Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 A catalyst for low-temperature CO2 activation
A catalyst for low-temperature CO2 activation
A low-valence carbon-doped ruthenium oxide-based catalytic material achieved a catalytic trinity of superior activity, selectivity and stability during the conversion of carbon dioxide into methane at low temperatures.
- Xin Zhang
- & Abhishek Dutta Chowdhury
-
-
News & Views |
 A large library for tiny catalysts
A large library for tiny catalysts
Atomically dispersed catalysts show great promise, but their design is challenging. A library of catalysts spanning 37 elements was created to uncover unified principles for catalyst design.
- Ziyi Chen
- , David Morris
- & Peng Zhang
-
Letter |
 Unlocking synergy in bimetallic catalysts by core–shell design
Unlocking synergy in bimetallic catalysts by core–shell design
Nanomaterials may present interesting catalytic properties, but well-defined model systems are rare. Here, a Au–Pd core–shell catalyst is investigated for selective hydrogenation of butadiene, with shell-thickness-dependent catalytic activity, high selectivity and activity 50 times greater than that of alloyed counterparts.
- Jessi E. S. van der Hoeven
- , Jelena Jelic
- & Petra E. de Jongh
-
Article |
 Insight into the effects of confined hydrocarbon species on the lifetime of methanol conversion catalysts
Insight into the effects of confined hydrocarbon species on the lifetime of methanol conversion catalysts
The methanol-to-hydrocarbons reaction on zeolites produces olefins from many sources, but catalyst stability is a major challenge. Here, by combining operando measurements and simulations, the formation and identification of deactivating carbonaceous species throughout the reaction are achieved.
- I. Lezcano-Gonzalez
- , E. Campbell
- & A. M. Beale
-
News & Views |
 Torn between two sites
Torn between two sites
Mild Lewis and Brønsted acid sites within the confined porous structure of a Nb–Al-containing zeolite work in co-operation to efficiently break down bio-based γ-valerolactone to butenes.
- Baira Donoeva
- & Krijn P. de Jong
-
Article |
 Bio-inspired hydrophobicity promotes CO2 reduction on a Cu surface
Bio-inspired hydrophobicity promotes CO2 reduction on a Cu surface
Aqueous electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 into alcohol and hydrocarbon fuels is a sustainable route towards energy-rich chemical feedstocks. A superhydrophobic surface of hierarchically structured Cu dendrites exhibits a significant increase in CO2 reduction selectivity.
- David Wakerley
- , Sarah Lamaison
- & Victor Mougel
-
Article |
 Dynamic charge and oxidation state of Pt/CeO2 single-atom catalysts
Dynamic charge and oxidation state of Pt/CeO2 single-atom catalysts
The catalytic activity of metals supported on oxides depends on charge and oxidation states, but charge transfer at the interface is not well understood. A model investigating the dynamic charges and oxidation states of Pt/CeO2 single-atom catalysts now clarifies the nature of the active site.
- Nathan Daelman
- , Marçal Capdevila-Cortada
- & Núria López
-
News & Views |
 Stable platinum in a zeolite channel
Stable platinum in a zeolite channel
Highly stable and active Pt–Sn sub-nanometre clusters are located in sinusoidal zeolite channels, leading to improved and more stable propane dehydrogenation catalysts.
- Bert M. Weckhuysen
-
Article |
 Regioselective generation and reactivity control of subnanometric platinum clusters in zeolites for high-temperature catalysis
Regioselective generation and reactivity control of subnanometric platinum clusters in zeolites for high-temperature catalysis
Subnanometre Pt clusters show high catalytic activity, but can sinter and so reduce reactivity. Here, authors localize Pt clusters in one zeolite channel, preventing sintering and allowing highly stable and selective catalytic propane dehydrogenation.
- Lichen Liu
- , Miguel Lopez-Haro
- & Avelino Corma
-
News & Views |
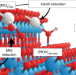 Catalytic sites are finally in sight
Catalytic sites are finally in sight
Controlled Pt loading on TiO2 nanoparticles enables single-site catalysts. With this, the coordination environment and catalytic activity can be obtained, allowing extraction of structure-function information.
- E. Charles H. Sykes
-
Article |
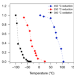 Structural evolution of atomically dispersed Pt catalysts dictates reactivity
Structural evolution of atomically dispersed Pt catalysts dictates reactivity
Oxide-supported isolated Pt-group metal atoms as catalytic active sites are of interest because of their unique reactivity. Isolated Pt species are now shown to adopt a range of local coordination environments and oxidation states in response to environmental conditions.
- Leo DeRita
- , Joaquin Resasco
- & Phillip Christopher
-
Article |
 Surface distortion as a unifying concept and descriptor in oxygen reduction reaction electrocatalysis
Surface distortion as a unifying concept and descriptor in oxygen reduction reaction electrocatalysis
Tuning surface structure is key for electrocatalytic performance and stability of proton-exchange membrane fuel cells. Surface distortion as a structural descriptor can help to clarify the role of surface defects and to design enhanced nanocatalysts.
- Raphaël Chattot
- , Olivier Le Bacq
- & Frédéric Maillard
-
News & Views |
 Uniformity begets selectivity
Uniformity begets selectivity
A Pd4 cluster, supported by a metal–organic framework and formed by post-synthesis methods, shows high catalytic activity and selectivity for carbene-mediated reactions. This crystallographically precise material may lead to a large class of catalysts.
- Dong Yang
- & Bruce C. Gates
-
Article |
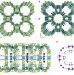 The MOF-driven synthesis of supported palladium clusters with catalytic activity for carbene-mediated chemistry
The MOF-driven synthesis of supported palladium clusters with catalytic activity for carbene-mediated chemistry
Mixed-valence clusters of Pd4 organized within a metal–organic framework exhibit robust catalytic capacities during carbene-mediated chemical reactions.
- Francisco R. Fortea-Pérez
- , Marta Mon
- & Emilio Pardo
-
Article |
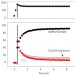 Dynamic restructuring drives catalytic activity on nanoporous gold–silver alloy catalysts
Dynamic restructuring drives catalytic activity on nanoporous gold–silver alloy catalysts
Dynamic restructuring behaviour and composition changes in bimetallic and nanoporous gold–silver alloys correlate to catalytic activity.
- Branko Zugic
- , Lucun Wang
- & Cynthia M. Friend
-
Article |
 Interfacial electronic effects control the reaction selectivity of platinum catalysts
Interfacial electronic effects control the reaction selectivity of platinum catalysts
Here the authors demonstrate how the reaction selectivity of catalytic platinum nanowires can be controlled through surface modification with organic ligands.
- Guangxu Chen
- , Chaofa Xu
- & Nanfeng Zheng
-
Letter |
 Counting electrons on supported nanoparticles
Counting electrons on supported nanoparticles
The electronic interaction between deposited metal nanoparticles and their support material can influence their functionality. Here, a quantification of the charge transfer between platinum nanoparticles and a ceria support is presented.
- Yaroslava Lykhach
- , Sergey M. Kozlov
- & Jörg Libuda
-
Letter |
 Spatially orthogonal chemical functionalization of a hierarchical pore network for catalytic cascade reactions
Spatially orthogonal chemical functionalization of a hierarchical pore network for catalytic cascade reactions
Porous materials functionalized with catalytic metals typically possess single catalytic functionalities. The hierarchical ordering of porous silica for directed transport between compartmentalized catalytic regions is presented.
- Christopher M. A. Parlett
- , Mark A. Isaacs
- & Adam F. Lee
-
-
Article |
 Platinum–cobalt bimetallic nanoparticles in hollow carbon nanospheres for hydrogenolysis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural
Platinum–cobalt bimetallic nanoparticles in hollow carbon nanospheres for hydrogenolysis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural
Although producing 2,5-dimethylfuran (DMF) from 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) is an attractive way to synthesize renewable fuels, achieving high yields for this reaction has proved difficult. PtCo bimetallic nanoparticle catalysts embedded in hollow carbon nanospheres now show improved catalytic performance for the hydrogenolysis of HMF to DMF (98% yield after 2 hours).
- Guang-Hui Wang
- , Jakob Hilgert
- & Ferdi Schüth
-
Letter |
 Controlling a spillover pathway with the molecular cork effect
Controlling a spillover pathway with the molecular cork effect
Spillover of reactants from one active site to another is important in heterogeneous catalysis but is notoriously hard to detect or control, especially for hydrogen. The hydrogen spillover pathway on a Pd–Cu alloy can now be controlled by reversible adsorption of a spectator molecule. This effect observed during a surface catalysed reaction should prove useful for controlling uptake and release of hydrogen in a model storage system.
- Matthew D. Marcinkowski
- , April D. Jewell
- & E. Charles H. Sykes

 Optimizing hierarchical membrane/catalyst systems for oxidative coupling of methane using additive manufacturing
Optimizing hierarchical membrane/catalyst systems for oxidative coupling of methane using additive manufacturing Setting stable catalysts
Setting stable catalysts