silva et al. experimentally demonstrate spatio-temporal isolation of single-attosecond soft X-ray pulses in the water window.
- Francisco Silva
- , Stephan M. Teichmann
- & Jens Biegert
-
Article |
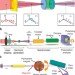 Towards enabling femtosecond helicity-dependent spectroscopy with high-harmonic sources
Towards enabling femtosecond helicity-dependent spectroscopy with high-harmonic sources
High-harmonic generation is now capable of delivering high-energy X-ray pulses with short duration, but achieving elliptical polarization remains challenging. Here, Lambert et al. use a cross-polarized two-colour laser field to produce elliptically polarized X-rays and measure magnetic circular dichroism in nickel.
- G. Lambert
- , B. Vodungbo
- & M. Fajardo
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-channel electronic and vibrational dynamics in polyatomic resonant high-order harmonic generation
Multi-channel electronic and vibrational dynamics in polyatomic resonant high-order harmonic generation
Strong-field ionization in molecules is more complex than in atoms with multiple channel dynamics and a coherent superposition of electronic states. Here, Ferré et al. develop multi-modal spectroscopy to measure those dynamics and reveal a resonant to non-resonant high-harmonic generation transition.
- A. Ferré
- , A. E. Boguslavskiy
- & Y. Mairesse
-
Article |
 Spatio–spectral structures in high-order harmonic beams generated with Terawatt 10-fs pulses
Spatio–spectral structures in high-order harmonic beams generated with Terawatt 10-fs pulses
Complex spatio-spectral structures are characteristic of high order harmonics generated with ultrashort high intensity pulses. Here, Dubrouil et al. demonstrate the structures originate from strong spatio-temporal coupling in the generating medium associated to the high nonlinearity of extreme UV generation.
- A. Dubrouil
- , O. Hort
- & E. Constant
-
Article |
 Waveforms for optimal sub-keV high-order harmonics with synthesized two- or three-colour laser fields
Waveforms for optimal sub-keV high-order harmonics with synthesized two- or three-colour laser fields
The promise of X-ray tabletop broadband light sources by high-order harmonics generated in a gas medium has been limited by low conversion efficiencies. Here, Jin et al.show a method to enhance the high harmonic generation by optimizing the waveform of synthesized two and three colour laser fields.
- Cheng Jin
- , Guoli Wang
- & C. D. Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Carrier-envelope phase-dependent high harmonic generation in the water window using few-cycle infrared pulses
Carrier-envelope phase-dependent high harmonic generation in the water window using few-cycle infrared pulses
The higher-harmonic generation of laser pulses is used to achieve short-wavelength attosecond pulses for ultrashort experiments, but has been limited in the achievable energy. Here, Ishii et al. develop a scheme to break this barrier and to achieve photon energies higher than the carbon Kedge of about 284 eV.
- Nobuhisa Ishii
- , Keisuke Kaneshima
- & Jiro Itatani
-
Article |
 Axis-dependence of molecular high harmonic emission in three dimensions
Axis-dependence of molecular high harmonic emission in three dimensions
Molecules emit high harmonics when driven by strong laser fields. Here, Spector et al. measure how the harmonic spectrum and strength depend on the laser polarization direction in the molecular frame, which leads to a better understanding of the high harmonic process.
- Limor S. Spector
- , Maxim Artamonov
- & Philip H. Bucksbaum

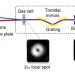 Tunable orbital angular momentum in high-harmonic generation
Tunable orbital angular momentum in high-harmonic generation