Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Ubiquity of Kelvin–Helmholtz waves at Earth’s magnetopause
Ubiquity of Kelvin–Helmholtz waves at Earth’s magnetopause
Although magnetic reconnection is recognized as the dominant mode for solar wind plasma to enter the magnetosphere, Kelvin–Helmholtz waves (KHW) have been suggested to also be involved. Here, the authors use 7 years of THEMIS data to show that KHW occur 19% of the time, and may be important for plasma transport.
- Shiva Kavosi
- & Joachim Raeder
-
Article
| Open Access Extreme 13C depletion of carbonates formed during oxidation of biogenic methane in fractured granite
Extreme 13C depletion of carbonates formed during oxidation of biogenic methane in fractured granite
Precipitation of 13C-depleted authigenic carbonate is a tracer of sulphate-dependent anaerobic methane oxidation, particularly in marine sediments. Here, the authors present extremely 13C-depleted carbonates from deep granitoid rocks suggesting the presence of microbial sulphate reducers and methane oxidisers.
- Henrik Drake
- , Mats E. Åström
- & Peter Sjövall
-
Article
| Open Access Deep groundwater and potential subsurface habitats beneath an Antarctic dry valley
Deep groundwater and potential subsurface habitats beneath an Antarctic dry valley
Conditions below the active permafrost layer in the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica, are thought to be ice cemented. Here, the authors use an airborne electromagnetic sensor to image the resistivity beneath the valley floor, which indicates the presence of high-salinity liquids at temperatures well below freezing.
- J. A. Mikucki
- , E. Auken
- & N. Foley
-
Article
| Open Access Low-buoyancy thermochemical plumes resolve controversy of classical mantle plume concept
Low-buoyancy thermochemical plumes resolve controversy of classical mantle plume concept
The classic mantle plume concept explains large igneous provinces and hotspot magmatism, but often contradicts observed surface uplift and plume morphology. Here, the authors present a plume model that better supports observations by considering low-buoyancy plumes containing up to 15% of recycled oceanic crust.
- Juliane Dannberg
- & Stephan V. Sobolev
-
Article
| Open Access Causal factors for seismicity near Azle, Texas
Causal factors for seismicity near Azle, Texas
Whether exploration causes earthquakes has been a matter of recent contention particularly regarding shale gas exploration. Here, the authors use hydraulic modelling and earthquake locations to show that brine production and wastewater injection in the Azle area are likely causing earthquakes.
- Matthew J. Hornbach
- , Heather R. DeShon
- & James H. Luetgert
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal preferred orientation of an amphibole experimentally deformed by simple shear
Crystal preferred orientation of an amphibole experimentally deformed by simple shear
Seismic anisotropy has been widely observed in the crust and mantle due to the crystal preferred orientation (CPO) of highly anisotropic minerals such as amphibole, though it is poorly constrained. Here, the authors present an experimental study showing that three CPOs exist depending on temperature and stress.
- Byeongkwan Ko
- & Haemyeong Jung
-
Article |
 Cracks in Martian boulders exhibit preferred orientations that point to solar-induced thermal stress
Cracks in Martian boulders exhibit preferred orientations that point to solar-induced thermal stress
Many rock cracks on Earth point north, suggesting that the Sun may be involved in their formation. Here, the authors compile this Earth data, collect similar data for rock cracks on Mars, and present modelling results, linking the origin of Mars rock cracks to thermal stress from the Sun.
- Martha-Cary Eppes
- , Andrew Willis
- & Beibei Zhou
-
Article |
 Selective ingress of a Samoan plume component into the northern Lau backarc basin
Selective ingress of a Samoan plume component into the northern Lau backarc basin
Ocean island basalts contain primordial and recycled crustal components, sourced from the deep mantle by plumes. Here, the authors examine Hf-Nd-He isotopes in ocean floor basalts south of Samoa and suggest that selective ingress of only the primordial component from the Samoan plume can occur.
- Oliver Nebel
- & Richard J. Arculus
-
Article |
 Micro-trace fossils reveal pervasive reworking of Pliocene sapropels by low-oxygen-adapted benthic meiofauna
Micro-trace fossils reveal pervasive reworking of Pliocene sapropels by low-oxygen-adapted benthic meiofauna
Meiofaunal burrowing is thought to produce sediment textures that appear devoid of animal activity, thus the record of meiofaunal activity remains unknown. Here, the authors apply a novel sampling and electron imaging approach to identify meiofaunal traces in Pliocene sapropels, a classic anoxic facies.
- S.C. Löhr
- & M.J. Kennedy
-
Article |
 Tetrahedrally coordinated carbonates in Earth’s lower mantle
Tetrahedrally coordinated carbonates in Earth’s lower mantle
The behaviour of subducted carbonates at high pressures within the Earth is still poorly understood. Here, the authors present experimental and theoretical evidence of a new carbon–oxygen bond in a high-pressure mineral phase, which has implications for the viscosity and mobility of carbonate melts.
- Eglantine Boulard
- , Ding Pan
- & Wendy L. Mao
-
Article
| Open Access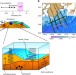 Ambient seafloor noise excited by earthquakes in the Nankai subduction zone
Ambient seafloor noise excited by earthquakes in the Nankai subduction zone
Excitations of seismic background noise are mostly related to fluid disturbances, and earthquakes have not been considered as a source due to their intermittent nature. Here, the authors use a seabed hydrophone array and show that background noise offshore Japan is mainly due to small earthquakes.
- Takashi Tonegawa
- , Yoshio Fukao
- & Yoshiyuki Kaneda
-
Article |
 Aerosol generation by raindrop impact on soil
Aerosol generation by raindrop impact on soil
Suspended dust and sea salt are currently considered to be two major sources of environmental aerosol particles. Here, Joung and Buie report another mechanism of aerosol generation from rainfall impact on porous soil surfaces, whereby elements can be delivered to the air.
- Young Soo Joung
- & Cullen R. Buie
-
Article |
 A very long-term transient event preceding the 2011 Tohoku earthquake
A very long-term transient event preceding the 2011 Tohoku earthquake
Slow slip events have been observed in different subduction zones, but their relationship to megathrust earthquakes remains elusive. Here, the authors postulate that a transient event may have led to the 2011 Tohoku earthquake as the hypocentre falls within a zone of positive Coloumb stress change.
- Yusuke Yokota
- & Kazuki Koketsu
-
Article |
 High-pressure radiative conductivity of dense silicate glasses with potential implications for dark magmas
High-pressure radiative conductivity of dense silicate glasses with potential implications for dark magmas
Understanding of the Earth’s interior requires insight into the thermal properties of silicate melts under high pressure. Here, the authors present high-pressure spectroscopic measurements of iron-enriched dense silicate glasses and infer the radiative conductivity of dense melts at the core–mantle boundary.
- Motohiko Murakami
- , Alexander F. Goncharov
- & Craig R. Bina
-
Article |
 Chemo-mechanics of salt damage in stone
Chemo-mechanics of salt damage in stone
Growth of salt crystals in pores is one of the most damaging weathering mechanisms for stone in ornamental structures and historical buildings. Here, the authors present a simple yet powerful treatment for predicting when salt damage will occur, quantifying this susceptibility to salt crystallization.
- Robert J. Flatt
- , Francesco Caruso
- & George W. Scherer
-
Article |
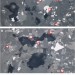 Magnetic force microscopy reveals meta-stable magnetic domain states that prevent reliable absolute palaeointensity experiments
Magnetic force microscopy reveals meta-stable magnetic domain states that prevent reliable absolute palaeointensity experiments
Obtaining reliable estimates of the absolute palaeointensity of the Earth’s magnetic field is difficult and many methods induce alteration. de Groot et al.present a means to see and explain changes in magnetization in unreliable samples, explaining why some samples systematically fail paleointensity experiments.
- Lennart V. de Groot
- , Karl Fabian
- & Mark J. Dekkers
-
Article |
 Formation of recent Pb-Ag-Au mineralization by potential sub-surface microbial activity
Formation of recent Pb-Ag-Au mineralization by potential sub-surface microbial activity
Studies suggest almost the same amount of biomass is present in subterranean settings as on Earth’s surface. Here, the authors propose that a large intraterrestrial microbial system was responsible for mineralization in southern Spain, and that microbes may play a major role in sub-surface ore-forming processes.
- Fernando Tornos
- , Francisco Velasco
- & Juan Manuel Escobar
-
Article
| Open Access Marine ice regulates the future stability of a large Antarctic ice shelf
Marine ice regulates the future stability of a large Antarctic ice shelf
Signs of instability in the Antarctic Larsen C ice shelf have raised concerns that it might soon collapse like its northern neighbour Larsen B. Kulessa et al.combine an ice-shelf model with satellite and geophysical data to show that despite dynamic similarities, Larsen C is presently stabilized by marine ice.
- Bernd Kulessa
- , Daniela Jansen
- & Peter R. Sammonds
-
Article
| Open Access Global link between deformation and volcanic eruption quantified by satellite imagery
Global link between deformation and volcanic eruption quantified by satellite imagery
Deformation is often used in volcano monitoring, but the associated hazard is hard to interpret. Biggs et al.analyse 20 years of global satellite data and show a strong statistical link between deformation and eruption, although deformation alone is not necessarily a precursor of imminent eruption.
- J. Biggs
- , S. K. Ebmeier
- & T. A. Mather
-
Article
| Open Access Elastic anisotropy of experimental analogues of perovskite and post-perovskite help to interpret D′′ diversity
Elastic anisotropy of experimental analogues of perovskite and post-perovskite help to interpret D′′ diversity
Seismological observations of the D′′ layer near the core–mantle boundary are difficult to interpret and the minerals present are unstable at ambient conditions. Yoneda et al.present experiments using analogues, suggesting the observations are due to preferred crystal orientations.
- Akira Yoneda
- , Hiroshi Fukui
- & Alfred Q. R. Baron
-
Article |
 Helium anomalies suggest a fluid pathway from mantle to trench during the 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake
Helium anomalies suggest a fluid pathway from mantle to trench during the 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake
The behaviour of fluids along fault planes is not well defined, despite geophysical evidence that they play an important role in earthquake generation. Here, Sano et al.present helium anomaly data and suggest that fluid flowed from the mantle to the trench during the magnitude 9 Tohoku-Oki earthquake.
- Yuji Sano
- , Takahiro Hara
- & Keiko Hattori
-
Article |
 Flow velocities of Alaskan glaciers
Flow velocities of Alaskan glaciers
Alaskan mountain glaciers are losing ice and contribute to sea level rise, but contributions from specific ice-loss mechanisms are not known. Here, calving losses in Central Alaska are found to equal 36% of the net regional mass change each year and regional flux is dictated largely by snow accumulation rates.
- Evan W. Burgess
- , Richard R. Forster
- & Christopher F. Larsen
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid changes in the electrical state of the 1999 Izmit earthquake rupture zone
Rapid changes in the electrical state of the 1999 Izmit earthquake rupture zone
Low-resistivity crustal fluids occur near fault zones, but their relation to earthquake generation is unclear. Here, electromagnetic data from the Izmit earthquake reflects the pressure-induced transition between isolated and interconnected fluids that is linked to foreshocks before large earthquakes.
- Yoshimori Honkura
- , Naoto Oshiman
- & Elif Tolak Çiftçi

 Volcano seismicity and ground deformation unveil the gravity-driven magma discharge dynamics of a volcanic eruption
Volcano seismicity and ground deformation unveil the gravity-driven magma discharge dynamics of a volcanic eruption