Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access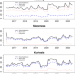 The asymmetric effects of climate risk on higher-moment connectedness among carbon, energy and metals markets
The asymmetric effects of climate risk on higher-moment connectedness among carbon, energy and metals markets
Here the authors explore the connectedness of the carbon, energy, and metals markets. They find asymmetric effects of climate risk with higher physical risk impacts on upward risk spillovers, and greater transition risk effects on the downside risk of kurtosis connectedness.
- Yuqin Zhou
- , Shan Wu
- & Lavinia Rognone
-
Article
| Open Access Climate-induced decline in the quality and quantity of European hops calls for immediate adaptation measures
Climate-induced decline in the quality and quantity of European hops calls for immediate adaptation measures
The effects of climate change on the yield and aroma of beer hops remains unknown. Here the authors demonstrate a climate-induced decline in the quality and quantity of traditional aroma hops across Europe and calls for urgent adaptation measures to stabilize international market chains.
- Martin Mozny
- , Miroslav Trnka
- & Ulf Büntgen
-
Article
| Open Access Impacts of marine heatwaves on top predator distributions are variable but predictable
Impacts of marine heatwaves on top predator distributions are variable but predictable
This study examines the effect of four marine heatwaves in the Northeast Pacific on the distributions of 14 top predators, revealing a wide-array of predator responses both among and within heatwaves. Predator responses were highly predictable, demonstrating capacity for early warning systems of heatwave impacts, similar to weather forecasts.
- Heather Welch
- , Matthew S. Savoca
- & Elliott L. Hazen
-
Article
| Open Access Assessing coupling interactions in a safe and just operating space for regional sustainability
Assessing coupling interactions in a safe and just operating space for regional sustainability
Here the authors propose an operationalizable framework, integrating safe and just operating space with Sustainable Development Goals, to assess regional sustainability and develops targeted strategies for actualizing sustainable development across scales.
- Dongni Han
- , Deyong Yu
- & Jiangxiao Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access Benefits of subsidence control for coastal flooding in China
Benefits of subsidence control for coastal flooding in China
Chinese coastal populations are concentrated in subsiding locations, and also subject to sea-level rise. Here the authors find that more areas, population and assets are exposed to coastal flooding by 2050 but realistic subsidence control measures can avoid additional risks.
- Jiayi Fang
- , Robert J. Nicholls
- & Peijun Shi
-
Article
| Open Access The role of urban trees in reducing land surface temperatures in European cities
The role of urban trees in reducing land surface temperatures in European cities
Urban trees influence temperatures in cities. The authors here investigate in spatio-temporal variations in their cooling effect and find 8-12 K decreased temperatures for tree-rich urban areas in Central Europe during hot summers, and up to 4 K for Southern Europe, respectively.
- Jonas Schwaab
- , Ronny Meier
- & Edouard L. Davin
-
Comment
| Open Access Impacts of climate change to African indigenous communities and examples of adaptation responses
Impacts of climate change to African indigenous communities and examples of adaptation responses
Climate change negatively impacts the livelihoods of indigenous communities across the world, including those located on the African continent. This Comment reports on how five African indigenous communities have been impacted by climate change and the adopted adaptation mechanisms.
- Walter Leal Filho
- , Newton R. Matandirotya
- & Richard Achia Mbih
-
Article
| Open Access Global LiDAR land elevation data reveal greatest sea-level rise vulnerability in the tropics
Global LiDAR land elevation data reveal greatest sea-level rise vulnerability in the tropics
Predicting the risk of flooding in coastal environments relies on accurate land elevation data, but this is not available in many parts of the world. Here the authors apply a global lowland digital terrain model derived from satellite LiDAR and determine that the regions most vulnerable to sea-level rise are in the tropics.
- A. Hooijer
- & R. Vernimmen
-
Article
| Open Access Agricultural subsidies and global greenhouse gas emissions
Agricultural subsidies and global greenhouse gas emissions
Agricultural sectors receive US$600 billion per year in government support, providing incentives for GHG emission-intensive production. Here, the authors show that removing this support will not reduce global GHG emissions by much; rather it will need to be radically redirected to contribute to climate change mitigation.
- David Laborde
- , Abdullah Mamun
- & Rob Vos
-
Article
| Open Access Deforestation reduces rainfall and agricultural revenues in the Brazilian Amazon
Deforestation reduces rainfall and agricultural revenues in the Brazilian Amazon
Deforestation in the Amazon region has suggested to influence precipitation in a non-linear way. Here, the authors show that forest loss is associated with decreasing precipitation after a scale-dependent threshold is crossed, which can cause stress on agriculture if deforestation is expanded.
- Argemiro Teixeira Leite-Filho
- , Britaldo Silveira Soares-Filho
- & Jan Börner
-
Article
| Open Access Calculation of external climate costs for food highlights inadequate pricing of animal products
Calculation of external climate costs for food highlights inadequate pricing of animal products
Agricultural greenhouse gas emissions not only amplify the global climate crisis, but cause damage currently unaccounted for by food prices. Here the authors show the calculation of prices with internalized climate costs for food categories and production systems, revealing strong market distortions.
- Maximilian Pieper
- , Amelie Michalke
- & Tobias Gaugler
-
Article
| Open Access Using insurance data to quantify the multidimensional impacts of warming temperatures on yield risk
Using insurance data to quantify the multidimensional impacts of warming temperatures on yield risk
The impacts of climate change on agricultural productivity remain debated. Here, the authors present new evidence for the magnitude and causes of U.S. crop insurance losses, using a database of production risk from 1989–2014 across 1733 counties for corn and 1632 counties for soybeans, and find that crop production risk will increase in response to warmer temperatures.
- Edward D. Perry
- , Jisang Yu
- & Jesse Tack
-
Article
| Open Access An integrative climate change vulnerability index for Arctic aviation and marine transportation
An integrative climate change vulnerability index for Arctic aviation and marine transportation
It is important to understand how physical changes in Polar regions influence social systems and populations. Here the authors develop an Arctic Climate Change Vulnerability Index focusing on aviation and marine infrastructure in future climate scenarios and show that transportation system vulnerability varies across the region depending on modeled hazards and transportation infrastructure types.
- Nathan S. Debortoli
- , Dylan G. Clark
- & Emilia P. Diaconescu

 The social costs of tropical cyclones
The social costs of tropical cyclones